Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Challenges Faced by India Due to its Increasing Population: A Comprehensive Analysis
Authors: Shaikh Mohammed Adin Dawood
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.61088
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
This paper examines the significant challenges that arise from India\'s expanding population. As urban areas swell and industries grow, there\'s immense pressure on resources and infrastructure, widening the gap between the rich and poor. The economy faces hurdles too, with fewer jobs and sluggish income growth. Environmental concerns escalate with increased pollution and the looming threat of climate change. Ensuring there\'s enough food for everyone becomes increasingly difficult, as does providing adequate healthcare and education. To address these issues, India must invest in education and job training, particularly for women, and leverage technological advancements to enhance efficiency. By addressing these challenges comprehensively, India can strive towards a future where every individual has equitable opportunities for success, despite the population growth.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
India became the world’s most populated country in the early 1980s. The exact year can vary slightly depending on different population estimates, but it is generally accepted that India surpassed China in terms of population around 1982 or 1983. Since then, India has remained the most populous country in the world.
A. Background
- Overview of India’s population growth and its global significance.
- Importance of understanding the challenges associated with increasing population.
B. Objectives of the Study
- Identifying key challenges stemming from population growth.
- Analyzing the impact on different sectors of the economy and society.
- Proposing strategies to address and mitigate these challenges.
II. METHODOLOGY
The analysis of challenges faced by India due to its increasing population will employ a multi-dimensional methodology encompassing both quantitative and qualitative approaches. Initially, a comprehensive literature review will be conducted to gather insights from existing research, government reports, and scholarly articles. This will be followed by the identification of key areas of impact such as healthcare, education, employment, infrastructure, and environment. Data collection will involve gathering relevant demographic, socio-economic, and environmental data from credible sources including census reports, government surveys, and academic studies. Quantitative analysis will be performed to examine population growth trends, correlations with socio-economic indicators, and projections for the future. Qualitative analysis will involve interviews, surveys, or case studies to capture stakeholder perspectives and experiences. The synthesis of findings will culminate in a detailed report highlighting the challenges and proposing evidence-based recommendations for addressing them effectively.
III. ANALYSIS
A. Challenges
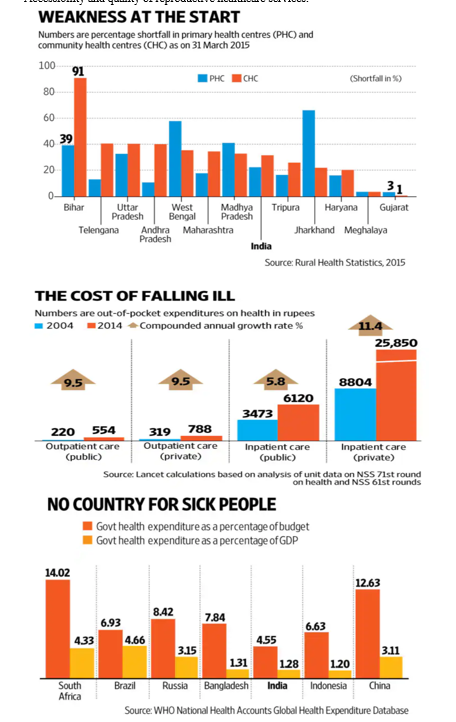
- Healthcare Challenges
- Overburdened Healthcare System:
- Strain on healthcare infrastructure and services.
- Increased demand for healthcare professionals.
- Maternal and Child Health:
- Impact of population growth on maternal and child health.
- Accessibility and quality of reproductive healthcare services.
- Overburdened Healthcare System:
2. Educational Challenges
- Overcrowded Schools and Colleges:
- Insufficient educational infrastructure to accommodate the growing population.
- Quality of education and its implications.
- Employment and Skill Development:
- Rising youth population and the challenge of providing adequate employment opportunities.
- The need for skill development programs to meet industry demands.
A More Detailed Summary
India faces several educational challenges due to its large and rapidly growing population.
Key challenges include:
- Access to Education: Despite significant progress in recent years, ensuring universal access to quality education remains a challenge. The sheer size of the population, especially in rural areas, makes it difficult to reach every child with educational opportunities.
- Overcrowded Classrooms: High population density often leads to overcrowded classrooms, making it challenging for teachers to provide individual attention to students. This can negatively impact the quality of education and student learning outcomes.
- Infrastructure and Resources: The demand for educational infrastructure and resources is immense. Many schools, particularly in rural areas, lack basic facilities such as classrooms, libraries, and sanitation facilities. Limited resources also affect the availability of teaching materials and technology.
- Teacher Shortages: Meeting the demand for qualified and skilled teachers is a persistent challenge. The growing student population requires a proportional increase in the number of well-trained educators. However, recruiting and retaining teachers, especially in remote areas, remains a significant hurdle.
- Quality of Education: While access to education has improved, the overall quality of education is a concern. Disparities exist between urban and rural areas, and the curriculum and teaching methods may not always align with the evolving needs of the job market.
- Gender Disparities: Gender-based disparities in education persist in certain regions, with girls facing challenges such as early marriage, cultural norms, and limited access to schools. Efforts are being made to address these issues, but progress is gradual.
- Vocational Training and Skill Development: India's education system is often criticized for focusing heavily on theoretical knowledge rather than practical skills. As the job market evolves, there is an increasing need for vocational training and skill development programs to prepare students for diverse career opportunities.
- Digital Divide: The digital divide is a significant challenge in the context of education. While technology has the potential to enhance learning experiences, disparities in access to digital devices and the internet can widen educational inequalities.
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach involving government initiatives, community involvement, and collaboration with non-governmental organizations to ensure that the education system can accommodate and provide quality education for the growing population in India.
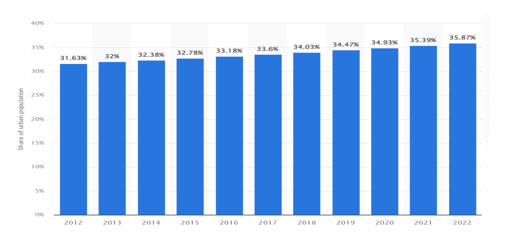
3.Urbanization Challenges
- Rapid Urbanization:
- Pressure on urban infrastructure and services.
- Slum proliferation and its socio-economic implications.
- Housing Shortages:
- Increased demand for affordable housing.
- Urban planning challenges and strategies for sustainable development.
India: Degree of urbanization from 2012 to 2022
4. Environmental Sustainability Challenges
- Natural Resource Depletion:
- Impact of population growth on water, land, and other resources.
- Strategies for sustainable resource management.
- Pollution and Climate Change:
- Population-induced environmental degradation.
- Mitigation measures for pollution and climate change.
A more detailed summary
India faces several environmental challenges linked to its population growth. Key issues include:
- Air and Water Pollution
- Rapid population growth has led to increased industrialization and urbanization, contributing to air and water pollution. The release of pollutants from industries and urban areas has resulted in deteriorating air quality and contamination of water bodies.
- Deforestation
- Population growth often leads to increased demand for resources, including land. This demand can result in deforestation as forests are cleared for agriculture, urban development, and other purposes. Deforestation negatively impacts biodiversity and contributes to climate change.
- Waste Management
- The growing population generates significant amounts of solid waste and sewage. Inadequate waste management infrastructure and practices can lead to the improper disposal of waste, causing pollution and health hazards.
- Land Degradation
- The pressure on land resources due to population growth, agricultural expansion, and urbanization can lead to land degradation. Soil erosion, loss of fertility, and desertification are some of the consequences, affecting agricultural productivity and ecosystem health.
- Resource Depletion
- Population growth contributes to increased demand for natural resources, such as water, minerals, and energy. Over-extraction and unsustainable use of these resources can lead to depletion and environmental degradation.
- Climate Change
- While not solely attributed to population growth within a specific country, the overall global population contributes to climate change. Increased emissions from various sources, including energy consumption and deforestation, contribute to India's vulnerability to the impacts of climate change.
- Loss of Biodiversity
- Habitat destruction and fragmentation due to population growth and development activities can lead to the loss of biodiversity. India is home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, and the decline in natural habitats threatens many species.
- Water Scarcity
- Population growth intensifies the demand for water, leading to over-extraction of groundwater and strain on surface water sources. This contributes to water scarcity in many regions, affecting agriculture, industry, and daily life.
Addressing these challenges requires comprehensive policies and strategies that focus on sustainable development, efficient resource management, and environmental conservation. Population control measures, combined with initiatives promoting sustainable practices, can contribute to mitigating the impact of population growth on the environment.
5. Policy and Governance Challenges
- Implementation Gaps:
- Challenges in implementing population-related policies.
- Strengthening governance mechanisms for effective policy execution.
- Social Inequality:
- Disparities in resource distribution and access to services.
- Inclusive policy formulation for social equity.
A more Detailed Summary
India faces several policy and governance challenges due to population growth. Some of the key challenges include:
- Resource Allocation: The rapid population growth puts pressure on the allocation of resources such as education, healthcare, and employment opportunities. Providing essential services to a growing population becomes a significant challenge for the government.
- Infrastructure Strain: The demand for infrastructure, including transportation, housing, and sanitation, increases with a growing population. This places a burden on the government to invest in and upgrade infrastructure to meet the needs of the expanding population.
- Employment Generation: The need to generate sufficient employment opportunities to accommodate the growing workforce is a critical challenge. Failure to provide jobs can lead to unemployment and underemployment issues, impacting economic stability and social well-being.
- Healthcare Services: A larger population requires an increased focus on healthcare services. The government must ensure access to quality healthcare, family planning, and maternal and child health services to manage the health implications of a large population.
- Education: Meeting the educational needs of a burgeoning population is a significant challenge. Adequate infrastructure, qualified teachers, and resources are required to ensure that the education system can accommodate the growing number of students.
- Environmental Impact: A rapidly increasing population can lead to greater environmental challenges, such as deforestation, pollution, and resource depletion. Sustainable development becomes crucial to mitigate the adverse effects on the environment.
- Urbanization Challenges: Rapid population growth contributes to urbanization, leading to the growth of slums and informal settlements. Managing urbanization requires effective urban planning, housing policies, and infrastructure development.
- Social Inequality: High population growth can exacerbate existing social inequalities, as resources may not be distributed equitably. Bridging the gap between different socio-economic groups becomes essential for fostering inclusive development.
- Family Planning and Reproductive Health: Ensuring access to family planning services and promoting reproductive health is crucial for managing population growth. Policies that encourage family planning and women's health can have a positive impact on population control.
- Political Will and Implementation: Implementing effective policies to address population-related challenges requires political will and commitment. Ensuring that policies are implemented efficiently and consistently is essential for achieving desired outcomes.
Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive and multi-faceted approach, involving coordination between various government departments, collaboration with non-governmental organizations, and community engagement.
6. Mitigation Strategies
- Population Control Measures:
- Strengthening family planning programs.
- Advocating for awareness and education on population control.
- Social and Economic Policies:
- Inclusive economic growth strategies.
- Fostering skill development and job creation.
- Urban Planning and Infrastructure Development:
- Sustainable urban development strategies.
- Infrastructure planning to accommodate population growth.
- Environmental Conservation:
- Promoting sustainable practices.
- Raising awareness on environmental conservation.
IV. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
A. Healthcare Challenges
Results: The overburdened healthcare system in India faces significant challenges due to the rapid population growth. Increased strain on healthcare infrastructure and services is evident, with a surge in demand for healthcare professionals.
Discussion: Addressing this challenge requires substantial investments in healthcare infrastructure, workforce training, and innovative solutions to meet the rising demand. Strategic planning, collaboration between public and private sectors, and technology integration can enhance the efficiency and accessibility of healthcare services.
Maternal and child health is adversely affected by population growth, emphasizing the need for comprehensive reproductive healthcare services. Enhancing accessibility and ensuring the quality of such services are critical steps toward mitigating the impact on the health of mothers and children.
B. Educational Challenges
Results: The educational sector grapples with challenges stemming from overcrowded schools and colleges, leading to compromised quality of education. Additionally, addressing the employment needs of the growing youth population is crucial, requiring a focus on skill development programs.
Discussion: To address overcrowded educational institutions, there is a need for increased investment in infrastructure, teacher training, and technology integration. Initiatives promoting vocational training and skill development can bridge the gap between education and employment, contributing to economic growth.
C. Urbanization Challenges
Results: Rapid urbanization poses challenges to urban infrastructure and services, leading to the proliferation of slums. Housing shortages exacerbate the situation, necessitating sustainable urban development strategies.
Discussion: Strategic urban planning, policies promoting affordable housing, and investment in infrastructure are imperative to manage the impacts of rapid urbanization. Sustainable development practices can address housing shortages and enhance the overall quality of urban life.
D. Environmental Sustainability Challenges
Results: Population growth contributes to natural resource depletion, pollution, and climate change. Air and water pollution, deforestation, and inadequate waste management are evident consequences of unchecked population growth.
Discussion: Mitigating environmental challenges requires a holistic approach, including sustainable resource management, stringent pollution control measures, and conservation efforts. Policies promoting environmental awareness and education can foster a sense of responsibility among the population.
E. Policy and Governance Challenges
Results: Implementation gaps in population-related policies and social inequality highlight governance challenges. The allocation of resources, infrastructure strain, and the need for employment generation demand a concerted effort from policymakers.
Discussion: Efforts should focus on addressing policy implementation gaps through effective governance mechanisms. Inclusive policies that bridge social inequalities are vital for achieving sustainable development. Political will and commitment are key factors in ensuring the success of population-related policies.
F. Mitigation Strategies
Results: Population control measures, social and economic policies, urban planning, and environmental conservation strategies offer potential solutions to address the challenges posed by population growth in India.
Discussion: Strengthening family planning programs, advocating awareness on population control, and promoting inclusive economic growth are foundational steps. Sustainable urban development, infrastructure planning, and environmental conservation policies should align with population control measures to achieve long-term success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the challenges posed by India’s rapid population growth are complex and multifaceted, affecting critical areas such as health, education, urbanization, environment environmental sustainability and governance As the most populous country in the world, India needs to tackle these challenges strategically to achieve sustainable development. Due to over-constrained infrastructure and increased demand for services, the health system faces stress, particularly affecting maternal and child health. Education is dealing with issues of overcrowded schools, lack of jobs and the urgent need for job opportunities and skills development to accommodate the growing number of young people. Rapid urbanization poses challenges in managing infrastructure and dealing with the socio-economic issues arising from increasing rural areas. Environmental sustainability is a major concern, and natural resource degradation, pollution, and climate change demand urgent attention on sustainability and they have been preserved Policy and governance challenges, including disparities in implementation and social inequalities, highlight the need for effective governance mechanisms and inclusive policies to ensure equitable resource allocation Bridging these gaps is essential for inclusive growth and reducing disparities between different socioeconomic groups. Mitigation strategies including population control, inclusive economic policies, sustainable urban planning, and environmental protection offer possible solutions in enforcing Family planning policies den, advocating awareness and encouraging skills development can help deal with population growth. Moreover, adopting sustainable practices and increasing environmental awareness are important steps to address environmental challenges. Navigating these challenges requires India to adopt a comprehensive, collaborative approach that includes government policy, community engagement and partnerships with NGOs, not as a consumption of these strategies effective implementation will not only reduce the impact of population growth on national development but also contribute towards a more sustainable and inclusive future for India and its diverse population.
References
[1] \"India\'s Population: The Rising Elephant\" by Tim Dyson (2010) [2] \"India Human Development Report 2019: Towards Social Exclusion Index\" by Institute for Human Development (IHD) [3] \"Population and Development in India\" by A.R. Gopalakrishnan (2014) [4] \"Population, Reproductive Health, and Economic Development in India\" edited by Gavin W. Jones and Pravin Visaria (2014) [5] \"India\'s Demographic Transition: Boon or Bane?\" by S. Irudaya Rajan and K.C. Zachariah (2011) [6] \"Urbanization in India: Challenges, Opportunities, and the Way Forward\" by Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, Government of India (2018) [7] \"Environmental Challenges of the 21st Century: Perspectives from India\" edited by R. B. Singh et al. (2015)
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Shaikh Mohammed Adin Dawood. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET61088
Publish Date : 2024-04-26
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

