Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Blockchain Based E-Voting and Electoral Fraud Detection
Authors: Prof. Sumit Shevtekar, Varad Kalambarkar
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.56370
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
By focusing on its applicability in the identification and mitigation of electoral fraud, this review article investigates the potential value of blockchain technology in enhancing the integrity of electronic voting (e-voting) systems. It is more important than ever to safeguard the legitimacy and security of democratic processes as e-voting becomes more popular worldwide. Blockchain offers a promising way to strengthen confidence and transparency in electronic voting because of its decentralized organization and immutable record. This review analyzes blockchain’s potential for detecting and preventing electoral fraud, explains its benefits and drawbacks, and supports its viability with relevant case studies. This work adds to the continuing conversation about robust and durable e-voting systems by combining existing studies.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Electronic voting, sometimes known as e-voting, has become a popular replacement for outdated paper-based voting systems in the modern day. It promises to make voting more convenient, approachable, and effective. However, as e-voting becomes more widely used, worries about electoral fraud have moved to the forefront of conversation. The term ”electoral fraud” refers to a variety of dishonest acts that have the potential to taint elections and produce unfair or erroneous results. These worries, along with the desire to increase confidence in e-voting systems, have sparked a lot of interest in researching cutting-edge technology to protect the democratic process.
This paper’s main goal is to investigate the crucial part played by blockchain technology in solving the problems caused by electoral fraud in electronic voting systems. The immutable and decentralized properties of blockchain have the potential to strengthen the security, accountability, and transparency of the electronic voting process. This article aims to analyze the benefits, difficulties, and practical applications of employing blockchain for electoral fraud detection and prevention in electronic voting systems.
A paradigm shift in how people exercise their democratic rights has been brought about through electronic voting. Voting is made possible through a variety of electronic devices, including computers and cellphones, by leveraging digital technologies. E-voting has unquestionable benefits, such as greater accessibility and lower administrative expenses, but it also raises new security risks. E-voting raises a variety of electoral fraud problems, such as vote tampering, voter impersonation, hacking, and the potential for insider assaults.
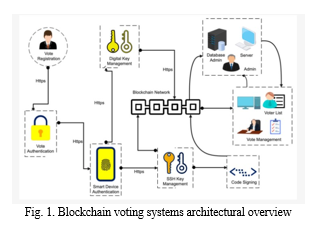
This study explores the cutting-edge possibility of utilizing to address these issues in light of those worries. It seeks to provide a complete view on the potential and constraints of this method, shedding light on how blockchain can improve the security and integrity of e-voting systems. And system architecture is as follow :
- Voter Registration: Voters are required to register and provide their identity information. This information is verified and recorded on the blockchain. Each registered voter is issued a unique digital identity.
- Identity Verification: Identity verification mechanisms, such as biometrics or digital signatures, are used to ensure that only eligible voters can participate.
- Voting Interface: Voters access a secure voting interface, which can be a web application or a mobile app, to cast their votes. This interface should be user-friendly and accessible.
- Ballot Creation: Election administrators create digital ballots, specifying the candidates or choices available to voters. The ballots are then cryptographically hashed and stored on the blockchain.
- Casting Votes: Voters log in using their digital identity and make their selections on the digital ballot. The chosen options are cryptographically signed and added to the blockchain as a transaction. Double-spending prevention mechanisms are implemented to ensure that a voter can cast only one vote.
- Consensus Mechanism: The blockchain network employs a consensus mechanism, such as Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), or other algorithms, to validate and add new blocks of transactions to the chain. This consensus ensures that all nodes in the network agree on the validity of the votes.
- Privacy and Encryption: Techniques like zero-knowledge proofs or homomorphic encryption can be used to protect the privacy of voters while still allowing their votes to be counted.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts can be used to automate various aspects of the election process, such as tallying votes, ensuring only eligible voters participate, and triggering events like the closing of the voting period.
- Tallying and Results: Once the voting period ends, the votes are tallied using the blockchain data. The results are transparent, and anyone can audit the process, promoting trust in the election outcome.
II. LITERATURE SURVEY
The use of blockchain technology in electronic voting (evoting) systems to prevent electoral fraud has drawn considerable interest from both academic and business communities. A review of the literature in the field indicates a growing body of work that highlights the advantages and disadvantages of using blockchain technology to improve the security and reliability of electronic voting.
A. Blockchain Fundamentals
Numerous sources provide a foundational understanding of blockchain technology, emphasizing its decentralized structure, cryptographic security, and immutability, making it suitable for e-voting applications.
B. Electoral Fraud in E-Voting
Literature highlights the various forms of electoral fraud, including vote manipulation, identity fraud, and cyberattacks, which pose significant threats to e-voting systems’ credibility.
C. Advantages of Blockchain
Researchers recognize blockchain’s potential to introduce transparency and trustworthiness in e-voting. Features such as the tamper-resistant ledger, cryptographic security, and consensus mechanisms are highlighted as advantageous.
D. Challenges and Considerations
The literature emphasizes scalability issues, usability concerns, and regulatory challenges as potential roadblocks in implementing blockchain-based e-voting systems. Privacy and anonymity concerns are also addressed.
E. Blockchain Use Cases
Real-world case studies and pilot projects demonstrate the practical applications of blockchain in e-voting. These examples showcase the technology’s ability to improve transparency, security, and auditability.
F. Security and Fraud Prevention
Scholars explore the role of smart contracts in automating fraud prevention measures, while also highlighting blockchain’s potential to detect and deter electoral fraud in real-time.
G. Usability and Accessibility
Research touches on user experience and accessibility issues, aiming to ensure that blockchain-based e-voting systems are user-friendly for a diverse electorate.
H. Legal and Regulatory Framework
Several studies discuss the legal and regulatory considerations in implementing blockchain in e-voting, including compliance with data protection and electoral laws.
III. PROBLEM STATEMENT
Despite the greater accessibility and efficiency that electronic voting (e-voting) systems promise, there are serious concerns about the security and integrity of electoral processes. Election fraud incidents, including vote tampering, voter impersonation, and cyberattacks, pose serious risks to the legitimacy of electronic voting systems. To address these issues and secure the democratic process while boosting public confidence, creative solutions are required.
A. Security Vulnerabilities
E-voting systems are susceptible to various forms of cyber threats, including hacking, data manipulation, and denial-ofservice attacks, compromising the confidentiality and integrity of votes.
B. Electoral Fraud
Instances of electoral fraud, whether through vote buying, identity theft, or insider manipulation, undermine the fairness and legitimacy of election results in e-voting systems.
C. Lack of Transparency
Traditional e-voting systems often lack transparency, making it difficult to verify the accuracy of the results and detect fraudulent activities.
D. Usability and Accessibility
Ensuring that e-voting systems are user-friendly and accessible to all, including individuals with disabilities, is a significant challenge.
E. Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Implementing new technologies like blockchain in e-voting systems requires adherence to legal and regulatory frameworks, complicating the adoption process.
IV. PROPOSED SYSTEM
The proposed system aims to leverage blockchain technology to create a secure, transparent, and fraud-resistant evoting platform. It includes the following key components and features:
- User-Friendly Interface: A user-friendly and accessible interface to facilitate voterparticipation, ensuring usability for a broad range of users.
- Secure Voter Authentication: Robust voter authentication mechanisms, including biometrics, government-issued IDs, or secure two-factor authentication, to prevent unauthorized access.
- Blockchain Network: Utilization of a blockchain network with two options: Public Blockchain: For maximum transparency and trust. Private Blockchain: To cater to specific governmental or organizational needs.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts to define the rules and processes of the election, automating fraud prevention measures, such as verifying voter eligibility and tallying votes.
- Voting Process: A secure and encrypted voting process where votesare time-stamped, immutable, and tamper-resistant once added to the blockchain.
- Real-time Monitoring: Real-time monitoring of the voting process by election officials and authorities to ensure a smooth and secure election.
- Voter Privacy and Anonymity: Techniques like zero-knowledge proofs and ring signatures to protect voter privacy and maintain the anonymity of votes.
8. Security Measures
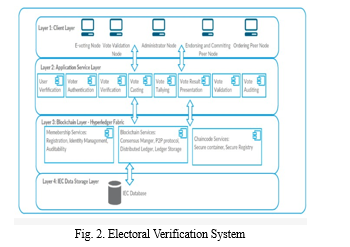
Implementation of stringent security protocols, including data encryption, firewall protection, and secure access controls to safeguard against cyberattacks.
9. Fraud Detection Algorithms: Utilization of advanced fraud detection algorithms and machine learning models to identify and report suspicious patterns or anomalies in the voting data.
10. Immutable Audit Trail: The blockchain ledger creates an immutable audit trail of all activities, allowing for the easy detection of irregularities or fraud attempts. Results and Reporting: Automated calculation of election results from the blockchain data and transparent reporting to the public to maintain credibility.
11. Post-Election Analysis: Utilization of blockchain data for post-election analysis, auditing the results, and identifying any discrepancies or irregularities.
12. Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring that the system complies with legal and regulatory requirements, including data protection and electoral laws.
13. User Support and Helpdesk: A dedicated user support and helpdesk system to assistvoters with any issues, inquiries, or technical difficulties during the e-voting process.
The proposed system integrates blockchain’s decentralization, immutability, and transparency features to provide a comprehensive solution for secure and fraud-resistant e-voting. It balances user-friendliness, privacy, security, and regulatory compliance to foster public trust and maintain the integrity of the electoral process.
V. FUTURE WORK
As we move forward, there are several avenues for future work and research in the domain of blockchain-based e-voting and electoral fraud detection:
- Scalability: Research and development efforts should focus on improving the scalability of blockchain-based evoting systems to accommodate large-scale elections and mass participation.
- Usability and Accessibility: Enhancements in user interfaces and accessibility features are essential to ensure that the system remains user-friendly and inclusive for all voters.
- Privacy-Preserving Techniques: Further exploration of advanced privacy-preserving techniques, like homomorphic encryption or multi-party computation, to enhance voter privacy while maintaining the anonymity of votes.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Collaboration with legal experts and policymakers to establish robust regulatory frameworks that support the adoption of blockchain-based evoting systems while addressing legal and compliance challenges.
- Interoperability: Research on blockchain interoperability to ensure that e-voting systems can seamlessly communicate and share data with other systems, including government databases and electoral commissions.
- Blockchain Security: Continuous research on blockchain security to stay ahead of emerging threats and vulnerabilities that may compromise the integrity of e-voting systems.
- International Collaborations: Encouraging international collaborations to share best practices, case studies, and standards for blockchain-based e-voting, fostering global trust in the technology.
Incorporating these future research directions will contribute to the ongoing evolution of blockchain-based e-voting systems and further strengthen their role in ensuring secure, transparent, and fraud-resistant electoral processes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the incorporation of blockchain technology into electronic voting (e-voting) systems presents a possible remedy for the pressing issues of election fraud and security flaws. The suggested system offers a complete framework for secure and transparent electronic voting by combining userfriendly interfaces, strong voter verification, smart contracts, and real-time monitoring with blockchain’s decentralization, immutability, and transparency. The approach fosters public confidence, promotes justice, and lowers the risks of election fraud by preserving the integrity of the democratic process. The system’s ability to spot and stop fraudulent actions is further strengthened by the use of fraud detection algorithms and an immutable audit record.
References
[1] Shahzad, B.; Crowcroft, J. Trustworthy Electronic Voting Using Adjusted Blockchain Technology. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 24477–24488. [2] Daramola, O.; Thebus, D. Architecture-Centric Evaluation of Blockchain-Based Smart Contract E-Voting for National Elections. Informatics 2020, 7, 16. [3] Tan, W.; Zhu, H.; Tan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Da Xu, L.; Guo, K. A novel service level agreement model using blockchain and smart contract for cloud manufacturing in industry 4.0. Enterp. Inf.Syst. 2021. [4] Jard´?-Cedo, R.; Pujol-Ahull´ o, J.; Castell´ a-Roca, J.; Viejo, A. Study` on poll-site voting and verification systems. Comput. Secur. 2012, 31, 989–1010. [5] Zhang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Hu, Y.; Huang, S.; Cao, S.; Chopra, A.; Huang, S. A Privacy-Preserving Voting Protocol on Blockchain. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 11th International Conference on Cloud Computing (CLOUD), San Francisco, CA, USA, 2–7 July 2018; pp. 401–408. [6] Riemann, R.; Grumbach, S. Distributed Protocols at the Rescue for Trustworthy Online Voting. arXiv 2017, arXiv:170504480. [7] Li, K.; Li, H.; Hou, H.; Li, K.; Chen, Y. Proof of Vote: A HighPerformance Consensus Protocol Based on Vote Mechanism Consortium Blockchain. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 19th International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications; IEEE 15th International Conference on Smart City; IEEE 3rd International Conference on Data Science and Systems (HPCC/SmartCity/DSS), Bangkok, Thailand, 18–20 December 2017; pp. 466–473. [8] Sadia, K.; Masuduzzaman, M.; Paul, R.K.; Islam, A. Blockchain Based Secured E-voting by Using the Assistance of Smart Contract. arXiv 2019, arXiv:191013635. [9] Sudharsan, B.; Tharun, R.V.; Krishna, N.M.P.; Raj, B.J.; Arvindh, S.M.; Alagappan, M. Secured Electronic Voting System Using the Concepts of Blockchain. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 10th Annual Information Technology, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference (IEMCON), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–19 October 2019; pp. 0675–0681. [10] Bohme, Rainer, and Stefan Koppell E-voting and Blockchain the future of voting.” Journal of Innovation Economics Management2020/3( 2020) 11- 28. [11] Salefu Ngbede Odaudu, Umoh J Imeh and Umar Alfa Abubakar 2019 BIDS: Blockchain based intrusion detection system for electoral process Int. Conf. on Electronics, Computer and Computation (ICECCO) ( Abuja: Nigeria). [12] Syada Tasmia Alvi, Mohammed Nasir Uddin, Linta Islam Digital voting: A blockchain-based e-voting system using biohash and smart contract 2020 Third International Conference on Smart Systems and Inventive Technology (ICSSIT) (2020), pp. 228-233. [13] Venkata Naga Rani B, Akshay S, Arun kumar M , Ishwar Kumar M A , (2019) , Decentralized E-Voting System,International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology.
Copyright
Copyright © 2023 Prof. Sumit Shevtekar, Varad Kalambarkar. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET56370
Publish Date : 2023-10-30
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

