Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Design and Fabrication of Automated Accumulator for Waste Management
Authors: P. Gokul, S. Madhava Reddy, K. Sudhakar Reddy, D. Manoj Kumar, P. Sirisha, P. Ravali
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.63481
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
In today\'s society, the escalating issue of improper waste disposal looms large. As population density swells, so does the volume of waste produced, straining landfill capacities, polluting the environment, and posing grave health risks. Traditional waste collection approaches fall short, proving costly, laborious, and inadequate in addressing the mounting problem. This underscores the urgent need for innovative solutions. Enter the automated accumulator: a pioneering system designed to revolutionize waste management by streamlining processes and boosting efficiency. Combining cutting-edge sensor technology, robotics, and data analytics, the automated accumulator redefines waste management efficiency. Through instantaneous waste identification and categorization, it revolutionizes resource distribution, slashes manual labor requirements, and curtails environmental pollution. This ambitious project endeavors to unveil an innovative solution poised to completely transform the landscape of waste management, targeting the mitigation of environmental and health risks associated with mishandled waste, thereby elevating the holistic well-being of communities. The urgent imperative driving this endeavor is crystal clear: we must pioneer a comprehensive solution that not only optimizes the intricate processes of waste collection and sorting but also prioritizes the well-being of sanitation workers by lightening their workload while simultaneously fostering a culture of environmental responsibility and sustainability. The creation and rollout of an automated accumulator mark a major advancement in waste management, addressing the pressing need for effective waste handling while supporting sustainability objectives through recycling promotion and environmental protection.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Waste management is a crucial aspect of modern life and environmental sustainability. The generation of waste has increased significantly, posing serious challenges to all ecosystems. Effective waste management is very essential to promote sustainable development. This report provides a comprehensive overview of various waste management strategies, technologies, and their implications for a sustainable future.
Waste can be broadly classified into two categories: solid waste and liquid waste. Solid waste includes household waste, industrial waste, and hazardous waste, while liquid waste comprises wastewater from domestic and industrial sources. Each type requires specific treatment methods to minimize its impact on the environment.
The waste management hierarchy outlines the preferred methods for dealing with waste, prioritizing reduction and recycling over disposal.
The hierarchy includes five key steps:
- Source Reduction: Minimizing waste generation at the source through practices such as reusing products, reducing packaging, and promoting sustainable consumption.
- Reuse: Encouraging the reuse of products or materials to extend their lifecycle, reducing the need for new resources.
- Recycling: The process of converting waste materials into new products, reducing the demand for raw materials and energy.
- Recovery: Extracting valuable materials or energy from waste through technologies like incineration or anaerobic digestion.
- Disposal: The least preferred option, involving the safe disposal of residual waste in landfills or incineration facilities.

II. LITERATURE REVIEW
Waste management is a critical aspect of environmental sustainability, with numerous studies exploring various dimensions of this complex issue. Waste management includes waste reduction strategies, recycling technologies, public awareness, the environmental and economic impacts. Studies, such as those by Wilson and Araba (2015), highlight the significance of waste minimization through sustainable consumption patterns and the promotion of the "reduce, reuse, and recycle" strategy. These works stress the need for proactive measures to reduce the generation of waste, emphasizing the role of individual and community behaviors in achieving sustainable waste management.
There are traditional waste management systems like periodic and routine clearing by the municipal corporation. But even though these routine maintenances are carried out we often come across overflowing garbage bins from which the garbage spills on to the streets. When trash vans/trucks come irregular to homes, many civilians empty their overloaded dustbins in open spaces. [1] Ineffective waste management leads to pollution. The pollution created by humans have become the major factor that caused destructions to the surrounding environment
Several designs and projects have been conducted throughout the world on waste management in the hope of reducing the waste generation especially the pollution [3]. It ranges from autonomous, mechanical, and human-based computation designs.
A few of the projects on waste management are:
Smart e- dustbin, a smart way of handling the garbage by using the IOT protocol for transmitting the dustbin status wirelessly, which can notify to the concerned person via emails to replace the filled dustbin.[1]
It focuses to develop a model of smart dustbin which can be effectively used at public places in smart cities. A smart city is incomplete without a smart waste management system.[4] Public awareness and education play a significant role in waste management strategies. These initiatives instill environmentally responsible habits among the population that encourage collective responsibility for waste reduction. Governments implemented regulations and policies to guide waste disposal practices, ensuring that industries and individuals adhered to responsible waste management guidelines.
The Indian government has implemented several initiatives and schemes to address the challenges of waste management in the country. One of the prominent programs is the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, launched in 2014 with the aim of making India clean and open defecation-free. This mission focuses on proper waste disposal and has significantly contributed to raising awareness about the importance of cleanliness.

To specifically target the issue of solid waste management, the government introduced the Solid Waste Management Rules in 2016. These rules emphasize waste segregation at the source, encouraging citizens to separate biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste.
III. PROBLEM STATEMENT
Day by day as the population is increasing and the waste produced is also increasing which in turn resulting of landfills and causing diseases to living beings and it pollutes the land. Another major problem is that to provide the basic necessities of the growing population we require various types of materials and resources but due to mixing of different waste is leading to wastage of material which cannot be recovered to the recycling facilities. The existing waste management practices practiced in dump yards pose a significant health and environmental problems. This is due to lack of effective waste segregation system. In dump yards the waste of industries, household, and hazardous waste are mixed together which in result hinders the potential of material recovery which leads to losing of valuable material in dump yards.
A. Proposed Solution
The objective of this paper is to address the mentioned problem by constructing an automated accumulator for collecting and sorting of waste. The main objective if this system is to do the waste management with minimum human intervention, making the process more automated and beneficial to society. The main tasks performed by this system id to automated collection of waste and automated sorting of waste. This system can be used to clean up the dump yards and landfills and provide the recyclable waste to recycling stations. This innovation not only contributes to cleaner environment but also for better waste management.
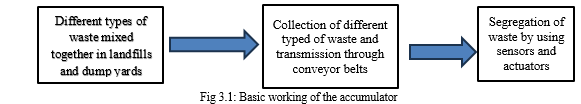
The accumulator gathers the different waste and transmits the waste by using conveyors after the collection mechanism it goes to segregation unit where the waste is segregated by using sensors and actuators.
IV. METHODOLOGY
The process of waste management is highly complicated and which consists of various hard tasks which can’t be achieved automatic. The system is designed with a high mechanism which performs various tasks to achieve a nice waste management. The tasks combined is to achieve efficient waste management. The tasks are the basic steps for segregation of waste. The following are the tasks performed by accumulator.
- Collection of waste
- Transmission of waste
- Segregation of waste
A. Collection of Waste
The initial and crucial step for waste management is collection of waste. To sort the waste and to achieve the further goals with the waste we need to collect the waste to achieve this we need a sophisticated mechanism so that we can collect different types of waste. In dump yards and landfills the waste is scattered everywhere and the different wastes are mixed. It is a hard task to collect the waste. To achieve this, we need a well built and quick mechanism which can collect degradable waste, recyclable waste, and metal waste. After the collection of waste, the waste is sent to the further processes.
B. Transmission of Waste
The next step is to transmission of waste it is the crucial step where the waste is transferred from stating point of the system to ending point. The main components for transmission are conveyor belts, with the help of the conveyor belts the waste is sent from collection unit to segregation unit. We used different conveyors depending on the tasks as to send waste from lower to upper places we use stepped conveyors, to make sure that waste reached to segregation unit in a single order we use spiral conveyor. At the end of the system to send waste into dustbin we use conveyor belts.
C. Segregation of Waste
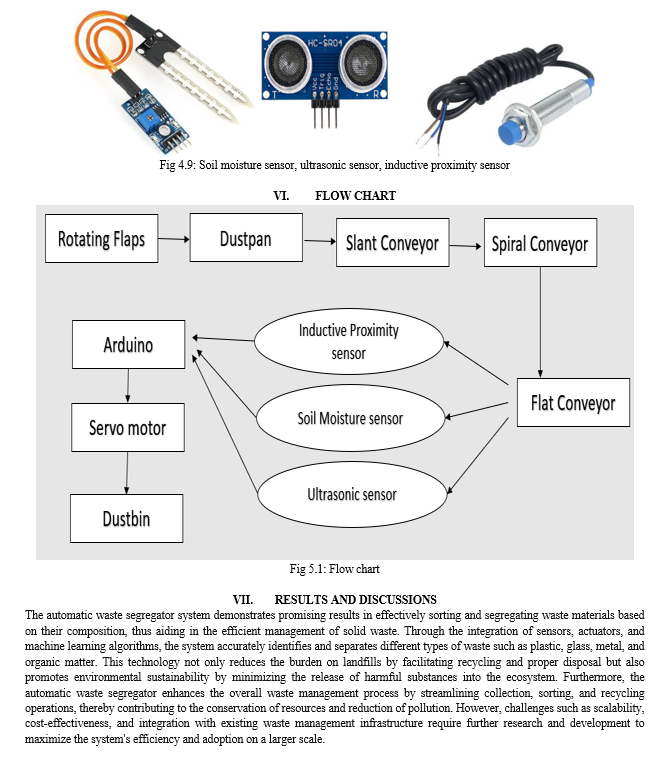
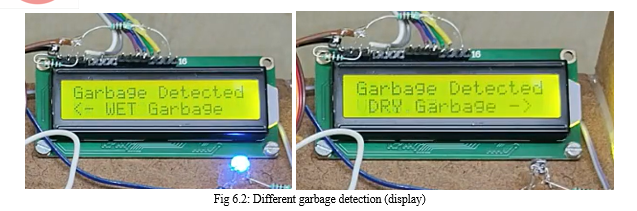
The last step to segregate the waste, the segregation of waste means dividing the waste into their respective categories. In present situation in many dump yards this segregation process is done by using robotic arms, hand picking method, magnetization method where all the processes involve most human intervention. In this system the sorting of waste is done in automatic way by using sensors and actuators. We use different sensors which are used to detect the different wastes and send the electrical signal to Arduino and the signal is sent to servomotor. The servo motor is connected to rotating dustbin where it is divided into 3 parts to collect recycled waste, bio degradable waste and metal waste.
D. Mechanism
The overall mechanism of the system is that at first, we use rotating flaps to pick up the waste from the ground. The flaps push the waste towards the stepped conveyor belt with help of dustpan. The waste is carried through the stepped conveyor which is kept slant. From the slant conveyor belt the waste is sent to spiral conveyor. The spiral conveyor task is to send the waste one by one to the segregation unit. The segregation unit is placed on the last conveyor belt. The sensors are placed on the conveyor belt to the side of conveyor belt. Sensors are connected to Arduino board. When the sensors send signals to their connected pins the Arduino board sends the signals to servo motor to make the degrees of rotation. The servomotor is connected to dustbin as shown in the figure. The dustbin is divided into 3 equal parts where each parts contains their respective type of wastes like degradable waste, metal waste and dry waste.
To make the system semi-automatic we used RC controlled system as we connected wheels on the chassis and fixed motors and motor drivers, this motor drivers are connected to Arduino. With the help of Bluetooth module that is connected to Arduino, it pairs with the Bluetooth devices and controls the movement of the accumulator. Finaly, we have successfully built the working model of the system where we have done some changes to make sure the system performs the various tasks and overcome the different problems.
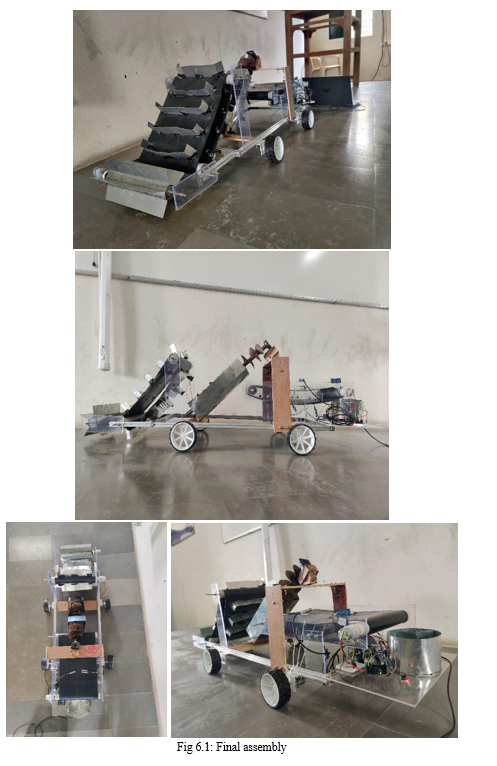
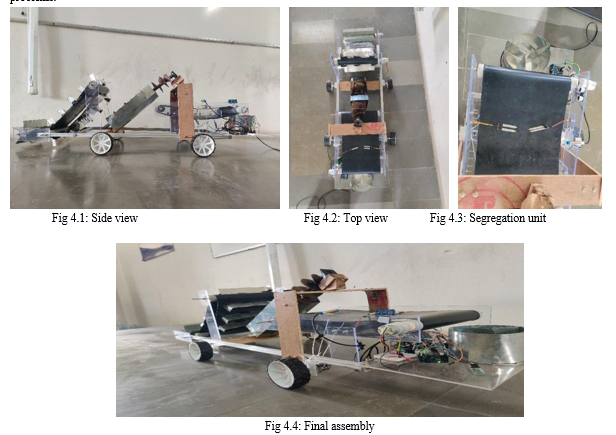

A. Efficiency
Efficiency in waste segregation systems is usually measured by the area covered, but for our prototype, we focused on time. Although our system operates in a small area, the time required for waste segregation is similar to larger systems. Our prototype's efficiency is between 55-60%, meaning it correctly segregates more than half of the waste within the given time frame. This is a good result for a prototype, showing promise for future scaling.
B. Efficiency Calculation
General efficiency = Σ(P*WAGR)
P = Total population of the particular area.
WAGR = Waste amount generation rate.
Conclusion
The Automatic Waste Segregation System, integrated within the accumulator, represents a groundbreaking advancement in waste management. Its innovative mechanism not only automates the collection of waste but also meticulously segregates it into distinct categories, namely metal, dry, and wet waste. The system\'s uniqueness lies in its ability to detect the surrounding waste automatically, enabling a seamless and proactive waste management process. The incorporation of sensors, intricately connected to a control unit, empowers the system to identify and categorize waste types accurately. This not only enhances the overall efficiency of waste segregation but also underscores the system\'s adaptability to diverse waste materials. By automating both collection and segregation, this system stands as a testament to its effectiveness and forward-thinking design, offering a more sustainable and technologically advanced solution to modern waste management challenges. In essence, the Automatic Waste Segregation System within the accumulator heralds a new era in waste management, aligning with the imperative for smarter, more efficient, and environmentally conscious solutions. A. Future Scope 1) Advanced sensor technology enables precise detection and identification of diverse materials, significantly improving the efficiency of waste segregation systems. 2) Seamless connection to urban infrastructure for optimized waste management. 3) Utilizes renewable energy and efficient components to reduce carbon footprint. 4) AI optimizes sorting, predicts waste patterns, and improves efficiency. 5) Educates users on proper disposal and tracks recycling contributions. 6) Reduced costs and savings enhance broader adoption and implementation.
References
[1] Kolhatkar, C., Joshi, B., Choudhari, P., & Bhuva, D. (2018). Smart E-dustbin. 2018 International Conference on Smart City and Emerging Technology (ICSCET). doi:10.1109/icscet.2018.8537245. [2] Dugdhe, S., Shelar, P., Jire, S., & Apte, A. (2016). Efficient waste collection system. 2016 International Conference on Internet of Things and Applications (IOTA). doi:10.1109/iota.2016.7562711. [3] Hirdi Othman, Mohammad Iskandar Petra, Liyange Chandratilak De Silva, & Wahyu Caesarendra (2019). Automated trash collector design. The 8th Engineering International Conference 2019. Journal of Physics: Conference series. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1444/1/012040. [4] Rohit, G. S., Chandra, M. B., Saha, S., & Das, D. (2018). Smart Dual Dustbin Model for Waste Management in Smart Cities. 2018 3rd International Conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT). doi:10.1109/i2ct.2018.8529600. [5] B.S. Susha, Rahul Madhukara Shanbog, Shaik Hussain, Shreyas H. K, Shreyas S (2021). Automatic Segregation Of Waste using Robotic Arm. International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT). Paper id: IJCRT2107532. [6] Tiwari, C., & Nagarathna, K. (2017). Waste management using solar smart bin. 2017 International Conference on Energy, Communication, Data Analytics and Soft Computing (ICECDS). doi:10.1109/icecds.2017.8389615. [7] Aleena VJ, Kavya Balakrishnan, Rosmi TB et al. Automatic Waste Segregator and Monitoring System. Journal of Microcontroller Engineering and Applications. 2016; 3(2): 1–7p. [8] M. Rajeshwari, Mandara B.L, Meghana M.V, Meghana G, & Vaishnavi C (2019). Automatic waste segregator. International Journal of Latest Engineering Research and Applications (IJLERA).
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 P. Gokul, S. Madhava Reddy, K. Sudhakar Reddy, D. Manoj Kumar, P. Sirisha, P. Ravali. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET63481
Publish Date : 2024-06-27
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

