Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Evaluating Financial Inclusion through PMJDY: A Case Study of Barachh Village
Authors: Saurabh Garg
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.65390
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
One of the innovative steps taken to shove financial incorporation within India is an enterprise called Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY ) which was started in the year 2014. The main aim is to make sure that common reach to bank services with at least one primary bank account per household. With the offering of zero-balance accounts, PMJDY made banking reach even the most backward sections of society: people living in village areas and having low incomes. The scheme is significant in terms of bringing millions into the formal banking system, who were earlier financially excluded. Moreover, the PMJDY has facilitated the use of government subsidies and benefits that can be deposited directly into the accounts of intended beneficiaries, thus reducing leakages and ensuring that the intended recipients have availed the support entitled to them. The scheme also propagates a move toward digital payments with the end goal of making people financially literate enough to become more inclusive toward participating in the economy. The research has been conducted and tries to discover the success rate and awareness level of the inclusion process in Barachh Village, situated in the Shahdol district. The study has collected both primary and secondary data concerning the bank accounts opened under the scheme. The financial inclusion process of PMJDY and its socio-economic backgrounds are linked through the use of percentage and graphical methods.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
In the year 2014 government of India set up Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana as a financial incorporation scheme. This scheme's goal is to provide common reach to bank services in India to every household in India, with a focus on the unbanked and underbanked population.
This scheme provides a multiple of financial services such as basic bank services, insurance, and pension products. PMJDY has been successful in increasing financial incorporation in India, with cores of people opening bank accounts for the first time. This scheme has also promoted digital payments and financial education
II. OBJECTIVES OF PMJDY SCHEMES
- Universal Banking: Universal access to banking is the heart of this scheme, aimed at providing a basic savings bank account for everyone.
- Financial Inclusion: The process of bringing the unbanked population into formal banking.
- Credit Access: Offering credit to common people with PMJDY, particularly in backward societies.
- Insurance and Pension – Under this scheme, basic insurance products as well as a pension have been provided to the account holders.
- Remittances Facility The facility provided to the customer for remitting money to beneficiary for purpose of family maintenance, credit etc.
- Financial Education —This scheme aims to raise the financial literacy of beneficiaries.
III. SIGNIFICANCE
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMDJY) has helped in the development of rural areas by extending banking services to the hitherto unbanked populace. Here, it has strengthened millions of rural homes from the yoke of financial deprivation by providing them access to primary banking services such as a savings account-passbook, ATM card-debit, and/or credit with Rs. 5 lakhs overdraft facility under no condition or security cover (no collateral) besides different insurance schemes. Therefore, they have been able to better participate in the formal economy and increase their financial literacy, supposedly making them more efficient in claiming government subsidies.
PMJDY has had the added advantage of transferring government subsidies directly into the bank accounts of beneficiaries, thereby curtailing leakages to a great extent and ensuring benefits flow through to intended recipients. This has had the effect of creating widespread poverty and decreasing rural area inequality.
Barachh is a village in the east-central part of Madhya Pradesh situated within Shahdol district. Barachh is located 90 km away from its district headquarter. The total population of Barachh is 4552, out of which 2339.272 are female (51.4%) and 2212.272 are male (48.6%).
The rationale was to go deep and understand the impacts brought by the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana scheme in the case of village Barachh, benefits/outcomes as well challenges associated with PMJDYS for this selected village.
IV. RESEARCH OBJECTIVES
- To estimate the awareness of PMJDY in the study area Barachh ·
- To study the present situation of PMJDY in Barachh Village.
- To identify the channels from where people come to know about PMJDY in Barachh village
- To analyze the challenges faced by the people of Barachh in availing PMJDY.
- Recommendations for improving the scheme implementation to ensure a smoother process.
V. METHODOLOGY
The study aims to analyze the financial inclusion journey in the village of Barachh. The primary research will be conducted with the Gram Panchayat of Barachh, a village in Shahdol. The survey will involve direct interaction with the people of the village to gain insight into the ground reality of the financial inclusion plan in Barachh, with a sample size of 200 people in the village Barachh. Secondary resources used, will include financial inclusion reports published by the RBI and the government of India, as well as newspaper articles, scholarly research books, journals, and articles.
VI. REVIEW OF LITERATURE
Numerous research papers have been published on financial inclusion. These included both state and national studies.
Pradhan Mantri Jan-Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) has brought the nation into financial inclusion. A succinct summary of the various research projects that are currently available below.
Thomas Shijimole ,(2024) The study concludes that PMJDY is a successful financial inclusion initiative, but there is room for improvement. PMJDY may not be fully understood by certain segments of society due to illiteracy or inconvenience. Customer satisfaction is crucial, and people are less satisfied with bank staff behavior To secure a high level of customer satisfaction for PMJDY account holders, the government and banking officials should take steps to make better staff service and conduct
Gupta Kamini, (2023), Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) One of the vital instruments for driving financial inclusion in India has been Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY). This is how millions of people, unbanked and underprivileged started getting linked with a formal financial system as well. The massive number of accounts opened under PMJDY indicates its success. The government's attempts to roll out Rupay cards and publicize the scheme have also aided in its success. PMJDY has assisted in lowering alteration and drainage of social welfare schemes through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT), PMJDY has all in itself to really main initiative for removing poverty in India and encouraging financial
Shah, N. (2023 ) , The PMJDY Program is a wonderful example of Financial Inclusion and upliftment for the people Below the Poverty Line (BPL) in India. Delivery of formal banking services and credit to the excluded communities has also improved. More research is required to grasp the nature of credit expansion via PMJDY accounts (if any) and process macroeconomic changes & regional variations for tailoring it accordingly. Thus the PMJDY program has had a beneficial effect on socio socio-economic condition of marginalized communities in India.
Modi & Baral (2021) have analyzed the data of PMJDY. This report aims to provide a summary and analysis of the PMJDY data. The Government of India is Scattering Since the primary intention of this study was to decide what ′Financial inclusion in India has been advanced by PMJDY′. Through this program, millions of people have been able to get access to banking and financial servers by providing bank accounts, especially for poor or underprivileged sections. This has enabled beneficiaries to directly receive benefits from the government into their accounts, thereby minimizing leakages of a welfare delivery system that until then often saw only half or even less reaching intended recipients. PMJDY has also enabled people to save themselves from the clutches of usurious money lenders.
Singh & Kumar(2020) The paper studies a Financial Inclusion Index(IIF) to quantify the level of financial inclusion across Indian districts. The FII includes three new dimensions: commercial bank branches, agricultural credit accounts, and non-agricultural credit accounts. The study found that financial inclusion has increased slightly from 2011 to 2018, but many districts remain under-included. The PMJDY framework has shown limited success in improving financial inclusion. The study recommends a coherent strategy with systemic changes in the financial system, strengthening financial institutions, and addressing digital literacy. Data availability is a limitation and future studies should evaluate the impact of financial inclusion on poverty reduction and economic growth. In all, the plan has been one of the biggest financial liberation moves and served for economic empowerment in India.
Shukla Nikita, (2019), has analyzed that Villages like Rajghat and Manjhgawa have seen an increase in financial inclusion thanks to the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY). While men are more aware due to higher account ownership, the scheme attracts customers across demographics. To build on this, the govt can improve infrastructure, create awareness of digital payments (with ABC programs), simplify and reduce paperwork for people to adopt banking in their lives; offer micro-leveraging financial products.
VII. The SCHEME UNDER OPERATION BEFORE LAUNCHING PMJDY
Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT): The DBT scheme was introduced in January 2013 to transfer subsidies and benefits directly into the bank accounts of beneficiaries eliminating leakages by the Government, This further pushes the concept of financial inclusion.
National Financial Inclusion Mission (NFIM): Launched in 2011, NFIM focuses on financial literacy training for all residents of the country. Improving access to a vast range of basic services such as savings account consumer credit insurance and pensions; making transactions affordable accessible and safe- digital payments domestic remittances etc.
Financial Inclusion Fund (FIF): The FIF was created in 2012 to support financial institutions and banks to expand the umbrella of ultimate rural financial inclusion.
Requirement of PMJDY scheme
Is an inspiring financial incorporation scheme that was incorporated in India on August 28, 2014 with the main aim of promoting financial incorporation to all households across the country, especially among backward sections
Formal Financial Services: A substantial number of people, particularly in rural India did not have access to any formal financial services; This disenfranchisement prevented them from full participation in the formal economy, and hence economic development.
- Excessive rates: High interest rate fueled informal sector borrowing and were believed to have made people lifelong victims of debt through what was later termed as predatory lending.
- Government Subsidies & Freebies: Had the conventional delivery channels been inefficient, it must have grounded governments in addressing subsidies and free natural resources to beneficiaries. Economic Empowerment : Recognize the role of Financial Inclusion as a tool for Economic empowerment -- particularly women and marginalized groups
- Economic Empowerment: The role of Financial Inclusion also recognized as a vehicle for economic empowerment, especially women and marginalized groups.
- Digital India: The Digital India campaign was launched by the government to work on digital literacy and transactions, for which PMJDY holds a significant place With the ideal to solve these problems and reinforce fiscal integration leaded several outcomes economically for millions of Indians, PMJDY was a step towards granting bank accounts and access to financial services.
VIII. DATA ANALYSIS
The study was conducted in the village Barachh a small village in the district of Shahdol in Madhya Pradesh, the sample size of this research paper was 200 people in the village.
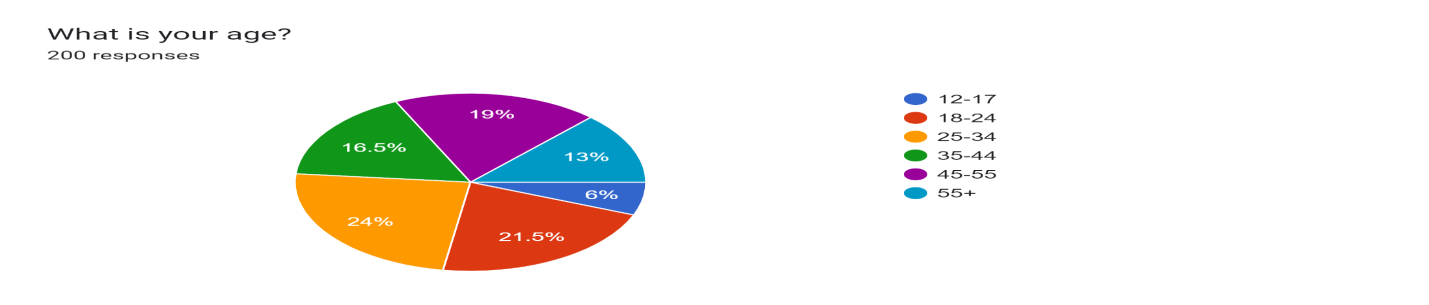
Figure 1
Figure 1 shows that there are 6% of respondents fall in the category of 12-17 years, 21.5% people fall in the category of 18-24 years, 24% people fall in the category of 25-34,16.5% people fall in the category of 35-45, 19% people fall in the category of 45-55 and 13% people fall in the category of 55+ are the age group is PMJDY account in the village barachh.
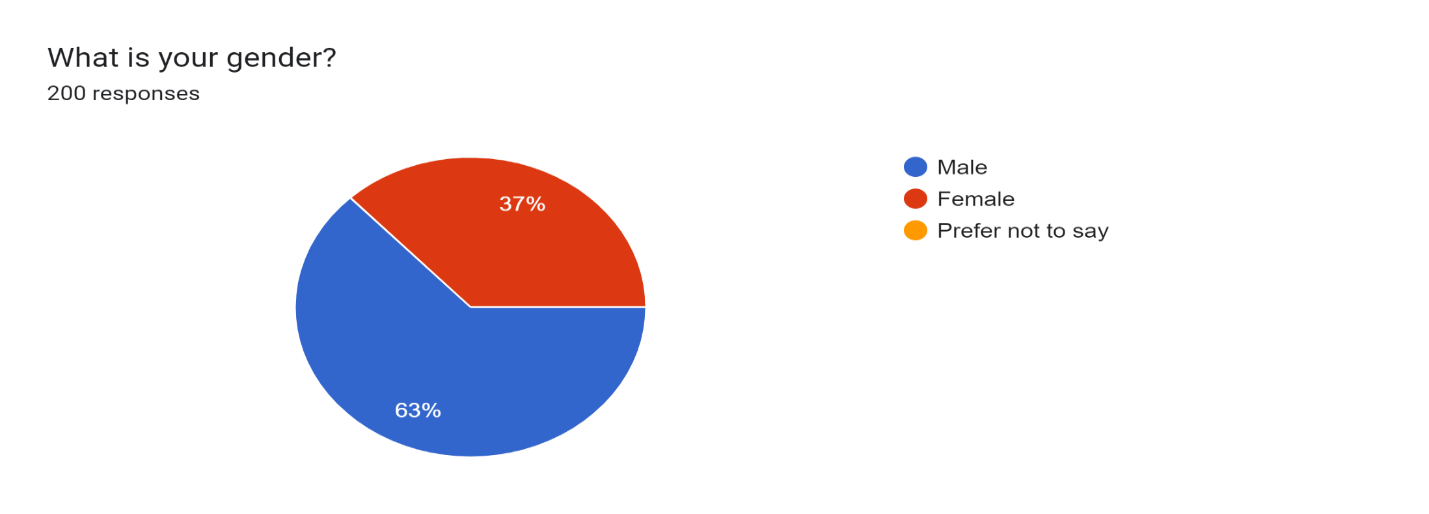
Figure 2
Figure 2 shows that 63% of respondents are male and 37% are female which manifests that there are more numbers of males than females having PMJDY bank accounts in the village of Barachh.
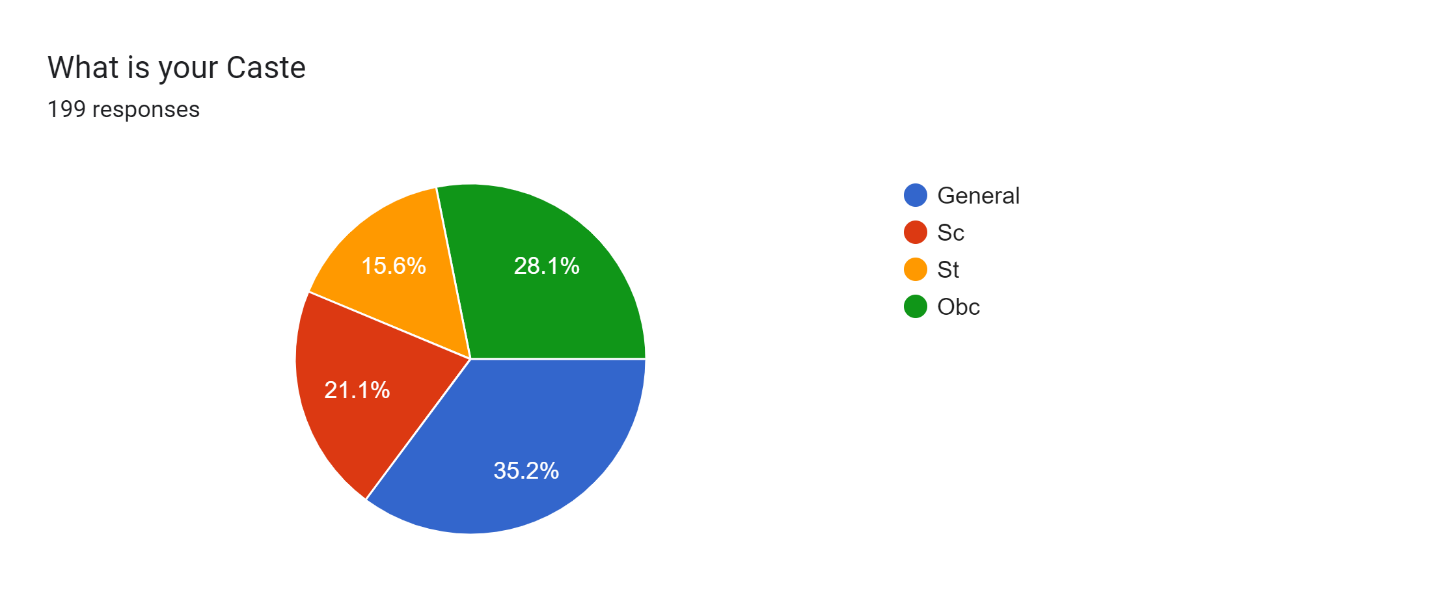
Figure 3
Figure 3 shows that there are 35.2% of respondents fall in the category of general, 21.1% people fall in the category of SC, 15.6% people fall in the category of ST,28.1% people fall in the category of OBC are the caste division in the village having PMJDY account in the village barachh.
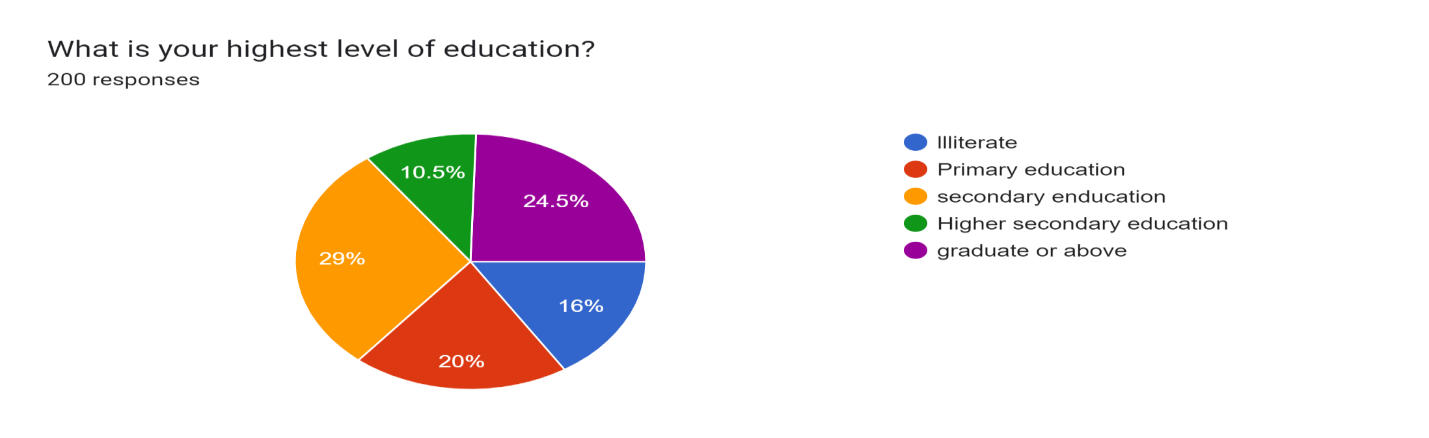
Figure 4
Figure 4 shows that there are 24.5% of respondents are graduated, 20% have only primary education, 16% people are illiterate,29% of people have secondary education, and 10.5 % of people have higher secondary education in Barachh village.
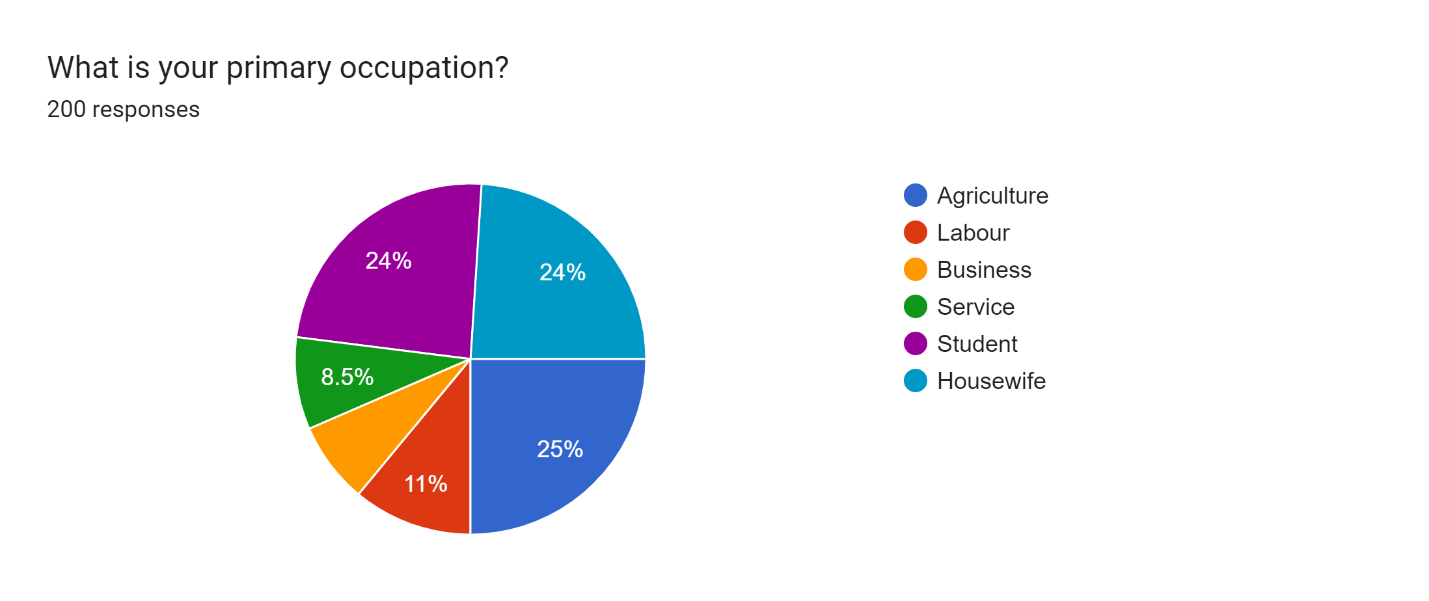
Figure 5
Figure 5 shows the major professions of 200 participants:- This chart is split into 6 regions, all of them representing different jobs. Breakdown of the percentages for each occupation:
- Agriculture: 25%
- Labour: 11%
- Business: 8.5%
- Service: 8.5%
- Student: 24%
- Housewife: 24%
The most of respondents are farmers, combining 25% of the responses. Not far behind is the Housewife category at 24% and students both at 24% and 8.5% defined themselves as businesspersons or Service, making these the smallest categories (eight and a half percent each), are occupational groups in the village having PMJDY accounts.
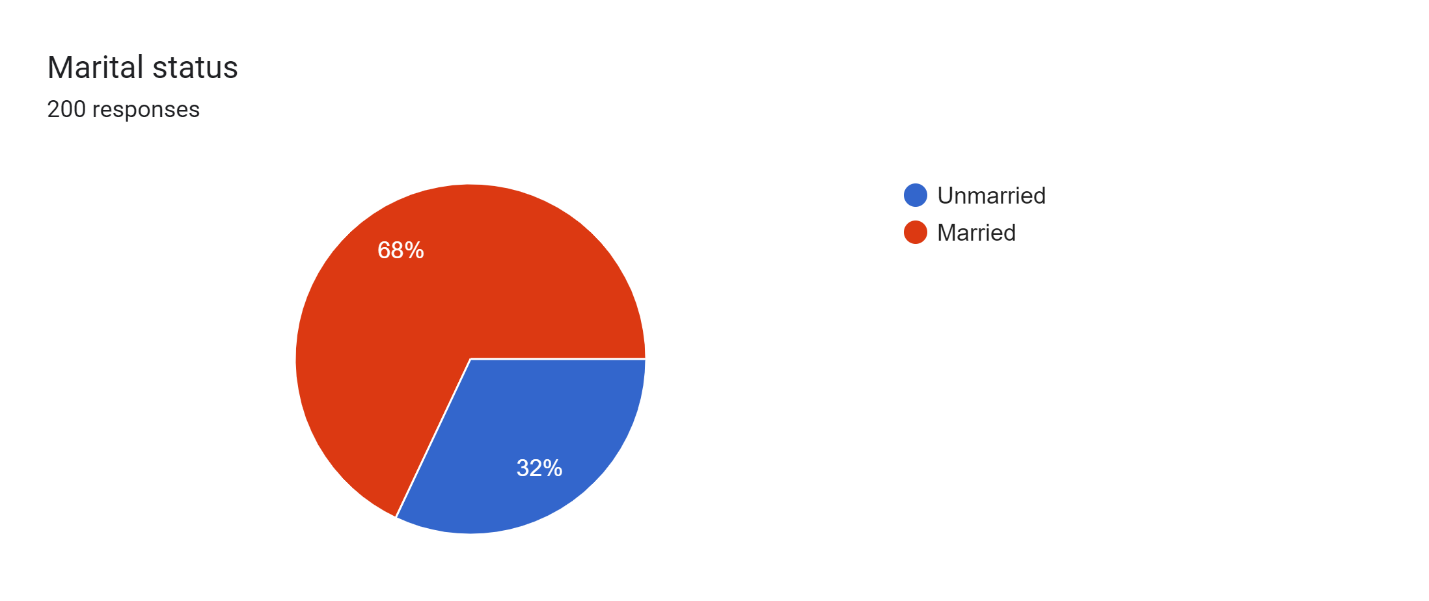
Figure 6
Figure 6 shows the number of respondents from each marital status in the form of a pie for Barachh Village with a total of 200 responses This article is split into two parts: The Table
- Unmarried: 32% of the respondents
- Married couples: 68% of the respondents
This data reveals that most of the respondents in Barachh Village are married with a percentage 68% and unmarried forms to be 32%. This implies that more of the village is married, are Marital groups in the village have PMJDY accounts.
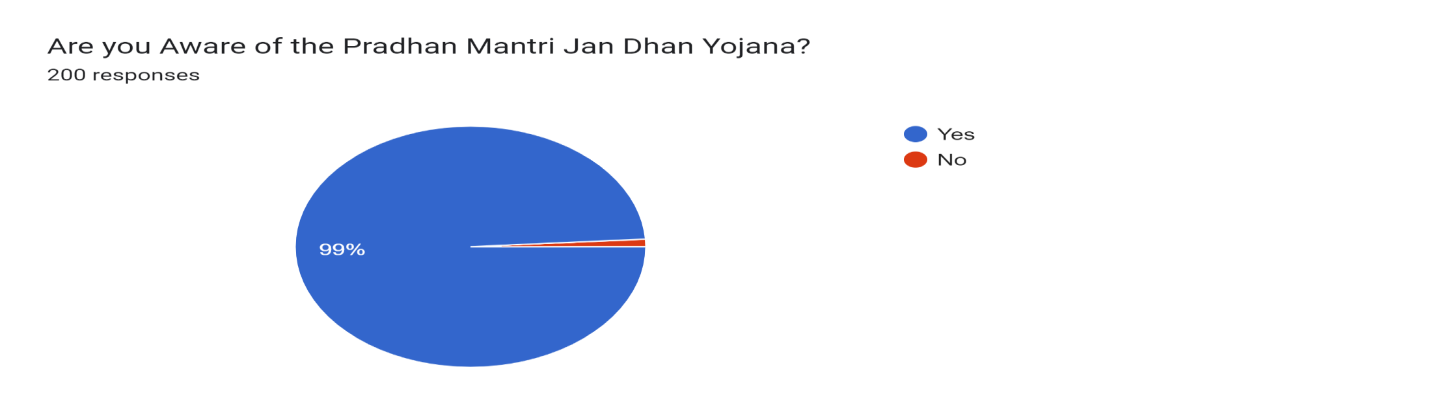
Figure 7
Figure 7 shows that most of the people in the Barachh village are aware of PMJDY schemes. Thus We can say that government and other officials played an important role in making people aware about PMJDY.
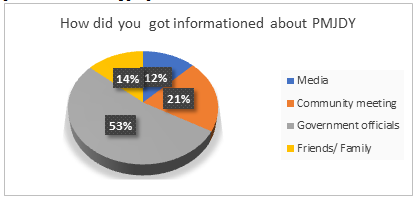
Figure 8
Figure 8 shows that government officials played an important role in awakening the people of Barachh to get the benefits of the PMJDY scheme with 53%. community meeting comes second position in making aware people about PMJDY scheme, friends and family with 14% and media with 12% in line to make people aware about scheme at Barachh village .
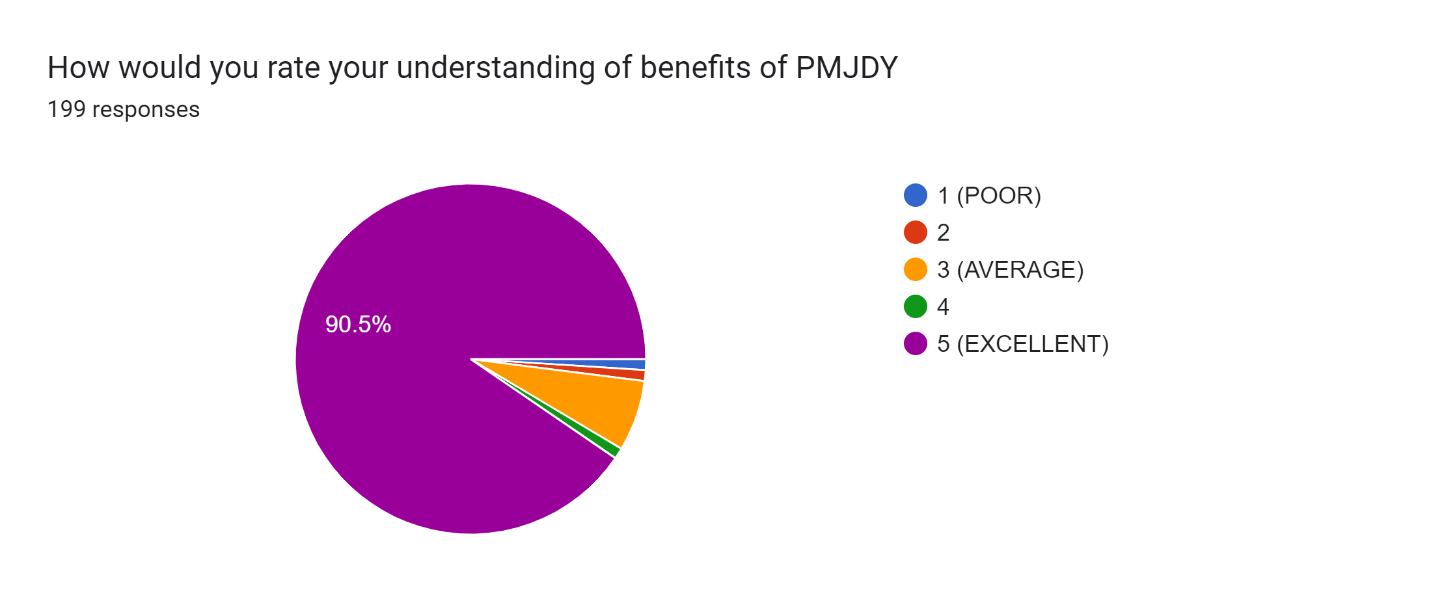
Figure 9
Figure 9 shows that most people are getting benefits through PMJDY schemes and are satisfied with these schemes thus eliminating the outflow of government benefits to the people in the village Barachh.
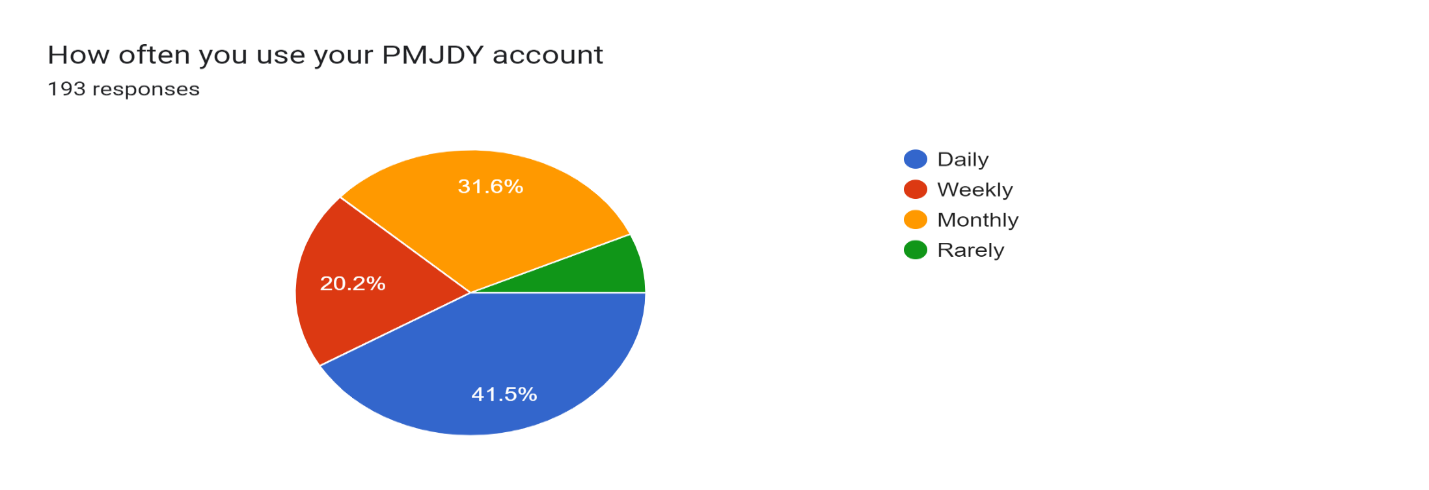
Figure 10
Figure 10 shows the percentage of people using PMJDY (Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana) Accounts among 193 total respondents from Barachh village. The distribution is;
41.5% account for daily utilization of their PMJDY account
- 6.7% use it rarely.
- 20.2% use it weekly.
- 31.6% use it monthly.
This indicates that where a certain number of the population uses their PMJDY accounts very frequently, an approximately equal or larger percentage use it only occasionally for multiple days or sometimes even not once in many months.
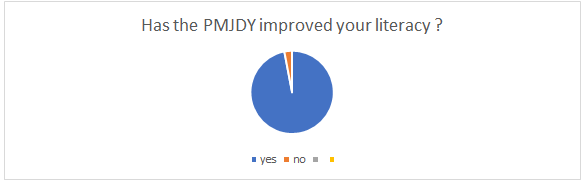
Figure 11
Figureb 11 reprsent that out 200 residents 194 resident of barachh village has accepted that PMJDY has improved there fancial literacy and awarness. .
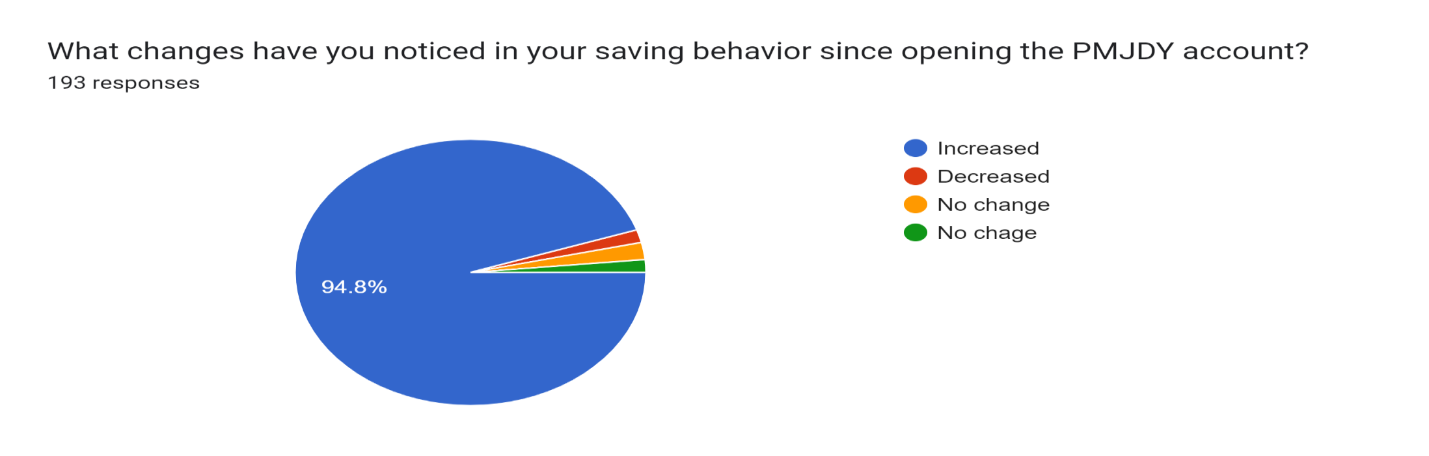
Figure 12
Figure 12 shows that using of PMJDY account the saving behavior of people in the Barachh village has increased thus leading to the rise in the livelihood of the people of Barachh.
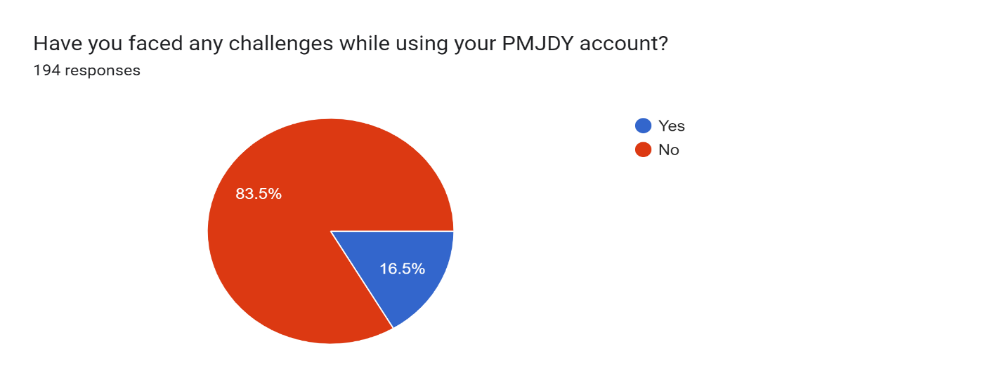
Figure 13
Figure 13 shows that 83.5% of respondents did not face challenges while using their PMJDY account while 16.5% faced challenges while using the PMJDY schemes
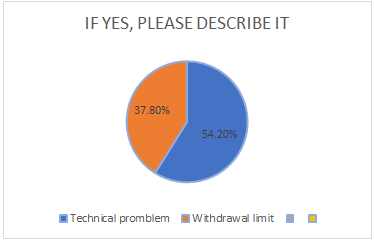
Figure 14
Figure 14 shows that 54.20% of people face technical problems whereas has 37.80% of people face Withdrawal limit problems.
Thus, we can say that these two major problems have to tackled for smooth working of PMJDY.
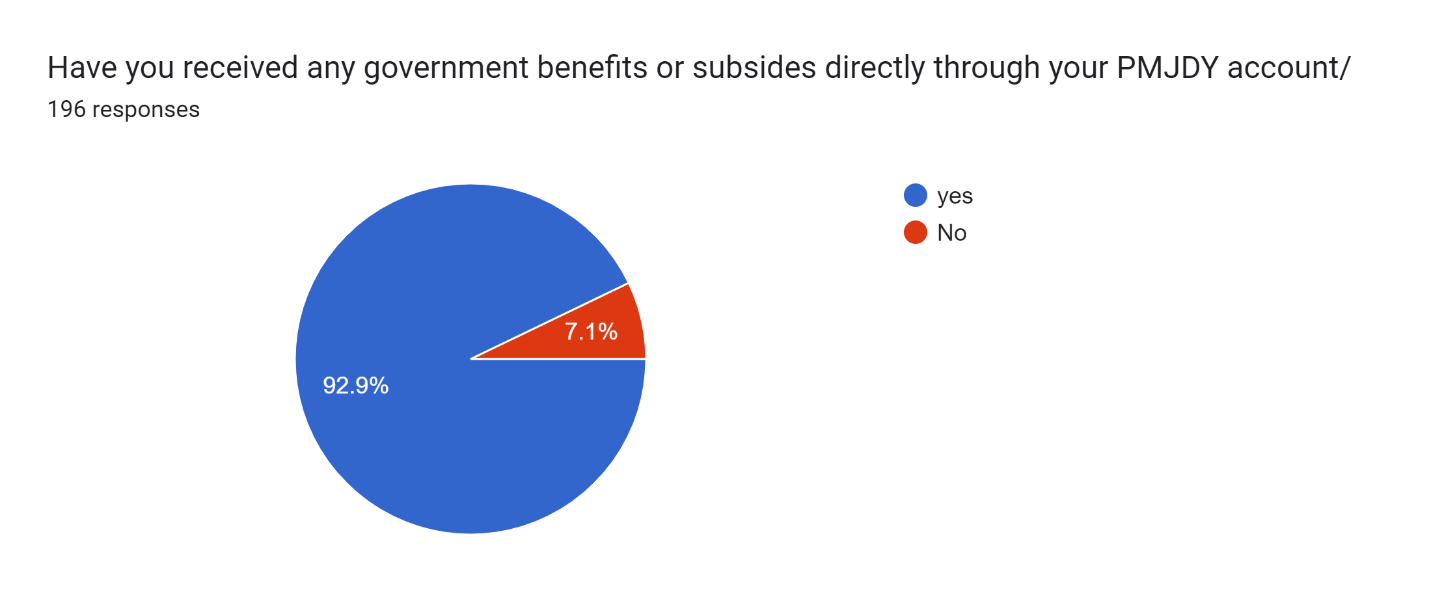
Figure 15
Figure 15 shows that most of the people in Barachh get government benefits 92.9% and there 7.1% of people do not get government benefits.
Thus, the staff supports and assists people in opening accounts and filling out forms, ensuring satisfactory service.
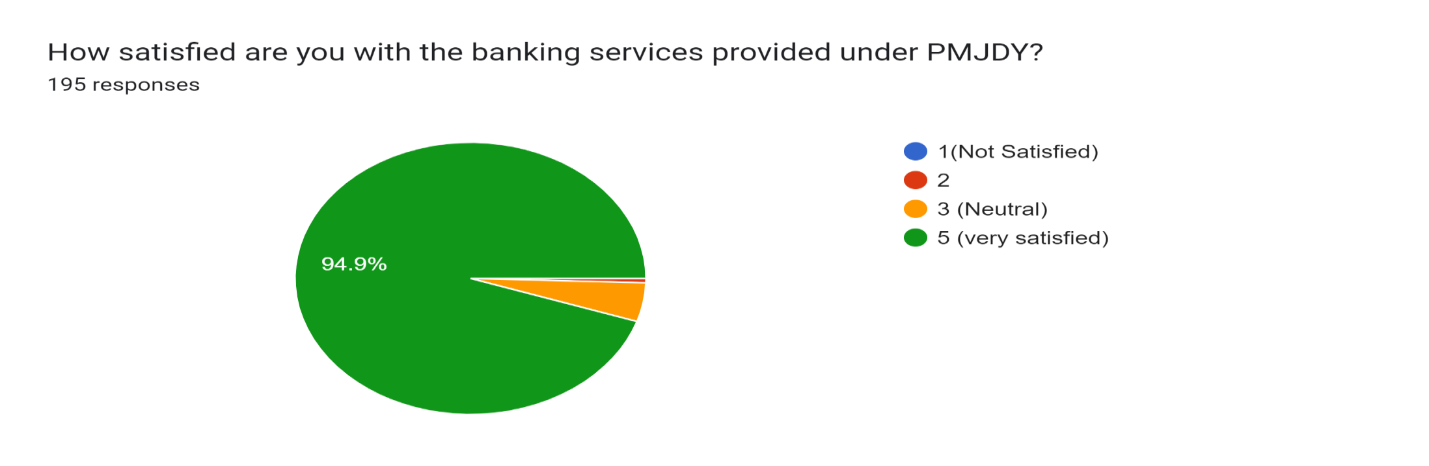
Figure 16
Figure 16 shows that most people are satisfied with the PMJDY scheme in Barachh village with 94.9% , the staff supports and assists people in opening accounts and filling out forms, ensuring satisfactory service.
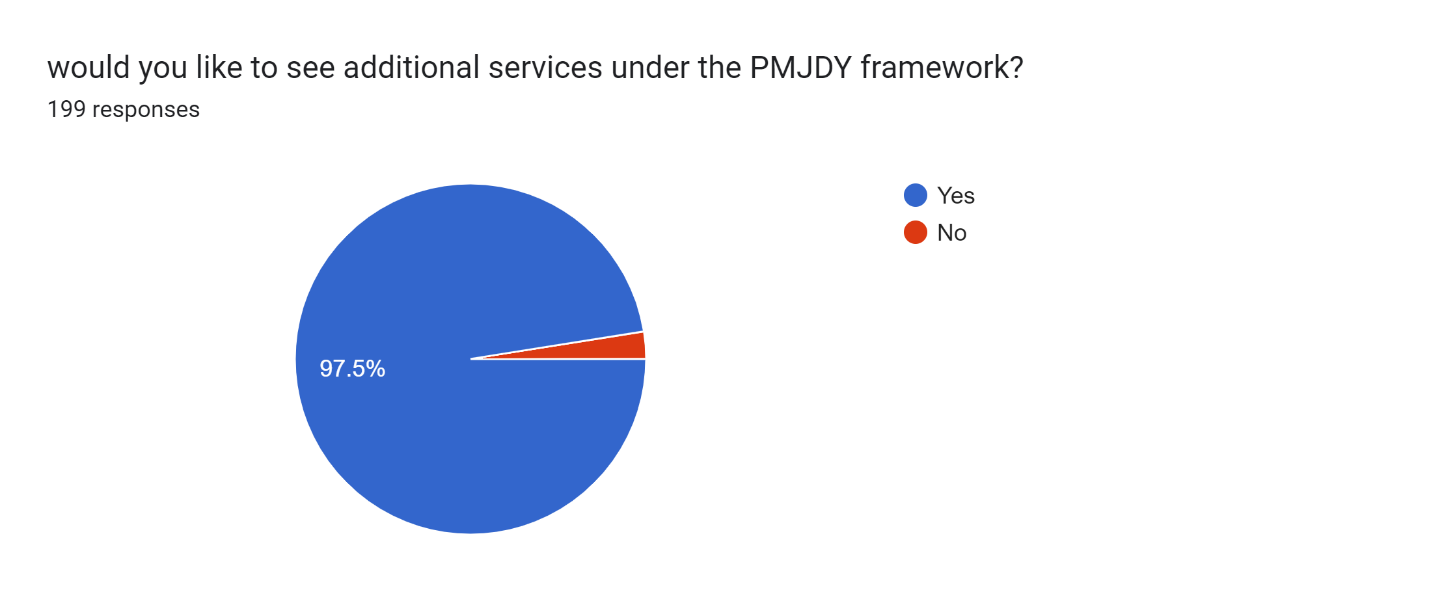
Figure 17
Figure 17 shows that 90% of respondents in Barachh Village, and nearly all the rest (29 out of 30) say they want more services to be offered under the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana. This is a signal of the increasing need for more expansion and improvements in its implementations.
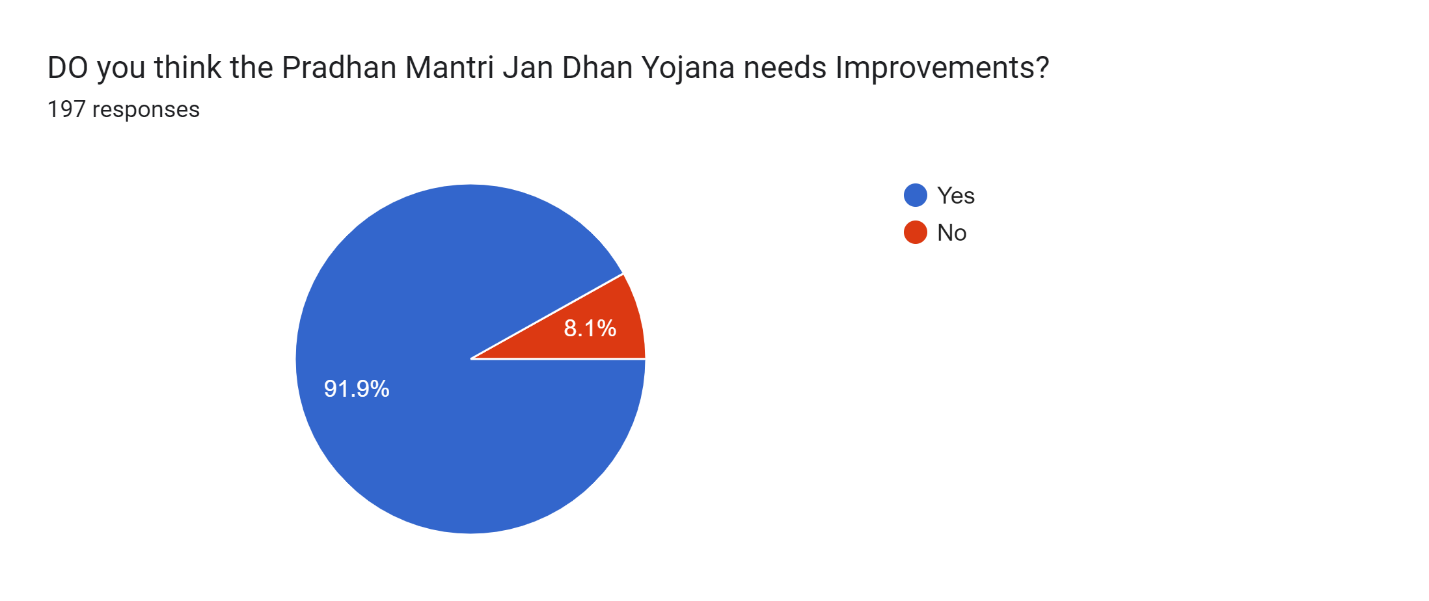
Figure 18
Figure 18 Shows that a whopping 91.9 % of respondents in the Barachh Village believe that Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) requires improvement This indicates that the scheme has plenty of room for improvement in better serving residents.
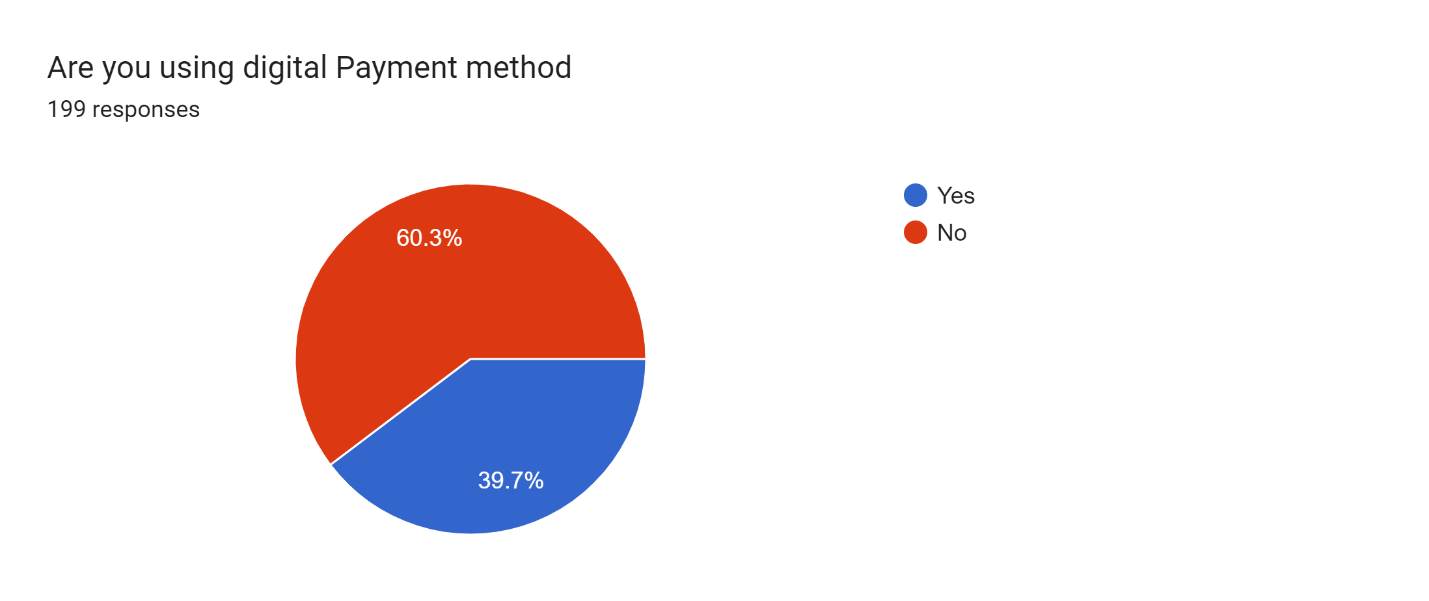
Figure 19
Figure 19 demonstrates that 60.3% do not use digital payments in Barachh village, and 39.7% are using it as their payment method.” This clearly shows that most of villagers are not using digital payments.
IX. FINDING OF ANALYSIS
A. Demographic Profile
- AGE: Age-wise most of the PMJDY account holders are basically between the 18–34 age group (Basically Young people).
- Gender: PMJDY has been referred to as a game changer in the financial inclusion of females due to their greater share taken by women— however, we found more males to have accounts than females which indicates a gender gap.
- Caste: General category accounts have the highest representation with respect to PMJDY account holders followed by OBCs, SCs, and STs.
- Education: Most of the account holders (64%) are educated up to the secondary level and thereafter mostly 20% are down at primary education levels and 16% of account holders cannot read or write.
B. Socioeconomic Profile
- Occupation: Among PMJDY account holders, Students, housemakers, agriculture & labor seem to be the prime occupations thereby proving the success of financial inclusion for rural and workers.
- Household structure: 68% of account holders were married, again suggesting that family circumstances may influence financial inclusion.
C. PMJDY Awareness and Usage
- Awareness-The data shows that most of the residents know about these schemes, The main sources of which were Government officials and Community meetings.
- Benefits: A large proportion of the respondents have gained from PMJDY schemes in terms of financial inclusion and other benefits available to them by the government.
- Challenges:
- As an Account holder, sometimes they face some technical problems and sometimes they face issues with a withdrawal limit.
- In Barachh village the prominent share are of those who do not use Digital Payment through PMJDY accounts, which suggests further requirements on Digital Literacy & Infrastructure
D. Financial Literacy and Behaviour
- Financial Literacy: Among the respondents evidently, the PMJDY scheme has played an important role in incentivizing better financial consciousness.
- Saving Behavior: PMJDY accounts have increased the saving habits of people and helped in employment.
E. Recommendations for assessing the success of pmjdy Scheme
- Demographic Targeting- The scheme has been able to target more Men and youth, and catches the eye of the General Cast(public) On the other hand it is thought to be somewhat more popular among females, SC, and St outside of our batch than males, also a bit among illiterates.
- Financial Literacy: There is a continued need for proper financial literacy, especially of the lower segments to avail benefits from PMJDY accounts in an effective way.
- Digital Inclusion: To promote the uptake of digital payments through PMJDY accounts, key enablers like addressing technical challenges and promoting digital literacy will be crucial.
- Schemes Expansion: PMJDY will be more beneficial if the services offered under this scheme can also be expanded to a larger extent attracting many beneficiaries.
These recommendations can hence help the PMJDY scheme perform a more active role in ensuring financial inclusion and livelihood improvement of people of Barachh village.
Conclusion
Barachh village had posted impressive growth in financial inclusion, courtesy of PMJDY. The scheme has helped in opening hundreds of Thousands of accounts which was never under a formal banking system before and these people now have access to basic financial services. Although PMJDY faced many challenges including the limited digital literacy and infrastructure, it has bettered the social conditions of village residents. The Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) scheme has helped to narrow down the gap of financial inclusion especially in rural sectors where a majority of unbanked people are concentrated. This access has been advantageous to a number of people who have ventured in the economy. In addition to this, the program has made it easier for government aid to reach people by allowing such benefits to be credited directly to their bank accounts in the form of cash transfers and even subsidies. This system has managed to curb leakages and has been able to target the beneficiaries effectively. In addition, there has been an improvement in financial education among Kenyans courtesy of PMJDY, as more individuals have become knowledgeable about content related to digital payment systems and financial inclusion as a whole. The economic effects of the program are clear in the rural villages where there are rising levels of income and financial services which in turn have improved communities’ standards of living hence enhancing economic development. But, the study also mentioned some of the challenges PMJDY beneficiaries are facing like technical difficulties and withdrawal limits to battle against. Combatting these challenges and disseminating digital literacy will be important to improve the effective operation of this program. In Barachh village, the PMJDY scheme has proven to be a successful initiative in advancing financial inclusion. Efforts to further better the mechanism and help people who own accounts overcome their woes would all contribute in aiding its success
References
[1] Modi, S., & Kumar Baral, S. (n.d.). Role of Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) in Promoting Financial Inclusion in India: An Assessment. Mekal Insights, 1(2).https://www.igntu.ac.in/MekalInsight/Vol5-Issue1-2-year-2021/10.pdf http://staloysiuscollege.ac.in/Publications/JOURNALS/j Department Files/Commerce/nikita%20shukla/PMJDY.pdf [2] A STUDY ON ROLE OF PRADHAN MANTRI JAN -DHAN YOJANA AS A TOOL OF FINANCIAL INCLUSION. (n.d.). https://doi.org/10.33472/AFJBS.6.Si2.2024.3441-3456 [3] Kamini Gupta - Articles - Scientific Research Publishing. (2014). Scirp.org. https://www.scirp.org/journal/article s?searchcode=Kamini++ Gupta&searchfiel d=authors&page=1 [4] Hetalkumar N Shah. (2019). Google.co.in. [5] https://scholar.google.co.in/citations?user=llRtR2AAAAAJ&hl=enhttps://pib.gov.in/PressNoteDetails.aspx?NoteId=152053&ModuleId=3#:~:text=Total%20Accounts,into%20the%20formal%20financial%20system. [6] https://pmjdy.gov.in/about#:~:text=The%20plan%20also%20envisages%20channeling,and%20pushing%20the%20Direct%20Benefits [7] https://www.livemint.com/money/personal-finance/pradhan-mantri-jan-dhan-yojana-from-benefits-to-impact-all-you-need-to-know-11697440909622.html#:~:text=PMJDY%20is%20designed%20to%20create,habit%20of%20savings%20among%20households. [8] https://typeset.io/papers/impact-of-pradhan-mantri-jan-dhan-yojana-pmjdy-on-socio-95t513g60h [9] https://pmjdy.gov.in/
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Saurabh Garg. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET65390
Publish Date : 2024-11-20
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

