Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Analysis of Cryptocurrency, People and Future
Authors: Supragya Pandey, Dr. Devesh Katiyar, Mr. Gaurav Goel
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2022.41634
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Cryptocurrency is a technology developed 14 years ago. It represents valuable and intangible objects which are used electronically in different applications and networks such as online social games, online social networks, virtual worlds, and peer-to-peer networks. While it may not dethrone traditional fiat currency, it could change how systems around the world interact with each other. A SWOT analysis of cryptocurrency is presented, which elucidates some of the recent events and movements that could influence whether cryptocurrency contributes to a shift in economic standards.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
. A. Blockchain
A blockchain is a distributed, digitalized, decentralized database that is shared among the nodes of a computer network. As a database, a blockchain stores information electronically in digital format.
B Blockchain to Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies are part of an ecosystem based on Blockchain technology, as it too is a decentralized, digital system. It uses cryptography for security and isn’t operated and run by a single authority, making it difficult for anyone, even for the government, to track or manipulate it.
C. Blockchain Decentralization
What a blockchain does is allow the data held in that database to be spread out among several network nodes at various locations. This not only creates redundancy but also maintains the correctness of the data stored therein—if somebody tries to alter a record at one instance of the database, the other nodes would not be changed and thus would prevent anyone from doing so. If one user tampers with a cryptocurrency’s record of transactions, all other nodes would verify with each other and easily pinpoint the node with the incorrect information. This system helps to establish an exact and transparent order of events. This way, no single node within the network can change the information held within it. Because of this, the history and information (such as transactions of a cryptocurrency) are unalterable. Such a record could be a list of transactions (such as with a cryptocurrency), but it also is possible for a blockchain to hold other diversified information like legal contracts, state identifications, or a company’s product inventory.
II. THE CRYPTOCURRENCY MARKET
A. The Global Landscape
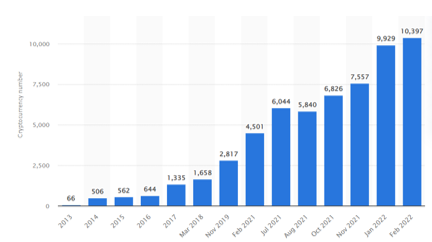
There are nearly over 10,000 as of 2022 - a drastic increase from just a little number of digital coins in 2013. Note, however, that a large portion of these cryptocurrencies might not be that important. As the creation process of a cryptocurrency is very open, it is relatively easy to create one. Indeed, it is believed that the top 20 cryptocurrencies make up nearly 90 percent of the total market.
B. Rise in India
India, with a population of 138 crores (data as of 2020), has been on an economic resurgence for the last few years. As of 2021, India has the second-highest number of cryptocurrency users worldwide, second only to Vietnam. In addition to the increase in user population, the crypto market in India also grew by 641 percent in the year. This exponential growth happened majorly due to the ease in crypto investments, which hardly take hours, compared to investing in other equities which could take days to set up your account before you can start investing.
With an estimated 15 million active crypto users, India has been stuck in regulatory oblivion since the Supreme Court in 2020 overturned a central bank ban on digital tokens. The Government of India in budget 2022-23 unveiled a tax on crypto transactions without formally declaring that it won’t ban trading, a move that became representative of the confusion.
III. STRENGTHS
A. Transaction Speed
If you want to send someone a handsome sum of money domestically or internationally across the border, it takes a minimum of 3 hours to a maximum of 5 business days for the transaction to be completed.
Transaction of funds through cryptocurrencies can be done in a matter of minutes as no third-party intermediatory is required. Once the block is settled into the blockchain and confirmed by a peer-to-peer network, the money is available to be used.
B. Transaction Cost
The cost of transacting in cryptocurrency is relatively cheap compared to other financial services. Transferring money internationally could even cost a fortune.
Cryptocurrency transactions are usually less expensive. However, demand on the blockchain can increase transaction costs. Even so, the average transaction cost remains lower than using any traditional money transfer fees even on the busiest blockchains.
C. Accessibility
Any Tom, Dick & Harry can use cryptocurrency. One just needs a personal computer or a mobile phone, with an internet connection. As there is no identity verification, background check, or credit check, the setting up of an e-cryptocurrency wallet is easy compared to a traditional bank account and can be done in a matter of minutes. This ensures that the person can make financial transactions while staying anonymous and not using the services of centralized authorities.
D. Security
Cryptocurrencies are secured by cryptography and due to it, it eliminates the chance to counterfeit or double-spend. As it is decentralized, it is nearly impossible for any person, authority, or even government to interfere or manipulate it. Public Keys and Private Keys are used for secure transactions, with different types of incentive systems such as Proof-of-Work or Proof-of-Stake. If one loses his private key, then even he cannot recover his funds. With the addition of more computing power in the network, the transactions become even more secure.
E. Privacy
As there is no identity verification, background check, or credit check, to make an account at any type of financial institution to make cryptocurrency transactions, a certain level of privacy is maintained. There’s only a wallet address on the block, but no identifying information about the user. People can further use various methods to mask their identity.
F. Transparency
Every cryptocurrency transaction happens on a publicly distributed blockchain ledger. With the help of certain tools, one can loop up transaction data. including where, when, and how much money was sent from a wallet address. Anyone can also see how much fund is stored in a wallet. With this, people can prove that they sent the money, or the money was received, or that they have sufficient funds available for the transaction.
G. Diversification
Cryptocurrency investments can produce profits. It offers investors diversification from traditional financial assets such as stocks and bonds. Its price fluctuations remain uncorrelated to other markets and hence make it a good tool for portfolio diversification. Cryptocurrency markets have gone through the roof in value over the past decade, at one point reaching almost $2 trillion. As of 1 April 2022, Bitcoin was valued at more than $768 billion in crypto markets.
H. Inflation Protection
Most of the big cryptocurrencies have either a fixed number of coins or at the least, have capped their potential circulation growth. So, the growth of fiat currency supply outpaces the supply of a cryptocurrency, and the price of cryptocurrency is bound to increase.
IV. LIMITATIONS
Even though transactions through cryptocurrencies are semi-anonymous, they leave a digital trail which, when one puts their mind to it, can be deciphered & hence exploited. The blockchain is shared publicly, which leaves a lot of room for attackers to get creative with their malicious intents. The blockchain has been put under several stress tests by the users just to prove that it’s unbreakable. The feature of cryptocurrency has thus been acting like a double-edged sword.
Cryptocurrencies have developed a controversial reputation due to them being a means for criminals to perform nefarious activities such as money laundering and illicit purchases. Cryptocurrencies have also become a favorite of hackers who utilize them for ransomware crimes. And in the white markets, a very limited group of online merchants openly accept cryptocurrency as payment. So, it makes it very unfeasible to rely on them as a currency. Even sometimes, governments can impose a ban on them to retain their power to keep tabs on all the online transactions happening in the country.
Cryptocurrency also takes a lot of time to understand. Even with a lot of resources available, including but not limited to official documentation, video tutorials, coaches, etc., one still needs to dedicate a lot of time to wrap their head around the working of cryptocurrency. Investors and even simple users should also be educated about scammers and their malicious means of scamming people, like phishing, social engineering, etc.
Up to a point, cryptocurrencies operate at a lightning speed. But when the blockchain reaches a certain capacity limitation, transaction processing speed becomes slow, which can be very frustrating to users and can cause huge financial losses.
If a hard disk drive crashes, a virus destroys data, and the wallet file is corrupted, or if you lose your virtual wallet, the cryptocurrency has essentially been forsaken. There’s nothing that can be done to recover it. These coins will be forever lost in the system. This can bankrupt a rich cryptocurrency investor within seconds with no way of recovery.
Since there’s no centralized authority controlling & moderating it, no one can calculate a minimum valuation for any cryptocurrency. If a large group of users one fine day decided to dump (cash-in) their cryptocurrency & leave it entirely, the value of that cryptocurrency will plummet severely (or may even become worthless in some cases) and will cause great loss to users who were holding a large sum of funds in that cryptocurrency The decentralized nature is both boon and bane for any cryptocurrency.
Stock markets exists for more than a couple of centuries. Fiat currency for first used in the 11th century. Gold is used in trade for over a millennium by humans. Compared to all of them, cryptocurrency is relatively very new, in its infancy stages, one can say. The concept only really emerged with the publicizing of a white paper on Bitcoin in 2008. Hence, the future of cryptocurrency is very uncertain & one needs to be a brave soul to enter the unchartered areas waters. If cryptocurrencies are widely adopted, and if a flaw is found in the system, the exploiter can gain a tremendous amount of money at the expense of the economy.
V. FUTURE SCOPE
Cryptocurrency is far ahead in the race to become the most innovative and transformative technology in the financial systems. The peer-to-peer system helps solve the traditional banking problems. Other peer-to-peer technologies like torrent and Napster transformed the file-sharing & music industry respectively by decentralizing file storage and cutting out the middleman. Innovative technologies begin by solving a particular problem in an industry. For example, in a third-world country, if there is a large population of people who don’t have access to bank accounts, due to any reason: like not having all the required documents, cryptocurrency can solve this problem as it requires one to just have a smartphone with an internet connection to start. People can make transactions just by scanning QR codes displayed on their phones through applications.
With the growth of the user base, demand for better cryptocurrency applications and networks increases. This creates a large market for developers and designers to create and design the infrastructure and its user interface. Cryptocurrencies have the support of their ever-growing community of users and developers.
Many businesses are beginning to observe the worth of using cryptocurrencies in international transactions, especially when trade needs to occur quickly in response to an emergency. Money can be sent across borders, but it will arrive days later and not even the full amount, with all the hidden charges and unexplained fees deducted. A good example of this emergency need is an online company suffering due to the sanctions and restrictions imposed on its home country by other countries in the event of war. In this scenario, the ability to do transactions is important, for every minute the company is handicapped to send or receive money, profits are being lost. Cryptocurrency has a key advantage over orthodox currencies thanks to its agility in making fast peer-to-peer transactions, especially in international business-to-business scenarios.
Cryptocurrency has an upper hand over traditional card-based vendors in that it gets rid of the irrelevant costs and fees for any transaction. This is a major reason why internet stores and marketplaces are starting to adopt it. It minimizes the transaction cost, lessens the transaction time, and hence it encourages the buyers to shop more and spend more money.
Several laws are being passed by countries to validate the status of cryptocurrency as a legal mainstream device. The less regulation, the better. They’re taxed like property ad not like currencies, which is why it attracts long-term and short-term capital gains and losses.
Cryptocurrency has the biggest potential to act as a sort of commodity. The commodity market is a widely accepted form of trade all around the world, and cryptocurrency has seemingly started to mimic the attributes of gold. Gold is special because of its acceptance everywhere and it has been a long-standing holder of value. Because of the ease of buying cryptocurrencies through its complex-yet-simple online system. If major cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, continue to be a sound haven for inflating currencies, it will gain validity from investing population and push it deeper into becoming more mainstream.
VI. THREATS
Cryptocurrency has a lot of obstacles in its journey before it can become a norm. The fluctuation in its value puts doubt in the mind of users as well as investors. This makes it even harder for cryptocurrency to get general acceptance. Cryptocurrencies are also familiar with fraud and theft, as crypto exchange companies set up faulty systems. The news of these frauds makes news and can easily sway the popular opinion against the normalization of cryptocurrency. Also, there are no hard legislations and laws put in place for cryptocurrencies, which again acts as a deterrent for the layman to not use cryptocurrency, as laws give a sense of legality. Markets and governments are insensitive to new technologies. All in all, these factors combined limit the user’s trust in cryptocurrency.
Lack of trust happens in investors as well. Many startups have failed and closed due to security reasons. The fixes to the flaws and loopholes in the technology are also generally slow. The lack of centralizing nature makes it difficult to make a unified effort to maintain and secure every server. Even if one were to set out to regulate every node in the peer-to-peer network, it would come at the cost of freedom and anonymity which is the USP of cryptocurrency.
In the free market the other competitors, mainly the already well-established technology giants, are attempting to create an alternative to cryptocurrency. As a result, it will have a hard time competing with them as they are nearly every household name. Additionally, the technology giants have deep pockets and a foothold in the smartphone application market to their advantage, compared to cryptocurrency’s small-time players.
Another grave threat to cryptocurrency is government regulations that need to be specified. Cryptocurrency is yet to be classified if it’s a security, currency, commodity, or capital asset, and each one would have a different effect on how cryptocurrency is to be adopted. The wrong type of legislation will deliver a severely sharp blow to cryptocurrency’s legitimacy as a currency.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency, though may increase the revenue for companies or may make the life of a normal person easier by being an ideal payment system, is still in its early stages. It has moved past its adoption phase. Iceland for one has launched its official cryptocurrency. The cryptocurrency communities are working hard to push it mainstream by solving the age-old banking problems by innovating. The above paper indicates that even though cryptocurrency has its fair share of problems, it’s well on its way to becoming the next widely accepted currency. There’s a lot of room for improvement, research, and innovation. Even the technology behind cryptocurrency, blockchain could be exploited in other fields like smart contracts. Until some years ago, the virtual currency was unheard of. Today, the market penetration has been of such a level that even kids and teenagers are requesting their elders to abandon all their traditional financial instruments and invest in cryptocurrency.
References
[1] Omanovi?, A. Arnaut-Berilo, A. Zaimovi?: Effectiveness of cryptocurrency portfolio management before and during COVID-19 pandemic An International Serial Publication for Theory and Practice of Management Science (2020) [2] I. Makarov, A. Schoar Trading and arbitrage in cryptocurrency markets J. Financ. Econ., 135 (2) (2020) [3] C. Alexander, M. Dakos A critical investigation of cryptocurrency data and analysis Quant. Finance, 20 (2) (2019), pp. 173-188 [4] Bearman, J. (2015, May). The Untold Story of Silk Road, Pt. 1. Retrieved from Wired.com Website: https://www.wired.com/2015/04/silk-road-1/ [5] Bitcoin: A New Global Economy. (2015, August 4). Retrieved July 2016, from BitPay, Inc. Website: https://blog.bitpay.com/bitcoin-a-new-global-economy/ [6] Balaji, S. (2017, June 21). On Bitcoin, India\'s Government and Tech Companies Find Common Ground. Retrieved from Forbes: https://www.forbes.com/sites/sindhujabalaji/2017/06/21/bitcoin-indiaregulation/#353844e87e4a Christian Beer, B. W. (2015, January 28). [7] Bitcoin – The Promise and Limits of Private Innovation in Monetary and Payment Systems. Retrieved from Research Gate: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271473884 [8] Consumers of Cryptocurrency. (2018, February). Retrieved from www.pwc.com. [9] Abadi, J., and Brunnermeier M.. 2018. Blockchain economics. Working Paper, Princeton University. [10] King, R. S. (2013, December 17). By reading this article, you’re mining bitcoins. Retrieved from Quartz.com Website: http://qz.com/154877/by-reading-this-page-you-are-mining-bitcoins/ [11] Magro, P. (2016, July 16). What Greece can learn from bitcoin adoption in Latin America. Retrieved July 2016, from International Business Times Website: http://www.ibtimes.co.uk/what-greece-can-learn-bitcoin-adoption-latin-america-1511183
Copyright
Copyright © 2022 Supragya Pandey, Dr. Devesh Katiyar, Mr. Gaurav Goel. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET41634
Publish Date : 2022-04-20
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

