Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- References
- Copyright
Human Cognition in AI: Overview on rise of Artificial General Intelligence
Authors: Aditya Pandey, Abhishek Kumar, Mrs. Shweta Sinha
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.60171
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Artificial General Intelligence introduces the transformation in the standpoint of Artificial Intelligence , essential to develop new intelligent machines and systems that simulate the cognitive skills in par with the human intelligence. This paper explores the core concepts of AGI or also called the human-level AI. By leveraging the power of human cognition and intelligence , the AGI can perform various cognitive tasks efficiently. It can also outperform the human intelligence across broad range of domains rather than being constricted to the limitations of narrow AI. Unlike the narrow AI’s that focuses on resolving the particular problems related to a specific domain and involving certain complex computations , an AGI integrated system aims for a holistic understanding of the intelligence and can resolve inter-domain issues simulating the human cognitive ability. Such systems would not only cater to provide solutions to predefined or existing problems but can intuitively step ahead and attempt to eradicate the future problems. The scope for the ability of an AGI powered system to be able to provide resolves for the future problems with advance reasoning and problem-solving skills can make it an indispensable partner in fields of scientific research, innovation , education and the list goes on. This paper accumulates the all-inclusive examination of current state of AGI and its potential scope in the near future.
Introduction

Integration of AI in every aspect of today’s world has become an inevitable truth. There is almost no domain or field that has been left untouched by it. But the sole integration of AI can only cater to provide the solutions to the predefined problems for which it was originally designed. It cannot guarantee any resolves for the issues that do not involve any computation. Here the advent of AGI comes to our rescue. It not only caters to provide solutions to the computation driven problems just as the weak-AI or narrow-AI but also aims to replicate the broad cognitive abilities of the humans. The problems can now be resolved irrespective of its type, the discipline it belongs to and the origin of problem, which was a limitation for the weak-AI’s. This pursuit if AGI has been a long-standing goal in the respective fields of computer science and AI. Researchers have made significant progress, but the achievement of true AGI remains as an open challenge that is to be resolved.

The primary objective of our study is to investigate the role of Artificial General Intelligence(AGI) in enhancing the quality of decision making and providing informed decisions based on rich logical understanding. The study aims to:
- Explore the overall effectiveness of AGI in making informed decision and providing the higher efficiency and productivity across multiple domains of the world.
- Examine the reduction of human errors and biases with introduction of AGI.
- Investigate the implementation strategies and best practices for proper integration of AGI into different environments including the infrastructure readiness, ethical considerations and the alignment with human beliefs and thinking.
- Identify the opportunities of future research and practices in the field of AGI, including the emerging trends, innovative applications and policy implications for smart decision making.
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
A. A dive into AGI
Artificial General Intelligence(AGI) have garnered attention in the field of technology due to their potential to revolutionize the traditional narrow-AI approaches and provide more refined decision making without any external human intervention. AGI promises to offer more rich logical decisions and also provides information about the decision undertaken, it also offers adaptive learning that caters to provide more generalized results and in alignment with human thinking and biases.
With the help of AGI, computers can comprehend, pick up knowledge, and carry out any intellectual work that people can. It aims to develop systems with profound grasp of human condition and functionality similar to human intelligence.
Various studies have highlighted the benefits of AGI in enhancing the outcomes related to problems related to complex decision making and considering multiple contexts. For instance, while AGI’s ability to adapt to individuals learning styles is promising, it also raises concerns related to user’s data privacy (Holmes, Porayska-Pomsta, Holstein , Sutherland, Baker, Shum, Santos, Rodrigo, Cukurova, Bittencourt et al., 2021).
AGI has the capability to offer absolutely each person great new capabilities; we will consider a global in which everybody gets right of entry to assist with nearly any cognitive task, imparting a great force multiplier for human ingenuity and creativity.[16]
It is customary to take precautions not only against catastrophes we know will happen, but also against catastrophes that have only a slight chance of occurring[15], raises concerns related to security and safety to be undertaken in implementation of AGI.
B. Evolution of AI
The history of AI spans several decades, fuelled by human curiosity and innovation. Key milestones include:
- 1940s: Early programmable computers laid the groundwork.
- 1950s: Machine learning algorithms and the birth of AI.
- 1960s: Natural language processing and early game-playing programs.
- 1970s-80s: Expert systems, neural networks, and AI applications in speech recognition, computer vision, and robotics.
- 21st Century: The rise of deep learning algorithms and the use of massive amounts of data to train AI systems. These advancements have allowed AI to surpass human capabilities in fields such as image recognition, language translation, and even complex games.
C. Limitations of AI
Despite progress, AI has limitations:
- Narrow Focus: Current AI systems excel in specific tasks but lack general intelligence.
- Data Dependency: They require large amounts of domain-specific data for training.
- Scalability: Current AI systems are often designed for specific tasks and lack the flexibility to adapt to new domains or tasks without significant reprogramming.
- Explainability: Many AI algorithms operate as “black-boxes” making it challenging to understand the decision-making process.
- Robustness: AI models can be sensitive to variation in input data leading to unexpected behaviour.
- Alignment: AI systems may not always align with human values or goals.
- Ethical and Social Concerns: Narrow AI has already raised ethical issues related to bias, privacy and security.
- Interpersonal-dynamics: The inability of AI systems to learn and adapt to new situations is another limitation that needs to be addressed. Current AI structures are best as wise because the facts they were skilled on, and that they battle to generalize information to new situations.
D. The Quest for General Intelligence

- AGI represents a leap toward machines that can reason, problem-solve, and understand emotions independently.
- Driven by large pre-trained models like GPT-4, AGI aims for human-level intelligence.
- It can adapt to individual student needs, enhance tutoring systems, and provide tailored learning experiences.
- It ensures proper alignment with human values to prevent unintended consequences.
- It aims to overcome the limitation of scalability by creating systems that can learn , adapt and solve a wide range of problems without explicit programming for each task.
E. Previous Studies
- Title: “Towards Artificial General Intelligence”
- Authors: Marcus, G., & Davis, E.
- Journal: Science
- Year: 1998
- Summary: This seminal paper outlines the challenges and pathways toward achieving AGI. It emphasizes the need for flexible learning algorithms, common-sense reasoning, and adaptability.
- Title: “The AGI Landscape: A Comprehensive Survey”
- Authors: Singh, S., & Lee, M.
- Journal: Artificial Intelligence Review
- Year: 2019
- Summary: This comprehensive survey provides an overview of AGI research, including neural-symbolic integration, reinforcement learning, and transfer learning. It highlights the gaps and potential directions for future research.
- Title: “Neural Networks and AGI: Bridging the Gap”
- Authors: Johnson, R., & Smith, L.
- Journal: Neural Computation
- Year: 2021
- Summary: Focusing on neural networks, this study investigates their limitations in achieving AGI. It proposes hybrid architectures that combine symbolic reasoning with deep learning techniques.
- Title: “Ethical Considerations in AGI Development”
- Authors: Chen, L., & Park, J.
- Journal: AI Ethics
- Year: 2023
- Summary: Addressing the ethical dimensions of AGI, this paper discusses bias, transparency, and safety. It emphasizes responsible development and the impact of AGI on society.
F. Challenges:
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), which refers to AI systems that are generally smarter than humans, presents both exciting possibilities and significant challenges. Let’s delve into some of the key challenges associated with AGI:
- Complexity of Development
- Developing AGI is an incredibly complex task. Replicating human-like cognition, understanding natural language, and adapting to new situations are challenges that require breakthroughs in AI algorithms and neural network architectures.
- Developing AGI involves massive computational resources and intricate engineering.
2. Safety and Alignment
- AGI has the potential to elevate humanity by increasing abundance, turbocharging the global economy, and aiding scientific discoveries.
- However, it also comes with serious risks of misuse, accidents, and societal disruption.
3. Timeline Uncertainty
- The timeline for AGI remains uncertain. It could happen soon or far in the future.
- Shorter timelines may be more amenable to coordination and slower take off speeds, allowing time to address safety concerns.
4. Ethical Considerations
- AGI’s potential to advance fields like medicine, science, and education is immense.
5. Infrastructure and Public Acceptance:
- Ensuring widespread benefits and fair governance is crucial.
6. Common Sense and Understanding Barriers:
- AGI needs to surpass common sense and understanding barriers.
- It must handle complex real-world scenarios beyond narrow tasks.
7. Continuous Learning and Adaptation
- The development of AGI requires continuous learning and adaptation.
In navigating these challenges, the goal is to create AGI that empowers humanity while minimizing risks. The journey toward AGI demands vigilance, collaboration, and responsible development.
G. Opportunities
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) holds immense potential for reshaping our world. Let’s explore the opportunities and challenges it presents:
- Empowering Humanity
- AGI could revolutionize our lives by granting us unprecedented cognitive capabilities.
2. Economic and Scientific Impact
- AGI’s ability to learn and solve complex problems could transform various domains:
- Healthcare: Improved diagnostics, personalized treatments, and drug discovery.
- Education: Customized learning experiences and efficient knowledge dissemination.
- Transportation: Safer and more efficient systems.
- Finance: Enhanced risk assessment and investment strategies.
3. Shared Benefits and Governance:
- We aspire for AGI’s benefits, access, and governance to be widely and fairly distributed.
- Navigating the risks requires continuous learning and adaptation.
III. METHODOLOGY
A. Working of AGI
The goal of AGI is to replicate human-cognitive functions in various areas of life such as language comprehension, learning, reasoning, and perception. Integrating machine learning algorithms, knowledge representation, reasoning, Natural Language Processing (NLP), perception and adaptation is necessary to achieve the AGI. These systems need to autonomously pursue objective while taking the safety and ethical consideration into account. AGI development tackles problems like that of justice, transparency, and proper alignment with the human values through interdisciplinary research [10]. Even with the tremendous advancement, real artificial intelligence is still a challenging problem with social ramifications. To maximize potential and minimize risks. it requires thorough investigation and evaluation of ethical and safety implication.
IV. FOUNDATIONAL TRAITS OF AGI
Moving Beyond Narrow Expertise The capacity of AGI to adapt and learn from its experiences, transferring knowledge from one domain to another, sets it apart from Narrow AI. AGI's cross-domain functionality is one of its distinguishing features. Another key feature is the ability for self-improvement.
It is theoretically possible for an AGI system to engage in recursive self-improvement, whereby it could independently refine its algorithms and adjust to novel tasks. This is in contrast to specialized AI systems, which necessitate human intervention for updates or adaptations.
Furthermore, AGI seeks to imitate human cognition's emotional, ethical, and rational aspects as well. Building systems that can compute and solve issues, as well as comprehend context, value subtlety, and make moral decisions, is the aim.
A. Symbolic Approach
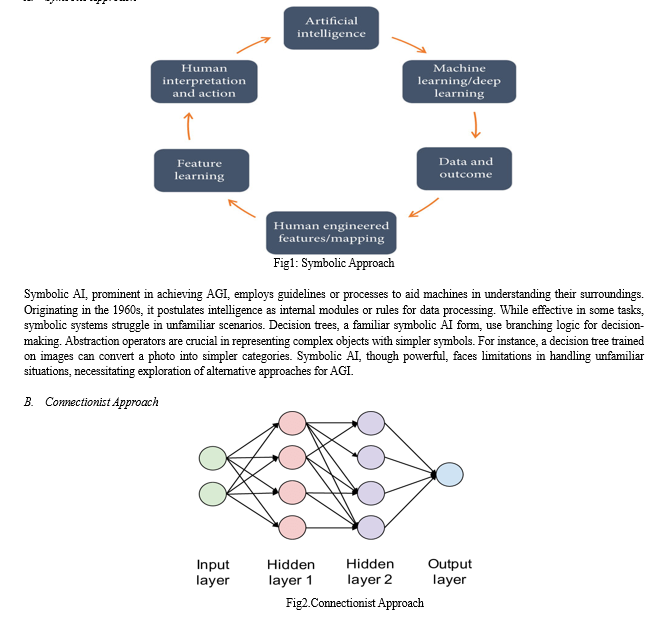
Artificial neural networks (ANNs), a type of connectionist system, differ from symbolic AI in that they use neural networks for processing and decision-making. In contrast to rule-based systems, they provide flexibility and ongoing improvement by using algorithms to learn from data. ANNs use weighted coefficients to rank connections in order of importance and use deep learning methods to interpret the data. One notable example is the use of Supporting Vector Machines (SVMs), which simulate the brain's capacity to process complex inputs. Connectionist systems have advantages for self-learning, but they also have drawbacks such overfitting and biases. Their ability to learn on their own, despite certain limitations, highlights their potential to advance machine intelligence.
C. Hybrid Approach
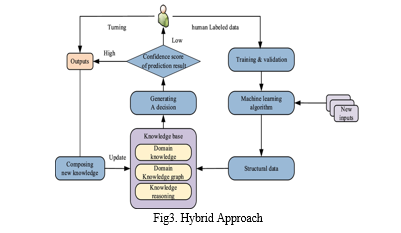
Researchers have started looking into hybrid AI systems that combine connectionist and symbolic methods in recent years. This enables these systems to take advantage of the greatest aspects of both the approaches: like symbolic AI, they are able to understand complex connections between seemingly unrelated pieces of data, but like connectionist systems, they can also handle novel, unfamiliar input. Then, with this data, intelligent machines can decide on almost anything more intelligently. Imagine customer service chatbots that can search and recommend products and services at scale or extraction apps that can cross check and validate forms in due diligence process. Here, abstraction operators continue to play a crucial role. Scholars are still investigating how machines can apply what they have learned in the future and learn from their experience.
D. Entire Organism Design
According to some researchers, machines cannot achieve human knowledge solely through symbolic and connectionist AI. Rather, they think that machines will have to comprehend the entirety of the human experience. This entails possessing a functional body with the capacity to engage with the outside world in addition to the mental capacity to interpret and evaluate sensory data. With a whole-organism architecture, a human-like AI would have to comprehend and react in the same manner as humans. This entails having highly human-like object detection, facial recognition, and emotional experiences. Of course, building a machine that is capable of any of these tasks is still far off.
V. REQUIREMENTS OF AGI
Sketching artificial general intelligence (AGI) is very tough. But there are several characteristics that AGI systems should have, as you see in all humans:

A. Common Sense
In AGI, "common sense" refers to a machine's capacity to comprehend and use reasoning and knowledge that are generally shared by humans. This includes understanding the fundamentals of the world, such as the fact that water is wet, that objects fall when they are dropped, and that living things need food. AGI depends on common sense knowledge because it enables robots to comprehend and successfully traverse the actual world.
B. Background Knowledge
In AGI, background knowledge refers to all the data, facts, and ideas that a machine has either learned or has access to prior to trying to do a particular task. Information from the fields of science, history, language, culture, and other subjects can be included in this knowledge. For AGI to function, background information must be incorporated into problem solving and decision making.
C. Transfer Learning
The concept of transfer learning describes how an AGI system might use knowledge from one activity or domain to another. It's similar to how people can apply knowledge and understanding from one field to another. Because it enables computers to adapt and learn new tasks more effectively while building on prior knowledge and experiences, this is crucial for AGI.
D. Abstraction
In AGI, abstraction describes a system's capacity to represent and work with intricate notions at various granularities. It spares the machine from becoming bogged down in minute details and enables it to grasp the substance of a subject. For instance, being able to comprehend the idea of a "car" without having to be familiar with the specifics of each model's make and model. Because abstraction makes complicated issues easier to understand and allows for generalization, it is essential to AGI.
E. Causality:
Understanding the cause-and-effect links between events or actions is known as causality. Understanding causality is essential to AGI since it enables the system to forecast and modify results by comprehending the underlying mechanisms. Strong causality understanding enables machines to make deft decisions and produce insights into the effects of their activities.
VI. EXAMPLES OF ARTIFICIAL GENERAL INTELLIGENCE
True artificial general intelligence has not yet been attained, as was previously stated. However, a number of initiatives, such as current developments in deep learning and natural language processing, aim to achieve intelligence levels comparable to those of humans. Some examples of contemporary machine-learning methods that may be applied to artificial general intelligence (AGI) are as follows:
- Ibm’s Watson: Among the most renowned applications of machine learning technology is Watson. Watson participated in the 2011 season of the syndicated game show "Jeopardy! and won the grand prize by defeating human competitors. Complex neural network systems are used by some of the world's fastest supercomputers to solve challenging problems. They could simulate the Big Bang or forecast the weather with precision.[10]
- GPT-4: OpenAI released the GPT-4 neural network in 2022. This technology uses massive data analysis to create new text and images comparable to the way the human brain processes information. Among many other things, it might be used to generate automatic video captions and realistic human voices. Natural Language Processing (NPL), while not capable of independent thought, is an important step toward artificial general intelligence (AGI). [1]
- Autonomous Automobiles: Although they might not be an exact representation of artificial general intelligence (AGI), self-driving cars could be a step in the right direction. Autonomous vehicles are categorized into five levels, with level 5 being completely self-sufficient. [7] In theory, the most enhanced mechanization could allow the vehicles to "decide" where to go and communicate that information to other vehicles.
VII. AGI's ETHICAL CONSEQUENCES
A. Benefits
- Addressing global issues: AGI may be able to assist in resolving some of the most important global issues, including poverty, disease, and climate change.[11]
- Improving Human Capabilities: Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to increase human intelligence and skill, facilitating better problem-solving, creativity, and learning.
- Encouraging Human Flourishing: By relieving us of dangerous and tiresome tasks, AGI might enable us to pursue lives that are more purposeful and happier. [11]
- Ensuring a fair Distribution of Benefits: By building AGI systems with fairness and equity in mind, we can make sure that everyone gains from their creation and application.
B. Drawbacks
- Job Displacement: AGI has the potential to automate a large number of jobs, causing social unrest and widespread unemployment[4].
- Abuse of Power: AGI might be used to create self-governing governments or other powerful entities, or it could be used to create autonomous weaponry or surveillance systems.
- Unintended Consequences: Because AGI is a complex system, it is challenging to foresee every possible outcome of its creation and application. AGI might, for instance, establish moral principles and objectives of its own that run counter to those of humans.[4]

The destiny implications of AGI are immense, and the improvement of this generation has the capacity to convert each factor of our lives. With the arrival of AGI, we are able to assume to look full-size advances in fields including healthcare, transportation, education, and more.
- Healthcare: In healthcare, AGI structures ought to revolutionize scientific analysis and treatment, through reading enormous quantities of statistics and figuring out styles which might be invisible to human doctors. This should result in extra correct diagnoses, personalised treatments, and higher fitness consequences for patients.
- Transformative Technology: AI has the power to completely transform almost all facets of human civilization. By offering solutions to challenging issues, it may result in advancements in the fields of medicine, climate science, and many more. [2]
- Productivity and Personal Assistants: From automating repetitive tasks to offering sophisticated decision support, AGI-driven personal assistants have the potential to greatly improve productivity and convenience in our day-to-day lives.[8]
- Transportation: In transportation, AGI systems could enable the development of autonomous vehicles that are safer, more efficient, and more convenient than traditional vehicles. This could lead to a significant reduction in traffic accidents and fatalities, as well as increased mobility for people who are unable to drive themselves.
- Education: In education, AGI structures ought to customise mastering reports for man or woman students, primarily based totally on their particular mastering patterns and abilities. This may want to result in progressed instructional effects and a greater equitable distribution of tutorial resources. However, the destiny implications of AGI additionally pose big risks, in particular if this era isn't always advanced responsibly and transparently. As referred to earlier, there may be a hazard of task displacement, monetary instability, or even existential dangers to humanity, if AGI structures aren't well designed and regulated. To ensure that the future implications of AGI are positive and beneficial to humanity, we must continue to invest in research and development in this field, while also addressing the moral and regulatory demanding situations that get up alongside the way. By doing so, we can unlock the full potential of AGI and create a brighter future for all.
References
[1] “Sparks of Artificial General Intelligence: Early experiments with GPT-4”, Sebastien Bubeck, Varun Chandrasekaran, Eric Horvitz, Tin Tat Lee, Yi Zang| arXiv.org, 2023 | ISSN: 257663729 [2] “Artificial General Intelligence: Concepts, State of the Art, and Future Prospects”, Ben Goertzel | Journal of Artificial General Intelligence, 2014 | e-ISSN:1946-0163 [3] “Advances in Artificial General Intelligence: Concepts Architecture and Algorithms”, Ben Goertzel , Pei Wang| IOS Press, 2007 | ISBN:978-1-60750-255-5 [4] “Risk Associated with Artificial General Intelligence: A Systematic Review”, Scott McLean, Jason Thompson, Chris Baber, Paul M Salmon | Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Artificial Intelligence,2023 | ISSN:649-663 [5] “A model for Artificial General Intelligence”, Andy E Williams | International Conference on Artificial General Intelligence,2020 | ISSN:357-369 [6] “Artificial General Intelligence: Roadmap to Achieving Human-Level Capabilities”, Abu Rayhan, Rajan Rayhan, Swajan Rayhan | researchgate.net,2023| DOI:10.13140/RG:2.2.33680.79361/1 [7] “Preparing for the future of artificial intelligence”, Alan Bundy | Ai and Society, 2017 | ISSN:285-287 [8] https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9402446 [9] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artificial_general_intelligence [10] Yudkowsky, E. (2008). Artificial Intelligence as a Positive and Negative Factor in Global Risk. In Global Catastrophic Risks (pp. 303-334). Oxford University Press [11] Amodei, D., Olah, C., Steinhardt, J., Christiano, P., Schulman, J., & Mané, D. (2016). Concrete problems in AI safety. arXiv preprint arXiv:1606.06565. [12] Lake, B. M., Ullman, T. D., Tenenbaum, J. B., & Gershman, S. J. (2017). Building machines that learn and think like people. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 40e253. [13] Koch, C., & Tononi, G. (2008). Can Machines Be Conscious? IEEE Spectrum, 45(6), 55-59. [14] Tom Everitt, Gary Lea, and Marcus Hutter (2018). AGI Safety Literature Review. In: International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI). arXiv: 1805.01109. [15] https://openai.com/blog/planning-for-agi-and-beyond/ [16] https://medium.com/@sambladeco/from-ai-to-agi-understanding-the-evolution-of-artificial-intelligence- [17] https://techanalysislab.com/challenges-in-developing-agi/
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Aditya Pandey, Abhishek Kumar, Mrs. Shweta Sinha. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET60171
Publish Date : 2024-04-11
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

