Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Experimental Studies on Water Quality Analysis Integrating GIS Mapping at Aarang
Authors: Anisha Agrawal, Ms. Nayanika Dasgupta, Dr. Vaishali Pendese, Dr. Debabrata Mukhopadhyay
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.56248
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Groundwater is a primary source of drinking water in our country but day by day increment of groundwater contamination due to various anthropogenic activities and anthropogenic activities makes the life difficult especially for the rural people. Groundwater is getting contamination rapidly due to various anthropogenic activities as well as some natural sources. In the direction, assessment of water quality analysis is the basic requirement for nurturing human being and its evolution. Water Quality Index (WQI) parameter has been widely used in determining water quality globally. Conventional method used for computing WQI is tedious and takes longer time because it involved processing for larger datasets. The present investigation aims to provide the suitability of groundwater in the specified region using GIS (Geographic Information System) of physiochemical parameters, that are used in drinking purpose, domestic works and household chores. Locations are marked using GPS and the parameters are also used to find out about the WQI (Water Quality Index). The parameters are compared with the BIS (Bureau of India Standards) for checking the suitability of groundwater. The present approach output can be beneficial to the administrators in making decisions on groundwater quality but also gaining inside into the trade of between system benefit and environment requirement.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Groundwater is a primary source of drinking water in our country but day by day increment of groundwater contamination due to various anthropogenic activities and anthropogenic activities makes the life difficult especially for the rural people. The main question is that the available water in the bore wells/ dug wells is usable for domestic and household purposes or not? The miraculous achievement of science and technology has increased the rate of utilization of groundwater for domestic, industrial and irrigation purposes multiple folds throughout the world over the last few decades. Excessive use of chemicals and pesticides for agricultural purpose often results in leaching and mixing into the groundwater. The rapid growth of urbanization in India, has influenced the accessibility and quality of groundwater because of the over exploitation and inappropriate and unscientific waste disposal. As indicated by World Health Origination (WHO), use of inappropriate or polluted water causes around 80% of total diseases in human beings. Furthermore, the quality of contaminated groundwater cannot be improved or re-established by preventing contaminations from source. Therefore, understanding and determining the water quality is imperative in the study of water resources and environmental engineering. According to World Health Origination (WHO), the use of contaminated water causes around 80% of total diseases in human. Pollution in the groundwater system is a severe threat to public health as well as the economic and social life and wellbeing of the world (Milovanovic 2007).Therefore, monitoring the groundwater quality and controlling the pollution level in groundwater is the need of the hour (Simeonov et al. 2003; Simeonova et al. 2003). Aarang, also known as "The town of temples" of Chhattisgarh, is a block and a Nagar Palika in Raipur District in the state of Chhattisgarh, India. It is situated near the eastern limits of Raipur City and close to Mahasamund City. Aarang is an ancient town, which was ruled by the Haihayas Rajput dynasty. It is famous for its many Jain and Hindu temples which belong to the 11th and 12th centuries; these are the Mand Deval Jain temple, the Mahamaya temple, the Panchmukhi temple and the Hanuman temple. Aarang, a prosperous ancient town, known for its many Jain and Hindu temples, is located on the west bank of the Mahanadi River, a Nagar Palika in Raipur District in Chhattisgarh, at 21.2°N 81.97°E. It has an average elevation of 267 metres (876 ft). It is 36 kilometres (22 mi) from Raipur on National Highway 53 (N.H.53), a four lane expressway to Durg passing through Aarang. It is 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) from Mahasamund city. There is also a four-lane road from Aarang to Tumgaon. The nearest airport is the Raipur Airport situated near Mana Camp, which is 23.8 kilometres (14.8 mi) away from Aarang. Aarang Is located beside National Highway 53 that connects Kolkata to Mumbai. As of 2001 India census, Aarang had a population of 16,593. Males constituted 51% of the population and females 49%. Aarang had an average literacy rate of 64%, higher than the national average of 59.5%; with 60% of the males and 40% of females’ literate. 16% of the population is under 6 years of age.
As of 2011, the population reported was 19,091, an increase of 1.3% over the 2001 figure, which gives a density figure of 812.7/km2 over the Nagar Panchayat area of 23.49 square kilometres (9.07 sq. mi). In the present stuff, the sample collected and the values obtained and compared with the BIS (Bureau of Indian Standards) values and the solutions given accordingly. The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) is the National Standards Body of India under the Ministry of consumer affairs, food and public distribution, government of India. BIS certification enables the certificate holder to offer a third-party guarantee of quality, safety and reliability of products to the customers and is mainly required for the import of items. A Water Quality Index (WQI) is a means by which water quality data is summarized for reporting to the public in a consistent manner. The parameters involved in the WQI are dissolved oxygen, pH, total dissolved solids, hardness, calcium, magnesium, total alkalinity, electrical conductivity. The numerical value is then multiplied by a weighting factor that is relative to the significance of the test to water quality. A Water Quality Index (WQI) is a means by which water quality data is summarized for reporting to the public in a consistent manner. Globally, India is ranked 120th among 122 countries in WaterAid's water quality index. The index was first developed by Horton in 1965 to measure water quality by using 10 most regularly used water parameters. The method was subsequently modified by different experts. The correlation between independent parameters can be neglected in the plot since these plots mostly empirical based on the specific values.
II. METHODOLOGY
The groundwater samples from open and bore wells (36 sites) are collected which are extensively used for household chores and domestic purposes in the area. The identification of the sampling points is performed using topographic sheets and GPS and the maps are prepared using QGIS 3.30.3. Topographic sheets are utilized for the preparation of base map and to recognize the general features of the area. GPS technique is utilized to identify the geographic position of each sampling point.
A. Sample Collection
The sample is collected during March and April, during summer season. A total of 15 parameters were considered for study. The concentration of the parameters is compared with the acceptable limits prescribed by BIS, (2012). Acceptable limits of potassium, bicarbonate and sodium are reported in Chaurasia et al., (2018) and WHO, (2012). GIS maps are plotted using the obtained values from the parameters.
B. Plotting of GIS Maps
STEP ONE: PREPARE- Select coordinate system and select UTM.
STEP TWO: MAP – Take a new map and select area. Mark the points using longitude and latitude.
STEP THREE: LABEL- Turn on the layers and label them.
STEP FOUR: FINISH- Insert a new map. Choose an appropriate coordinate system. Add the key map to your layout. Size and scale it in the same way you did above for the main map.
V. Water Quality Index (WQI)
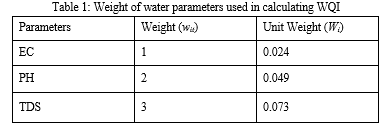
The WQI provides a qualitative estimate regarding the suitability of a water sample for different purposes based on the concentration of different parameters. Parameters considered for the evaluation are then compared with WQI classification of water parameters. In a decreasing order the influence of different parameters can be presented as chromium, sodium, fluoride, potassium, chloride, conductivity, total dissolved solid, alkalinity, bicarbonate and pH. Contributions of rest of the parameters on overall water quality are much less compared to these parameters. To calculate the WQI, a random weight (wi) between 1 to 4 is assigned to each parameter with reference to their comparative significance in general water quality. In case of the present samples, the highest weigh (4) is assigned to Cr and the lowest (1) is assigned to EC.


IV. ACKNOWLEDGMENT
I wish to express my deep and sincere gratitude toward my guide Mrs. Nayanika Dasgupta for providing excellent guidance, encouragement, enthusiastic inspiration and support throughout the work. It would never have been possible for me to take this project to completion without her valuable suggestions and innovative ideas. Being the true mentor, she not only showed how to conduct the thesis work but also taught me to be a human being with great integrity.
Consider myself extremely fortunate to have had a change of working under his supervision. I would like to acknowledge the innumerable contributions of respected Dr. Vaishali Pendese, HoD Chemical Engineering Department, Prof. (Dr.) D. Mukhopadhyay, Dean (Chemical Engineering and project) for their helpful solution and comments enriched by experience, which improved my ideas for betterment of the project. Additionally, I would like to thanks the faculty member of Chemical Engineering Department for their support in the form of both suggestions and understanding. It will be my pleasure to acknowledge utmost co-operating and valuable suggestion given by my colleagues from time to time. I really appreciate their support for always being useful source of information. I am forever obliged to my parents, family members and friends for their perdurable encouragement to me and unwavering faith in my ability to succeed. Lastly, I thank God, the Almighty for helping me in entire endeavour.
Conclusion
The experiment offers a map of physio-chemical parameters and treatment for chromium. This represents the latest water quality which is been used for household chores and domestic purposes. In this study use of GIS software has been done which is used for mapping. In the study it has been found that chromium was the parameter which has maximum samples which were out of range and an experiment has been done to reduce chromium content levels in water. The following findings were discovered: 1) The study provides significant information regarding ground water quality in parts of command area. 2) As per the classification based on TDS, 91.5% parentage of samples are moderately hard, based on chlorine 94.5% water is Brackish salt. 3) In 36 samples, 11 samples of electrical conductivity accurate the range that is prescribed BIS and this increase in values of electrical conductivity indicates that salinity and temperature are increased as when salinity and temperature increase the conductivity also increases which has a negative effect on the quality of water, this is because the higher the conductivity the higher number of impurities (dissolved substances chemicals, minerals) are in the water. 4) Among the 36 samples, 1 sample of pH of water is out of range the value of the sample is 8.51 and when the pH of water becomes greater than 8.5 the water test can become more bitter and this can lead to calcium and magnesium carbonate building up in the pipes, this value of PH can cause skin to become dry, itchy and irritated. 5) The values of TDS amongst the 36 samples were found to be satisfactory, all the samples were in the range between 250 to 600 and this range is good for use of water for domestic purposes and household chores. 6) All the samples of alkalinity were in range, hands safe for domestic purpose and household works. 7) All the samples of chloride were in range and good for use household chores and domestic purposes. 8) All the samples of calcium and magnesium were in range and the water is good and safe for used in domestic purposes and household works. 9) All the samples of potassium, nitrate, sulphate, bicarbonate, fluoride are in rains and hence they are safe for use in household works and domestic purposes. 10) All the 36 samples 1 sample of iron was found to be out of range, the value was not too high, hence safe for domestic use. 11) All the 36 samples of total hardness were in range hence can we used for domestic purpose and household works. 12) In a total of 36 samples 17 samples of chromium were out of range, chromium exposure can cause skin and eye irritation. It can be hence concluded that the overall quality of the area is good. Due to the usage of pesticides in the area, since the area there is presence of heavy metals like chromium in water. To reduce the chromium content in water banana peel gives better result as compared to the orange peel adsorbents. nutrient management practices and regular monitoring of soil health to increase yields.
References
[1] Dhruw, M., & Pandey, V. K. (2023). Land surface temperature estimation of a distributary of Mahanadi canal command using LANDSAT-7 and LANDSAT-8 satellite data using Sebal algorithm for rice and wheat crops. [2] Atta, H. S., Omar, M. A. S., & Tawfik, A. M. (2022). Water quality index for assessment of drinking groundwater purpose case study: area surrounding Ismailia Canal, Egypt. Journal of Engineering and Applied Science, 69(1), 83. [3] Bushero, D. M., Angello, Z. A., & Behailu, B. M. (2022). Evaluation of hydrochemistry and identification of pollution hotspots of little Akaki river using integrated water quality index and GIS. Environmental challenges, 8, 100587. [4] Nathan, R. J., Barr, D., & Rosengren, R. J. (2022). Six fruit and vegetable peel beads for the simultaneous removal of heavy metals by biosorption. Environmental technology, 43(13), 1935-1952. [5] Sahu, D. K., Samadhiya, V. K., Chandrakar, T., Netam, S., & Sahu Mahendra, H. (2021). Macro and micro nutrient status of research farm, college of agriculture and research station Kurud. District Dhamtari, Chhatisgarh. The Pharma Innovation International Journal SP, 10(8), 32-35. [6] Oladipo, J. O., Akinwumiju, A. S., Aboyeji, O. S., & Adelodun, A. A. (2021). Comparison between fuzzy logic and water quality index methods: A case of water quality assessment in Ikare community, Southwestern Nigeria. Environmental Challenges, 3, 100038. [7] Singha, S., & Pasupuleti, S. (2020). Delineation of groundwater prospect zones in Arang block, Raipur district, Chhattisgarh, Central India, using analytical network process. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 95, 609-615. [8] Singh, S., Bhardwaj, A., & Verma, V. K. (2020). Remote sensing and GIS based analysis of temporal land use/land cover and water quality changes in Harike wetland ecosystem, Punjab, India. Journal of environmental Management, 262, 110355. [9] Ahmed, S., Khurshid, S., Sultan, W., & Shadab, M. B. (2020). Statistical analysis and water quality index development using GIS of Mathura City, Uttar Pradesh, India. Desalination and Water Treatment, 177, 152-166. [10] Andualem, T.G. and Demeke, G.G. (2019) Groundwater potential assessment using GIS and remote sensing: A case study of Guna tana landscape, upper blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Jour. Hydrol. Reg. Stud., v.24, pp.100610. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejrh.2019.100610. [11] Singha, S., Pasupuleti, S., Durbha, K. S., Singha, S. S., Singh, R., & Venkatesh, A. S. (2019). An analytical hierarchy process-based geospatial modeling for delineation of potential anthropogenic contamination zones of groundwater from Arang block of Raipur district, Chhattisgarh, Central India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78, 1-19.
Copyright
Copyright © 2023 Anisha Agrawal, Ms. Nayanika Dasgupta, Dr. Vaishali Pendese, Dr. Debabrata Mukhopadhyay. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET56248
Publish Date : 2023-10-21
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

