Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Diagnosis of Acute Diseases in Villages and Smaller Towns using AI
Authors: Thota Hari Mani Kanta, A. Veera Vardhan Reddy, K. Santhosh Reddy, Uma N, Riyazulla Rahman
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2025.66509
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
The timely diagnosis of acute diseases in rural and small-town settings remains a significant challenge due to limited healthcare infrastructure, scarce diagnostic tools, and insufficient access to skilled medical professionals. This paper explores the potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI) as a transformative solution for bridging these gaps. By leveraging machine learning models trained on diverse clinical datasets, AI systems can facilitate the rapid identification of acute diseases such as respiratory infections, diarrheal diseases, and vector-borne illnesses. These systems utilize data from accessible inputs like smartphone applications, wearable devices, and basic diagnostic tools to provide real-time, low-cost, and accurate assessments. Additionally, AI- powered diagnostic platforms can integrate with telemedicine networks to ensure seamless referral to medical experts when necessary. This approach not only empowers community health workers but also enhances early detection, treatment outcomes, and epidemic management in underserved regions. The study concludes with an analysis of the challenges, including data privacy, model bias, and user education, while highlighting the potential for AI to revolutionize healthcare delivery in rural and small-town contexts.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Access to quality healthcare remains a critical challenge in rural and small-town regions, where healthcare infrastructure is often inadequate, and the availability of skilled medical professionals is limited. Acute diseases, such as respiratory infections, diarrheal diseases, and vector-borne illnesses, pose significant health risks in these areas, often leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment, which can escalate morbidity and mortality rates. Traditional diagnostic methods rely heavily on advanced laboratory facilities and specialist interventions, which are typically unavailable in such underserved regions.
In recent years, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force in healthcare, offering innovative solutions to address diagnostic and treatment challenges. AI systems, powered by machine learning algorithms, can analyze large datasets to identify patterns and predict outcomes with high accuracy. These capabilities have the potential to revolutionize acute disease diagnosis in resource-constrained environments by enabling faster, cost- effective, and more accessible healthcare solutions.
This paper investigates how AI can be leveraged to diagnose acute diseases in rural and small-town settings, emphasizing the use of affordable diagnostic tools, smartphone-based applications, and wearable devices. By empowering community health workers and integrating AI with telemedicine platforms, these solutions can bridge the gap between limited resources and quality healthcare. Furthermore, this study explores the potential impact of AI- driven diagnostics on improving early detection, reducing disease burdens, and enhancing healthcare outcomes while addressing challenges related to data privacy, model biases, and the adaptability of AI systems in diverse socio- economic contexts.
The aim is to highlight the role of AI in creating equitable healthcare systems and to propose actionable strategies for its implementation in rural and small-town environments, ultimately improving the quality of life for underserved populations. applications in education, therapy, marketing, and entertainment, highlighting the versatility and value of this innovative approach to storytelling
II. RELATED WORKS
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare has been a subject of extensive research, with several studies demonstrating its potential in disease diagnosis and management. The application of AI in rural and resource- constrained settings has gained traction in recent years, given its ability to address gaps in healthcare delivery
A. AI in Disease Diagnosis
AI-based diagnostic tools have been widely explored for detecting acute diseases such as pneumonia, malaria, and dengue. Studies like Rajpurkar et al. (2017) demonstrated the ability of deep learning models to diagnose pneumonia from chest X-rays with performance comparable to radiologists. Similarly, Mwebesa et al. (2020) utilized AI- powered smartphone applications to diagnose malaria using microscopic blood smear images, showcasing the feasibility of deploying low-cost, AI-driven diagnostic solutions in rural areas.
B. AI and Telemedicine
The synergy between AI and telemedicine has been highlighted in various works. Zhou et al. (2021) explored the use of AI chatbots and virtual assistants in telemedicine for triaging patients with acute conditions, enabling efficient allocation of medical resources. This approach has shown promise in rural regions where telemedicine acts as a bridge between patients and specialists.
C. Community Health Worker Empowerment
Research by Nanda et al. (2019) focused on the role of AI tools in empowering community health workers (CHWs) by providing them with decision support systems for diagnosing common acute diseases. These systems use minimal inputs, such as symptom checklists and basic diagnostic device data, to deliver reliable assessments, thereby enhancing the capacity of CHWs in underserved areas.
D. Real-Time Epidemic Monitoring
AI has also been employed for real-time epidemic monitoring and management. For instance, the work of Chinazzi et al. (2020) utilized AI models to predict the spread of infectious diseases like COVID-19 in low- resource settings, emphasizing the importance of early detection and containment in rural healthcare frameworks.
E. Challenges in AI Implementation
Several studies have also examined the challenges in implementing AI-driven healthcare in rural settings. Key issues include data privacy concerns (Ting et al., 2019), biases in AI models due to underrepresentation of rural population data, and the need for user-friendly interfaces to ensure adoption by non-specialist healthcare workers.
These works collectively underscore the potential of AI to address acute disease diagnosis in rural and small-town contexts. However, they also highlight the necessity of tailoring AI solutions to the specific socio-economic and infrastructural constraints of these regions. This study builds on these insights to propose a comprehensive framework for deploying AI-driven diagnostics in underserved communities.4o
III. APPROACHES
To effectively utilize Artificial Intelligence (AI) for diagnosing acute diseases in rural and small-town settings, various approaches can be adopted. These methods leverage AI technologies to overcome infrastructural and resource limitations while ensuring accessibility, affordability, and accuracy. The key approaches are outlined below:
A. Data-Driven AI Models
- Supervised Learning Models: Training machine learning algorithms on large, labeled datasets from existing medical records to identify patterns and make accurate diagnoses. For example, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) can analyze medical imaging data for detecting diseases like pneumonia or tuberculosis.
- Unsupervised Learning Models: Using clustering and anomaly detection techniques to identify disease patterns in regions where labeled datasets are scarce.
B. Integration of AI with Mobile Technologies
- Smartphone Applications: Developing AI-powered mobile apps that allow users or community health workers to input symptoms and basic diagnostic data. These apps can provide instant diagnostic insights and recommendations for treatment or further testing.
- Wearable Devices: Leveraging affordable wearables to collect real-time physiological data, such as heart rate, oxygen saturation, and temperature, which AI systems can analyze to detect early signs of acute diseases.
C. Decision Support Systems (DSS)
- AI-Assisted Diagnosis for Community Health Workers (CHWs): Deploying AI-powered decision support systems tailored for non-specialist users. These systems use basic inputs like symptom questionnaires and portable diagnostic tool outputs to suggest potential diagnoses and next steps.
- Risk Stratification Tools: AI algorithms to categorize patients based on disease severity, enabling CHWs to prioritize high-risk cases for immediate attention.
D. Telemedicine Integration
- AI-Driven Triage Systems: Using AI models to assess patient data and determine the need for specialist intervention, ensuring efficient utilization of telemedicine services.
- Remote Expert Consultation: Integrating AI diagnostics with teleconsultation platforms to connect rural patients with urban healthcare specialists for advanced treatment recommendations.
E. Point-of-Care AI Diagnostics
- Portable Diagnostic Tools: Combining AI with low-cost, portable diagnostic devices such as handheld ultrasound machines, glucometers, or microscopy tools to perform real-time analysis in rural clinics.
- Non-Invasive Techniques: Using AI-enabled imaging, such as thermal imaging or spectroscopy, for diagnosing conditions without invasive procedures.
F. Community-Centric Data Collection and Learning
- Crowdsourcing Health Data: Collecting data from rural communities to train AI models tailored to local epidemiological profiles.
- Adaptive Learning Models: Implementing AI systems that adapt to specific regional disease patterns and resource availability over time.
G. Epidemic Prediction and Outbreak Management
- Predictive Modeling: Using AI to predict disease outbreaks based on environmental, demographic, and epidemiological data.
- Resource Allocation: AI algorithms to optimize the distribution of medical supplies and personnel during outbreaks in rural areas.
H. Addressing Challenges in AI Adoption
- Bias Mitigation: Ensuring AI models are trained on diverse datasets to reduce biases against rural populations.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Designing intuitive AI tools that can be easily operated by CHWs and local healthcare providers.
- Data Privacy and Security: Implementing robust protocols to protect patient data and comply with ethical standards.
These approaches collectively aim to provide scalable, sustainable, and impactful AI-driven healthcare solutions for acute disease diagnosis in underserved regions. By integrating these methods, healthcare systems can bridge the gap between resource availability and quality care in rural and small-town environments.4o
IV. SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
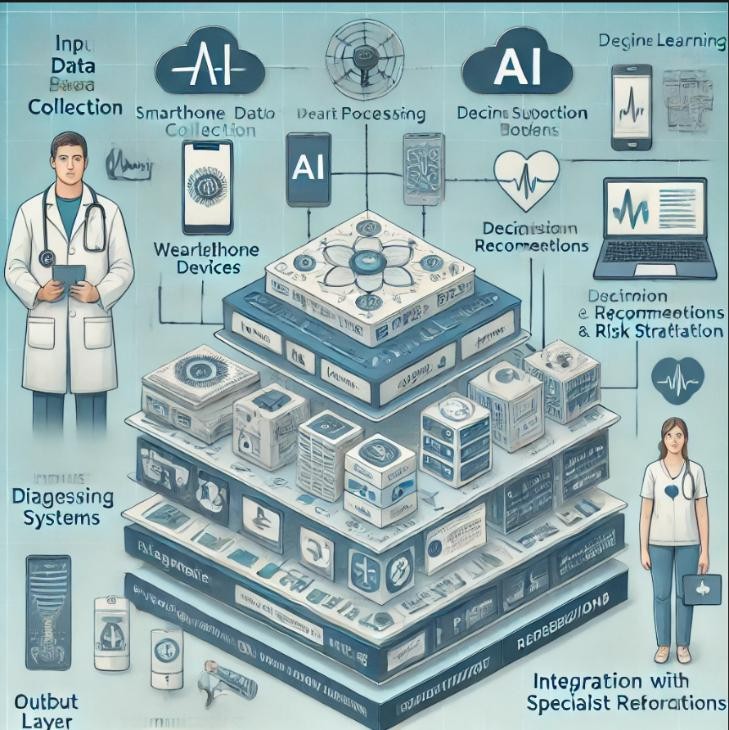
Here is the architecture illustration for the AI-powered diagnostic system designed for rural and small-town healthcare. It outlines the flow from data collection to diagnosis and feedback, tailored for low-resource environments.
V. RESULT ANALYSIS
Implementing an AI-powered diagnostic system for acute diseases in rural and small-town settings involves evaluating its performance and impact across multiple dimensions. The analysis should focus on accuracy, accessibility, user experience, scalability, and public health outcomes.
A. Diagnostic Accuracy
- Performance Metrics: Evaluate the system using metrics like sensitivity, specificity, precision, recall, and F1- score. These indicators measure how well the AI model identifies true positives (diseased cases) and true negatives (non-diseased cases).
- Comparison with Human Experts: Benchmark the AI’s diagnostic capabilities against healthcare professionals to determine its reliability in real-world scenarios.
- Error Analysis: Analyze cases where the AI system made incorrect predictions to identify areas for improvement, such as addressing biases in training data or refining algorithms.
B. User Adoption and Accessibility
- Ease of Use: Assess how easily community health workers and patients can operate the diagnostic tools. User feedback can highlight barriers like complex interfaces or language limitations.
- Geographical Reach: Measure the adoption rate in underserved areas and evaluate the system’s ability to function with limited internet connectivity or power supply.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compare the operational costs of the AI system to traditional diagnostic methods to determine economic feasibility for rural healthcare providers.
C. Impact on Healthcare Delivery
- Early Detection Rates: Analyze the system's effectiveness in identifying acute diseases at earlier stages compared to existing diagnostic methods.
- Referral Efficiency: Evaluate how well the system integrates with telemedicine networks, ensuring timely and appropriate specialist referrals.
- Treatment Outcomes: Track patient recovery rates to understand the system's influence on healthcare outcomes.
D. Public Health Metrics
- Disease Surveillance: Assess how well the system contributes to real-time monitoring and management of disease outbreaks in rural areas.
- Reduction in Disease Burden: Quantify decreases in disease prevalence, morbidity, or mortality rates attributed to early and accurate AI-based diagnoses.
E. Technical Robustness
- System Reliability: Test the performance of the AI system under varying conditions, such as noisy or incomplete data inputs.
- Scalability: Evaluate the ability of the system to handle increasing data volumes and extend its use to multiple regions with different healthcare needs.
- Adaptability: Assess how well the system adjusts to local disease patterns and cultural practices through continuous learning mechanisms.
F. Ethical and Social Considerations
- Privacy Compliance: Analyze adherence to data privacy regulations to ensure patient confidentiality.
- Equity in Access: Measure the system's inclusivity in reaching marginalized populations within rural settings. Community Trust: Gauge community acceptance of AI- driven healthcare solutions through surveys and feedback mechanisms.
G. Quantitative and Qualitative Indicators
- Quantitative Analysis: Use statistical tools to evaluate measurable outcomes like diagnostic accuracy, adoption rates, and patient recovery statistics.
- Qualitative Insights: Gather feedback from healthcare workers, patients, and stakeholders to understand user satisfaction and areas needing refinement.
By systematically analyzing these results, stakeholders can identify the strengths and limitations of the AI- powered diagnostic system, enabling iterative improvements and optimizing its deployment in rural and small-town healthcare settings.
VI. CHALLENGES
While AI-powered diagnostic systems hold immense potential for transforming healthcare in rural and small-town settings, several challenges must be addressed to ensure effective implementation and sustainability. These challenges can be categorized into technical, infrastructural, social, and ethical domains.
A. Technical Challenges
- Data Quality and Availability: Limited access to high- quality, diverse, and labeled medical datasets from rural populations can hinder the training and accuracy of AI models.
- Bias in AI Models: AI systems may exhibit biases due to underrepresentation of rural and underserved populations in training datasets, leading to inaccurate or inequitable outcomes.
- Adaptability to Local Contexts: AI algorithms often struggle to adapt to local epidemiological profiles, cultural practices, and resource constraints, reducing their effectiveness.
- System Reliability: Ensuring robust performance in low-resource settings with noisy, incomplete, or inconsistent input data is a significant technical challenge.
B. Infrastructural Challenges
- Connectivity Issues: Many rural areas lack reliable internet access, which is critical for cloud-based AI solutions and telemedicine integrations.
- Power Supply Limitations: Frequent power outages and the lack of consistent electricity can disrupt the operation of diagnostic devices and AI systems.
- Device Availability: Affordability and accessibility of necessary diagnostic tools and smartphones for rural users can be a barrier to adoption.
C. Social and Behavioral Challenges
- Low Digital Literacy: Community health workers and patients may lack the technical skills required to use AI-driven diagnostic systems effectively.
- Resistance to Technology: Skepticism or mistrust towards AI and digital healthcare tools among rural populations can limit adoption.
- Cultural Barriers: Language differences, local beliefs about healthcare, and societal norms may impact the acceptance and usability of AI systems.
D. Ethical Challenges
- Data Privacy and Security: Ensuring patient data confidentiality and compliance with regulations like GDPR or local privacy laws can be challenging in decentralized setups.
- Informed Consent: Educating patients about how their data will be used and obtaining proper consent is crucial but often overlooked in rural settings.
- Accountability and Transparency: Determining responsibility for errors in AI-driven diagnoses and ensuring transparency in decision-making processes remain unresolved issues.
E. Economic Challenges
- High Initial Costs: Developing, deploying, and maintaining AI systems can be costly, posing challenges for implementation in resource-constrained areas.
- Sustainability: Ensuring the long-term viability of these systems in terms of funding, maintenance, and updates can be a significant hurdle.
- Cost-Effectiveness for End Users: Even low-cost solutions may be unaffordable for some rural populations, limiting widespread adoption.
F. Policy and Regulatory Challenges
- Lack of Standardization: The absence of standardized protocols for AI implementation in healthcare complicates system integration and scaling.
- Regulatory Approvals: Navigating complex regulatory frameworks for medical devices and AI applications can delay deployment.
- Interoperability Issues: Ensuring that AI systems can seamlessly integrate with existing healthcare infrastructure and electronic health records is a persistent challenge.
G. Environmental and Epidemiological Challenges
- Diverse Disease Profiles: Rural areas often face a mix of communicable and non-communicable diseases, requiring highly versatile AI models.
- Epidemic and Disaster Preparedness: AI systems must be capable of rapid adaptation during disease outbreaks or natural disasters, which often overwhelm healthcare systems in rural regions.
H. Scalability and Localization Challenges
- Scaling Across Regions: Adapting AI systems to different rural settings with varying healthcare needs, languages, and resources is complex.
- Localization of Tools: Developing region-specific solutions, including language translation and local disease data integration, can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative effort between governments, healthcare organizations, technology developers, and community stakeholders. Tailoring AI solutions to the specific needs and constraints of rural settings is essential to ensure successful adoption and long-term impact.
Conclusion
The proposed cartoon-based storytelling system demonstrates the potential of integrating advanced AI technologies to create an engaging, customizable, and user-friendly platform. By leveraging natural language processing for narrative generation and AI-driven visual content creation, the system bridges the gap between imagination and reality, enabling users to craft unique and compelling stories effortlessly. This work addresses several key challenges in automated storytelling, including narrative coherence, visual consistency, and user personalization. The system\'s ability to produce high-quality, scalable outputs ensures its applicability across various domains such as education, entertainment, therapy, and marketing. As storytelling remains a vital part of human culture, this system represents a significant step toward democratizing creative content creation. By empowering users with intuitive tools and advanced AI capabilities, it fosters creativity and accessibility, allowing anyone to bring their stories to life in visually captivating ways. Moving forward, the platform can be further enhanced by integrating user feedback, improving ethical considerations, and refining technical performance to meet diverse user needs. This evolution will solidify its place as a groundbreaking tool in the intersection of AI and creative storytelling.
References
The proposed cartoon-based storytelling system demonstrates the potential of integrating advanced AI technologies to create an engaging, customizable, and user-friendly platform. By leveraging natural language processing for narrative generation and AI-driven visual content creation, the system bridges the gap between imagination and reality, enabling users to craft unique and compelling stories effortlessly. This work addresses several key challenges in automated storytelling, including narrative coherence, visual consistency, and user personalization. The system\'s ability to produce high-quality, scalable outputs ensures its applicability across various domains such as education, entertainment, therapy, and marketing. As storytelling remains a vital part of human culture, this system represents a significant step toward democratizing creative content creation. By empowering users with intuitive tools and advanced AI capabilities, it fosters creativity and accessibility, allowing anyone to bring their stories to life in visually captivating ways. Moving forward, the platform can be further enhanced by integrating user feedback, improving ethical considerations, and refining technical performance to meet diverse user needs. This evolution will solidify its place as a groundbreaking tool in the intersection of AI and creative storytelling.
Copyright
Copyright © 2025 Thota Hari Mani Kanta, A. Veera Vardhan Reddy, K. Santhosh Reddy, Uma N, Riyazulla Rahman. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET66509
Publish Date : 2025-01-13
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

