Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Data Protection in the Cloud: Ensuring Security and Compliance for Organizational Data
Authors: Narasimha Rao Alugoju
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.66087
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
The widespread adoption of cloud computing has transformed the way organizations store, process, and access data, offering unparalleled scalability and flexibility. However, this shift to cloud-based infrastructures has also introduced new vulnerabilities and security challenges. Cyberattacks targeting cloud environments, including data breaches, unauthorized access, and misconfigurations, threaten the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information. This article examines the critical strategies and technologies necessary to safeguard organizational data in the cloud, focusing on encryption, access management, and continuous monitoring. Emphasis is placed on achieving compliance with regulatory frameworks such as HIPAA, GDPR, and CCPA, while balancing operational efficiency. Through case studies and real-world examples, it highlights best practices for organizations to fortify their cloud security posture, mitigate risks, and maintain stakeholder trust. By aligning security measures with emerging threats and compliance requirements, this work provides a comprehensive roadmap for navigating the complexities of cloud data protection.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
As organizations increasingly migrate their operations to the cloud, the potential for innovation and operational efficiency has grown exponentially. Cloud computing offers unparalleled scalability, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility, revolutionizing how businesses manage and process their data ([10]). However, this digital transformation also introduces significant security challenges, making data protection a critical concern for organizations across industries ([7]).
This article explores the complexities of safeguarding sensitive information in cloud environments, delving into both the opportunities and risks associated with cloud adoption. It highlights the importance of implementing robust security strategies to mitigate risks such as unauthorized access, data breaches, and regulatory non-compliance ([3], [4], [5]). Moreover, it underscores the necessity of aligning cloud security measures with existing legal frameworks, such as HIPAA ([4]), GDPR ([3]), and CCPA ([5]), to ensure compliance while maintaining operational efficiency.
By examining advanced data protection techniques—such as encryption ([6]), identity management ([7]), and real-time monitoring ([8])—this paper aims to provide organizations with actionable insights to secure their cloud infrastructures. It further emphasizes the role of collaboration between cloud service providers and users in creating a secure ecosystem, where both technical and human factors are equally addressed ([7]). Ultimately, this article argues that while the migration to cloud computing presents challenges, these can be effectively navigated through proactive measures, fostering a secure and compliant digital future. Through a combination of strategic planning, advanced technologies, and adherence to best practices ([1], [2]), organizations can protect their data while fully leveraging the transformative potential of the cloud.
The following graph shows the steady increase in data breaches targeting cloud environments from 2015 to 2023. The trend emphasizes the growing need for robust security measures and proactive risk mitigation strategies to protect sensitive data.

Figure 1: Data Breaches Over Time in Cloud Environments
II. CORE MECHANISMS AND IMPACT OF DATA PROTECTION IN CLOUD ENVIRONMENTS
The shift to cloud computing has revolutionized organizational data management, enabling scalability, cost efficiency, and global access ([10]). However, the migration of sensitive data to cloud environments also presents significant challenges. Protecting data in the cloud requires understanding the fundamental mechanisms that ensure its confidentiality, integrity, and availability while maintaining compliance with regulatory standards ([1], [2]).
A. Scalability and Accessibility in Data Protection
Cloud environments offer unparalleled scalability, enabling organizations to store and manage vast amounts of data ([10]). However, this scalability introduces unique security challenges. With larger datasets distributed across multiple locations, the attack surface expands, increasing vulnerability to breaches. Implementing scalable security solutions like data encryption, access control policies, and real-time monitoring is critical to addressing these risks ([7]).
For instance, advanced encryption methods such as AES-256 ensure that data remains secure both in transit and at rest ([6]). These measures are further enhanced by role-based access control (RBAC), ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data, even as the system scales to accommodate growth ([7]).
B. Shared Responsibility Model
Cloud security operates under the shared responsibility model, wherein the cloud service provider (CSP) and the organization share distinct security roles ([7]). CSPs ensure the security of the cloud infrastructure, including physical servers, storage, and networking components. Organizations, on the other hand, are responsible for securing the data and applications they host within the cloud ([10]). Failure to clearly delineate these responsibilities can lead to security lapses. For example, misconfigured cloud storage buckets have been a common cause of data breaches, underscoring the need for organizations to proactively manage configurations and adhere to best practices ([7]).
C. Personalization and Advanced Threat Protection
The flexibility of cloud platforms enables organizations to adopt tailored threat detection and prevention systems ([8]). Utilizing artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), CSPs offer solutions capable of identifying anomalous behavior indicative of potential attacks ([6]).
For example, anomaly detection algorithms can flag unusual login patterns, such as logins from unauthorized locations or devices, helping prevent unauthorized access ([8]). Similarly, AI-driven solutions allow for real-time assessment of potential threats, such as distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks or ransomware ([7]).
D. Regulatory Compliance and Governance
Compliance with global data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) ([3]) and Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) ([4]), is paramount for organizations operating in the cloud. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties and reputational damage ([5]).
To meet these requirements, organizations must implement measures like data masking, logging, and regular audits ([7]). Additionally, leveraging CSP-provided compliance tools can simplify adherence to regulatory mandates ([2]).
Following chart highlights the financial penalties associated with non-compliance under major regulatory frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA. It underscores the importance of aligning cloud security measures with these regulations to avoid significant financial and reputational damages.
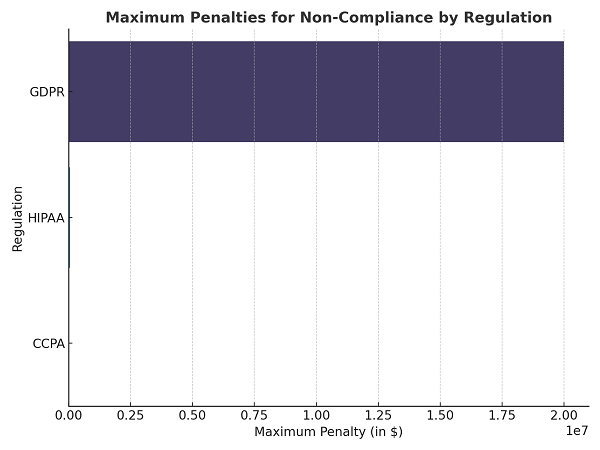
Figure 2: Maximum Penalties for Non-Compliance by Regulation
E. Global Impact of Cloud Data Protection
The adoption of cloud-based data protection strategies has a profound global impact. By ensuring robust security measures, organizations not only mitigate financial losses but also bolster customer trust and operational resilience ([7]). Additionally, these strategies enable secure cross-border data flows, facilitating international business and collaboration ([3]).
For example, industries like healthcare benefit significantly from cloud data protection by securely managing electronic health records (EHRs) and ensuring compliance with privacy laws like HIPAA ([4]). This capability enhances the global exchange of medical research while protecting patient privacy ([4]). The following figure illustrates the key mechanisms and impacts of data protection in cloud environments, focusing on scalability, shared responsibility, advanced threat protection, and regulatory compliance. It highlights the essential interplay between technical solutions, organizational strategies, and regulatory adherence to ensure secure and resilient cloud operations. The chart below showcases the risk reduction potential of core mechanisms like encryption, identity access management, and continuous monitoring, emphasizing their critical role in cloud data protection.

Figure 3: Core Mechanisms and Impact of Data Protection in Cloud Environments
III. OPTIMAL SCENARIOS FOR CLOUD DATA PROTECTION
Cloud data protection strategies can be most effective when applied in specific contexts that leverage the strengths of cloud platforms and advanced technologies ([10]). These optimal scenarios include environments with high data volume, complex compliance requirements, and dynamic workloads, where cloud services can mitigate risks while enhancing operational efficiency ([1], [7]).
A. High-Volume Data Processing and Storage
Cloud environments excel at managing vast datasets, but this requires robust protection to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability ([10]).
- Scalable Security Architectures: Organizations can deploy scalable encryption and access controls to secure large-scale data operations. For instance, automatic encryption provided by cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS) ensures that all data is encrypted at rest and in transit ([7]).
- Real-Time Monitoring: Advanced threat detection systems, powered by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), analyze high volumes of activity to identify anomalies and potential breaches ([6], [8]).
B. Regulated Industries
Industries like healthcare, finance, and government must adhere to strict compliance standards, making tailored cloud data protection essential ([4], [5]).
- Healthcare: The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) necessitates safeguards like data encryption, role-based access, and audit trails to protect patient information in electronic health records (EHRs). Cloud service providers (CSPs) often offer specialized compliance tools to help organizations meet these requirements ([4]).
- Finance: Systems such as AI-driven fraud detection monitor financial transactions in real-time, identifying patterns indicative of fraud, money laundering, or other financial crimes ([8]).
C. Global Business Operations
Cross-border data flows require compliance with varying regulatory standards and secure data access across geographies ([3], [5]).
- Data Localization Solutions: For compliance with regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), CSPs enable region-specific data storage and processing, ensuring data sovereignty ([3]).
- Collaboration and Secure Access: Secure collaboration tools provided by cloud platforms, such as Microsoft Azure and Google Workspace, allow global teams to work on sensitive data without compromising security ([7]).
D. Dynamic Workloads and Disaster Recovery
Cloud platforms support dynamic workloads and disaster recovery scenarios, ensuring data availability even during disruptions ([7]).
- Elastic Workloads: Cloud services scale resources up or down based on workload demands while maintaining secure configurations. For example, during high-demand periods, organizations can deploy additional virtual servers with predefined security settings ([10]).
- Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS): Cloud-based disaster recovery solutions replicate critical data and applications across multiple locations, enabling rapid restoration in the event of failure ([7]).
E. Critical Infrastructure Protection
Organizations managing critical infrastructure, such as energy grids or transportation systems, require advanced protection against cyber threats ([1], [8]).
- Integration with OT Security: Cloud platforms can integrate with operational technology (OT) systems to monitor and protect critical infrastructure from cyber-attacks, using AI-driven analytics to detect threats in real-time ([8]).
By aligning these scenarios with tailored cloud security measures, organizations can maximize the effectiveness of their data protection strategies, reducing risks and enhancing overall resilience ([1], [2]). Following bar chart illustrating the effectiveness of various cloud data protection strategies for high-volume data operations.
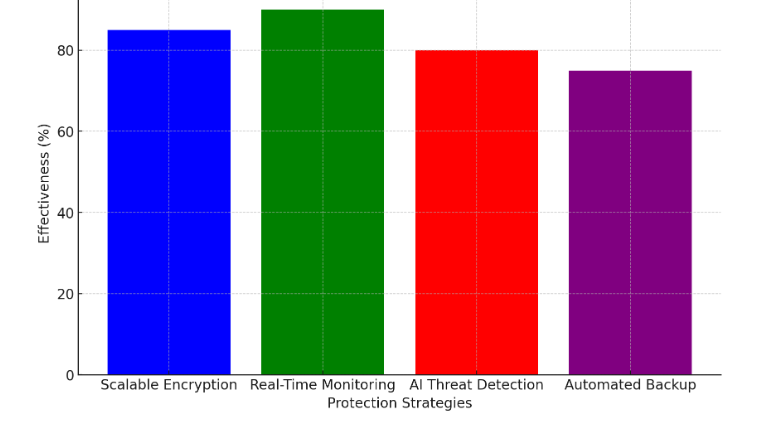
Figure 4: Effectiveness of Cloud Data Protection Strategies for High-Volume Data Operations
IV. COMMON PITFALLS AND STRATEGIES FOR CLOUD DATA PROTECTION
While cloud platforms offer robust security features, certain pitfalls can undermine data protection if not adequately addressed. These challenges include misconfigurations, over-reliance on cloud providers, and inadequate incident response planning ([7], [10]).
A. Misconfigurations and Human Errors
- Risk: Misconfigured storage buckets or improper access settings are a leading cause of data breaches ([7]).
- Strategy: Employ automated configuration checks and best practices, such as the AWS Well-Architected Framework, to minimize risks ([7]).
B. Over-Reliance on Cloud Providers
- Risk: Assuming that CSPs handle all security aspects can lead to gaps in application-level or user-specific protections ([10]).
- Strategy: Adopt the shared responsibility model, ensuring that your organization manages application security, user access, and sensitive data within the cloud ([7]).
C. Insufficient Incident Response
- Risk: Without a clear plan, organizations may struggle to respond effectively to breaches or disruptions ([8]).
- Strategy: Establish incident response playbooks and leverage CSP-provided tools like AWS GuardDuty or Google Chronicle to streamline detection and response ([7]).
By proactively addressing these pitfalls, organizations can create a secure and compliant cloud environment, enabling them to harness the full potential of cloud computing while minimizing risks ([1], [7]).
Conclusion
The migration of organizational data to the cloud marks a pivotal transformation in how businesses operate, offering unparalleled scalability, cost-efficiency, and innovation ([10]). However, these advantages are accompanied by significant security and compliance challenges that demand proactive and robust approaches ([7]). To safeguard data in cloud environments, organizations must implement comprehensive security measures that address confidentiality, integrity, and availability. These measures include advanced encryption techniques ([6]), continuous monitoring ([8]), and stringent access controls tailored to their specific requirements ([7]). Moreover, aligning data protection strategies with industry regulations such as GDPR ([3]), HIPAA ([4]), and CCPA ([5]) ensures compliance while building trust among stakeholders. Success in cloud data protection hinges on addressing challenges such as misconfigurations ([7]), over-reliance on cloud service providers ([10]), and rapidly evolving cyber threats ([8]). By leveraging cutting-edge technologies like AI-driven anomaly detection ([8]), multi-factor authentication ([7]), and real-time response mechanisms ([7]), organizations can mitigate risks and ensure robust data protection. Looking forward, innovations in areas like homomorphic encryption, zero-trust architecture, and adaptive machine learning models hold promise for enhancing cloud data security ([6], [8]). As organizations embrace these advancements, fostering collaboration among governments, technology providers, and industry leaders becomes imperative ([1], [2]). Together, they can establish a secure, compliant, and resilient digital ecosystem that supports the growth and sustainability of modern enterprises.
References
[1] National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), Framework for Improving Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity, Version 1.1, Apr. 2018. [Online]. Available: https://www.nist.gov/cyberframework [2] International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), ISO/IEC 27017:2015 – Code of Practice for Information Security Controls for Cloud Services, 2015. [3] European Union, General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Regulation (EU) 2016/679, Apr. 2016. [Online]. Available: https://gdpr-info.eu [4] Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA), Standards for Privacy of Individually Identifiable Health Information, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 2003. [Online]. Available: https://www.hhs.gov/hipaa [5] California Legislature, California Consumer Privacy Act of 2018 (CCPA), Cal. Civ. Code § 1798.100 et seq., 2018. [Online]. Available: https://oag.ca.gov/privacy/ccpa [6] M. Qiu, K. Gai, and B. Thuraisingham, \"Privacy-preserving data encryption strategy for big data in mobile cloud computing,\" IEEE Transactions on Big Data, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 226–235, Dec. 2016. [7] Amazon Web Services (AWS), AWS Security Best Practices, Nov. 2022. [Online]. Available: https://aws.amazon.com [8] G. Zhao, X. Li, J. Wang, and Y. Liu, \"Trust-aware and privacy-preserving protection of user data in cloud computing,\" IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 380–394, 2020. [9] S. Zawoad, A. K. Dutta, and R. Hasan, \"SecLaaS: Secure logging-as-a-service for cloud forensics,\" in 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Security and Privacy in Emerging Areas of Communication Networks, pp. 73–82, 2013. [10] P. Mell and T. Grance, The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing, Special Publication 800-145, NIST, Sep. 2011. [Online]. Available: https://www.nist.gov
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Narasimha Rao Alugoju. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET66087
Publish Date : 2024-12-24
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

