Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Automatic Medicine Reminder for Elder People Using Real Time Clock Module
Authors: Mr. G. Narendra, S. Vamshi, B. Nikhil Reddy, B. Jessy Sania
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.63384
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
As individuals age, their cognitive abilities diminish, leading to increased instances of forgetfulness, particularly in adhering to medication schedules. This poses significant health risks, including improper dosages or medication errors among the elderly. To address this issue, this study proposes an enhanced automatic medicine reminder system utilizing an RTC module integrated with an ESP32 microcontroller to facilitate precise medication timing and consistency. Furthermore, the inclusion of a GSM module enables caretakers to remotely monitor patients\' adherence by receiving real-time notifications on their smartphones. This enhanced system offers a proactive approach to medication management, enhancing patient safety and caregiver oversight in geriatric healthcare settings.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
The care and well-being of elderly individuals, particularly in managing their medication intake, pose significant challenges as they age. Observations within family settings often reveal the distress and potential health risks associated with missed doses or incorrect medication administration due to the decline in memory and cognitive abilities among the elderly. This issue becomes even more pronounced in the absence of regular supervision, highlighting the urgent need for reliable and effective solutions to support medication adherence in aging populations Moreover, the challenges extend beyond familial environments to public healthcare systems, where lapses in supervision further exacerbate the situation. Instances of missed doses or improper medication use in public hospitals underscore the critical need for enhanced monitoring and intervention strategies to ensure the safety and well-being of elderly patients. In response to these pressing concerns, this paper proposes an innovative approach to medication management through the development of an automatic medicine reminder system. Leveraging advanced technologies such as RTC modules and ESP32 microcontrollers, this system aims to provide a reliable means of tracking medication schedules and promoting consistent intake among elderly individuals. Furthermore, the integration of GSM modules enables remote supervision by caregivers, addressing the need for enhanced oversight and intervention in both familial and public healthcare settings.
II. WORKING
Major Working of Enhanced Automatic Medicine Reminder System:
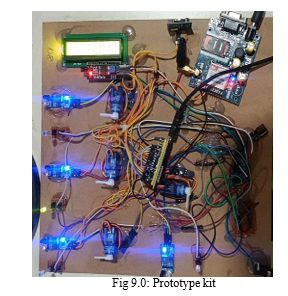
- Compartmentalized Medicine Storage: The medicine box is divided into four compartments, each equipped with a lid controlled by a servo motor. This compartmentalization allows for the organized storage of different medications, simplifying the medication management process.
- Integration with Real-Time Clock (RTC) and ESP32 Microcontroller: The medicine box is connected to a real-time clock and an ESP32 microcontroller. These components work in tandem to process the scheduled medication activities. The RTC ensures accurate timekeeping, while the ESP32 microcontroller manages the overall functionality of the system.
- Medication Alert System: At the designated time for medication intake, the ESP32 microcontroller activates a buzzer and LED light to alert the patient. This auditory and visual cue serves as a reminder for the patient to take their medication from the specified compartment.
- Interaction with IR Sensors: Each compartment is equipped with specific IR sensors. These sensors detect the movement of the patient as they access the medication. When the patient interacts with the compartment, the corresponding IR sensor triggers the servo motor to open the lid, granting access to the medication.
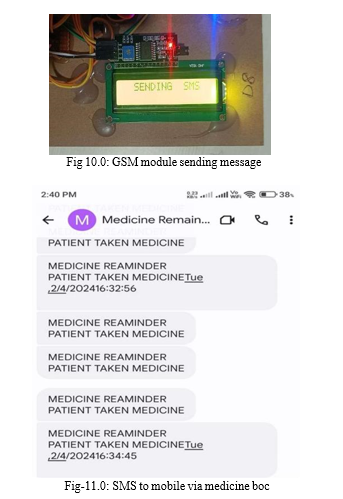
- Communication with Caretaker via GSM Module: Upon accessing the medication, the IR sensor sends a signal to the ESP32 microcontroller, which in turn activates the GSM module. The GSM module sends a message to the designated caretaker, notifying them that the medication has been taken. This communication provides real-time updates to the caretaker, ensuring proactive monitoring of the patient's medication adherence.
- Disabling Alert System: Once the medication has been accessed and the IR sensor detects movement, the buzzer and LED light are automatically turned off. This feature prevents unnecessary alerts and ensures a seamless user experience for the patient.
In summary, the enhanced automatic medicine reminder system utilizes a combination of compartmentalized storage, real-time clock integration, IR sensors, servo motors, ESP32 microcontroller, GSM module, and alert mechanisms to facilitate efficient medication management and remote monitoring for elderly individuals.
III. METHODS AND EXPERIMENTAL DETAILS
A. Hardware Requirements for the Module
- ESP 32 Microcontroller
- DS1307 Real Time Clock (RTC) Module
- IR Sensors
- Buzzer
- Servo motors
- LED Lights, LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) Module
- GSM (Global System for Mobile communication)
B. Software Requirements
Arduino IDE & Embedded C language Hardware
1) ESP 32
This microcontroller offers 36 GPIO ports for versatile digital interfacing, 14 ADC ports for precise analog-to-digital conversion, and 2 DAC ports for generating analog signals. With a clock rate of 240MHz, it delivers high computational performance. Its 16MB flash memory and 250KB SRAM provide ample storage and efficient data handling capabilities, making it suitable for a variety of embedded applications and IoT projects.


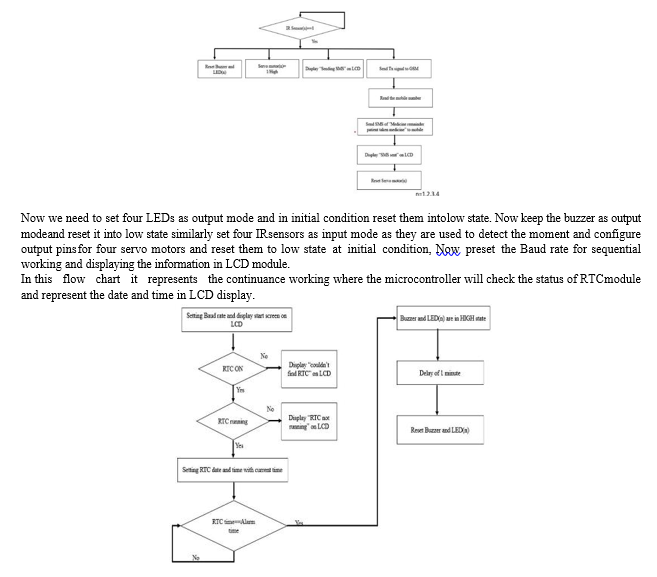
If RTC current time matches with preset alarm time in microcontroller then it will activate the buzzer and respected LED to HIGH state. After one minute delay it will automatically reset the buzzer and LED. In case the person fails to take the medicine or refuses to, the lid will not open and the buzzer will automatically stop after a preset time and will be put on snooze.
Then after taking the medicine the message will be sent to the care taker and servo motors will control the operation this detection of moment in the pill box.
The above flowchart represents the implementing process of Automatic Medicine Remainder for Elder People Using RTC module. The setup consists of a small box divided into multiple compartments, each having a lid to open and an IR sensor attached to it.
The box is connected to a real time clock, a microcontroller device ESP 32 which processes the activities and accordingly displays the pill details and time of intake on the LCD attached to the box and a GSM module which sends message to the family physician or members in case the pill is not taken. The box consists of several compartments each having a pill for a definite time of the day.
An electronic real time clock, with factory predetermined time interval, is automatically activated in sync with the pill intake timings. The real time clock will start beating and as it reaches the stipulated time of pill-intake, the buzzer will go on and message will be displayed regarding which pill to take and time to take each pill. The pill dispenser may be preloaded by the patient himself or may be preloaded by someone assisting the patient once a day, thereby minimizing or totally eliminating the possible confusion as to when to take the prescribed medicine and what dosages to take.
- Now if the person/user takes the pills, i.e. opens the lid, the IR Sensor attached to the lid will detect that the lid is opened and hence will send the output to Arduino which will stop the buzzer. This will be taken into the log registering the person has taken his medicine successfully.
- In case the person fails to take the medicine or refuses to, the lid will not open and the buzzer will automatically stop after a preset time and will be put on snooze. Then after taking the medicine the message will be sent to the care taker and servo motors will control the operation this detection of moment in the pill box.
V. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
Advancement in medication management solutions, particularly tailored to address the needs of elderly individuals and their caregivers. Through meticulous design and integration of various components, the automatic medicine reminder system offers a comprehensive approach to ensuring timely medication intake and enhancing caregiver oversight.
At its core, the system relies on the precise coordination between the RTC module, ESP32 microcontroller, IR sensors, servo motors, GSM module, and alert mechanisms to facilitate seamless medication reminders and communication channels. When the RTC matches the preset alarm time, the system triggers visual and auditory cues, manifesting as a blinking LED light and an activated buzzer. This serves as an effective prompt for the patient to take their medication, mitigating the risks associated with forgetfulness or incorrect dosage intake. The integration of IR sensors adds an additional layer of functionality by enabling the automatic opening of the compartment lid as the patient approaches the medicine box. This feature not only enhances user experience by simplifying access to medication but also ensures that the medication intake process is seamless and effortless for elderly individuals, who may experience mobility challenges or dexterity issues.
One of the most innovative aspects of the system is its ability to facilitate real-time communication between the patient and their caregiver through the GSM module. Upon the patient accessing the medication, a transmission signal is sent to the GSM module, which then promptly notifies the designated caretaker. This proactive communication mechanism allows caregivers to stay informed about the patient's medication adherence status, even when they are not physically present, thereby fostering peace of mind and enabling timely intervention if necessary. Furthermore, the system's ability to reset automatically after sending the notification ensures optimal efficiency and minimizes unnecessary alerts, preserving the user experience and avoiding potential disruptions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the automatic medicine reminder system developed in this project represents a significant advancement in addressing the critical issue of medication management, particularly for elderly individuals and patients requiring regular medication intake. The primary objective of the device is to ensure that individuals adhere to their medication schedules promptly and accurately, thereby enhancing their overall health outcomes and quality of life. One of the key strengths of this system lies in its simplicity, affordability, and high accuracy. By integrating essential components such as the RTC module, ESP32 microcontroller, IR sensors, servo motors, GSM module, buzzer, and LEDs, the system offers a user-friendly solution that is accessible to a wide range of users. The inclusion of visual and auditory cues, such as the blinking LEDs and activated buzzer, further enhances the ease of use and ensures that patients are promptly reminded to take their medication at the prescribed times. Moreover, the system\'s ability to automatically notify family members or caretakers when the patient takes their medication is a significant benefit. This feature not only provides reassurance to caregivers but also enables them to remotely monitor the patient\'s medication adherence, thereby facilitating timely intervention if necessary. The real-time communication capability offered by the GSM module strengthens the support network surrounding the patient, fostering a collaborative approach to healthcare management. Overall, the automatic medicine reminder system holds immense potential in improving medication adherence rates and reducing the risks associated with missed doses or incorrect dosage intake among elderly individuals and patients with chronic conditions. By promoting independence, enhancing caregiver oversight, and streamlining medication management processes, this innovative solution has the power to positively impact the lives of millions of individuals worldwide. As further advancements and refinements are made, it is conceivable that similar technologies will become integral components of modern healthcare systems, contributing to improved patient outcomes and overall well-being.
References
[1] S. Mohapatra, P.K. Sahoo, Internet of medical things: applications and research issues in healthcare monitoring, in: IoT Applications for Healthcare Systems. EAI/Springer Innovations in Communication and Computing, Springer, Cham, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-91096-9_1 et al. [2] A.P. Sankar, D.C. Nevedal, S. Neufeld, M.R. Luborsky, what is a missed dose? Implications for construct validity and patient adherence, AIDS Care 19 (6) (2007)775–780, https://doi.org/10.1080/09540120600708501. [3] A. Jabeena, A.K. Sahu, R. Roy, N.S. Basha, Automatic pill reminder for easy supervision, in: 2017 International Conference on Intelligent Sustainable Systems (ICISS), 2017, pp. 630–637, https://doi.org/10.1109/ISS1.2017.8389315. [4] K. Gupta, A. Jain, P.H. Vardhan, S. Singh, A. Amber, A. Sethi, MedAssist: automated medication kit, in: 2014 Texas Instruments India Educators’ Conference (TIIEC), 2014, pp. 93–99, https://doi.org/10.1109/TIIEC.2014.024. [5] A. Chinnasamy, R. P. J, S.R. Ahmed, A. S, Cloud computing based medical assistance & pill reminder, in: 2022 6th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), Madurai, India, 2022, pp. 628–633, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICCS53718.2022.97883 98. [6] B. Kumar, W.W. Goh, S. Balakrishnan, Smart medicine reminder device for the elderly, in: 2018 Fourth International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication & Automation (ICACCA), 2018, pp. 1–6, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICACCAF.2018.8776734. [7] Y. Bai, T. Kuo, Medication adherence by using a hybrid automatic reminder machine, in: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), 2016, pp. 573–574, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCE.2016.7430735. [8] A. Mathew, J. Paul, K. Nair S, U.S. Sachin, S. Koncherry, C.V. Raghu, Design and implementation of a smart medicine dispenser, in: TENCON 2019 - 2019 IEEE Region 10 Conference, TENCON), 2019, pp. 1059–1064, https://doi.org/10.1109/TENCON.2019.8929483. [9] M.P. Kumar, U. Rani Nelakuditi, IoT and I2C protocol based M-health medication assistive system for elderly people, in: 2019 IEEE 16th India Council International Conference (INDICON), 2019, pp. 1–4, https://doi.org/10.1109/INDICON47234.2019.903 0322. [10] S. Jayanth, M.B. Poorvi, M.P. Sunil, MED- Alert: An IoT device, in: 2016 International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT), 2016, pp. 1–6, https://doi.org/10.1109/INVENTIVE.2016.78249 00. [11] D. Salama, A. Minaam, Smart drugs: improving healthcare using smart pill box for medicine reminder and monitoring system, Future Computing and Informatics Journal 3 (2) (2018) 443–456, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcij.2018.11.008. [12] M. Naeem, G. Paragliola, A. Coronato, A reinforcement learning and deep learning based intelligent system for the support of impaired patients in home treatment, Expert Syst. Appl. 168 (114285) (2021) 1–12, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.114285. [13] M. Ciampi, A. Coronato, M. Naeem, S. Silvestri, An intelligent environment for preventing medication errors in home treatment, Expert Syst. Appl. 193 (116434) (2022)1–11, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.116434. [14] M.A. Kader, M. Nayim Uddin, A. Mohammad Arfi, N. Islam, M. Anisuzzaman, Design & implementation of an automated reminder medicine box for old people and hospital, in: 2018 International Conference on Innovations in Science, Engineering and Technology (ICISET), 2018, pp. 390–394, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICISET.2018.8745654. [15] M.T. Brown, J.K. Bussell, Medication adherence: WHO cares? Mayo Clin. Proc. 86 (4) (2011) 304–314, https://doi.org/10.4065/mcp.2010.0575. [16] A. Kamilaris, A. Pitsillides, Mobile phone computing and the internet of things: a survey, IEEE Internet Things J. 3 (6) (Dec. 2016) 885–898, https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2016.2600569.
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Mr. G. Narendra, S. Vamshi, B. Nikhil Reddy, B. Jessy Sania. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET63384
Publish Date : 2024-06-20
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

