Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare 5.0: Strengthening Practices for Medicos
Authors: Kuldeep Kaur
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.63611
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
From the beginning, the Healthcare sector stood a pioneer for the development of Artificial Intelligence technology. Numerous research and discussion have been conducted till today based on the idea of Artificial Intelligence. This is because of the nature of the amenities and the susceptibility of ample portion of consumers. In the present study, a blended approach both qualitative and quantitative has been applied to determine the constituents of Artificial Intelligence for healthcare industry and analysis is conducted to find its effect on value formation along with market performance. By analysis of the patient perspective, it revealed the ways in which different Artificial Intelligence components contribute to healthcare organizations and provide improved patient-centered health care.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Artificial Intelligence (AI) expanded the wings practically in all domain recently including the field of Healthcare for several diagnosis and treatments. Artificial Intelligence technologies provide resolutions for diverse health care issues comprising of machine learning, deep learning etc. Research of Triantafyllidis and Tsanas (2019) have shown that deep learning algorithms help to detect diabetic retinopathy with 90% accuracy. Powles and Hodson (2017) observed that the majority of AI enabled healthcare services are using Watson’s IBM or Google’s Deep mind Health for detecting precise diseases subsequently collecting the data by mobile apps. The practice of Artificial Intelligence in the healthcare sector raises due to the complication of existing medications that require huge information for analysis. Thus, tapplication of AI in healthcare recommends several advantages from affluence of intricate computations, high accuracy to effective decision making. AI algorithms are generally trained by large data compiled from diverse health practices. Because of abundant dataset, the algorithm recognizes similar sets of items, relations between subject attributes in addition to desired results (Kaur, 2017, Rathore, 2022). AI software program can be accessible to massive end users that may be a patient, a pharmaceutical company, insurance provider etc.
II. REVIEW OF LITERATURE
Although Artificial Intelligence plays an important role in Healthcare industry still there are two contradictory viewpoints regarding its application. Some people find it as worthless while others find it extremely relevant. Makda (2021) observed that engagement of AI tools in the healthcare section become difficult because people are scared of machines working on their bodies. Triantafyllidis (2019), Kumar et. al. (2024) proposed that Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) with application of different technologies in medical practices improves diagnosis of patients, prevention and also clinical judgement. Murali and Sivakumaran (2018) observed that amongst the major disorders associated to cancer, neurology and diabetes, AI techniques are used. According to Sun (2019), AI can contribute to the expansion of an additional reasonable universal healthcare system. Manne and Kantheti (2021) proposed that Artificial Intelligence technologies might not be able to entirely substitute the doctors but they may be able to support them with better and precise outcomes.
Lai et al. (2020) study showed the large number of the doctors had positive opinions towards application of Artificial Intelligence in healthcare. Some of the physicians emphasized that Artificial Intelligence can completely revolutionize their area of expertise, also patient care while rest of them stated that it would just accelerate recent advances in medical practices. In the study of Giansanti et al. (2021), several medical radiography technicians along with healthcare workers were asked for their experiences towards radiology infrastructure. Most of the respondents favour that AI increases human intelligence, some trusted that it would substitute human judgement while few said it has no effect.
Artificial Intelligence mimic human cognitive functions. A significant revolution in healthcare occurs by the increasing amount of health records in addition to the rapid progress of analytics approaches. AI works with both structured and unstructured data. Machine learning, neural network and recent deep learning methods are utilized for structured data.
Jiang (2017) proposed that Cardiology, neurology and cancer treatment demand AI techniques. Artificial intelligence not only remarkably boosts patients care but also lowers medical expenditures. Due to the increased population, innovative ways are needed to intensify the efficacy and competence of the health services sector with low expenses (Pee, 2018). Ardan (2020) analyzed that specific Technology of Google precisely shapes an AI model of human brain that helps to enhance the distinct and decision-making procedures by healthcare professionals. IBM's Watson identified accurate medicine through AI remarkably for cancer recognition and treatment.
Today, numerous AI technologies use by life sciences companies and healthcare professionals to provide advice for patient assessment, monitoring and administrative tasks (Davenport, 2019). Deep learning is gradually being used for the recognition of clinically important patterns in MRI images that stay often undistinguishable to the human eye (Vial, 2018). Fakoor (2013) recommended that Deep learning is a more innovative technology that employs Artificial Neural Network (ANN) models to infer outcomes by multiple layers of variables to spot probably infectious tumours in radiography images. In comparison to Computer-aided detection (CAD), the blend of deep learning and radiomics provides improved diagnostic accuracy in the field of Oncology (Davenport, 2019).
In comparison to diverse forms of AI, Robotic Process Automation technology i.e. RPA is more clear, affordable, accessible and used widely in the healthcare sector (Hussain, 2014). To enhance various treatment methods, automatic health records are crucial for healthcare area and the doctors for obtaining new information (Eren A, 2008).
Review of literature including study of Venkatesh et al. (2013), Kaushik (2022, 2023) recommended that in the fields of AI, due to the complexity of healthcare facilities, use of both quantitative and qualitative strategy to collect samples from both methods to get more reliable conclusions. Present study aims to find out the changing aspects of influence of AI and related technologies in the healthcare sector by using a two-stage sequential design.
In the first step, an exploratory qualitative study including detailed questioning was done to understand the perspective of patient. A purposive sampling method was applied to recognize health professionals- doctors, hospital IT workers and administrative employees working in several important private and public hospitals in Uttar Pradesh. An open-ended questionnaire provided to the selected candidates after sampling. Subsequently, quantitative study conducted to evaluate the effect of AI from the perspective of practitioners. The analysis was done to find out the influence of AI driven services in the hospitals of U.P., its effectiveness on practitioners and on raising patient satisfaction levels.
The major focus of the present study is to understand the effect of several AI supported healthcare sectors, to provide improved patient-centered care followed by evidence-based medicine assisted through the detailed studies. This study also includes analysis of the Patient’s perception.
Hypothesis
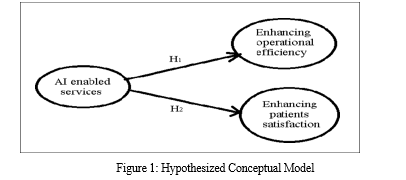
On the basis of review of literature, the effect of AI enabled facilities in hospitals is hypothesized as follows:
H1: AI enabled services have a positive effect on operational efficacy of practitioners.
H2: AI enabled services have a positive effect on improving the patients’ satisfaction.
III. METHODOLOGY
For quantitative assessment of hypothesized model, a measurement scale was prepared. To evaluate content validity of questionnaire, survey tool was pre-tested by numerous academicians and experts.
IV. ANALYSIS OF DATA
Table 1- Demographic characteristics of the respondents
|
Demographic variables |
Frequency |
Percentage (%) |
|
Department wise distribution of Healthcare professionals |
|
|
|
Doctors |
42 |
35% |
|
Nurses and Paramedical Staff |
41 |
38% |
|
Administrators |
28 |
12% |
|
Others |
11 |
16% |
|
Gender |
|
|
|
Female |
86 |
53% |
|
Male |
64 |
47% |
|
Hospital Type |
|
|
|
Government Hospital |
63 |
42% |
|
Private Hospital |
87 |
58% |
Table 2- Regression Weights of variables from different SEM Models
|
|
|
|
Estimate |
S.E. |
C.R. |
P |
|
AI |
|
Operational Efficiency |
.610 |
.054 |
8.530 |
<0.001** |
|
AI |
|
Patient Satisfaction |
.072 |
.050 |
1.618 |
0.031* |
* and ** indicates significant (p<0.05) and extremely significant (p<0.01)
V. MODEL FIT SUMMARY
Table 3- CMIN Model Results
|
Model |
NPAR |
CMIN |
DF |
P |
CMIN/DF |
|
Default model |
15 |
378.12 |
8 |
.000 |
54.15 |
|
Saturated model |
26 |
.000 |
0 |
.000 |
0 |
|
Independence model |
8 |
409.26 |
15 |
.000 |
30.24 |
Table 4- Basic difference of Model Results
|
Model |
IFI |
TLI |
NFI |
RFI |
CFI |
|
Default model |
0.290 |
-0.650 |
0.548 |
-0.692 |
0.28 |
|
Saturated model |
1.000 |
|
1.000 |
|
1.000 |
|
Independence model |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
VI. FINDINGS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
- Quantitative data analysis represented majority of female i.e. 53% while 47% male healthcare professionals. Findings observed by offering a centralized image of patients’ demographic data, standardizing and approving practical communication. It revealed that AI enabled devices can support healthcare organizations to enhance general patient satisfaction. The greater satisfaction of patient also increases the possibility that regular preventive healthcare should be a central point.
- Among 150 respondents, 58% often be at Private hospitals for health care while 42% respondents favour to obtain digital facilities at a Government hospital. AI promotes improved communication channels and the collection of deduced knowledge without wasting time. The study of Oinas-Kukkonen et al. (2008), Vardasca and Martins (2011), Kaur (2017) have shown that corporate impact and marketing methods do not truly make any influence on healthcare that favours the findings of present study.
- Findings have shown that the majority of the respondents are between the ages of 35 and 60. They believe that particularly the senior citizens need remedial treatment from healthcare organizations. Thus, an outline for Artificial Intelligence can also improve medicinal care by helping hospitals to realize needs of patients and increasing communication by observing systems that favours the study of Gillan (2018) and Mohiuddin (2019).
- The observation of Qualitative Study has shown the evolution and utility of diverse AI resolutions for medical sector is certainly emerging rapidly. On the basis of the outcomes of a qualitative study, a questionnaire was constructed and examined to regulate the way Artificial Intelligence might expand patient’s satisfaction by helping practitioners to work more proficiently.
- With the application of Artificial Intelligence, patients receive care in less time. AI-approved machines can distinguish the faces of patients and examine their behaviour to make a personalized response that in turn expands patients’ satisfaction. The study has recognized quite a lot of chief advantages of AI-enabled devices together with improved patient access. It includes better analysis of symptoms, evidence of accurate medication, money saving etc.
Conclusion
In the present study, a mixed-method approach is used by combining quantitative research via a survey and qualitative research through expert opinions. AI-empowered facilities might enlarge complete satisfaction of patients in the medical field by centralizing and rationalizing patient data. It empowers dynamic communication. Being attentive towards the medical demands of professionals can additionally benefit the healthcare sector to grow their outcomes. The application of AI in primary care empowers the doctors to rapidly respond the questions of patients with personalized treatment plans, early disease detection with enhanced accuracy, drug discovery and prompts them to arrive for better prevention care. Additionally for Medicos, Artificial Intelligence-equipped tools in the healthcare sector strengthen operational efficiency along with patients’ satisfaction.
References
[1] Davenport, T.H., Hongsermeier, T.M. & Mc Cord K., A. (2019). Using AI to improve electronic health records. Harvard Business Review. [2] Giansanti, D., Rossi, I. & Monoscalo, L. (2021). Lessons from the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Digital Radiology: The Submission of a Survey to Investigate the Opinion of Insiders. Healthcare, 9 (3), 331. [3] Gillan, C., Milne, E., Harnett, N., Purdie, T., Jaffray, D. & Hodges, B. (2018). Professional Implications of Introducing Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: An Evaluation Using Radiation Medicine as a Testing Ground. Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Sciences, 49 (1). [4] Hussain, M.I., Shamim, M., Sankar, R. & Kumar, M. (2014). The Effect of The Artificial Intelligence on Learning Quality & Practices In Higher Education. Journal of Positive School Psychology, 6 (6), 1002-1009. [5] Jiang, Y., Zhi, H., Dong, Y., Li, H., Ma, S. & Wang, Y. (2017). Artificial intelligence in healthcare: past, present and future. Stroke and vascular neurology, 2 (4), 230-243. [6] Kaur, K. (2017). Investigating the impact of Metacognition on Critical Thinking with Structural Equation Modeling: Dynamics of Reasoning. International Journal of Informative and Futuristic Research (IJIFR), 4 (11), 8475-8482. [7] Kaushik, P. (2022). Role and Application of Artificial Intelligence in Business Analytics: A Critical Evaluation. International Journal for Global Academic & Scientific Research, 1 (3), 01-11. [8] Kaushik, P. (2023). Enhanced Cloud Car Parking System Using ML and Advanced Neural Network. International Journal of Research in Science and Technology, 13 (1), 73-86. [9] Kumar, A., Chaudhary, K., Jaiswal, E., Rai, P., Gupta, K. & Er. R. (2024). Explainable Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare. International Journal for Multidisciplinary Research, 6 (2), 1-7. [10] Lai M.C., Brian, M. & Mamzer, M. F. (2020). Perceptions of artificial intelligence in healthcare: findings from a qualitative survey study among actors in France. J Transl Med, 18, 14. [11] Makda, A., Saifi, M., Arakkal, M. R., Sadek, M. & Kallatra, A. Q. Z. (2021). Impact of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare. Project, American University of Sharjah. [12] Manne, R. & Kantheti, S. C. (2021). Application of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Chances and Challenges. Current Journal of Applied Science and Technology, 40 (6), 78-89. [13] Murali & Sivakumaran (2018). Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare- A Review. International Journal of Modern Computation, Information and Communication Technology, 1 (6), 103-110. [14] Pee, L. G., Pan, S. & Cui, L. (2018). Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare Robots: A Social Informatics Study of Knowledge Embodiment. Journal of the Association for information Science and Technology, 70 (4). [15] Powles, J. & Hodson, H. (2017). Google DeepMind and Healthcare in an Age of Algo-rithms. Health and Technology, 7, 351-367. [16] Rathore, R. (2022). A Review on study of application of queueing models in Hospital sector. International Journal for Global Academic & Scientific Research, 1 (2), 1-6. [17] Sezgin, E. (2023). Artificial intelligence in healthcare: Complementing, not replacing, doctors and healthcare providers. DIGITAL HEALTH, 9, 1-5. [18] Sun, Q. & Medaglia, R. (2019). Mapping the Challenges of Artificial Intelligence in the Public Sector: Evidence from Public Healthcare. Government Information Quarterly, 36 (2), 368-383. [19] Triantafyllidis, A. K. & Tsanas, A. (2019). Applications of machine learning in real-life digital health interventions: review of the literature. J Med Internet Res, 21.
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Kuldeep Kaur. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET63611
Publish Date : 2024-07-11
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

