Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Advancement of Improved M30 Grade Concrete with Red Mud and Iron Ore Slickens and their Classification
Authors: Aatif Rasheed Ansari , Charan Singh Thakur
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.54787
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
India is a developing country and in various developing countries like India economical construction along with economical construction material plays a vital role in the development of country. Waste material in construction can play tremendous role to make it economical and durable due to some of its specific properties relevant to construction materials. This dissertation shows comparative and experimental study on utilization of Red Mud and Iron Ore Slickens by replacement of Cement and fine aggregates in concrete. In this project red mud and Iron ore slickens are added in concrete by weight of cement and fine aggregate in the proportion of 1%, 2%, 3%, 4% & 10%, 20%, 30%, 40% respectively. Workability and compressive strength test are performed on concrete and their results are being evaluated and compared.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Concrete is one of the major materials used in construction industry and also most important materials used in public works and structural construction project. Concrete is used in construction since ages now which implies that we have used tons of concrete and also will continue to use it. As concrete is widely used construction material but at the same time also it is not environment friendly material as it destroys and uses abundant quantity of natural resources and also it also has a environmental impact as after its use it is deposited in land as a filler material.
A. Red Mud
Red mud is the iron rich residue produced from the digestion of bauxite. It is one of major solid waste obtained from Bayer process of alumina production. In general, about 2-4 tons of bauxite is required for production of each tone of alumina (Al2O3) and about one tone red mud is generated. Since the red mud is generated in large quantities, it has to be stored in large confined and impervious ponds, therefore the bauxite refining is gradually encircled by the storage ponds. At present about 60 million tons of red mud is produced on an annual basis worldwide which is not being disposed or recycled satisfactorily.
B. Iron Ore Slickens
India is one of the biggest iron ore producers and exporter in the world. Mining plays an important role in harnessing natural ore, but during this operation a lot of waste is generated. Proper waste management and disposal of this waste is need of the hour so that it can cause minimal damage to the environment. Iron ore tailings (IOT) are such waste produced during mining of iron from its ore. The rapid growth in the surface mines led the production of Iron Ore tailings which remains as overburden. In future, the proportion of iron ore wastes produced is likely to increase due to higher demand for iron ore. Moreover, dumping leads to loss of valuable land.


II. MATERIAL AND METHODS
A. Cement
Table 1: Properties of Cement
|
S. NO |
Property |
Value |
|
1 |
Fineness |
3.82% |
|
2 |
Initial Setting Time |
41 min |
|
3 |
Final Setting Time |
197 min |
|
4 |
Specific Gravity |
3.14 |
|
5 |
Soundness |
2 mm |
|
6 |
Compressive Strength |
7 Days – 24.56 MPa |
|
28 Days – 37.84 MPa |
B. Water
Consolidating water with a cementitious material a structural bond is developed by the procedure of hydration. The concrete glue ties the total together, fills voids inside of it, and makes it workable. A lower water-to-bond proportion yields more grounded, tougher cement, while more water gives workable cement with a higher droop. Tainted water used to make cement can bring about issues when setting or in creating untimely disappointment of the structure. Hydration includes various responses, frequently happening in the meantime. As the responses continue, the results of the concrete hydration handle slowly bond together the individual sand and rock particles and different segments of the solid to shape a strong mass. Water used for concrete should be free from injurious number of oils, acids, alkalis, salts, sugar, organic materials or other substances. Water which is used in this project is confirming to the specification of IS 456: 2000.
Coarse Aggregates
Table 2: Properties of Coarse Aggregate
|
S. No. |
Property |
Value |
|
|
1 |
Crushing Value |
14.90% |
|
|
2 |
Impact Value |
11.32% |
|
|
3 |
Abrasion Value |
12.54% |
|
|
4 |
Specific Gravity |
2.62 |
|
|
5 |
Water Absorption |
0.64% |
|
|
6 |
Bulk Density |
1680 Kg/m3 |
|
|
7 |
Flakiness and Elongation Index |
11.86% |
|
|
8 |
Gradation |
Sieve No. |
% Passing |
|
40 mm |
100 |
||
|
20 mm |
92.25 |
||
|
10 mm |
9.64 |
||
|
4.75 mm |
1.23 |
||
Fine Aggregates
Table 3: Properties of Fine Aggregates
|
S. No. |
Property |
Value |
|
|
1 |
Specific Gravity |
2.60 |
|
|
2 |
Bulking |
30.21% |
|
|
3 |
Water Absorption |
0.92% |
|
|
4 |
Bulk Density |
1590 Kg/m3 |
|
|
5 |
Gradation |
Sieve No. |
% Passing |
|
10 mm |
100.00 |
||
|
4.75 mm |
100.00 |
||
|
2.36 mm |
97.32 |
||
|
1.18 mm |
78.57 |
||
|
600 microns |
69.88 |
||
|
300 microns. |
16.40 |
||
|
150 microns |
0.32 |
||
|
Conforming to grading zone II of IS 383-1997 |
|||
C. Red Mud
Table 4: Properties of Red Mud
|
S. No. |
Property |
Value |
|
1 |
Specific Gravity |
2.83 |
|
2 |
pH |
11.5 |
|
3 |
Fineness |
4.10% |
|
Composition of Red mud |
||
|
S. No. |
Components |
Weight% |
|
1 |
Al2O3 |
21-23 |
|
2 |
Fe2O3 |
38-43 |
|
3 |
SiO2 |
12-17 |
|
4 |
TiO2 |
1.5-2 |
|
5 |
CaO |
1.5-2 |
|
6 |
Na2O |
3-5 |
D. Iron Ore Slickens
Table 5: Properties of Iron Ore Slickens
|
S. No. |
Property |
Value |
|
1 |
Specific Gravity |
2.62 |
|
2 |
Relative density |
1.24 gm/cc |
|
3 |
Fineness Modulus |
1.15 |
|
4 |
Water Absorption |
10% |


Table 6: Mix Designation of Concrete
|
Material |
Red Mud Content |
Iron ore slickens content |
Mix Name |
|
Plane concrete |
-- |
-- |
CC |
|
Red Mud + iron ore slickens |
1% (3.78 Kg) |
10% (66.5 Kg) |
RM11 |
|
1% (3.78 Kg) |
20% (133 Kg) |
RM12 |
|
|
1% (3.78 Kg) |
30% (199.5 Kg) |
RM13 |
|
|
1% (3.78 Kg) |
40% (266 Kg) |
RM14 |
|
|
2% (7.56 Kg) |
10% (66.5 Kg) |
RM21 |
|
|
2% (7.56 Kg) |
20% (133 Kg) |
RM22 |
|
|
2% (7.56 Kg) |
30% (199.5 Kg) |
RM23 |
|
|
2% (7.56 Kg) |
40% (266 Kg) |
RM24 |
|
|
3% (11.34 Kg) |
10% (66.5 Kg) |
RM31 |
|
|
3% (11.34 Kg) |
20% (133 Kg) |
RM32 |
|
|
3% (11.34 Kg) |
30% (199.5 Kg) |
RM33 |
|
|
3% (11.34 Kg) |
40% (266 Kg) |
RM34 |
|
|
4% (15.12 Kg) |
10% (66.5 Kg) |
RM41 |
|
|
4% (15.12 Kg) |
20% (133 Kg) |
RM42 |
|
|
4% (15.12 Kg) |
30% (199.5 Kg) |
RM43 |
|
|
4% (15.12 Kg) |
40% (266 Kg) |
RM44 |
Table 7: Mix Proportion of Concrete Mix
|
Cement |
378 kg/m3 |
|
Water |
170 kg/m3 |
|
Fine Aggregate |
665 kg/m3 |
|
Coarse Aggregate |
|

III. EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
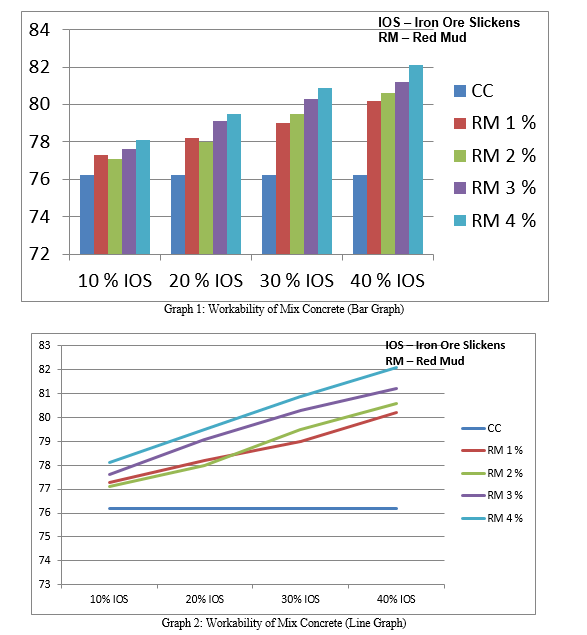
A. Workability of mix Concrete
Table 8: Workability of mix Concrete
|
S. No. |
Mix ratio (Red Mud + Iron Ore Slickens) |
Mix Name |
Slump (mm) |
|
1 |
0% + 0% |
CC |
76.2 |
|
2 |
1% + 10% |
RM11 |
77.3 |
|
3 |
1% +20% |
RM12 |
78.2 |
|
4 |
1% +30% |
RM13 |
79 |
|
5 |
1% + 40% |
RM14 |
80.2 |
|
6 |
2% + 10% |
RM21 |
77.1 |
|
7 |
2% + 20% |
RM22 |
78 |
|
8 |
2% + 30 % |
RM23 |
79.5 |
|
9 |
2% +40% |
RM24 |
80.6 |
|
10 |
3% +10% |
RM31 |
77.6 |
|
11 |
3% +20% |
RM32 |
79.1 |
|
12 |
3% +30% |
RM33 |
80.3 |
|
13 |
3% + 40% |
RM34 |
81.2 |
|
14 |
4% + 10% |
RM41 |
78.1 |
|
15 |
4% + 20% |
RM42 |
79.5 |
|
16 |
4% + 30 % |
RM43 |
80.9 |
|
17 |
4% + 40 % |
RM44 |
82.1 |



 ???????
???????
Conclusion
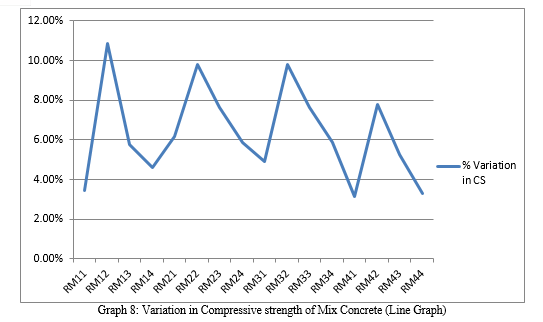
A. Conclusion When concrete is mixed with Red mud and Iron ore slickens it has been observed that there is an increase in both compressive strength and workability of concrete. 1) It is observed that compressive strength first increases upto 20 % iron ore slicken mix afterwards it starts decreasing. 2) By this study it is concluded that all the mix are usable but highest compressive strength is observed in RM32 mix. 3) It can also be concluded that all the mix ratios containing 20 % iron ore slickens are optimum. 4) By this study it is concluded that all mix are useable, but RM22, RM32 mixes gives better compressive strength. It is also concluded that RM32 is the optimum value for mix. 5) It is safe to say that red mud and iron ore slickens both can be used in concrete for replacement upto a certain limit. B. Future Scope 1) There is also a scope of replacing cement with red mud in a higher percentage which can be taken into consideration. 2) There is a scope of using red mud with iron ore slickens for ground brick manufacturing.
References
[1] Krikar M-Gharrib Noori , Hawkar Hashim Ibrahim “ Mechanical Properties Of Concrete Using Iron Waste As A Partial Replacement Of Sand” 4th International Engineering Conference on Developments in Civil & Computer Engineering Applications (2018) 204-215 [2] K.Deepika, S.Ananthakumar, R.Mariadoss, J.Nanthagopal and V.Saravanakumar “Experimental Investigation of Concrete by Red Mud as Replacement of Cement and Using Strengthening Admixture” IJIRSET, Vol. 6, Issue 3, (2017) 3928-3933. [3] Sithar Pateliya, Chetan Solanki “Experimental studies on concrete utilizing red mud as a partial Replacement of cement” IJARIIE-ISSN(O)-2395-4396, Vol-3 Issue-2 2017, 5408-5415. [4] Shivam Tiwari, Anubhav Rai, Y.K. Bajpai “ Effect of Partial Replacement of Sand by Iron Ore Tailings on the Compressive Strength of Concrete” IRJET, Vol 2, Issue 12, (2017), 1169-11763 [5] Ali Umara Shettima, Mohd Warid Hussin , Yusof Ahmad and Jahangir Mirza “Evaluation of iron ore tailings as replacement for fine aggregate in concrete” Construction and building materials, 120 (2016) 72-79 [6] Kiran Kumar M S, Raghavendra Naik, Harish K S, Ramesh M “Experimental Study on Utilization of Red Mud and Quarry Dust in Cement Mortar and Concrete” International Journal of Civil and Structural Engineering Research (2016), Vol. 4, Issue 1, 324-330 [7] Sowmyashree T, Manjunath C S, Arpitha D J, Panditharadhya B. J “Comparison on Durability Properties of Red Mud as a Partial Replacement of Cement with Hydrated Lime for Different Grades of Concrete with and without Superplasticiser” International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT), ISSN: 2278-0181, Vol. 5 Issue 05 (2016) 572-577. [8] Zhong-xi Tian, Zeng-hui Zhao, Chun-quan Dai and Shu-jie Liu “Experimental Study on the Properties of Concrete Mixed with Iron Ore Tailings” Advances in Materials Science and Engineering Volume 2016, Article ID 8606505, pp 1-9 . [9] Siddu Karthik C S, Panditharadhya B J, Sowmyashree T, Arpitha D J “Properties Of Concrete With Red Mud As Partial Replacement Of Cement With Hydrated Lime And Superplasticizer” International Journal Of Engineering Sciences & Research Technology 5.(5): May, 2016 [10] Mahin Sha O B, Remya C P, Salja P A, Shifal K S “ Red Mud Concrete” IRJET, Volume: 03 Issue: 04, April-2016, 2582-2585
Copyright
Copyright © 2023 Aatif Rasheed Ansari , Charan Singh Thakur . This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET54787
Publish Date : 2023-07-15
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

