Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Adaptive Cybersecurity in the Digital Age: Emerging Threat Vectors and Next-Generation Defense Strategies
Authors: Harish Kumar Reddy Kommera
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.64226
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
This article examines the rapidly evolving landscape of cybersecurity, focusing on emerging threats and innovative defense mechanisms. We analyze four key threat vectors: Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), ransomware, Internet of Things (IoT) vulnerabilities, and social engineering attacks. These threats pose significant risks to organizations, including data breaches, financial losses, and operational disruptions. In response, we explore cutting-edge defense mechanisms such as Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for threat detection, Zero Trust Architecture for access control, blockchain for data integrity, behavioral analytics for insider threat detection, and quantum cryptography for enhanced encryption. The article also outlines best practices for cybersecurity, including regular software updates, strong password policies, employee training, and security audits. By synthesizing current research and industry trends, this article provides a comprehensive overview of the cybersecurity landscape, emphasizing the need for continuous adaptation and vigilance in the face of evolving cyber threats.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
In an increasingly interconnected digital landscape, cybersecurity has become a critical concern for organizations and individuals alike. The rapid evolution of technology has not only brought unprecedented opportunities but also given rise to sophisticated cyber threats that can compromise data integrity, privacy, and operational continuity. According to the 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report, the landscape of cyber threats continues to evolve, with ransomware attacks, social engineering, and system intrusion remaining prevalent across various industries [1].
As cyber attackers continuously refine their techniques, the cybersecurity field must adapt and innovate to stay ahead of emerging threats. This article examines the current state of cybersecurity, focusing on advanced persistent threats (APTs), ransomware, Internet of Things (IoT) vulnerabilities, and social engineering attacks. Additionally, we explore cutting-edge defense mechanisms, including artificial intelligence-driven threat detection, zero trust architecture, and quantum cryptography, which promise to reshape the cybersecurity landscape [2]. By analyzing these threats and countermeasures, this study aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the challenges and opportunities in modern cybersecurity, emphasizing the need for continuous adaptation and vigilance in an ever-changing digital environment.
II. EMERGING CYBERSECURITY THREATS
A. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
- Definition and characteristics APTs are sophisticated, long-term cyber intrusions orchestrated by well-resourced actors, often nation-states or organized crime groups. These threats are characterized by their persistence, stealth, and adaptability. APTs typically involve multiple attack vectors and exploit various vulnerabilities to maintain long-term access to a target's network.
- Impact on organizations The impact of APTs can be severe and far-reaching. Organizations may suffer from intellectual property theft, financial losses, reputational damage, and compromised operational integrity. In some cases, APTs can remain undetected for months or even years, allowing attackers to gather sensitive information or manipulate critical systems over extended periods.
B. Ransomware
- Evolution of ransomware attacks Ransomware has evolved from simple file encryption to more sophisticated attacks involving data exfiltration and double extortion tactics. Modern ransomware operations often employ a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model, where developers lease their malware to affiliates, expanding the scope and frequency of attacks.
- Economic and operational consequences The economic impact of ransomware is staggering, with global damages predicted to reach $265 billion annually by 2031 [3]. Beyond immediate financial losses from ransom payments, organizations face significant operational disruptions, data loss, and potential legal and regulatory consequences.
C. Internet of Things (IoT) Vulnerabilities
- Risks associated with interconnected devices The proliferation of IoT devices has expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals. Many IoT devices lack robust security measures, making them vulnerable to exploitation. Common vulnerabilities include weak authentication, unencrypted communications, and infrequent software updates.
- Potential for large-scale attacks Compromised IoT devices can be weaponized into large botnets, capable of launching devastating Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. The interconnected nature of IoT also means that a breach in one device can potentially compromise entire networks or critical infrastructure systems.
D. Social Engineering Attacks
- Psychological manipulation techniques Social engineering attacks exploit human psychology rather than technical vulnerabilities. Techniques include phishing, pretexting, baiting, and tailgating. These attacks often leverage fear, urgency, or authority to manipulate victims into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security.
- Bypassing technical security measures By targeting the human element, social engineering attacks can bypass even the most sophisticated technical security measures. A recent study found that 82% of breaches involved the human element, including social engineering, errors, and misuse [4].
|
Threat Type |
Description |
Key Impacts |
|
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) |
Long-term, stealthy cyber intrusions by well-resourced actors |
Intellectual property theft, Financial losses, Reputational damage, Compromised operational integrity |
|
Ransomware |
Malware that encrypts data and demands ransom for decryption |
Financial losses, Operational disruptions, Data loss, Potential legal consequences |
|
IoT Vulnerabilities |
Security weaknesses in interconnected devices |
Expanded attack surface, Potential for large-scale DDoS attacks, Compromise of entire networks |
|
Social Engineering Attacks |
Psychological manipulation to gain unauthorized access or information |
Bypass of technical security measures, Data breaches, Financial fraud |
Table 1: Emerging Cybersecurity Threats and Their Impacts [3, 4]
III. INNOVATIVE DEFENSE MECHANISMS
A. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- Application in threat detection AI and ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate cyber threats. These technologies enable more accurate and efficient threat detection compared to traditional rule-based systems. However, the development of trustworthy AI systems for cybersecurity applications requires mechanisms for verifying claims about their performance and reliability [5].
- Real-time response capabilities AI-driven security systems can respond to threats in real-time, often faster than human analysts. This rapid response capability is crucial in mitigating the impact of cyber attacks. AI can automatically isolate infected systems, update firewall rules, or initiate other defensive measures without human intervention. The challenge lies in ensuring these autonomous systems make reliable and verifiable decisions [5].
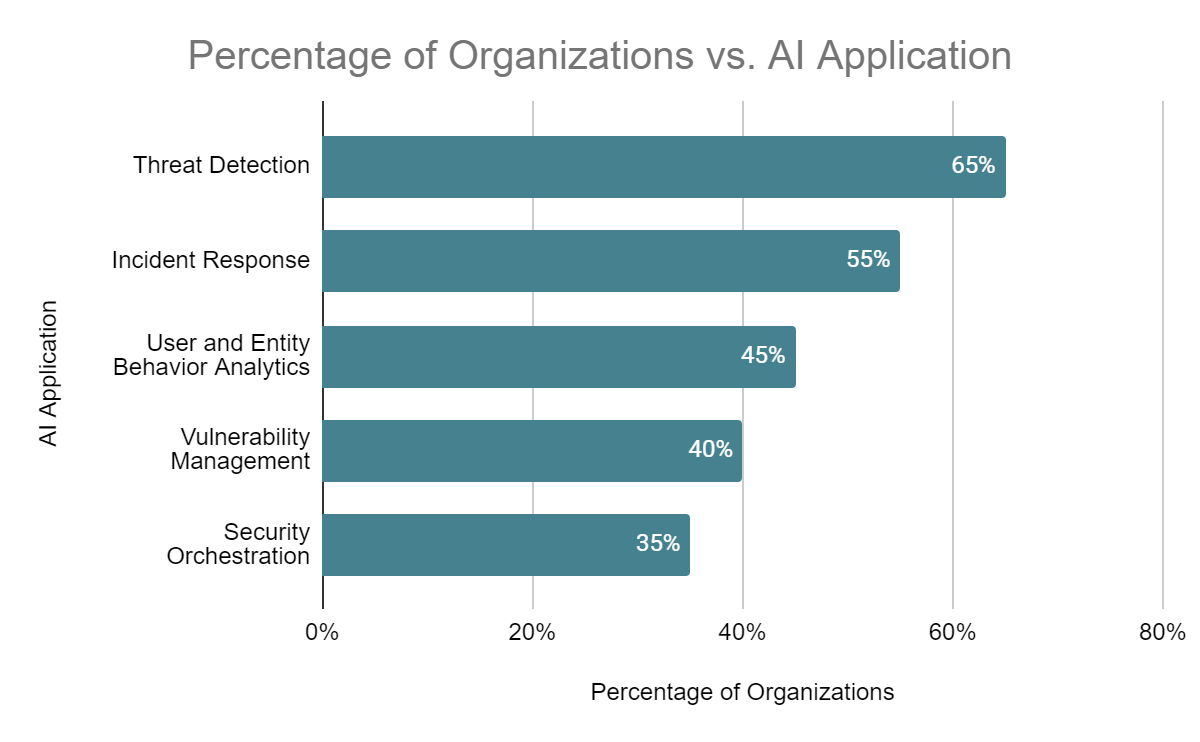 Fig. 1: Adoption of AI in Cybersecurity (2023) [5]
Fig. 1: Adoption of AI in Cybersecurity (2023) [5]
B. Zero Trust Architecture
- Principles of zero trust security model The zero trust model operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify." It assumes that threats can come from both outside and inside the network perimeter. This approach requires continuous authentication and authorization for all users and devices, regardless of their location or network connection [6].
- Benefits in mitigating unauthorized access By implementing strict access controls and continuous monitoring, zero trust architecture significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. It limits the potential damage from compromised credentials or insider threats by ensuring that users only have access to the resources they need for their specific tasks.
C. Blockchain Technology
- Use in secure transactions and data integrity Blockchain technology provides a decentralized and immutable ledger for recording transactions and data. In cybersecurity, it can be used to create tamper-proof logs of system activities, secure supply chain management, and enhance the integrity of digital identities.
- Advantages of tamper-proof ledgers The distributed nature of blockchain makes it extremely difficult for attackers to alter or falsify records without detection. This property is particularly valuable for maintaining the integrity of audit logs, which are crucial for investigating security incidents and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
D. Behavioral Analytics
- Monitoring user activities Behavioral analytics involves analyzing patterns of user behavior to establish a baseline of normal activities. This approach can detect anomalies that may indicate compromised accounts or insider threats. By continuously monitoring user actions, systems can identify deviations from typical behavior patterns that may signal a security risk.
- Detecting insider threats and compromised accounts Advanced behavioral analytics can detect subtle indicators of insider threats or account compromise that might be missed by traditional security measures. For example, it can identify unusual data access patterns, abnormal login times, or unexpected changes in user behavior that could indicate a security breach.
E. Quantum Cryptography
- Fundamentals of quantum-based encryption Quantum cryptography leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to create theoretically unbreakable encryption. It uses the quantum properties of photons to generate and distribute encryption keys. Any attempt to intercept or measure these quantum keys would alter their state, alerting the communicating parties to the presence of an eavesdropper.
- Potential for unbreakable encryption While current encryption methods may be vulnerable to future quantum computers, quantum cryptography offers the potential for truly secure communication. Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) systems are already being implemented in some high-security environments, providing a level of security that is resistant to both classical and quantum computing attacks.
IV. BEST PRACTICES FOR ENHANCING CYBERSECURITY
A. Regular Software Updates
- Importance of patching Regular software updates are crucial in addressing known vulnerabilities that cybercriminals often exploit. Patches released by software vendors typically fix security flaws, improve functionality, and enhance overall system performance. According to a recent study, 60% of data breaches in 2019 involved vulnerabilities for which a patch was available but not applied [7].
- Implementing update policies Organizations should establish and enforce policies for timely software updates across all systems and devices. This includes operating systems, applications, firmware, and security software. Automated update mechanisms can help ensure consistent and prompt application of patches.
B. Strong Password Policies and Multi-Factor Authentication
- Password best practices Implementing strong password policies is fundamental to cybersecurity. These policies should enforce the use of complex passwords, regular password changes, and restrictions on password reuse. Password managers can help users generate and securely store strong, unique passwords for each account.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring two or more verification factors to gain access to an account or system. These factors typically include something the user knows (password), something they have (security token), and something they are (biometric verification). According to the Microsoft Digital Defense Report 2023, implementing MFA can block 99.9% of account compromise attacks [8].
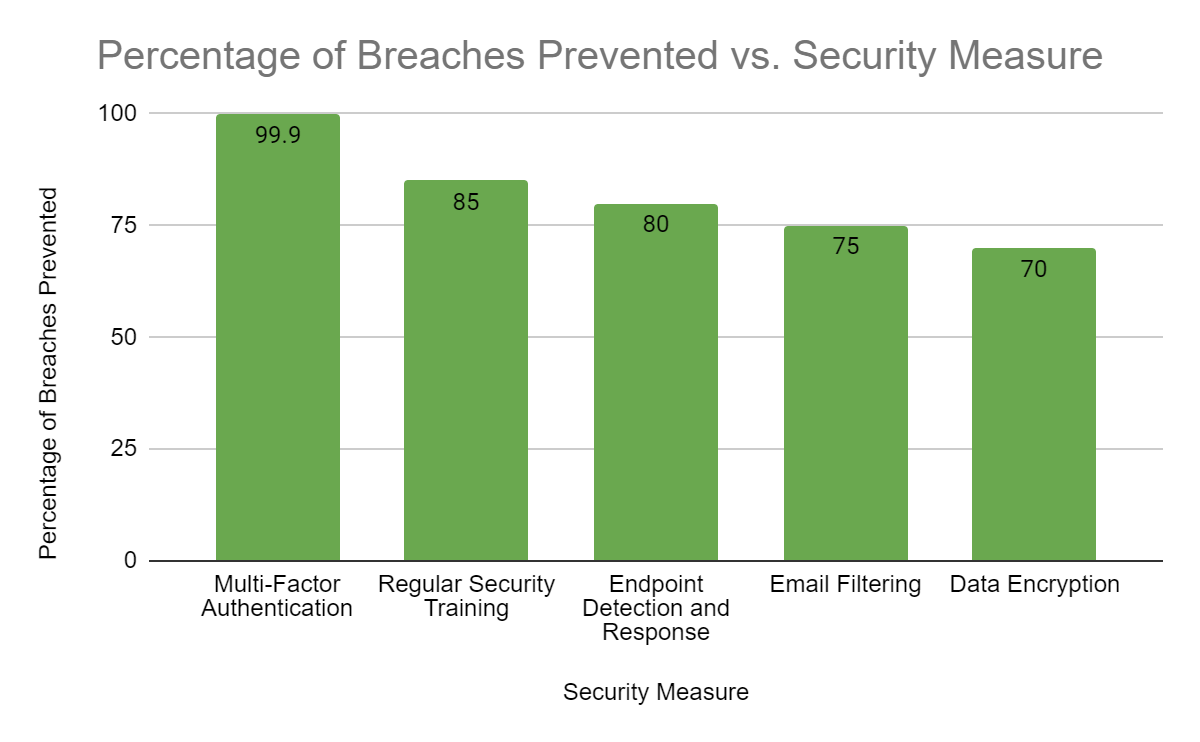 Fig. 2: Effectiveness of Security Measures in Preventing Breaches (2023) [8]
Fig. 2: Effectiveness of Security Measures in Preventing Breaches (2023) [8]
C. Employee Training and Awareness Programs
- Developing a security-aware culture Human error remains a significant factor in cybersecurity incidents. Regular training and awareness programs can help employees recognize and respond to potential security threats. These programs should cover topics such as phishing identification, safe browsing habits, and proper handling of sensitive information.
- Simulated attacks and assessments Conducting simulated phishing attacks and other security assessments can help gauge the effectiveness of training programs and identify areas for improvement. These exercises provide practical experience in identifying and responding to real-world threats.
D. Conducting Regular Security Audits
- Comprehensive security assessments Regular security audits help organizations identify vulnerabilities, assess the effectiveness of existing security measures, and ensure compliance with relevant regulations. These audits should cover all aspects of an organization's IT infrastructure, including networks, applications, and physical security measures.
- Penetration testing Penetration testing, or ethical hacking, involves simulating real-world attacks to identify weaknesses in an organization's security posture. This proactive approach can uncover vulnerabilities that might be missed by automated scanning tools and help prioritize remediation efforts.
- Continuous monitoring and improvement Cybersecurity is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and improvement. Organizations should establish metrics to measure the effectiveness of their security programs and use the insights gained from audits and assessments to refine and enhance their security strategies continually.
|
Best Practice |
Key Components |
Impact |
|
Regular Software Updates |
Timely patching, Automated update mechanisms |
Addresses known vulnerabilities, Reduces risk of exploitation |
|
Strong Authentication |
Complex password policies, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) |
Blocks 99.9% of account compromise attacks |
|
Employee Training |
Phishing awareness, Safe browsing habits, Data handling procedures |
Reduces human error-related incidents, Creates a security-aware culture |
|
Regular Security Audits |
Comprehensive assessments, Penetration testing, Continuous monitoring |
Identifies vulnerabilities, Ensures compliance, Improves overall security posture |
Table 2: Cybersecurity Best Practices and Their Impact [7, 8]
V. DISCUSSION
A. Integration of Defense Mechanisms
The effective integration of various defense mechanisms is crucial for creating a robust cybersecurity posture. Organizations must adopt a holistic approach that combines technological solutions with human-centric strategies. For instance, the integration of AI-driven threat detection systems with behavioral analytics can significantly enhance an organization's ability to identify and respond to complex cyber threats. Similarly, combining zero trust architecture with strong authentication methods like MFA creates multiple layers of security that are difficult for attackers to breach.
However, integration also presents challenges. Different security solutions may not always be compatible, leading to potential gaps in coverage or operational inefficiencies. Organizations must carefully plan and execute the integration of various security tools and practices to ensure seamless operation and comprehensive protection.
B. Challenges in Implementing new Technologies While emerging technologies offer powerful new defense capabilities, their Implementation Comes with Significant Challenges
- Skill gap: The rapid evolution of cybersecurity technologies has created a substantial skills gap in the workforce. According to a recent study, 57% of organizations report that the cybersecurity skills shortage is putting them at risk [9]. This shortage makes it difficult for organizations to effectively implement and manage advanced security solutions.
- Cost considerations: Advanced cybersecurity technologies often require significant financial investment, not only in the technologies themselves but also in training and infrastructure upgrades. This can be particularly challenging for small and medium-sized enterprises with limited resources.
- Regulatory compliance: As new technologies are implemented, organizations must ensure they remain compliant with evolving data protection and privacy regulations. This can be complex, especially for global organizations dealing with multiple regulatory frameworks.
- User adoption: New security measures, particularly those that change user workflows (like zero trust architectures), may face resistance from employees. Overcoming this resistance requires effective change management and user education.
C. Future Trends in cybersecurity As the cybersecurity landscape continues to evolve, several trends are likely to shape the future of the Field
- AI-driven cybersecurity: The use of AI and machine learning in both offensive and defensive cybersecurity operations is expected to increase. This includes more sophisticated AI-powered threat detection and response systems, as well as AI-generated phishing attacks and malware [10].
- Quantum-safe cryptography: With the advancement of quantum computing, there's a growing focus on developing quantum-resistant encryption methods to protect against future quantum-enabled attacks.
- Extended Detection and Response (XDR): XDR solutions, which provide holistic and coordinated threat detection and response across multiple security layers, are likely to become more prevalent.
- Cloud-native security: As more organizations move their operations to the cloud, cloud-native security solutions that are built specifically for cloud environments will become increasingly important.
- Privacy-enhancing technologies: With growing concerns about data privacy, we can expect to see more widespread adoption of privacy-enhancing technologies like homomorphic encryption and secure multi-party computation.
- Cybersecurity mesh architecture: This emerging trend involves creating a flexible, composable architecture integrating widely distributed and disparate security services.
As these trends unfold, organizations will need to stay agile, continuously updating their security strategies to address new threats and leverage new defensive capabilities. The future of cybersecurity will likely involve a complex interplay of advanced technologies, evolving threat landscapes, and an ever-increasing focus on privacy and data protection.
Conclusion
The rapidly evolving landscape of cybersecurity presents both significant challenges and opportunities for organizations and individuals alike. As this article has explored, emerging threats such as Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), ransomware, IoT vulnerabilities, and sophisticated social engineering attacks continue to pose substantial risks to digital assets and operations. However, the development of innovative defense mechanisms, including AI-driven security systems, zero trust architectures, blockchain technology, behavioral analytics, and quantum cryptography, offers powerful new tools for combating these threats. The effective implementation of these technologies, combined with best practices such as regular software updates, strong authentication policies, comprehensive employee training, and ongoing security audits, can significantly enhance an organization\'s cyber resilience. Looking ahead, the field of cybersecurity will likely be shaped by the increasing use of AI, the advent of quantum-safe cryptography, the rise of cloud-native security solutions, and a growing focus on privacy-enhancing technologies. As cyber threats continue to evolve in complexity and scale, it is imperative for organizations to adopt a proactive, adaptive approach to cybersecurity, continuously updating their strategies and leveraging emerging technologies to stay ahead of potential attackers. The future of cybersecurity will require not only technological innovation but also a commitment to developing a skilled workforce, fostering a culture of security awareness, and maintaining agility in the face of an ever-changing threat landscape.
References
[1] Verizon, \"2024 Data Breach Investigations Report,\" Verizon Business, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.verizon.com/business/resources/reports/dbir/ [2] N. Popper, \"A.I. Is Mastering Language. Should We Trust What It Says?,\" The New York Times, 2022. [Online]. Available: https://www.nytimes.com/2022/04/15/magazine/ai-language.html [3] Cybersecurity Ventures, \"Global Ransomware Damage Costs Predicted To Exceed $265 Billion By 2031,\" Cybercrime Magazine, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://cybersecurityventures.com/global-ransomware-damage-costs-predicted-to-reach-250-billion-usd-by-2031/ [4] IBM Security, \"Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024,\" IBM, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.ibm.com/reports/data-breach [5] M. Brundage et al., \"Toward Trustworthy AI Development: Mechanisms for Supporting Verifiable Claims,\" arXiv, Cornell University, 2020. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.07213 [6] S. Rose, O. Borchert, S. Mitchell, and S. Connelly, \"Zero Trust Architecture,\" National Institute of Standards and Technology, NIST Special Publication 800-207, 2020. [Online]. Available: https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/SpecialPublications/NIST.SP.800-207.pdf [7] Ponemon Institute, \"Costs and Consequences of Gaps in Vulnerability Response,\" ServiceNow, 2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.servicenow.com/content/dam/servicenow-assets/public/en-us/doc-type/resource-center/analyst-report/ponemon-state-of-vulnerability-response.pdf [8] Microsoft, \"Microsoft Digital Defense Report 2023,\" Microsoft Security, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/business/microsoft-digital-defense-report [9] (ISC)², \"2021 (ISC)² Cybersecurity Workforce Study,\" (ISC)², 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.isc2.org/Research/Workforce-Study [10] Gartner, \"Gartner Top 10 Strategic Technology Trends for 2023,\" Gartner, Inc., 2022. [Online]. Available: https://www.gartner.com/en/articles/gartner-top-10-strategic-technology-trends-for-2023
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Harish Kumar Reddy Kommera. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET64226
Publish Date : 2024-09-13
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

