Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
A Bird view on Sushrutokta Ganas in Management of Thyroid Disorders
Authors: Dr. Abhishek S, Dr. Shivananda B. Karigar, Dr. Sampatkumar Bellamma, Dr. Megha T, Dr. Sahil Bhavsar
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.63755
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Thyroid disorders are emerging as common health concern in India as well as worldwide. Thyroid dysfunction prevalence is rising at an alarming rate in Indian population more prevalent among the females. Hyper and hypothyroidism may be due to disease of thyroid gland secondary to malfunction in the hypothalamus. In Ayurveda thyroid disorder can be understood with the concept of agnivaishamyata and galaganda/gandamala. Various etiological factors highlighted in classical text like atisevana of madhura rasa, mithya ahara vihara, vishamashana and pathogenesis shows increased vata & kapha leads to Medhodhatu accumulation in galapradesha leading to galaganda. Condition like Hyperthyroidism can be compared with vata pittaja lakshanas and Hypothyroidism can be compared with vata kaphaja lakshanas. Thyroid disorder is derangement of thyroid hormones and most of the cases it’s associated with disorders like Obesity, Diabetes mellitus, Anaemia, Amenorrhea etc. Based on basic clinical involvement and presentation of thyroid dysfunction basic drugs can be selected for the treatment. Here is attempt to critically review of thyroid management with mainly focusing on sushrutokta ganas. Most of the thyroid disorder are associated with kapha meda vikaras hence ganas which acts on kapha medha dhatu can be used in thyroid disorder. Acharya Sushruta has designed ganas in such a way that all the drugs in the Ganas have similar properties and shows similar action when used as combination, among 37 ganas there are 6 ganas which shows action on kapha dosha and medha dhatu, which mainly shows action in thyroid disorder and associated complaints like Obesity, Diabetes mellitus, Anaemia etc.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Thyroid disease is an umbrella term for the condition that affects thyroid function. Hyper and hypothyroidism are the two main types of thyroid disease which are mainly caused due to Agnivaishamyta, which interns lead to vitiation of the kapha and vata dosha’s and vitiation of Medha dhatu, which accumulates in gala pradesha and which is known as Galagand. The term thyroid dysfunction includes two different conditions like hypo and hyperthyroidism. In hypothyroidism, there is decrease in metabolic rate due to decrease T3, T4 hormone secretion level and show symptoms like Bradycardia, Constipation, Weight gain etc. In hyperthyroidism, there is increased metabolic rate due to increase T3 T4 hormone secretion level and show symptoms like Tachycardia, Weight loss etc.
Mainly focusing on Sushrutokta ganas(1) explained in 38th chapter Dravyasangrahaneeya adhyaya by Acharya Sushruta in Sushruta Samhita sutra sthana, Among 37 ganas there are many ganas which shows action on kapha dosha and medha dhatu like Varunadi gana, Asanadi gana, Trikatu gana etc which all targets kapha dosha and medha dhatu which are the main reason behind the thyroid dysfunction.
II. AIMS AND OBJECTIVES
Present study aims to review Sushrutokta ganas. The objective of this study is to explore Sushrutokta ganas in management of thyroid dysfunction.
III. MATERIALS AND METHODS
A. Varunadi Gana(2),(3)
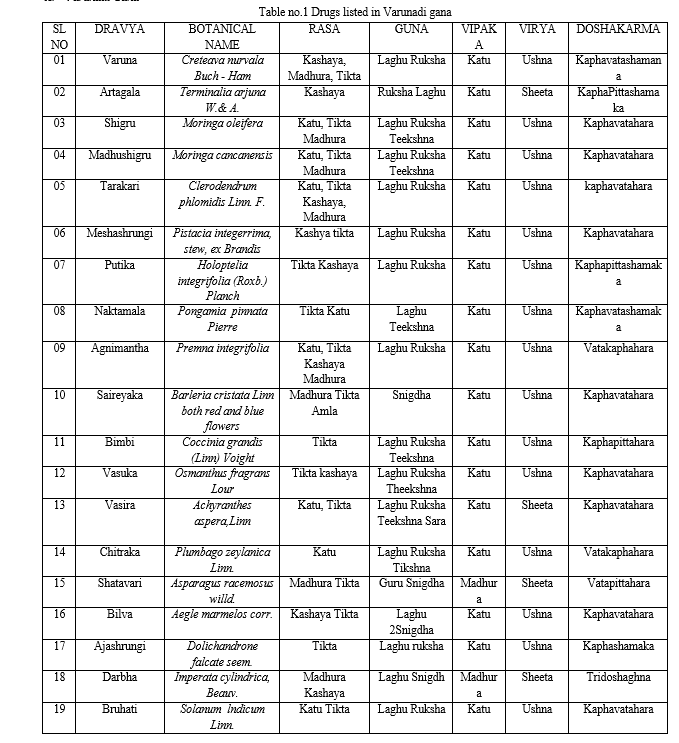
Varunadi Gana, it was observed that the predominant rasas are Tikta, Kashaya and Katu. Additionally, these drugs exhibit properties such as Laghu, Ruksha, and Teekshna. All the dravyas in Varunadi Gana have Ushna veerya with the exception of Darbha and Shatavari and vasira. In terms of Vipaka, most of the drugs have Katu vipaka, except for Shatavari and Darbha which have Madhura vipaka. Shatavari is vatapitta samaka, and Putikaranja is kapha-pitta samaka, while all others act as Kaphavatasamaka, indicating their effectiveness in balancing Vata and Kapha doshas. This group gets rid of Kapha and Medas and also destroys headache, Gulma and internal abscess (4).
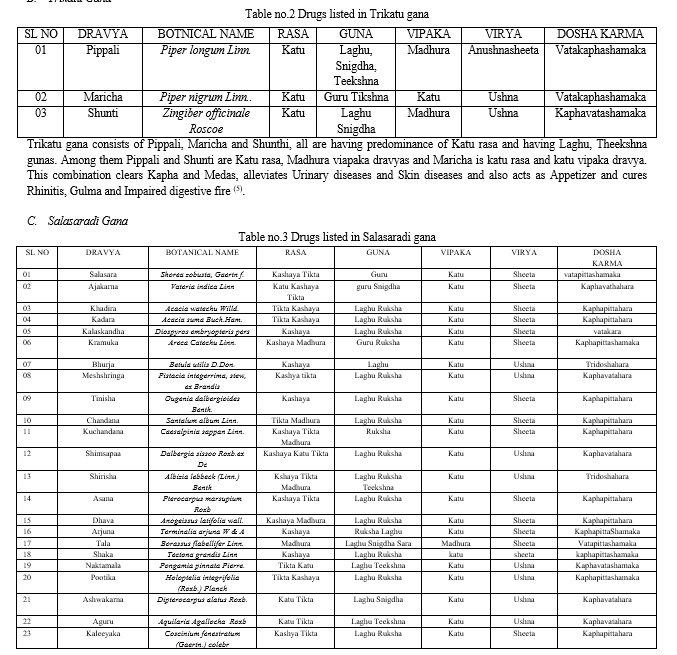
Salasaradi gana dravyas are commonly have Kashaya & Tikta rasa and Laghu & Ruksha guna. All constituent dravyas of this gana have Katu vipaka except plant Tala which have Madhura vipaka. Among 23 total dravyas 15 dravys are of sheeta virya and 8 dravys are of Ushna virya. This group destroys skin diseases and mitigates Prameha and Pandu (anemia). It dries up Kapha and medas (6).
D. Lodhradhi Gana
Table no.4 Drugs listed in Lodhradi gana
|
SL NO |
DRAVYA |
BOTANICAL NAME |
RASA |
GUNA |
VIPAKA |
VIRYA |
DOSHAKARMA |
|
01 |
Lodhra |
Symplocos recemosa, Roxb. |
Kashaya Tikta |
Laghu Ruksha |
Katu |
Sheeta |
Kaphapittahara |
|
02 |
Savaralodhra |
Symplocos crataegoides |
Kashaya Tikta |
Laghu Ruksha |
Katu |
Sheeta |
Kaphapittahara |
|
03 |
Palasha |
Butea monosprema (Lam.) Kuntze. |
Katu Tikta Kashaya |
Laghu snigdha |
Katu |
Ushna |
Kaphahara |
|
04 |
Kutannata |
Oroxylum indicum (Linn.) vent. |
Tikta Kashaya |
Laghu Ruksha |
Katu |
sheeta |
Tridoshagna |
|
05 |
Ashoka |
Sraca asoca, (Roxb) De wilde. |
Kashaya Tikta |
Laghu Ruksha |
Katu |
Sheeta |
Kaphapittahara |
|
06 |
Phanji |
Clerodendrum serratum spreng |
Tikta katu kashaya |
Laghu Ruksha |
Katu |
Ushna |
Kaphavatahara |
|
07 |
Katphala |
Myrica nagi, Thunb |
Kashaya Tikta katu |
Laghu Ruksha |
Katu |
Sheeta |
Vatakaphahara |
|
08 |
Elavaluka |
Pranus avium L. |
Kashaya Tikta |
Laghu |
Katu |
Sheeta |
Kaphapittashamaka |
|
09 |
Shallaki |
Boswellia serrata Roxb. |
Kashaya Tikta Madhuara |
Laghu Ruksha |
Katu |
Sheeta |
Kaphapittahara |
|
10 |
Kadamba |
Anthocephalaus cadamba Miq. |
Kashaya Madhura Lavana |
Ruksha Guru |
Katu |
Sheeta |
Tridoshahara |
|
11 |
Sala |
Shorea zobusta, Gaertn f. |
Kashaya Tikta |
Guru |
Katu |
Sheeta |
vatapittashamaka |
|
12 |
Kadali |
Musa sapientum Linn |
Madhura Kashaya |
Guru Sigdha |
Madhura |
Sheeta |
Vatapittashamaka |
Dravyas included in lodhradi gana have pridominance of Kashaya and Tikta rasa, Sheeta virya. In context of vipaka except kadali all the dravys have Katu viapaka. It alleviates Meda and Kapha and is useful in mitigating Yonirogas, have Stambhana property and improves colour and acts as antidote to poisons.7.
E. Arkadi Gana
Table no.5 Drugs listed in Arkadi gana
|
SL NO |
DRAVYA |
BOTANICAL NAME |
RASA |
GUNA |
VIPAKA |
VIRYA |
DOSHAKARMA |
|
01 |
Arka |
Calatropis procera (Ait) f. |
Katu Tikta |
Laghu Ruksha Tikshna |
Katu |
Ushna |
Vatahara |
|
02 |
Alarka |
Calatropis gigantea |
Katu Tikta |
Laghu Ruksha Tikshna |
Katu |
Ushna |
Vatahara |
|
03 |
Karanja |
Pongamia pinnata Pierre. |
Tikta Katu |
Laghu Teekshna |
Katu |
Ushna |
Kaphavatashamaka |
|
04 |
Nagadanti |
Baliospermum montanum Muell - Arg |
Katu |
Guru Teekshna |
Katu |
Ushna |
Kaphapittahara |
|
05 |
Mayuraka |
Achyranthes aspera,Linn
|
Katu, Tikta |
Laghu Ruksha Teekshna Sara |
Katu |
Sheeta |
Kaphavatahara |
|
06 |
Bharangi |
Clerodendrum serratum spreng |
Tikta katu kashaya |
Laghu Ruksha |
Katu |
Ushna |
Kaphavatahara |
|
07 |
Rasna |
Pluchea lanceolata oliver and Hiern |
Tikta Guru |
Guru |
Katu |
Ushna |
Kaphavata Shamaka |
|
08 |
Indrapusphi |
Gloriosa suparba Linn |
Katu Tikta |
Laghu Teekshna |
Katu |
Usna |
Kaphavatashamaka |
|
09 |
Kshudrashveta |
Clitorea ternatea Linn Linnatea |
Katu Tikta Kashaya |
Laghu Ruksha |
Katu |
Sheeta |
Tridoshahara |
|
10 |
Mahasveta |
Clitorea ternatea Linn Linnatea |
Katu Tikta Kashaya |
Laghu Ruksha |
Katu |
Sheeta |
Tridoshahara |
|
11 |
Vrischikali |
Pergularia daemia (Forssk) Chiov |
Katu Tikta Kashaya |
Laghu Ruksha |
Katu |
Sheeta |
Pittakaphashamaka |
|
12 |
Alavana |
Celasrtrus paniculatus Willd |
Katu Tikta |
Teekshna |
Katu |
Sheeta |
kaphavatahara |
|
13 |
Tapas vriksha |
Balanites roxburghii Planc h |
Tikta |
Laghu |
Katu |
Ushna |
kaphavatahara |
Dravyas enlisted in Arkadi gana commonly have Katu and Tikta rasa, Ushna veerya and Katu vipaka. This group is useful in mitigating Kapha, Meda and Vi?ha. It palliates worm-infestation and skin disorders and specifically does cleansing of the wound (8).
IV. DISCUSSION
Thyroid disorders are understood based on the disorders related to Kapha meda vikaras. Thyroid disorders manifests based on secretion of thyroid hormone, hence by looking into clinical presentations in a patient, and based on Ayurvedic principles of pharmacology, the various ganas mentioned in Sushruta samhita can be choosen to treat the patients of thyroid disorders. As per Ayurvedic concept, Dhatvagnimandya caused by kapha dosha vikriti results in vitiation of Medo dhatu which obstructs the srotas leading to vitiation of vayu (due to margavarodha) and that increased vata hampers the Dhatwagni again. The Potential action of varunadi gana attributes to counteract the snigdha, shita, guru, manda, slakshna, and sthira gunas of Kapha dosha by its qualities like ruksha, ushna, laghu and teekshna gunas. These opposite characteristics make these drugs a favorable option for addressing Kapha-medaja rogas. Varunadi gana dravyas which are mainly indicated in Kapha meda vikaras can be administered in case of hypothyroidism because most of clinical presentation in hypothyroidism appears to have involvement of Kapha and meda dhatu.
The Varunadi gana is Kaphavatahara and has deepana karma which helps in correcting the margavarodha which in turn cures medo vikara.
The majority of drugs in the Varunadi gana possess deepana karma, contributing to the stimulation of agni and thereby rectifying the mandagniavastha. The diseases indicated typically involve both Kapha and Vata in their pathogenesis, often associated with margavarana or srotorodha. Additionally, the relationship of Kapha and Medas asraya-asrayi suggests the utility of Varunadi Gana in all conditions with medo dushti. Varunadi gana dravyas shows activity against pro inflammatory cytokines and thus it prevents differentiation of monocytes to macrophages. So It can be used in the inflammatory condition like Autoimmune disorders, Hashimoto thyroiditis etc. and also varunadi gana inhibit the expresseion of adipogenic and lipogenic genes. Hence it can be used in conditions like Hypothyroidism associated with Hypertryglyceridemia, Hypercholesterolemia etc.It is proven to be as lithotriptic agent.
Trikatu gana aslo by virtue of Katu rasa and Ushna virya mainly acts on kapha and vata doshas. Trikatu gana has Laghu ,Ruksha & Teekshna Gunas and Deepana, Pachana, Sthaulya hara, Meda hara and Kapha-vata hara karma. By these properties it does amapachana first in kostha. Later on it stimulates the digestive fire and maintains it. Then it reaches to the deeper dhatus and then stimulates the dhatwagni. There it does further ama pachana which is accumulated at the dhatu level. Just like that it reaches to meda dhatu level and there it stimulates the diminished medo dhatwagni in Hyporthyroidism, does digestion of ama meda and prevent the further ama formation by maintaining normalcy. Since Diabetes mellitus, obesity, PCOS/PCOD are commonly associated with Hypothyroidism one single gana can manage these condition properly if it is used with proper yukti of physician.
The dravyas of Salasaradi gana possesses majorly Kashaya, Tikta Rasa, Katu vipaka, laghu ruksha guna and Sheeta virya. which pacify the Kapha dosha and Meda dhatu. It is majorly composed of prithvi and vayu mahabhuta. In thyroid disorders, there may be manifestation of various skin disorders like Acne vulgaris, Myxodema, Dry skin and hairs, Excessive perspiration etc. because of metabolic changes and hormonal disturbance. Salasaradi gana dravyas can be used in this condition becauase it is having Kashaya rasa predominantly which is told to be as Rakta shodhaka. It also does kapha meda shoshana and reduces excessive kleda from the body. Thus it cures Skin diseases. Oxidative stress to thyroid gland can hamper the normal secretion of the gland and results in hypothyroidism. Kashaya rasa is considered as the anti-oxidant. Hence it reduces the oxidative stress and normalise the function of the thyroid gland. Being Katu vipaka which does the Agni deepana and Aama pachana and also decreses the Srotorodha caused by the Sheeta, Guru, Picchila Singdha gunas by opposite properties like Laghu, Ruksha gunas. Along with these properties Tikta rasa and Sheeta virya being Pitta shamaka controls the metabolism. Thus, Salasaradi gana can be used in effective management of Kushta, Prameha, Pandu roga and mainly acts and dries up abnormal kapha and meda. Lodhradi gana majorly have Madhur, Tikta, Kashay rasa, Ruksha, laghu guna, Sheeta veerya, Katu vipak and Tridosha shamaka (mainly kaphavataghna). By keen observation we can see that majorly used part of dravyas in lodhradi ganas are heartwood and bark. It possesses highest amount of Kashaya rasa compared to other parts. Kashaya tikta rasa along with Sheeta virya will increases ruksha guna inside the body. Which in turn decreases the excessive kleda and does the shoshana of excessive meda. It also possesses anti-oxidant, hypolipidemic and healing properties. In condition like autoimmune thyroid diseases, the immune cells of our body attacks the healthy tissues due to increased oxidative stress. Where Lodhradi gana drayas being anti-oxidant, immunomodulators and adaptogenic activity improves the cytochrome P-450 that involves in oxidative metabolism of drug and other xenobiotics which decreases the oxidative stress and promote body defence system. Thus it promotes mental and physical health and improves the immune system. Due to Ushna and Tikshna Guna of lodhradi Gana Dravya impact the virya of medication goes into the body. In females, there will be srotorodha because of kapha vikriti which results in abnormal movement of vata and disturbance of pitta in yoni pradesha. There may be formation of granthi or manifestation of yoni roga. Which may be correlated to the PCOD/PCOS. Lodhradi gana dravyas increases the agni at minute levels and decreases accumulated kapha dosha and medo dhatu. Ushna and Tikshna guna of dravyas opens the srotorodha and causes normal movement of vata. Lekhana property of these dravyas is responsible for reduction of the size of the granthi, therefore lodhradi gana cures the symptoms of yoni roga along with normal maintainance of thyroid functions. Nyagrodhadi gana dravyas also possess similar property and it can be used in same conditions like Lodhradi gana.
Arkadi gana mainly having Katu rasa, Katu vipaka, Ushna virya dravyas. In general, they have lekhana property. Because of this lekahana property, it decreases the kapha and meda accumulation in gala pradesha and maintain normalcy of thyroid gland. It also has antimicrobial property which helps in decreasing the risk of infection.
V. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
I would like to thank Dr. Rajashekhar S Ganiger sir HOD Dept of Dravyaguna TGAMC Ballari for guiding me and also extend my sincere thanks to Dr Asha Acharya, Dr. Kumari Triveni, Dr. Guruprasad hegde, Dr. Vitkare Akshay for helping me to gather valid source of information .
Conclusion
Ayurveda is a science where not only the treatment protocols are already mentioned clearly and stand true even in today’s times, but also there has been immense freedom given to the practitioner to decide the treatment as per the individual’s conditions. All the Karyadravyas are Ausadha, there is no Karyadravya in this universe which is devoid of medicinal properties, these dravyas needs to be used according to ones Yukti and Artha.(9) After having analysed the Do?ha variation, the drugs in the Ganas can be used individually, in the form of separate gana or in combination of multiple ganas also.(10) In the different individual after assessing the Doshaja condition, the Ga?as are to be used individually, or as a combination as per the situation. At times two, three or four of the dravyas may be used or all of them. This is applicable in case of these ganas only and not in any other yoga (formula compound). Classification of these drugs on the basis of pharmacological actions on the various systems of the body and the mind seems more scientific. The drugs having same Rasa, Guna, Virya, Vipaka are compiled and collected under single group. Such drugs need to be standardized as per SOPs and make these group of drugs available in the market for the clinical application. The purpose of this study is to get a clear vision about these ganas at one glance. This research work will help the researchers and practitioners to easily use the groups based on the doshaja conditions. Many eminent Ayurveda Practitioners are already using these ganas for better results in various disorders successfully. The exploration of other ganas should also be done to get an evidence based efficacy for clinical utility on the both Ayurvedic and Contemporary Science parameters.
References
[1] Acharya Sushruta, Susruta Samhita with English translation of text and Dalhanas commentry,edited and translated by Prof.Vasant C Patil and Dr Rajeshwari N.M Chaukhambha publications Newdelhi Edition;First 2018, Vol 1sutrasthan 38th chapter Dravyasangrahaniyam Adhyaya Page no-387 [2] Bhavamishara Bhavaprakasha Original text along with commentary and translation by Dr Balusu sitaram Chaukambha Orientalia Varanasi Reprint edition - 2022 Vol 1 [3] Pandit Narhari Rajanighantu edited with Dravyagunapraashika hindi commentary by Dr.Indradeva Tripathi Chowkamba Krishnadas Academy Varanasi [4] Acharya Sushruta, Sushruta Samhita with English translation of text and Dalhanas commentry,edited and translated by Prof.Vaasant C Patil and Dr Rajeshwari N.M Chaukaambha publications New Delhi Eiition;First 2018, Vol 1sutrasthan 38th chapter Dravyasangrahaniyam Adhyaya shloka number 11 Page no - 389 [5] Acharya Sushruta, Sushruta Samhita with English translation of text and Dalhanas commentry,edited and translated by Prof.Vaasant C Patil and Dr Rajeshwari N.M Chaukhambha publications New Delhi Edition;First 2018, Vol 1sutrasthan 38th chapter Dravyasangrahaniyam Adhyaya shloka number 61 page no - 399 [6] Acharya Sushruta, Sushruta Samhita with English translation of text and Dalhanas commentry,edited and translated by Prof.Vaasant C Patil and Dr Rajeshwari N.M Chaukhambha publications New Delhi Edition;First 2018, Vol 1sutrasthan 38th chapter Dravyasangrahaniyam Adhyaya shloka number 9 page no - 389 [7] Acharya Sushruta, Sushruta Samhita with English translation of text and Dalhanas commentry,edited and translated by Prof.Vaasant C Patil and Dr Rajeshwari N.M Chaukhambha publications New Delhi Edition;First 2018, Vol 1sutrasthan 38th chapter Dravyasangrahaniyam Adhyaya shloka number 15 page no - 391 [8] Acharya Sushruta, Sushruta Samhita with English translation of text and Dalhanas commentry,edited and translated by Prof.Vaasant C Patil and Dr Rajeshwari N.M Chaukhambha publications New Delhi Edition;First 2018, Vol 1sutrasthan 38th chapter Dravyasangrahaniyam Adhyaya shloka number 17 page no - 391 [9] Acharya Sushruta, Susruta Samhita with English translation of text and Dalhanas commentry,edited and translated by Prof.Vaasant C Patil and Dr Rajeshwari N.M Chaukhambha publications Newdelhi Edition;First 2018, Vol 1sutrasthan 41st chapter Dravyasangrahaniyam Adhyaya shloka number 9 page no - 421 [10] Acharya Sushruta, Susruta Samhita with English translation of text and Dalhanas commentry,edited and translated by Prof.Vaasant C Patil and Dr Rajeshwari N.M Chaukhambha publications Newdelhi Edition;First 2018, Vol 1sutrasthan 38th chapter Dravyasangrahaniyam Adhyaya shloka number 83 page no - 403
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Dr. Abhishek S, Dr. Shivananda B. Karigar, Dr. Sampatkumar Bellamma, Dr. Megha T, Dr. Sahil Bhavsar. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET63755
Publish Date : 2024-07-25
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

