Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Eye Abnormalities Detection Using Machine Learning
Authors: Prof. B. R. Ban, Shubham Lipane, Prathamesh Dagade, Sakshi Chavan, Narendra Gadhe
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.60644
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
The most common cause of irreversible visual impairment and incapacity around the world is glaucoma. In any case, the larger part of patients are uninformed of their condition. Despite headways in innovation, diagnosing the movement of glaucoma remains a challenge in clinical hone. Observing glaucoma movement ordinarily includes a manual examination of the retinal layer, which is time-consuming. This issue can be tended to by computerizing glaucoma conclusions utilizing profound learning and machine learning strategies. A comprehensive survey of various computerized glaucoma forecast and discovery strategies was conducted in this orderly audit. Over 100 papers on machine learning (ML) strategies were analyzed, covering outlines, strategies, goals, execution, benefits, and downsides, with clear charts and tables. Machine learning approaches such as the Resnet calculation and Convolutional Neural Organize are commonly utilized for diagnosing and foreseeing glaucoma. Through precise audits, the most solid strategy for glaucoma discovery and forecast can be distinguished to improve future treatments. Cataracts are the driving cause of visual This ponder gives a comprehensive outline of current headways in machine learning strategies for assessing and classifying cataracts utilizing ophthalmic pictures. The study highlights the qualities and shortcomings of existing investigations and addresses challenges related to independent cataract classification and evaluating utilizing machine learning procedures, advertising potential arrangements for encourage examination.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
As per the World Health Organization (WHO), the approximate number of individuals who experience vision impairment is 2.2 billion. Cataracts are the leading cause of blindness (greater than 50) worldwide, accounting for around 33 % of visual impairment. Patients with cataracts can enhance their quality of life and vision through early intervention and cataract surgery. These are effective ways to simultaneously lower the burden of cataract-related blindness on society and the blindness ratio. In terms of clinical practice, cataracts are defined as the loss of transparency in the crystalline lens area, resulting from protein clumping within the lens. Developmental anomalies, trauma, metabolic diseases, genetics, drug-induced alterations, age, and other factors are linked to them. Two of the main risk factors for cataracts are aging and genetics. There are several age-related types of cataracts.
It can be categorized as age-related cataracts, pediatrics cataracts (PC), and auxiliary cataract concurring to their causes. Depending on the area of the crystalline focal point darkness, they can be assembled into atomic cataracts (NC), cortical cataracts (CC), and back subcapsular cataracts (PSC). NC signifies the progressive clouding and the dynamic solidifying in the atomic locale. CC is the shape of white wedged-shaped and radially situated opacities and is created from the exterior edge of the focal point toward the center in a talked-like mold. PSC is granular opacities, and its side effects incorporate little breadcrumbs or sand particles, which are sprinkled underneath the focal point capsule.
The term “glaucoma” alludes to an assortment of conditions that all result in the dynamic degeneration of the optic nerve, which dynamically compounds vision and inevitably renders an individual daze. The movement of retinal ganglion cell misfortune in glaucoma is caused by compression of the visual field (VF), as well as unmistakable changes in the neuroretinal edge tissue in the optic nerve head (ONH). Glaucoma proceeds to be the greatest cause of lasting visual deficiency in the world despite the presence of reasonable treatments. By the year 2040, 111.8 million people are anticipated to have glaucoma, with those in Asia and Africa being excessively influenced. The lion's share of glaucoma patients are ignorant that they have the condition since it more often than not has no indications in the early stages. In any case, early location and Mediation can offer assistance decrease visual misfortune caused by glaucoma. In this way, early glaucoma location is significant and may be upgraded by the presentation of novel screening, demonstrative, and altered observing instruments. Watery liquid spillage and optic nerve damage increment the eye’s intraocular weight (IOP), which anticipates data from the eye from coming to the brain.
The most prominent cause of lasting visual deficiency in the world, glaucoma is moreover connected to a lower quality of life. Hazard components incorporate progressed astigmatism, feebleness, hereditary qualities, age, family history, systemic hypotension, smoking, race, systemic hypertension, vasospasm, utilization of systemic or topical solutions, obstructive rest apnea disorder, headache, and most essentially, a tall IOP.
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
The Existing tools for interview preparation predominantly focus on static question banks or mock interview platforms with limited adaptability and engagement. The innovative platform distinguishes itself by integrating AI and NLP, allowing for
dynamic question generation, personalized feedback, and an inter-active learning experience. Research in AI- driven interview assessments has gained momentum.
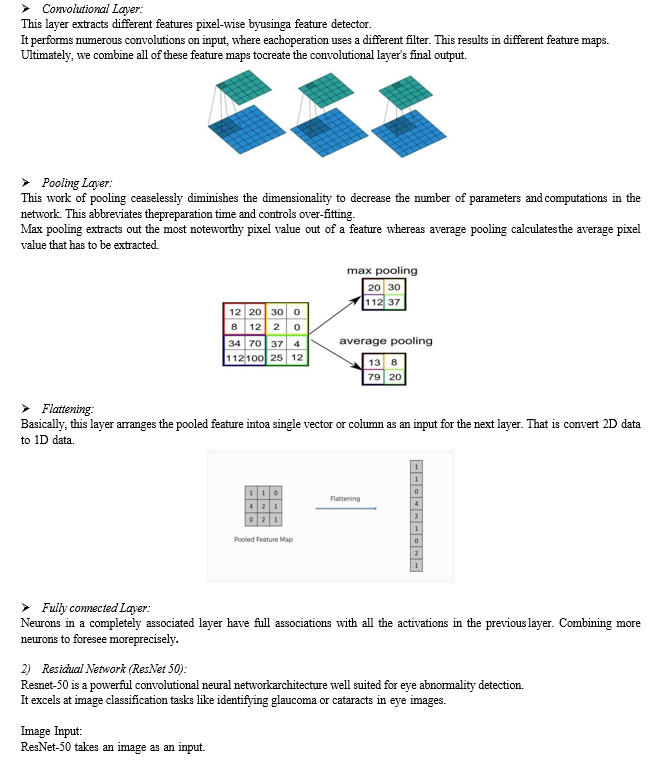
- This paper caters to these approaches that were used earlier for the segmentation ofOD and OC. The common tactics include thresholding which shows some response for the specific pixels that lie belowor above that intensity level. The drawback of this
- technique was that it has not been implemented On large-scale datasets. A limited number of solutions are deployed.
- The proposed framework uses 1450 color fundus images provided by Kaohsiung Chang Gung (KCG) Memorial Hospital in Taiwan. Combining the use of convolutional neural networks (CNN) with the proposed generalized loss function, the robust design of the experiment (DOE)outperformed most archival automatic glaucoma detection approaches in their effectiveness and simplicity. The paper focuses on a single type of eye disease and one method to detect disease.
- In this work, a programmed glaucoma classification procedure has been created by utilizing numerous deep-learning approaches. To begin with, a modern private dataset of 634 color fundus pictures has been collected and explained by two eye masters, a pediatric ophthalmologist and a glaucoma and refractive specialist, from Bangladesh Eye Healing Center, Bangladesh. Other, different profound learning models (EfficientNet, MobileNet, DenseNet, and GoogLeNet) have been utilized to identify glaucoma from fundus pictures. The framework is a less strong demonstration. Need to prepare more information comprising open and private eye fundus pictures and joining engineered pictures.
- In this think about, compact self-organized operational neural systems (self-ONNs) are proposed for the early Location of glaucoma in fundus pictures and their execution is compared against the Convolutional Neural Systems (CNNs) Over the ACRIMA, RIM-ONE, and ESOGU benchmark datasets, convolutional neural systems (CNNs) were tried. The exploratory discoveries appear that Self- ONNs can significantly diminish computational complexity in expansion to accomplishing progressed location exactness, which makes it a possibly valuable arrangement demonstration for biomedical datasets, especially when information is rare. Operational neural systems (ONNs), a as of late created heterogeneous arranged worldview, are a disadvantage of this article. containing one-of-a-kind non-linear neurons. ONNs are inferred from the generalized operational perceptrons (GOPs) that can learn those issues where MLPs come up short.
- This work presented a one-of-a-kind AI-based strategy for glaucoma discovery that coordinates worldly (energetic vascular) and spatial (inactive basic) information. Accuracy is less but can be improved further by changing a few parameters.
- The objective of this paper is to use convolutional neural networks based on a publicly available image dataset to classify cataract disease. This result shows that four distinct convolutional. neural networks (CNN) meta-architectures, including Inception V3, Inception ResnetV2, Exception, and DenseNet121, were applied by using the TensorFlow object detection framework. By using Inception ResnetV2, we were able to attain the advantage in cataract disease detection. The implementation is missing large and complex datasets. More practices of image processing techniques are not used. Moderate or less accuracy.
III. PROPOSED SYSTEM
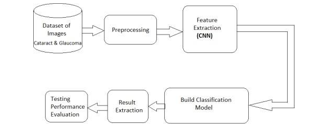
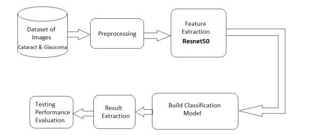
- Image Acquisition:
- The process begins with acquiring eye images containing information about the retina, particularly focusing on regions related to cataracts and glaucoma.
- This block represents the input data, which is a set of eyeimages.
2. Preprocessing:
- Raw images are preprocessed to enhance features and reduce noise. Common preprocessing steps include re- sizing, normalization, and augmentation.
- This block prepares the data for training and testing by ensuring consistency and improving the model’s abilityto learn relevant patterns.
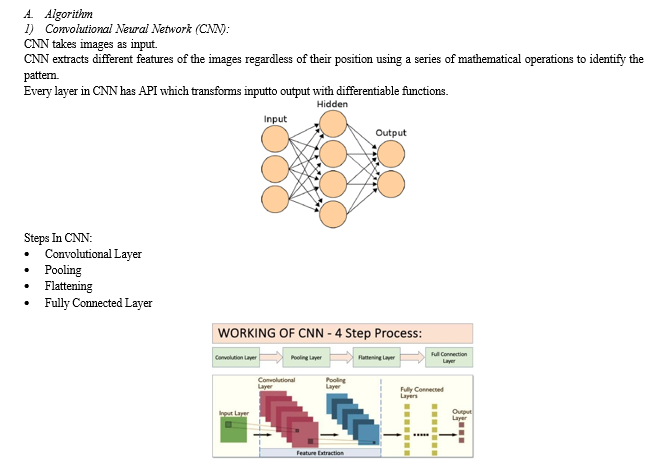
3. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN):
- The core of the architecture involves a CNN, a type of deep learning model designed for image- related tasks.
- The CNN block comprises multiple layers of convolutional, pooling, and Activation layers. These layers extract hierarchical features from the input images.
- ResNet (Residual Network):
- ResNet is a specific type of CNN architecture that includes skipping connections or residual connections.
- This block consists of residual blocks, each containing multiple convolutional layers with a shortcut connection, enabling the model to learn residual information.
- ResNet helps address the vanishing gradient problem and aids in training deeper networks.
- Training Model:
- The training block involves feeding the preprocessed images through the CNN and ResNet architecture.
- The model learns to identify patterns associated with cataracts and glaucoma by adjusting its weights during the training process.
- This block includes loss computation, backpropagation, and optimization steps to update the model parameters.
- Testing Model:
- After training, the model is tested on a a separate set of images not seen during training to evaluate its generalization performance.
- This block includes feeding test images through the trained model and evaluating its predictions against ground truth labels.
- Prediction:
- The final block represents the deployment phase where the trained model is used to make predictions on new, unseen images.
- The model outputs predictions indicating the likelihood of cataracts and glaucoma in the given eye image.
4. Interactions:
User Interaction: Users interact with the system through the UI component, uploading images and viewing diagnostic results.
5. Data Flow:
Data flows from the UI component to the Image Preprocessing Module, and then to the CNN Model for disease detection.The CNN Model outputs diagnostic results, which are then presented to the user through the Result Presentation Module.
6. Training and Evaluation Flow:
Data flows from the Training Module to the CNN Model fortraining, and from the Evaluation Module to the CNN Model for performance evaluation.
7. Integration:
The various components of the system interact with each other through well-defined interfaces and APIs, facilitating seamless communication and integration. External databases or data sources may be integrated for storing image data,model parameters, and diagnostic results.
IV. METHODOLOGY
- Data Collection: Gather a diverse dataset of labeled medical images that include cataract and glaucoma cases, sourced from various clinical settings.
- Data Preprocessing: Clean, normalize, and augment the dataset to ensure uniform quality and to increase the model’s robustness.
- Data Augmentation: This helps in improving the performance of algorithms by increasing the size of training dataset.
- Model Development: Implement the CNN and Resnet architecture for image classification, finetuning it for cataract and glaucoma detection.
- Training and Validation: Train the model using a portion of the dataset and validate its performance using a separate dataset.
- User Interface: Develop an intuitive user interface for medical professionals to upload images and receive automated diagnostic reports.


The training data consisting of 1101 images, divided into categories of cataract present, cataract absent, glaucoma present, and glaucoma absent, was crucial in training these models. Through data augmentation and preprocessing techniques, we enhanced the model's ability to learn and generalize from the limited dataset, resulting in promising validation accuracies.
VI. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
I would like to extend my heartfelt gratitude to everyone who contributed to the completion of this research paper. I extend my sincere appreciation to Prof. B.R.BAN for their invaluable guidance unwavering support, and insightful feed- back throughout the process. We would also like to thank all the Staff Members of the Comp Engineering Department, Savitribai Phule Pune University for their timely help and inspiration for the completion of the project. Special thanks to my colleagues and peers who have provided assistance and shared their knowledge during various stages of the research. This research would not have been possible without the collective efforts and support of these individuals and entities. Thank you everyone for becoming an integral part of this journey
Conclusion
This investigation has brought to light the developing concerns approximately the effect of cataracts and Glaucoma on vision and day-by-day life and has looked to make the location of this irregularity simpler. The display strategies of discovery such as opening light photography are not exceptionally successful and are perplexed with destructive side impacts. This show points to relieving these issues by utilizing Convolutional Neural Network & ResNet50, which do not require the genuine filtering of the patient’s retina, but as it were a picture of it. The prepared CNN and Resnet50 at that point check for the arrangement of a cataract layer and provide a final diagnosis. These use less time, and fewer assets and give a more precise result. As we have already examined, our framework is very primitive due to technological limitations, but there is plenty of room for improvement and headway. The CNN or Resnet50 preparation can be done more plan to be able to compensate for the interesting contrasts in each individual’s retina. The CNN model is recommended for eye abnormality detection, specifically for cataracts and glaucoma, due to its superior performance and interpretability. However, the ResNet-50 model\'s computational efficiency should be considered for deployment on resource-constrained devices. The project\'s implementation using Python, HTML, CSS, and Django framework provides a user-friendly interface for users to register, login, and upload eye images for detection, making it a valuable tool for eye care professionals and patients alike. The project\'s results and discussion section highlight the importance of using deep learning algorithms in eye disease detection and the potential for further development and advancement in this field. Overall, the project\'s findings contribute to the growing body of research on the use of artificial intelligence and deep learning in eye disease detection and demonstrate the potential for these technologies to improve the accuracy and efficiency of eye disease diagnosis. The project\'s results and discussion section provides a comprehensive analysis of the project\'s methodology, results, and implications, making it a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners in the field of eye care and artificial intelligence.
References
[1] Song, W. T., Lai, C., & Su, Y. Z. (2021). A statistical robust glaucoma detection framework combining retinex, CNN, and DOE using fundus images. IEEE Access, 9, 103772-103783. [2] Islam, M. T., Mashfu, S. T., Faisal, A., Siam, S. C., Naheen, I. T., & Khan, R. (2021). Deep learning-based glaucoma detection with cropped optic cup and disc and blood vessel segmentation. Ieee Access, 10, 2828- 2841. [3] Devecioglu, O. C., Malik, J., Ince, T., Kiranyaz, S., Atalay, E., & Gabbouj, M. (2021). Real-time glaucoma detection from digital fundus images using self- onns. Ieee Access, 9, 140031-140041. [4] Abdullah, F., Imtiaz, R., Madni, H. A., Khan, H. A., Khan, T. M., Khan, M. A., & Naqvi, S. S. (2021). A review on glaucoma disease detection [5] using computerized techniques. IEEE Access, 9, 37311- 37333. [6] Hasan, M. K., Tanha, T., Amin, M. R., Faruk, O., Khan, M. M., Aljahdali, S., & Masud, M. (2021). Cataract disease detection by using transfer learning-based intelligent methods. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2021. [7] Karamihan, K. C., Agustino, I. D. F., Bionesta, R. B. B., Tuason, F. C., Arellano, S. V. E., & Esguerra, P. A. M. (2019). SBC-Based cataract detection system using a deep convolutional neural network with a transfer learning algorithm. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering, 8(2), 4605-4613. [8] SoheilaGheisari1*, Sahar Sharifou1, Jack Phu2,5, Paul J. Kennedy3, AshishAgar4, Michael Kalloniatis2,5 & S. MojtabaGolzan1,” A combined convolutional and recurrent neural network for enhanced glaucoma detection”, Jan 2021 [9] Hagiwara, Y., Koh, J. E. W., Tan, J. H., Bhandary, S. V., Laude, A., Ciaccio, E. J., ... & Acharya, U. R. (2018). Computer-aided diagnosis of glaucoma using fundus images: A review. Computer methods and programs in biomedicine, 165, 1-12. [10] Almazroa, A., Alodhayb, S., Osman, E., Ramadan, E., Hummadi, M., Dlaim, M., ... & Lakshminarayanan,V. (2018, March). Retinal fundus images for glaucoma analysis: the RIGA dataset. In Medical Imaging 2018: Imaging Informatics for Healthcare, Research, and Applications (Vol. 10579, pp. 55-62). SPIE.
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Prof. B. R. Ban, Shubham Lipane, Prathamesh Dagade, Sakshi Chavan, Narendra Gadhe. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET60644
Publish Date : 2024-04-19
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

