Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- References
- Copyright
A Study on Cyber Frauds Post Digitalization in India
Authors: Manjunath M, Dr Selvi S
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.60191
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
In the modern era of Digitalization, Digital banking has become more relevant due to the latest demonetization happened in India. The digitization of banking has made financial transactions swift and brought luxurious banking from anywhere, anytime. Indian government is not only encouraging using the cashless transactions but also providing financial benefits on digital transactions. As the usage of digital banking transactions increased, it introduced different types of cyber frauds and the rate of fraudulent practices also got amplified, therefore sound knowledge of usage of digitalisation services is requisite to prevent fraudulent practices. The present study depicts the types of frauds happening post digitalization in banking Industry and also tries to figure out the different reasons responsible for the happening of frauds in the Indian Banking Sector.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Cyber fraud in India, like in many other countries, has become a significant concern due to the increasing reliance on digital technology and the internet. Here are some common types of cyber frauds prevalent in India
Types of Cyber Frauds:
- Phishing Scams: Phishing scams are attempts by scammers to trick you into giving out your personal information such as bank account numbers, passwords and credit card numbers. These scammers will contact you out of the blue, via email, text message, phone call or even through social media, pretending to be a legitimate business such as your bank, telephone company or even internet provider. The scammer may ask you to update them on your details so they can refresh their systems, they may even ask you to fill out a survey as you have the chance to win a prize at the end. But here is where the scammer can get access to your email address, phone number and more. Another way these scammers get hold of your information is to tell you that unauthorized or suspicious activity has been happening on your account, and they will then ask you for your information so they can sort it out¦. In fact, they are going to steal from you. Phishing attacks work the same as fraudulent phone calls which people are being educated on. You may have seen recent ad campaigns like this from Barclays.
- Online Scams: Online scams are basically scams that happen online. Whether that tricking you into giving out personal details online by an ad popping up telling you have won something and asking for your card details to pay for shipping. Sadly, you will never receive anything but you will start noticing weird transactions coming from your bank account.
- Malware It is the contraction of malicious software onto your system. It a piece of software written with the intent of causing harm to data and devices. Malware is the overarching name for different types of viruses such as a Troja. Malware is often done through a range of viruses that will get into your computer to cause havoc, by damaging your computer, tablet, phone so the culprits can steal credit card details and other personal information.
- Email Bombing An email bomb is more a form of internet abuse. Email bombing is an overload of emails directed to one email address, this will cause the person receiving the emails server to become sluggish or even crash. They may not necessarily be stealing anything from you but having a sluggish server can be a real pain and hard work to fix.
- Logic Bombs It act in the same way as a virus, but are small programs or sections of a program, which are triggered by an event. This event can be a certain date or time, a certain percentage of disk space filled, the removal of a file and so on. A program could then delete critical sections of code, rendering your software as useless. The people who implement logic bombs are most commonly installed by insiders who already had access to the system.
- Theft Internet theft is the broad term for any type of theft that happens over the internet, this can be done through many ways such as fake ads, fake emails, viruses and snooping. The aim of internet theft is to steal your personal information and use it to then steal money out of your bank account or make purchases using your details.
- Social Media Hack & Spamming Social media hacking is often done as a joke, like the attack by the people who hacked Burger King twitter account. And many celebrities that are hacked may end up following people they would not usually or put random statuses. Even though for the average joe seeing a celebrity or brand post weird stuff can be amusing, it is an invasion of privacy. However, a hacker can also spread unwarranted content that can be distressing to people who view this content, it can also cause your account to be reported and shut down. Social media spamming comes when a person makes a fake account and becomes friends or followed by the average person. This then gives the fake account the freedom to spam inboxes with bulk messaging; this can be done for spreading malware. Spamming can also spread malicious links created with the intent to harm, mislead or damage a user or their device. Clicking on the malicious link, which may be advertising a new iPhone or weight loss treatment, means you could be downloading malware which can lead to the theft of personal information. Another dark side of social media is the ability for malicious accounts to spam your output by constantly replying with negative messaging. A form of trolling. Whilst you can easily report such behaviour to the social media platform and they should remove the user, or you can block them from seeing your content, it‘s easy for people to set up new bot accounts in minutes and begin their attack again. Some people have too much time on their hands.
- Electronic Money Laundering Money generated in large volumes illegally must be laundered before it can be spent or invested. One way to launder money is to do it electronically through messages between banks which is known as a ?wire transfer¦. It had previously seemed impossible to monitor or screen wire transfers as they occur due to the tremendous volume on transactions going through on a day-to-day basis, however banks are clamping down on the issue and filing away any suspicious activity.
- Sales & Investment Fraud: The fraudsters source the contact details and available account information for savings or investment account holders, fraudsters can adopt the persona of an investment broker. They will then contact customers to entice them with easy and profitable opportunities, but they seem a lot more trustworthy because they talk about accounts you already own and real results.
- Amendments to the Information Technology Act (IT Act): The concerned agencies and the governing authority should start imposing the lawful measure and penalties to curb down the activities in economy in order to safeguards the interest of the citizen as they should feel safe in using these resources. The governing bodies should train up a special team of the people who are well versed in the detection of these activities and implement an ethical strategy to track down the crimes and react accordingly to the justice system.
- Public Awareness Campaign: The concerned authorities, banks, educational institution should organize an awareness programme in educating the public regarding these activities with a proper live example in order to increase the financial literacy in the society.
- Strengthening Regulatory Bodies: Regulatory bodies such as the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), and Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) should collaborate closely. In order to have an active participation in lowering the activities and enhancing safety concerns to the public. Indian legal system has several provisions in place to tackle cybercrimes. The Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000 is the primary legislation governing cybercrimes in India. The Act defines cybercrimes and provides for penalties and punishments for offences such as hacking, data theft and cyber tourism. Apart from the IT Act, several other laws also have provisions for cybercrimes. For example, the Indian Penal Code (IPC) has sections that deal with offences such as identity theft, cyberstalking, and online defamation. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has also issued guideline financial institution and banks.
- Implementation of CERT: This is expert group that handles computer security incidents which is important to enact to the security measures in the economy with a quick responsiveness to the problem reported in the portal.

II. INTRODUCTION AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE
A. Rationale for the Study and Motivation
India is a major concern for the global community. The introduction, growth and utilization of information and telecommunication technologies have been accompanied by an increase in illegal activities. With respect to cyberspace, anonymous servers, hijacked emails and fake websites are being used as a tool and medium for fraud by cyber scammers. Indian fraud on the Internet is an obvious form of cybercrime that has been affected by the global revolution. This form of crimes is not exclusive to large sums of money to participate into business proposals but also covers romance, lottery and charity scams. Estimates of the total losses due to this scam vary widely. Thus, there is a need for international cooperation to stamp out such illicit activities and protect Internet users. Although new techniques are constantly being implemented and regulations being adopted to combat and eradicate diverse forms of fraud, yet cyberspace is also providing new means and tools that facilitate committing these scams. Accordingly, to address and analyse some issues related to the use of cyberspace for fraud by cyber scammers especially financial Fraud and the techniques used. It will also provide an analysis of the existing legislative and regulatory framework and their efficiency in combating this form of cross-border crime taking India as a case study. This paper presents the historical origin of financial frauds and presents a small survey of some popular financial frauds committed in the recent years in India. Due to the most recent demonetization that occurred in India, digital banking has gained relevance in the current era of digitalization. Banking has become more digital, which has sped up financial transactions and enabled opulent banking from any location at any time. The Indian government offers financial incentives for digital transactions in addition to promoting the use of cashless transactions. The prevalence of fraudulent activities expanded along with the use of digital banking transactions, which also brought forth new kinds of cyberfraud. Consequently, in order to stop fraudulent activities, one must possess solid information about how to use digitalization services. The current paper outlines the various frauds that have occurred in the banking industry since digitization and attempts to identify the various causes of these frauds in the Indian banking system. The motivation of a fraudster, including a digital fraudster, stems from either greed or necessity. Fraudulent activities are still primarily motivated by greed in many nations and legal systems. A lot of people encounter or are given the chance to engage in fraud. The fraudster is not scared of others, and their knowledge, temperament, and demeanour allow them to carry out the scam with confidence. Additionally, there's a chance that decent people will join the wrong crowd of criminals who force them to commit fraud at the workplaces or businesses where they work.
- Rising Prevalence: As the technology enhanced the gain on improvising the standard of living and ease of transacting in the modern era the number of frauds also upshoot in the economy where the fraud was targeted to all class of economy specifically the corporate class and business class using the digital payment mechanism in day-to-day life because of the stringent work culture and schedules.
- Social Impact: In the mechanism the people who were the victim of frauds also started losing trust on their own members, family mates and outsiders and connection in all manner due to the unethical trap and game played by some citizen who aren’t responsible enough in contributing to the economy and having a good social status in the economy.
- Cyber Security: One of the main causes of India's cyberfraud problems in the digital age is inadequate cybersecurity procedures. Many companies, especially smaller ones, lack the knowledge or finances necessary to put strong security measures in place. This can involve utilizing out-of-date software that has known vulnerabilities, forgetting to update systems on a regular basis, or eschewing fundamental procedures like personnel training and secure password regulations. People may also be at risk if they are ignorant of the dangers that exist online. They could unintentionally give away personal information or access to their devices by clicking on dubious links, phishing scams, or reusing passwords across accounts. Because of this, there is a greater opportunity for hackers to take advantage of the situation. They can quickly breach weakly guarded networks, steal important data, and destroy digital infrastructure.
- COVID-19 Impact: The COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted global supply chains, dampened consumer demand, and led to economic uncertainty, affecting earning of the economy worldwide. Assessing the impact of the pandemic on cyber frauds in India and examining the resilience of the Indian economy amid crisis situations is critical for mitigating risks and fostering recovery.
- Credential Stuffing: Using Someone else identity is one of the not unusual cyber- crimes. In this sort of cyberattack, stolen account credentials which includes usernames and passwords are used to advantage unauthorized get entry to money owed through massive-scale automated login requests. These lists are to be due to breaches and may frequently be bought on the darkish web. In this kind of fraud, the hacker does no longer must play the password guessing game.
The hacker uses an automated process where he can log hundreds to hundreds of thousands of breached password and usernames the use of automated gear.
6. Internet of Things (IoT) Exploitation: Internet of factors, or IoT, devices can check with the swiftly developing quantity of physical gadgets capable of connecting to the internet. Unsecured Internet of Things (IoT) devices which include DVRs, domestic routers, printers and IP cameras are vulnerable to assault, when you consider that they’re frequently no longer required to have the equal level of safety as computer systems. To breach a monetary organization, attackers will target insecure devices to create a pathway to different systems. Once they have entry from the IoT device, they have got full get admission to the complete community, together with all patron data.
7. Pharming: Pharming is carried out through the net. When a patron logs in to a bank's website, the attackers hijack the URL in this type of way that they're routed to any other internet site this is fake however appears just like the financial institution's authentic internet site
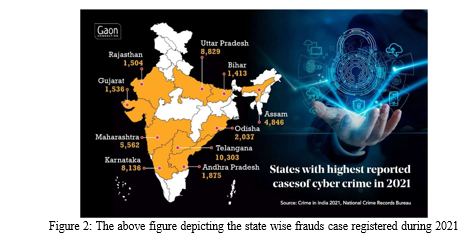
B. Statement of the Research Problem
The study aims to gain insights into the prevalence of fraud incidents, their financial losses due to fraudulent activities, and the underlying factors driving this trend. By understanding these aspects, organizations can better address the risk of fraud in the post digitalization. The era of digitalization gave a rise opportunity to the people to make the proper use of digitalization due to non-availability and the gestation period in which all the frauds which were initiated were part of the rural areas mostly from the northern state of the country namely Bihar, Odisha, Uttar Pradesh in which the documents shared by the initiator were the part of these regions.
Impact of digitalization on cyber frauds: One of the primary research problems is understanding the specific impact of the digitalization India. The demonetization gave the search for the new word era of cyber frauds which were only taking place in the less number post which due to shortage of currency notes and tender of currencies coins in the economy with introduction of the flexible payment gateways in the market the fraudster started taking a chance in making these activities has a real time work for their bread and butter having the risk facing legal consequence.
C. Review of Literature
Most of the Indian banks have launched their net banking and mobile banking web sites to facilitate the customers with on line availability of almost all banking merchandise. Internet banking is now a not unusual mode of stable and handy banking services. Internet Banking, additionally known as net-banking or online banking, is a digital charge device that permits the purchaser of a bank or a financial institution to make economic or non-economic transactions online thru the internet. This carrier offers online access to almost each banking service, historically to be had thru a neighbourhood branch including fund transfers, deposits, and online bill payments to the clients. Web banking can be accessed by any person who has enlisted for internet banking at the bank, having a functioning ledger or any monetary foundation. Subsequent to enrolling for web based financial offices, a client need not visit the bank each time he/she needs to profit a financial help. It isn't simply helpful yet in addition a protected strategy for banking. Net financial gateways are gotten by interesting User/Customer IDs and passwords.
Internet banking may be accessed through any individual who has registered for online banking on the financial institution, having an energetic bank account or any economic institution. After registering for online banking centres, a patron need not go to the bank every time he/she wants to avail a banking provider. It is not simply convenient but additionally a steady technique of banking. Net banking portals are secured by means of specific User/Customer IDs and passwords. There are three purposeful levels of Internet banking which can be informational, communicative and transactional. Under informational level, it's been identified that banks have the advertising records about the bank’s products and services on a standalone server. Communicative level of Internet banking lets in a few interplays between the bank’s structures and the consumer. Transactional level Internet banking allows bank clients to electronically switch budget to/from their bills, pay payments and conduct different banking transactions on-line.
- This study provides insights into the digitization of the banking industry and its impact on e-banking frauds.
- It highlights the technologies used by banking institutions to secure e-banking systems and identifies security vulnerabilities.
RBI, fraud with cybercrime 2019 In 2019–20, the overall value of bank frauds more than doubled. The total amount of fraud cases has climbed to Rs 1.85 lakh crore, up from Rs 71,543 crore in 2018-19, a 159% increase in value. According to data issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in its annual report, frauds also grew in volume by 28% to 8,707 incidents in 2019–20 from 6,799 occurrences in the previous year. Balasubramanian et al. (2014) examined the security issues and information system performance in online banking. 52 respondents to the study expressed concern that the information they provide online is not secure and that there is a chance that their bank's website would be compromised. Customers worry about malware threats as well.
a. Bharat Reddy (2024) Digital financial frauds in India: a call for improved investigation strategies
A recent report revealed that digital financial frauds accounted for a staggering ?1.25 lakh crore over the last three years in India. This study emphasizes the need for improved investigation strategies.
b. Soni R R, Soni Neena “An Investigative Study of Banking Cyber Frauds with Special Reference to Private and Public Sector Banks” “2024”
Use of technology in financial services of course has given a tremendous impetus to their development. However, due to heavy dependency on electronic and digital tools to carry out business and payment transactions, a serious threat has also been imposed to the safety and reliability of financial operations. Along with the growing trend of online and cyber transactions, the number of banking scams has also been on the rise affecting more and more people using banking technology tools. Frauds with online payments, ATM machines, electronic cards and net banking transactions have become a serious issue. Huge loss of money of people and institutions is caused every year due to these cyber frauds in banking firms, even after tight security measures in electronic transaction. Banks themselves have been found to be involved in fraudulent practices in a big way causing their customers enormous losses. This study is an effort to review and analyse the subject in Indian context with a comparative touch between private and public sector banks in the country
c. Dr Rakhi Tiwari Digital Banking: A Study of Fraudulent Practices in Indian Banks “2024”
This research focuses on the impact of digitalization on banking frauds. It examines fraudulent practices within Indian banks.
d. Priyanka Datta, Surya Narayana Panda, Sarvesh Tanwar “A Technical Review Report on Cyber Crimes in India” “2023”
In modern society the role of Internet and computer system is well recognized. People are greatly benefited with the development of networking and cyber space but some people are using this development in unethical way to have some illegal benefits. Recently different types of Social-networking attacks are witnessed by social networking sites user. Internal Revenue Service (IRS) impersonation scams, along with technical support scams are the most common type of tricks used by the attackers on unsuspecting victims in order to achieve financial benefits. The ratio of cyber-crime in India is constantly rising due to various reasons. Cyber-crlminals are very difficult to trace and this advantage is fully utilize by scammers. In this paper an intensive review has been done on cyber-crime in India. The studies shows that fraud cases are increasing and the victims are mostly in the age group of 20 – 29 years. Mostly children and women are affected. Thus, awareness programs are required for preventing or avoiding cyber-crime in India.
e. Upasana Ghosh “Online Financial Frauds and Cyber Laws in India - An Analysis” (2017)
With the advancement of technology, data protection and data privacy have become major concerns. This study explores the viewpoint of netizens on online financial transactions and whether existing cyber laws in India provide sufficient protection to privacy and confidentiality rights. It highlights common cybercrimes such as hacking, phishing, and vishing.
f. Robert B. Fried “Cyber Scam Artists”: A New Kind of con “2024”
Scam Artists have been around for centuries. Time progressed and technological innovations emerged and so have a new breed of con artist; the online fraudster. Utilizing various aspects and tools of the Internet, the online fraudster has become more successful than ever in defrauding a large target audience. So successful, that the issue has been the subject of much concern in recent years. Although, much is being done on multiple levels of government and within the public and private sectors, online fraud is still continuing to thrive. As long as the fraudster is motivated by greed and able to deceive others, fraud will always be in existence.
g. A Banerjee, D Barman “Cyber-Fraud is One Typo Away” “2024”
Spelling errors when typing a URL can be exploited by website-squatters: users are led to phony sites in a phenomenon we call parasitic URL naming. These phony sites imitate popular websites and try to extract personal information from unsuspecting users, or simply advertise and sell products to users. In this paper, we conduct a massive study in order to quantify the extent of this parasitic URL naming We start with a corpus of 900 popular websites, which we refer to as original URLs, and generate roughly 3 million URLs by varying the original names systematically and exhaustively. Over a period of 60 days, we analyze how many sites have URLs very similar to our original URLs. We find that parasitic URL naming is a wide- spread problem and quantify the extent of this issue. We believe that this work will provide the first step towards research and tools to combat web-fraud.
h. D Kannan “E-Frauds and Its Causes in Digital Transactions - A Myth or Reality” “2023”
Techno Transaction and online frauds.
i. AYUSH B. GURAV “CYBER CRIMES IN FINANCIAL ACTIVITIES” “2023”
Cyberlaw as a discipline continues to keep on developing at a very rapid pace. New advances in technology require new legal interpretations which have to be not just in sync with the requirements of the times but which must also mirror the aspirations, hopes and expectations of the users. In the present Article it contains a detail list of various kinds of financial cybercrimes committed through the means of Computer network and Internet by the fraudsters.
j. Suvrat Bahuguna, Ashok Wadje “Crimes in Cyberspace: Indian Scenario” “2023”
The recent advances made in the field of information technological all around the world has made people very tech savvy. People have indulged in over use of the technology and have become highly dependent over it. With such advancements and overuse of the technologies there has been observed a high increase in the number of crimes committed in the internet by people as it is considered the safest medium of committing a crime due to everything being virtual and there being no personal interaction of the criminal with the victim. Criminals spread viruses which in turn crash other people’s computers, steal identities of others, spread pornography etc. Until recently, experts in the field of IT had no knowledge and awareness in the area of cybercrimes, even the law enforcement officers did not have appropriate tools which were needed to tackle such problems as the old laws prevailing in the country were majorly silent on such crimes and the new laws introduced were not in accordance to the reality
k. Nitisha Aggarwal, Mitu Sehgal “An empirical analysis of Cyber Crimes, their prevention measures, and laws in India” “2023”
Cybercrime is pervasive, widespread, and becoming more intertwined with other elements of the criminal ecosystem. The Theft of a person's identity to the destruction of a nation's Internet connectivity as a result of a large attack on that nation's networking and computer capabilities are just a few examples. The term "Cybercrime" refers to any criminal activity involving computers or networks. Moreover, Cybercrime includes criminal acts committed online. Cybercrime is a new area of crime, and with each day that goes by, more and more new types of Cybercrime are becoming visible. This study examines the various types of Cybercrime, including those committed against people, property, and the government, and the steps taken to prevent these crimes
l. Ms Manisha Verma (2019) A Study on Fraud Analysis in Digital Banking in India
Due to the most recent demonetization that occurred in India, digital banking has gained relevance in the current era of digitalization. Banking has become more digital, which has sped up financial transactions and enabled opulent banking from any location at any time.
m. Yerra Shankar Rao, Hemraj Saini “Effect of Cyber Crime Indian Economy” “2023”
A lot of people in the world, mostly Indian have a limited knowledge of the crime occurring in cyberspace, known as cybercrime. Cybercrime happens in the world of computer and the Internet. This kind of crime has a severe impact on our economy, lives and society, because our society is becoming an information society, full of information exchange that is happening in cyberspace. Our research work is aimed at knowing the level of awareness of individuals on the existing phenomenon in India, and their impacts on India economy. A survey was carried out with the aims of getting these results using questionnaire as an instrument, the responses were quantitatively analysed using some statistical techniques. The results show that cracking, software piracy, and pornography among others are prevalent crimes in India.
n. Balsing Rajput “Cyber Economic Crime Typology” “2023”
This chapter explores the typology of cybercrime with theoretical briefing is explained and attempts to create a classification of cyber economic crime. The chapter explains various approaches like technological, criminological, psychological and sociological approaches to classify the cybercrimes. Cyber economic crimes are classified on the basis of modus used, amount of proceeds of crime, type of criminals or nature of threat agent and nature of victim or target. Classification based on the role of technology and dependence on technology is also considered. Most prevalent crime types are discussed in detail like phishing, ransomware, and credit/debit card frauds in cyberspace
o. Dr Yusuf Perwez, Syed Qamar Abbas, Jai Pratap Dixit, A Systematic Literature Review on the Cyber Security 2016
In recent years, the Internet has become an integral element of people's everyday lifestyles all across the world. Online criminality, on the other hand, has risen in tandem with the growth of Internet activity. Cyber security has advanced greatly in recent years in order to keep up with the rapid changes that occur in cyberspace. Cyber security refers to the methods that a country or organization can use to safeguard its products and information in cyberspace.
p. Syed Ubaid, Shakil, Mohammed Talha Alam, Shahab Saquib Sohail (2020) Rising Cyber Crime in Rural India: A Review
This paper analyses the increasing cyber-crime in India, especially in the rural areas, and cyber-attacks on service-providing government websites. Cyber-attacks are viewed within the context of important events to reveal the effectiveness of cyber-attack campaigns. The analysis highlights the range of cyber issues experienced during the lockdown in the country due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The paper shows how work- from-home campaigns digitalize the population, and how rural people become the victim of cyber-attacks. The analysis also emphasizes possible solutions to strengthen cyber security.
q. Supreeth Sandhu “Customers' usage behaviour of e-banking services: Interplay of electronic banking and traditional banking” “2020”
Digital finance which is facilitated by electronic banking is absolutely paramount for realising the developmental objectives of emerging economies. Success of service innovations in the field of electronic banking depends to a great extent on the perceptions and consumption patterns of the intended users of such services. This paper reports on a study that investigated customers' usage of electronic banking services in a multi-channel context. As e-banking usage is found still low, banks have scope for further propagation of technology and reaping its benefits. With the inclusion of technology, banks should not ignore the importance of employees as manual and electronic banking are found complementary to each other. There is still need to make electronic banking simpler and more secured as these are the major inhibitors of complete reliance on electronic media.
r. Surendra Kumar Saha “A Literature Review of Digitalization of the Banking Industry” “2019”
The development of information and communication technologies made modern payment methods possible. People's lives were made easier by the proliferation of smartphones and internet access, which also ushered in the age of digitalization. In addition to enhancing trade and commerce, digitalization also made smooth and quick money transactions. The entire research is based on an examination of the writings of many authors in the field. It discusses several forms of digital payments, the reasons why they are being used, how often it's being used, how will digital payments develop over the next few years, etc. It is also a fantastic approach to make the Indian government's Digital India initiative a successful program and turn our nation into a cashless economy. Following demonetization, there was an increase in digital payments, which paved the way for several digital wallets to enter India and enjoy long- term success. This study aims to identify the factors that various authors have considered when determining why people have adopted digital payments.
s. Suman Acharya, Sujata Joshi IMPACT OF CYBER-ATTACKS ON BANKING INSTITUTIONS IN INDIA: A STUDY OF SAFETY MECHANISMS AND PREVENTIVE MEASURES.
This research paper aims at studying the catastrophic impact of cybercrime on banking institutions, cyber security measures attempted to curb its e?ect and development of a robust cyber security mechanism. In recent years banks are its direct victim. In India, a number of banks generally fall prey to the massive malware attacks; it not only leaks valuable and sensitive information but also causes heavy financial losses. The objective of this study is to identify the business areas which are more susceptible to cyberattacks and to ensure customization and development of cyber security protocol. The study involves secondary data analysis from various web resources such as government websites, articles, and research papers available; it also includes case study analysis of di?erent cyber threats and crimes that caused huge financial loss in the past.
t. Gavin Oxburgh “Understanding cybercrime in ‘real world’ policing and law enforcement” “2020”
Cybercrime is a growing issue, still not fully understood by researchers or policing/law enforcement communities. Government reports assert that victims of cybercrime were unlikely to report crimes immediately due to the perception that police were ill- equipped to deal with these offences. Additionally, these reports identify policing issues including a lack of cybercrime knowledge. This paper reviews current research, providing a comprehensive account of cybercrime and addressing issues in policing such offences. We achieve this by describing the technological, individual, social and situational landscapes conducive to cybercrime, and how this knowledge may inform strategies to overcome current issues in investigations.
D. Identification of Research Gaps
- Gaps in Scale and Scope: While most studies acknowledge the rise of digital financial frauds in India, there is a lack of research on the specific scale and scope of the problem. This includes regional variations, demographics of victims, and types of frauds most prevalent.
- Focus on Investigation over Prevention: There seems to be a stronger emphasis on investigating past frauds compared to studies on preventative measures.
- Limited Focus on User Behaviour: While some studies touch on user awareness a deeper understanding of user behaviour and vulnerabilities to online scams is missing.
- Impact on Specific Demographics: The impact of digital frauds on vulnerable populations like rural communities or the elderly requires further exploration.
- Evolving Techniques of Fraudsters: Studies focusing on how fraudsters adapt their techniques with technological advancements are limited.
- International Comparison: A comparative analysis of digital fraud trends in India compared to other countries is absent.
- Effectiveness of Existing Laws and Enforcement: The effectiveness of existing cyber laws and law enforcement strategies in tackling digital frauds needs further investigation.
E. Theoretical underpinnings
- Theory of Routine Activities (RAT): According to RAT, there must be three conditions met for criminal action to occur: a motivated offender, a suitable victim, and the lack of capable guardians. Due to a surge in online financial transactions and the number of internet users expanding, many of whom are not familiar with cyber security procedures, digitalization presents an abundance of possible targets. Users are more vulnerable due to a lack of understanding or worse cybersecurity safeguards in particular areas.
- Diffusion of Innovation Theory: In today's world, where online banking and mobile wallets are increasingly popular, cybercriminals are taking advantage of these new technologies to create new ways to steal money. The ease of sharing information online makes it easy for these criminals to learn from each other. They can quickly spread successful scam techniques and adapt their methods based on what works and what doesn't. This constant innovation by hackers makes it even more important to stay informed about the latest online threats.
- Social Cognitive Theory: It suggests people learn by observing others' behaviour and its consequences. Exposure to successful cyber frauds, even though media portrayals, can influence individuals. They might see cybercrime as a viable option, especially if the focus is on the gains and not the repercussions
III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Scope of the Study
The study revolves around the Indian scenario of the cyber fraud occurrences with strategy used by the fraudsters post digitalization of banking activities. The study was conducted in the region of Bengaluru city in the limits of south east division of the cyber control of the government agencies.
The study completely depends upon the targeted population of the age group between 18 years till 60 years being the population size. This research conducted speaks about the incidents faced by the victims of cyber frauds in the city wherein the affected population are being the working-class people, entrepreneurs and college student. The study was conducted for a time period from June-2023 till March 2024 through a primary study by sharing a questionnaire.
B. Research Objective
- To understand the types of cyber fraudulent activities, post digitalization
- To evaluate the amount of financial loss occurred to victim of the cyber fraudulent activities
- To find out the suitable solution to the cyber fraudulent activities.
- To study impact of digitalization on digital banking activities.
- To analyse the effects of fraudulent activities in the economy.
C. Framing of Research Hypotheses
- Impact of Digitalization on Cyber Fraud:
- Null Hypothesis (Ho): There is no significant relationship between digitalization and cyber fraud occurrences.
- Alternative Hypothesis(H1): There is a significant relationship between digitalization and cyber.
2. Impact of age group and negligence factor on cyber frauds
- Null Hypothesis (Ho): There is no significant relationship between age group and negligence to cyber frauds
- Alternative Hypothesis(H1): The significant relationship between age and negligence to cyber frauds.
3. Impact of age group and being a victim of cyber frauds
- Null Hypothesis (Ho): There is no significant relation between age factor and being a victim of cyber frauds
- Alternative Hypothesis(H1): There is a significant relation between age factor and being a victim of cyber frauds
4. Impact of age group and reporting of the incidents
- Null Hypothesis (Ho): There is no significant relation between age factor and reporting of cyber frauds.
- Alternative Hypothesis(H1): There is a significant relation between age factor and reporting of cyber frauds.
D. Research Design
The research design is the methodological blueprint that outlines the strategies and procedures for collecting, analysing, and interpreting data. In the context of this study on Cyber Frauds post digitalization in India, the research design is carefully crafted to address the research objectives and test the formulated hypotheses. This section details the key components of the research design.
- Research Approach Quantitative Approach: The study adopts a primarily quantitative research approach to analyse numerical data, trends, and relationships. This approach allows for statistical analysis, hypothesis testing, and the exploration of patterns and trends in Cyber Frauds post digitalization
- Data Collection: Primary Data The research heavily relies on primary data collected from various sources, including government reports, academic journals, and industry publications. Time-series data Cyber Frauds post digitalization in India
- Random Convivence Sampling: Random Convivence Sampling categorizing data by sectors, regions, and time periods. This allows for a more in-depth analysis of of Cyber Frauds post digitalization in India.
- Validity and Reliability Cross- Verification The validity of findings will be enhanced through cross-verification of data from multiple sources. Robust statistical methods will be employed to ensure the reliability of results. Consistency checks and sensitivity analyses will be conducted to assess the robustness of the findings.
E. Methods for Data Collection
Primary Data: The primary data to the study is from the collection of information from the public who have undergone this situation or faced the same kind of issue within themselves or to their known one. A questionnaire was prepared relating to the topic and shared to respond accordingly by giving the instruction for the study required.
The study completely depends upon the targeted population of the age group between 18 years till 60 years being the population size. This research conducted speaks about the incidents faced by the victims of cyber frauds in the city wherein the affected population are being the working-class people, entrepreneurs and college student. The study was conducted for a time period from June-2023 till March 2024 through a primary study by sharing a questionnaire.
IV. DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
A. Techniques for Data Analysis
In accordance to the topic to conduct viable research and interpret on the data collected the data analysis methods were been adopted on the basis of the hypothesis framed to find out the inferences.
- Descriptive statistics: This is a broad category of techniques that are used to summarize the basic characteristics of a dataset. Common descriptive statistics include measures of central tendency (like mean, median, and mode) and measures of dispersion (like range, standard deviation, and variance).
- Inferential statistics: These techniques allow you to make generalizations about a population based on a sample of data. Common inferential statistics include hypothesis testing, which is used to test whether a particular hypothesis about a population is likely to be true.
B. Hypotheses Testing and Methods
Chi-Square Test: The Chi-Square test, is a statistical test used to compare observed data with data that would be expected under the hypothesis that the observations are independent. It’s particularly useful for dealing with categorical data and for determining
- Impact of Digitalization on Cyber Fraud:
- Null Hypothesis (Ho): There is no significant relationship between digitalization and cyber fraud occurrences.
- Alternative Hypothesis(H1): There is a significant relationship between digitalization and cyber fraud occurrences.
2. Impact of age group and negligence factor on cyber frauds
- Null Hypothesis (Ho): There is no significant relationship between age group and negligence to cyber frauds
- Alternative Hypothesis(H1): There is a significant relationship between age and negligence to cyber frauds.
3. Impact of age group and being a victim of cyber frauds
- Null Hypothesis (Ho): There is no significant relation between age factor and being a victim of cyber frauds
- Alternative Hypothesis(H1): There is a significant relation between age factor and being a victim of cyber frauds
4. Impact of age group and necessary action taken
- Null Hypothesis (Ho): There is no significant relation between age factor and necessary action taken.
- Alternative Hypothesis(H1): There is a significant relation between age factor and necessary action taken.
C. Data Interpretation
1. Impact of Digitalization on Cyber Fraud
In the accordance of the study the inferential statistics was used with the tool of cross tabs and technique Pearson Chi-Square test was used to analyse the data to interpret and to result upon the hypothesis drawn in results the statistic is relatively high. By conducting the analysis through the cross tabs tool, we could find that there is a significant relationship between digitalization and cyber fraud occurrences. Accordingly, we can draw a solution to reject the null hypothesis and accept alternative hypothesis.
|
Chart 1: Impact of Digitalization on Cyber Fraud |
|||
|
|
Value |
df |
Asymptotic Significance (2- sided) |
|
Pearson Chi-Square |
100.000 |
96 |
.370 |
|
Likelihood Ratio |
77.239 |
96 |
.920 |
Source: Primary Data
2. Impact of age group and negligence factor on cyber frauds
In the accordance of the study the inferential statistics was used with the tool of cross tabs and technique Pearson Chi-Square test statistic is 19.071, and the associated p-value is .087. With a significance level of .05, this p-value is higher than the threshold. As per the analysis so we can come to a conclusion to reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis in which the study conducted tells there is a significant relationship between age and negligence to cyber frauds.
|
Chart 2: Impact of age group and negligence factor on cyber frauds |
|||
|
|
Value |
df |
Asymptotic Significance (2- sided) |
|
Pearson Chi-Square |
19.071a |
12 |
.087 |
|
Likelihood Ratio |
21.594 |
12 |
.042 |
Source: Primary data
3. Impact of age group and being a victim of cyber frauds
In the accordance of the study the inferential statistics was used with the tool of cross tabs and technique The Pearson Chi-Square test statistic is 10.795, and the associated p-value is .029. Since this p-value is less than the significance level of
.05, we reject the null hypothesis. As per the analysis so we can come to a conclusion to reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis in which the study conducted tells there is a significant relationship between age and victim of cyber frauds
|
Chart 3: Age group and being a victim of cyber frauds |
|||
|
|
Value |
df |
Asymptotic Significance (2- sided) |
|
Pearson Chi-Square |
10.795 |
4 |
.029 |
|
Likelihood Ratio |
10.028 |
4 |
.040 |
Source: Primary Data
4. Impact of age group and necessary action taken
In the accordance of the study the inferential statistics was used with the tool of cross tabs and technique Pearson Chi-Square test statistic is 3.185, with a corresponding p-value of .527. Since the p-value is greater than the commonly used significance level of .05, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. As per the analysis so we can come to a conclusion to reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis in which the study conducted tells there is a significant relationship between age and necessary action taken.
|
Chart 4: Impact of age group and necessary action taken |
|||
|
|
Value |
df |
Asymptotic Significance (2- sided) |
|
Pearson Chi-Square |
3.185a |
4 |
.527 |
|
Likelihood Ratio |
3.864 |
4 |
.425 |
Source: Primary Data
|
Chart No: 5(a) No of victims according to age groups |
||
|
Age Groups |
Number of responses |
% |
|
18-25 |
6 |
24% |
|
25-30 |
5 |
20% |
|
30-40 |
7 |
28% |
|
40-50 |
2 |
8% |
|
50-60 |
5 |
20% |
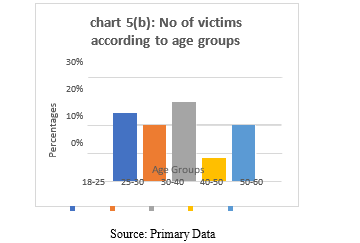
According to 24% of replies, 18-25 a group of young adults is vulnerable to cybercrime. This may be because they use the internet more frequently and may not have as much experience seeing and avoiding scams. According to age group of 25-30 years being 24% of replies, this group of young adults is vulnerable to cybercrime. This may be because they use the internet more frequently and may not have as much experience seeing and avoiding scams. According to age group of 30-40 years being 28% of replies, people in this group appear to be most vulnerable to cybercrime. They might be in more stable financial situations, which makes them desirable prey for more intricate frauds. At age group of 40–50 only 8% of suggesting a lower frequency of cyber fraud than other age groups. This does not, however, imply that they are immune from numerous internet scams. At age group of 50-60 around Twenty percent of respondents are between the ages of fifty and sixty, which is comparable to the 25–30 age group. Because they might have more disposable means and may not be as knowledgeable about the nuances of online security, they could be the focus of harassment.
The 32% of the comments, are related to the job frauds this type of fraud seems to be a major worry in the cyberspace. Online job seekers run the risk of falling for schemes that promise lucrative jobs or work-from-home opportunities; these scams can cause financial loss or identity theft. Fraud Related to E-Commerce this type of fraud has the largest rate (36%), indicating that it is a common threat. This includes a broad range of dishonest practices that target both customers and businesses, like phishing scams, money fraud, and phony internet stores. Property-Related Fraud this is another noteworthy problem in the cyber world, accounting for 20% of replies. This could include con games involving fraudulent real estate listings, fraudulent rentals, or mortgage scams that take advantage of people's ambitions to buy a home or invest in real estate. Virtual Gaming Although the percentage is 12%, fraud pertaining to virtual gaming still presents a risk to users of online gaming platforms. Scams that affect both casual and professional gamers could include those involving in-game purchases, account hacking, or fake gaming tournaments.
|
Chart 6(a): Chart representing type of financial fraud encountered by victims |
||
|
Type of financial fraud encountered |
No of response |
% |
|
Job Fraud |
8 |
32% |
|
E Commerce Related |
9 |
36% |
|
Property Related Fraud |
5 |
20% |
|
Virtual Gaming |
3 |
12% |

V. FINDINGS AND RECOMMENDATION
A. Research Outcome and Findings
- Increased Prevalence and Cost: With the introduction of the digital platform and social media with large no of startup and technological advancement there is a rapid growth in the cybercrime in which the rate of people falling in these scenario or becoming victim are increasing day by day bearing a huge cost in the form losing their hard earned money to these crime and legal authorities are also facing huge hinderance to find out the accused people to take necessary action against them in which the amount spent to find out these people are crossing the fixed border of state and country also in which the judicial authority have to change the type of punishment and law regarding to these activities in order to curb down the frauds and safeguards the victim and other public having a strong team to trace down and respond to the victim within due time in order to have strong relationship with the public and governing authorities.
- Challenges in Addressing the Issue: Lack of awareness and hesitancy to report cybercrimes create a blind spot. Many victims, unsure or embarrassed, stay silent. This hinders understanding the true scale of the problem, making it difficult to allocate resources effectively. Cybercrime thrives in the borderless world of the internet. Investigations become complex when chasing criminals operating across international boundaries. Law enforcement agencies need better international cooperation and robust digital forensics capabilities to track these virtual foes.
- The Ever-Shifting Arsenal of Cybercriminals: Cybercriminals are like cunning magicians, constantly pulling new tricks from their hats. While traditional methods like phishing emails and social engineering remain prevalent, be prepared for these emerging threats.
- SIM Swapping: This involves tricking your carrier into transferring your phone number to a SIM card controlled by the attacker, allowing them to intercept verification codes and potentially steal your funds.
- Mobile Wallet Woes: As mobile wallets gain popularity, vulnerabilities emerge. Malicious apps or stolen credentials can lead to attackers draining your digital funds.
- Crypto jacking: This stealthy attack uses your device's processing power to mine cryptocurrency for the attacker, potentially slowing down your device and driving up your electricity bill.
4. Impact of Digitalization on Banking Frauds: Digital banking operations are a vital requirement for both banks and society at large. Digital banking has shown to be beneficial in facilitating seamless financial transfers, which saves time and eliminates the need to wait in line at banks. Error-free transactions without human intervention have been achieved through the automation of banking procedures. Customers find online shopping to be highly handy as a result of this technologically advanced financial environment. They don't need to carry cash with them all the time to handle their substantial cash holdings. Different payment methods via smartphone apps, such as Paytm, Phone Pay, Airtel Pay, etc., have made minor daily transactions with money flow easier. Online banking features such as NEFT and other methods have made it easier for households to transfer money securely and deposit funds for things like insurance premiums, EMI, gas cylinder reservations, and online power bill payments. As a result, while greater digitization has greatly benefited society, it has also given rise to unethical ways to profit from it. This study's findings indicate that a rise in banking fraud is significantly impacted by a greater degree of digitization in the banking industry.
5. Rise In digital payment frauds attempts: To mitigate the negative impact on citizens and the economy, the government printed and circulated unauthorised currency. This was a significant step towards demonisation, as the economy temporarily stopped. The Ministry of Finance then introduced UPI through the National Payments CI (NPCI) as part of India's digital transformation. The government also launched several other initiatives, such as the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY). wherein the rise in cybercrime also affected citizens, who began losing money from their accounts because some of them were illiterate. These individuals shared the necessary credentials, and some of the fraudsters used those same credentials to access other accounts, increasing the number of frauds attempts to 30%.
6. Techno-Legal Issues: While India's digitalization has yielded many advantages, it has also resulted in a rise in cybercrimes, creating techno- legal obstacles for law enforcement and politicians. Technology development has led to an increase in the sophistication and complexity of cybercrimes. To carry out crimes like hacking, phishing, identity theft, online fraud, cyberbullying, and cyberterrorism, criminals take use of weaknesses in digital systems. Technology development has led to an increase in the sophistication and complexity of cybercrimes. To carry out crimes like hacking, phishing, identity theft, online fraud, cyberbullying, and cyberterrorism, criminals take use of weaknesses in digital systems. Large volumes of personal data are being collected and stored as a result of digitalization, which raises privacy and data protection issues. Data breaches and illegal access to personal data underscore the necessity of strong data protection regulations and enforcement protocols. It's possible that courts and law enforcement organizations lack the knowledge and experience needed to properly investigate and prosecute cybercrimes. Initiatives to continuously improve capacity are necessary to give staff members the abilities and information needed to defend against cyberattacks. Critical industries including banking, healthcare, and utilities are more vulnerable to cyberattacks due to their growing reliance on digital infrastructure. To reduce risks, cybersecurity infrastructure must be strengthened and proactive measures like encryption, network monitoring, and recurring security audits must be put in place. Raising public knowledge about cyber hazards and improving digital literacy are critical to reducing cybercrime. Individuals, corporations, and government entities can all benefit from education campaigns that promote cybersecurity knowledge and appropriate online conduct.
B. Theoretical Implication
- Social Learning Theory: According to the Social Learning Theory, people learn criminal behaviour through interactions with others, particularly peers and role models. In the digital age, cybercriminals can share strategies, tools, and knowledge via online forums and groups, encouraging the spread of cybercrime expertise. Understanding the social dynamics of cybercrime networks is critical for designing targeted interventions that interrupt criminal conduct.
- Strain Theory: This theory suggests that individuals engage in criminal behaviour when they experience strain or frustration resulting from the inability to achieve culturally prescribed goals through legitimate means. In the context of digitalization, disparities in access to technology, economic inequality, and limited opportunities in traditional sectors may contribute to the strain experienced by certain segments of the population, leading to involvement in cybercrimes as an alternative means of achieving financial gain or status.
- Legal Pluralism: This theoretical framework recognizes the coexistence of multiple legal systems and norms within a society, including formal legal institutions and informal mechanisms of social control. In the realm of cybercrime, legal pluralism highlights the need to reconcile traditional legal frameworks with emerging challenges posed by digitalization, such as jurisdictional issues, cross-border enforcement, and the harmonization of laws governing cyberspace.
- Surveillance Studies: This interdisciplinary field explores the societal implications of surveillance practices, including issues of privacy, power, and control. In the context of cybercrime, digital surveillance technologies are employed by both state and non-state actors for purposes such as monitoring online communications, detecting cyber threats, and profiling individuals for targeted interventions. The expansion of surveillance capabilities raises concerns about civil liberties and the potential for abuse of power in the name of security.
C. Managerial Implication
- Investment in Cybersecurity: Cybersecurity investments must be prioritized by organizations in order to avoid, detect, and respond to cyber threats. This comprises the deployment of effective firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption technologies, and security policies to preserve digital assets and sensitive information. The required agencies and governing authorities should also implement some number of strategies in order to curb down these cybercrime attacks wherein gives due importance to the public to safeguard their money.
- Risk Assessment and Management: Regular risk assessments and detailed risk management strategies are critical for detecting vulnerabilities, analyzing potential consequences, and implementing appropriate controls. Managers should include cybersecurity issues into larger business risk management frameworks to ensure that they correspond with organizational goals and priorities.
- Vendor Risk Management: Organizations often rely on third-party vendors and service providers for various business functions, increasing the risk of supply chain attacks and data breaches. Managers should implement robust vendor risk management programs, including due diligence, contractual agreements, and ongoing monitoring of vendor security practices.
- Board-level Oversight: Cybersecurity should be a regular agenda item at board meetings, with senior management providing updates on cyber risk exposure, mitigation efforts, and incident response preparedness. Managers should facilitate constructive dialogue among board members to foster a culture of accountability and ensure that cybersecurity receives the necessary attention and resources.
- Continuous Improvement: Cybersecurity is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, assessment, and improvement. Managers should establish mechanisms for collecting feedback, conducting post-incident reviews, and incorporating lessons learned into future cybersecurity initiatives to enhance organizational resilience against evolving cyber threats
D. Limitations of the Study
- Data Availability and Reliability: One of the primary challenges is the availability and reliability of data related to cybercrime incidents in India. Official crime statistics may not capture the full scope of cybercrimes due to underreporting, inconsistent reporting standards, and the secretive nature of cybercriminal activities. In some cases, victim are hesitant to register or file a report based on the incident due to unavoidable circumstances in which it becomes a problem for both the governing authorities and the users to get the data relating to it.
- Sampling Bias: If the study relies on specific data sources or samples, such as reported cybercrime cases or surveys of internet users, there may be inherent biases that limit the generalizability of findings. Accordingly, to the data collected it show there are some respondents who are il-literates and feel insecure to answer to the question put forward for example, certain demographic groups or regions may be overrepresented or underrepresented in the data.
- Methodological Constraints: The choice of research methods, such as surveys, interviews, or case studies, can introduce limitations. Each method has its strengths and weaknesses, and researchers must carefully consider the appropriateness of their chosen approach and acknowledge any limitations associated with it.
- Temporal Factors: Cybercrime is a rapidly evolving phenomenon, influenced by technological advancements, changes in online behaviour, and shifts in criminal tactics. A study conducted at a specific point in time may not capture long-term trends or emerging threats, necessitating ongoing monitoring and analysis.
- Cross-Cultural Variations: India is a diverse country with varying socio- cultural, economic, and technological landscapes. Cybercrime trends and responses may differ across regions, communities, and demographic groups, highlighting the importance of considering cultural context in the study's findings.
- Legal and Regulatory Framework: The effectiveness of cybercrime prevention and enforcement efforts in India is influenced by the country's legal and regulatory framework. Limitations or gaps in existing laws, enforcement mechanisms, and international cooperation agreements may impact the study's findings and recommendations.
- Digital Divide: Access to technology and internet connectivity varies across different segments of the population in India. Vulnerable groups, such as rural communities, low-income households, and marginalized individuals, may face barriers to accessing online resources and may be disproportionately affected by cybercrimes. Research on cybercrime involves sensitive information and raises ethical concerns related to privacy, consent, and data security. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and safeguard the confidentiality of participants' data while conducting their study. Cybercrime is a complex phenomenon that requires interdisciplinary insights from fields such as criminology, sociology, law, computer science, and psychology. A study that lacks input from multiple disciplines may provide a limited understanding of cybercrime dynamics and implications.
- Policy Implications: While research on cybercrime can inform policy development and intervention strategies, translating research findings into actionable policies requires careful consideration of political, economic, and social factors. The study's recommendations may face implementation challenges or unintended consequences in practice.
E. Conclusion
- With doing an analysis on the topic cyber frauds post digitalization in India there is a significant positive relation between the digitalization and occurrence of cyber frauds as it has given a proper platform the people who are in need of money can use this platform as a revenue earning platform.
- The research on cyber frauds post digitalization in India sheds light on the escalating challenges posed by fraudulent activities in the banking sector. The study underscores the critical need for enhanced cybersecurity measures, public awareness campaigns, and regulatory frameworks to combat the rising tide of cyber fraud. The impact of digitalization on cyber frauds has been profound, with the demonetization drive in India catalysing a surge in digital transactions and subsequently, fraudulent practices. The research highlights the various types of cyber frauds prevalent in the Indian banking industry and delves into the root causes driving these illicit activities.
- The study emphasizes the importance of understanding the motivations behind cyber fraud, ranging from greed to necessity, and the social implications of fraudulent practices on trust within communities. Inadequate cybersecurity procedures, lack of customer awareness, and the exploitation of vulnerabilities in IoT devices are identified as key factors contributing to India's cyber fraud challenges. The COVID-19 pandemic has further exacerbated these risks, necessitating a thorough examination of the resilience of the Indian economy amidst crisis situations.
- In conclusion, the research underscores the urgency of addressing cyber fraud through a multi-faceted approach that combines technological advancements, legislative reforms, and collaborative efforts between stakeholders. By analysing the impact of digitalization on cyber frauds in India, the study provides valuable insights for policymakers, financial institutions, and law enforcement agencies to strengthen cybersecurity infrastructure, mitigate risks, and safeguard the digital economy against fraudulent activities.
- By conducting an analytical analysis on the title cyber frauds post digitalization in India the conclusion drawn to the topic gives the importance of the responsibility and being responsible in order to safeguard themselves form these kinds of activities for the self- development and growth the nation.
F. Scope for future research
- Emerging Cybercrime Trends: Investigate new and emerging cybercrime tactics and techniques, such as ransomware, social engineering, phishing, and supply chain attacks. Analyse how these methods evolve over time and how perpetrators adapt to advancements in cybersecurity measures.
- Psychology of Cybercriminals: Explore the psychological profiles and motivations of cybercriminals to better understand their behaviour and decision-making processes. This could involve studying factors such as risk tolerance, moral reasoning, and personality traits associated with cybercriminal activity.
- Impact on Individuals and Organizations: Assess the financial, reputational, and psychological impact of cyber frauds on individuals, businesses, and governments. Investigate the short-term and long-term consequences of cyberattacks, including recovery costs, legal liabilities, and damage to brand reputation.
- Future Threat Scenarios: Anticipate future cybercrime trends and potential threat scenarios resulting from emerging technologies such as quantum computing, 5G networks, and artificial intelligence. Assess the implications of these developments for cybersecurity preparedness and risk management strategies.
References
[1] PWC Report on “Combating fraud in the era of digital payments” “2022” [2] ciso.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/why-are-online-frauds-still-happening-in- the-digital-age/88045034 [3] S. KALPANA, M. MAHALAKSHMI “CYBER CRIME: A GROWING THREAT TO INDIAN E-BANKING SECTOR” “JETIR December 2020. [4] Vineeth George “Digitalization of Payments Post Demonetization of Currency: Prospects and Challenges” “February 2019” [5] Prateeskha Barman Ricihika Kedia “CYBER CRIME IN INDIA WITH REFERENCE TO BANKING SECTOR” “2023” [6] https://www.hindustantimes.com/business/financial-fraud-top-cyber-crime-in-india- upi-e-banking-most-targeted-study-101695036325725 [7] Saurabh Mittal “A Study of Cyber Crime and Perpetration of Cyber Crime in India” “2019” [8] M. Dasgupta “CYBER CRIME IN INDIA: A COMPARATIVE STUDY” ”2021” [9] Priyanka Datta, Surya Narayana Panda, Sarvesh Tanwar “A Technical Review Report on Cyber Crimes in India” “2023” [10] Bharat Reddy (2024) Digital financial frauds in India: a call for improved investigation strategies [11] Dr Rakhi Tiwari Digital Banking: A Study of Fraudulent Practices in Indian Banks “2024” [12] AYUSH B. GURAV “CYBER CRIMES IN FINANCIAL ACTIVITIES” “2023” [13] Balsing Rajput “Cyber Economic Crime Typology” “2023” [14] Dr Yusuf Perwez, Syed Qamar Abbas, Jai Pratap Dixit, A Systematic Literature Review on the Cyber Security 2016 [15] Syed Ubaid, Shakil, Mohammed Talha Alam, Shahab Saquib Sohail (2020) Rising Cyber Crime in Rural India: A Review [16] Supreeth Sandhu “Customers\' usage behaviour of e-banking services: Interplay of electronic banking and traditional banking” “2020” [17] Surendra Kumar Saha “A Literature Review of Digitalization of the Banking Industry” “2019” [18] Sujata JoshiIMPACT OF CYBER-ATTACKS ON BANKING INSTITUTIONS IN INDIA: A STUDY OF SAFETY MECHANISMS AND PREVENTIVE MEASURES
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Manjunath M, Dr Selvi S . This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET60191
Publish Date : 2024-04-12
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

