Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Flood Detection and Monitoring using IOT
Authors: Vaishnavi Chitragar, Sanket Patil, Anushka Salve, Pratik Wagh, Vaishnavi Wakchaure
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.64688
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
One of the most destroying characteristic pf natures that can happen any place in the globe is flooding. In consideration to keep an eye on the surge circumstance particularly in a low line range, a framework was put and developed to track the Dam water level, Door opening status and precipitation level in real-time. A application-based data source for the open, reacting to their require for data on water conditions and flooding, and a Status page for data approximately flooding between the included specialists and specialists to move forward their obligations and participation are the two essential objectives of the made framework. A sensor organizes, a processing/transmission unit, and a database/application server make up the made framework. With the offer assistance of a remote sensor arrange that communicates with the application server over versatile Common Parcel Radio Benefit (GPRS), it is conceivable to remotely screen this real-time information of water condition. To encourage communication between the application server a microcontroller will be utilized. Ultrasonic sensors will be utilized to bring the correct level of the water in the dam. The entryway opening status will be picked up through a few sensors like water sensors and rain sensors. The versatile application which is made and associated with a few IOT Sensors will be having two major segments i.e. Flood Status and Emergency services. A few crisis administrations like healing centres, transport will be included in this application which will be valuable in the overwhelmed circumstances and post overflowed circumstances.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Natural disasters, such as floods, cannot be completely avoided. Their sudden occurrence can lead to significant destruction of homes and loss of life. There is no way to completely prevent natural calamities, and floods are no exception. Many existing flood monitoring systems have limited functionality, and a large portion of the population lacks access to vital meteorological information, which hinders their ability to track or anticipate flood events. Implementing a smart Internet of Things (IoT) flood monitoring system can address these challenges effectively, benefiting both urban and rural areas. This system would allow anyone with internet access to monitor conditions and receive alerts about potential flooding, enabling quicker responses. One of the most common natural disasters that can happen anywhere in the world is flooding. An intelligent system called the "IoT Early Flood Detection & Alert System" closely monitors many natural elements in order to forecast when a flood is likely to occur. [1] This allows us to take necessary precautions and reduce the damage that the flood might inflict. Devastating property damage and human casualties can result from natural catastrophes such as floods. In India, a country often affected by heavy rainfall, extreme weather events can trigger floods, especially during the monsoon season from June to October. Climate change and glacial melting exacerbate these risks, leading to tragic consequences, including loss of life and widespread damage. Government agencies often struggle with slow response times due to bureaucratic procedures, highlighting the need for real-time data monitoring to protect communities and minimize economic losses. Timely notifications are essential to relocate at-risk populations swiftly, aiming to reduce damage by at least 30%. The complexity of current systems can delay alerts, making it crucial for both government entities and the public to be aware of flood risks. Our proposed technology integrates weather forecasting with predictive capabilities, using water flow and ultrasonic sensors to monitor water levels and assess flood severity. This "IoT Early Flood Detection & Alert System" continuously tracks various environmental factors to predict flooding, allowing for proactive measures to mitigate potential damage. With Wi-Fi connectivity, data can be easily accessed from anywhere, enhancing community preparedness and response to natural disasters.[2]
In the face of increasingly unpredictable weather patterns due to climate change, the need for advanced flood monitoring and detection systems has never been greater. Internet of Things (IoT) technology offers a transformative approach to flood management by connecting sensors, data analytics, and communication networks to provide real-time monitoring and early warnings. Unlike traditional flood systems that rely on static data or manual intervention, IoT-based systems collect and transmit dynamic data from water levels, rainfall, and weather conditions, ensuring constant surveillance of at-risk areas. [3] These systems allow authorities and residents to respond quickly to flood threats, reducing the potential for damage and loss of life.
What sets IoT-enabled flood monitoring systems apart is their ability to operate autonomously across vast and remote areas, using low-power networks and edge computing. By integrating machine learning algorithms, these systems can predict flooding events more accurately by analysing patterns and triggering timely alerts. This real-time, accessible flood data empowers both urban and rural communities, ensuring that timely decisions can be made before a disaster strikes. As IoT technology continues to evolve, its role in flood detection will become a critical component of resilient smart cities, where adaptive systems can mitigate the devastating impacts of natural disasters. In an era marked by the escalating unpredictability of climate change, the imperative for sophisticated flood monitoring systems has reached critical levels. Traditional methods fall short in providing the timely data and insights needed to protect vulnerable communities. Enter the Internet of Things (IoT), a game-changing technology that merges sensors, data analytics, and communication networks to deliver real-time monitoring and alerts. By harnessing dynamic data from various environmental factors, IoT-based systems empower both urban and rural populations to respond swiftly to impending flood threats. [4]
What truly distinguishes these innovative systems is their capacity for autonomous operation in remote areas, leveraging low-power networks and advanced machine learning algorithms. This allows for more accurate predictions and timely warnings, transforming flood management into a proactive rather than reactive approach. As we look toward the future, integrating IoT technology into our flood detection strategies will be essential for building resilient smart cities capable of withstanding the challenges posed by natural disasters. The time to invest in these systems is now, ensuring we are better prepared for whatever the changing climate brings.
II. RELATED WORK
In the paper [1], It is understood that Flood management has become a crucial area of research due to the increasing frequency and severity of flooding events worldwide, exacerbated by climate change. This literature survey synthesizes recent advancements in information systems that utilize Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies for effective flood monitoring. Various studies highlight the deployment of IoT devices to collect real-time data on environmental variables such as temperature, precipitation, and water levels. These devices enable efficient data gathering crucial for timely flood warnings. The integration of cloud computing with IoT enhances data security and reliability, facilitating better management of the collected data. The visual representation of data through web-based dashboards allows for real-time monitoring and decision-making. The literature also addresses challenges related to data quality, such as missing or anomalous data in IoT networks. Researchers are exploring advanced techniques like tensor learning to address these issues. Ongoing research is focused on improving the adaptability of flood monitoring systems, enhancing predictive capabilities, and ensuring that these technologies are accessible to vulnerable populations.
In the paper [2], The paper addresses a Research that indicates a significant gap between perceived and actual incidence rates of water damage in households. For instance, a study found that while participants believed only 37% of households experience such issues, the actual figure is over 57% (Maer et al., 2022). Many existing flood detection systems leverage various technologies, including sensors that monitor water presence and provide alerts. These systems are critical for preventing water damage in residential and commercial buildings. Traditional systems typically require a stable internet connection or a central hub, which can be a limitation in emergencies (Maer et al., 2022). The primary causes of flooding identified include bursting pipes, corrosion, and faulty appliances, underscoring the need for effective monitoring systems. The technology used is this paper is Various commercially available flood detection systems, such as those from Fibaro, Wally, and Somfy, utilize wireless communication protocols (e.g., Z-Wave, ZigBee) but often depend on internet connectivity. This reliance can pose risks during outages (Maer et al., 2022). The literature suggests a clear gap in the availability of affordable, reliable, and autonomous flood detection systems. The work by Maer and Pop presents a promising solution that integrates IoT technology while overcoming key challenges faced by existing systems. In the paper [3], The paper addresses that Flooding remains one of the most catastrophic natural disasters globally, necessitating effective monitoring and alert systems. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology presents innovative solutions for real-time data acquisition and communication regarding flood risks. This literature survey highlights recent advancements and implementations in IoT-based flood monitoring systems, particularly in the context of smart cities. Disaster Management Systems Using IoT Varghese et al. (2019) proposed an IoT-based disaster monitoring system for dams. This system utilizes the ESP8266 WiFi module to relay data to a cloud server, enabling real-time monitoring and effective management of water-related issues. The emphasis on cloud connectivity enhances the system's scalability and accessibility The proposed IoT-based flood monitoring system utilizes a combination of ultrasonic sensors, GSM modules, and Arduino boards to detect and alert users of rising water levels. The system's architecture is designed to relay critical data to users in real-time, thereby enhancing public safety and emergency response efforts. By integrating various components such as LCD screens for display and GSM for communication, this system aims to provide a comprehensive solution for flood management.
In the Paper [4], It is understood that Natural disasters like floods result in significant loss of life and economic hardship. While prevention of these disasters is impossible, effective planning and monitoring can mitigate their impacts. Traditional flood warning systems often struggle with real-time data integration and timely alerts. This paper proposes an innovative flood monitoring and warning system based on a heterogeneous sensor network (Het-Sens), designed to provide accurate forecasting and prompt alerts. This low-cost, low-power system enhances existing flood response capabilities by using various sensors to monitor precipitation and water levels, transmitting critical data through reliable channels. Floods, particularly in regions like India, pose significant risks due to intense rainfall from monsoons, hurricanes, and other climatic events. The absence of effective early warning systems exacerbates the situation, leading to avoidable casualties and property damage. There is a pressing need for advanced flood forecasting and monitoring systems to provide timely alerts and enhance public safety. Data from the sensors is transmitted to a central base station, which processes the information and sends out alerts via RF transmitters that can override existing FM radio frequencies, ensuring broad and effective communication during emergencies.
In the paper [5], the concept focuses on various flood detection systems developed using IoT and sensor technologies. Here’s a brief overview based on the cited works. These studies illustrate the ongoing efforts to create reliable and cost-effective flood detection systems, particularly in developing regions, highlighting the importance of real-time monitoring and early warning mechanisms to enhance public safety during flood events. Variety of microprocessors and microcontrollers are required for the design of iot boards.. Using a dialect of features from the programming languages such as c and cpp, the microcontroller is programmed. A buzzer is an electronic device, which consists of a number of sensors connected to a control unit that determines whether to produce a warning in the form of a continuous or intermittent beeping sound. Once the water level, water flow, humidity level is been increased and sensed by the sensor, it shows the data in app. Many systems utilize multiple sensors (water level, flow, humidity) to gather comprehensive data about potential flooding conditions. The literature underscores the critical role of IoT in flood detection and management. By leveraging advancements in sensor technologies and communication systems, researchers are paving the way for more effective early warning systems. Future work should focus on enhancing the scalability, reliability, and integration of these systems into broader emergency management frameworks to maximize their impact in flood-prone regions.
In the paper [6], Flooding is a significant disaster in Sri Lanka, compounded by inadequate preparedness and communication during such events. This paper presents an Intelligent Flood Management System designed to enhance disaster response through automated communication, resource allocation, and safety location identification using genetic algorithms. The system operates via a smartphone ad-hoc network, ensuring continuous connectivity despite infrastructure failures. This research aims to improve decision-making and reduce risks associated with flooding in Sri Lanka. Floods frequently devastate Sri Lanka, leading to loss of life and property. Traditional flood management methods are inefficient and time-consuming. This paper proposes a systematic approach to manage all disaster phases—Mitigation, Preparedness, Response, and Recovery—through automated processes. Our mobile application utilizes a mesh network for communication and ensures effective resource allocation. Existing systems like Sahana Eden and Ushahidi lack automated responses and location management features. This research addresses these gaps by introducing an automated, location-aware flood management system. The Intelligent Flood Management System offers a comprehensive approach to disaster management in Sri Lanka, significantly improving communication, resource allocation, and safety measures during flooding events.
III. PROPOSED SYSTEM
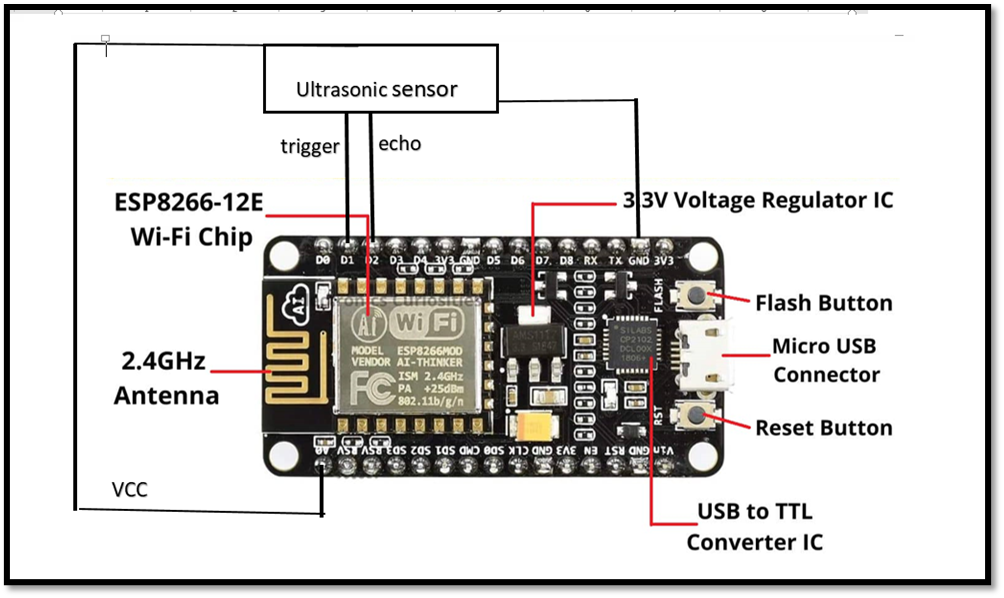 Fig. 1 A sample line graph using colors which contrast well both on screen and on a black-and-white hardcopy[9]
Fig. 1 A sample line graph using colors which contrast well both on screen and on a black-and-white hardcopy[9]
A. Key Components
- ESP8266-12E Wi-Fi Chip
- This is the central component of the system, responsible for providing internet connectivity via a 2.4GHz antenna. It connects to a cloud or local server to transmit data wirelessly.
- Ultrasonic Sensor
- This sensor is used to measure the distance to the water surface, likely to monitor the water level in the river. It works by sending a sound wave (trigger) and measuring the time taken for the echo to return after reflecting off the water surface.
- 3.3V Voltage Regulator IC
- Used to regulate the voltage supplied to the ESP8266 and ensure it operates at the required 3.3V, preventing overvoltage damage.
- Micro USB Connector
- Allows the system to be powered via a USB cable, often used for programming the microcontroller or providing power.
- USB to TTL Converter IC
- This converts USB signals to TTL logic levels, which is required for serial communication with the ESP8266 during programming and debugging.
- Buttons (Flash, Reset)
- The Flash Button is used when updating the firmware of the ESP8266.
- The Reset Button restarts the system.
This hardware setup would be used for a flood detection system where the ultrasonic sensor continuously measures water levels, and the ESP8266 transmits this data to a monitoring server. Alerts can be triggered when the water level reaches a critical threshold, which is then processed by software to provide early flood warnings.
Conclusion
The proposed Internet of Things (IoT) flood disaster management system aims to implement innovative strategies to reduce the risk of human casualties and damage to critical infrastructure from both natural and man-made disasters. This initiative outlines a plan to deploy affordable wireless sensor networks capable of detecting various disasters, including floods, wildfires, and landslides, and subsequently alerting residents along coastal areas. Ultimately, this study seeks to establish a foundation for IoT disaster management systems, highlighting insights from prior research and identifying future research directions to address challenges in disaster management effectively. IoT-based flood monitoring and detection systems present a powerful, forward-looking solution for minimizing the risks and damages caused by floods. By harnessing interconnected devices, real-time data collection, and predictive analytics, these systems provide a seamless, automated approach to flood management. They enable early detection, immediate alerts, and actionable insights, allowing for proactive responses and reducing the vulnerability of both urban and rural communities. As IoT technology continues to evolve, it will enhance the resilience of cities and regions, offering a scalable and accessible tool for disaster mitigation. Ultimately, the integration of IoT into flood detection marks a critical step towards creating smart, adaptive, and safer environments in the face of climate-induced challenges.
References
[1] A. J. Varghese, A. J. Thomas, A. Peter, B. P. Rajeev, K. S. Sajitha, & D. E. George, “IoT based Disaster Monitoring and Management System for Dams (IDMMSD)”, 1st International Conference on Innovations in Information and Communication Technology (ICIICT), 2019. doi:10.1109/iciict1.2019.8741464. [2] M Mousa, X Zhang, C Claudel. Flash Flood Detection in Urban Cities Using Ultrasonic and Infrared Sensors. IEEE Sensors Journal. 2016. [3] S. A. Shah, D. Z. Seker, S. Hameed, & D. Draheim, “The Rising Role of massive Data Analytics and IoT in Disaster Management”, Recent Advances, Taxonomy and Prospects. IEEE Access, pp1–1, 2019. doi:10.1109/access.2019.2913340 [4] E. Basha, et al “Design of early warning flood detection system for developing countries,” in Proc. of the Conference on Information and Communication Technology and Development, Dec 2007. [5] Emil-Daniel MAER, Adrian-Augustin POP, Dan-Cristian POPA, Ioana-Cornelia GROS, Hybrid water collecting and management system using Smart Home Technologies, 2021 28th International Workshop on Electric Drives: Improving Reliability of Electric Drives (IWED), Moscow, Russia. Jan 27 – 29, 2021. [6] Anjali Sharma, Alka Chaudhary, Ajay Rana, Anil Kumar, Flood Monitoring System using IoT, 2021 9th International Conference on Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization (Trends and Future Directions) (ICRITO) Amity University, Noida, India. Sep 3-4, 2021 . [7] Dang, Qi, Qimei Cui, Zhenzhen Gong, Xuefei Zhang, Xueqing Huang, and Xiaofeng Tao. \"AoI Oriented UAV Trajectory Planning in Wireless Powered IoT Networks.\" In 2022 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), pp. 884-889. IEEE, 2022. [8] Pushpa Rani, M., BashiruAremu, and Xavier Fernando. \"Forecasting Flash Floods with Optimized Adaptive NeuroFuzzy Inference System and Internet of Things.\" In Pervasive Computing and Social Networking: Proceedings of ICPCSN 2022, pp. 23-38. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2022. [9] M. Bhosale, and M. Chavan, “Review on Flood Monitoring and Early Warning System,” vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 455-461, 2019. [10] Ryan Hanson - Water Leak Detection System, Senior Project Electrical Engineering Department California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo 2017. [11] S. Sabu, and N. Elizabeth, “Kerala Floods - A Model of Rescue and Rehabilitation using Information Technology and Social Media based Crowdsourcing,” IEEE India Info. vol. 13, no. 3 Jul - Sep 2018. [12] S. Sabu, and N. Elizabeth, “Kerala Floods - A Model of Rescue and Rehabilitation using Information Technology and Social Media based Crowdsourcing,” IEEE India Info. vol. 13, no. 3 Jul - Sep 2018. [13] Conti Marco and Silvia Giordano. \"Mobile Ad Hoc Networking: Milestones, Challenges, and New Research Directions\"- IEEE Communications Magazine (2014)
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Vaishnavi Chitragar, Sanket Patil, Anushka Salve, Pratik Wagh, Vaishnavi Wakchaure. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET64688
Publish Date : 2024-10-19
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

