Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Introduction
- References
- Copyright
Imminent Impact of Human Resource Accounting in Indian Public Sector Industries
Authors: Randeep Gogoi, Dr. Santosh Marwadikumbhar
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.58022
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
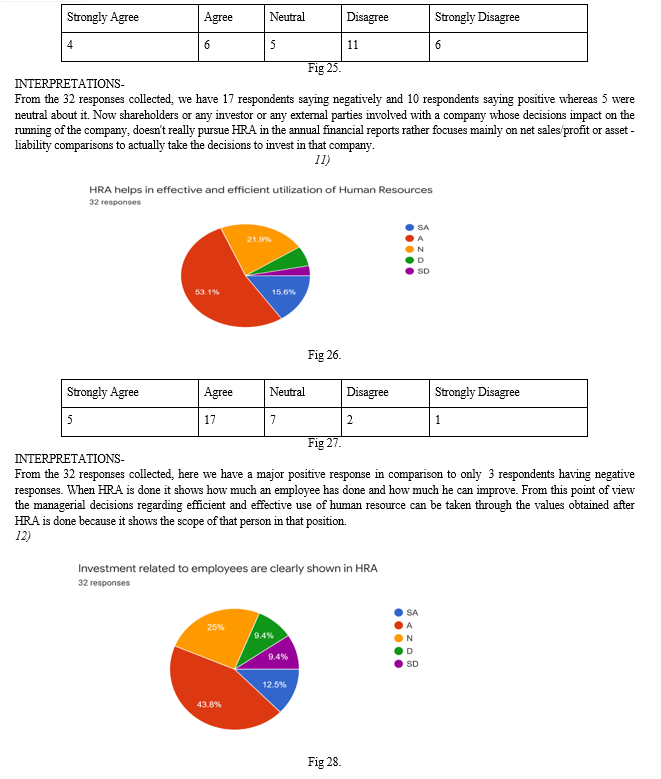
Introduction
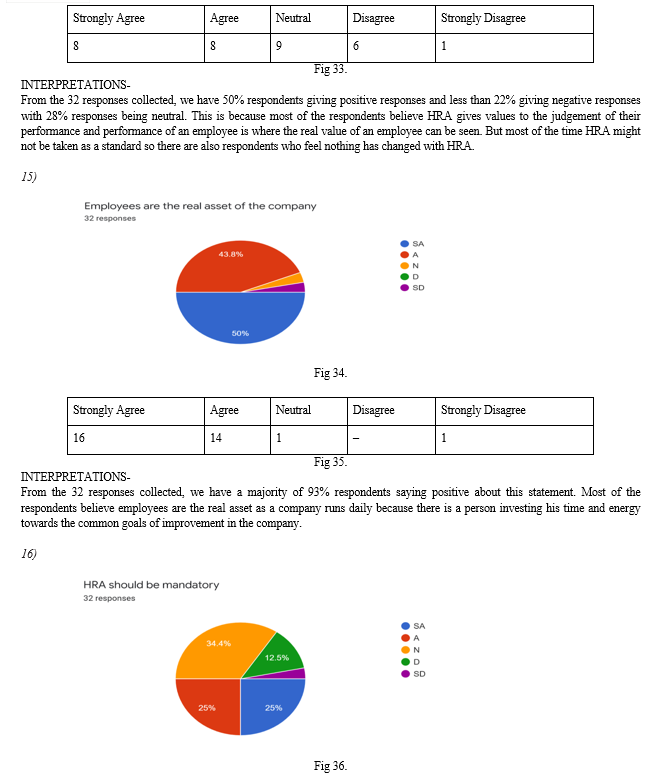
I. INTRODUCTION
A. What is Human Resources?
Human Resource Accounting (HRA) is the process of identifying and reporting investments made in an organization's workforce that are currently not accounted for in conventional accounting practice. It is an extension of standard accounting principles. Measuring the value of human resources can help organizations accurately document their assets. In other words, human resource accounting is a process of measuring the costs incurred by the organization to recruit, select, train, and develop staff.
- History Of Human Resources Accounting
The origins of human resource accounting can be traced to the work of Rensis Likert, a social psychologist who first used the term "human assets" in the late 1950s, which was later replaced by the term "resources" by later scholars. The heart of his work was
the intuitive expression of human resources in accounting terms. Likert's idea came at a time of growing awareness of the behavioral problems of the accounting system in particular and changes in social values ??in general (Akinsoyinu, 1992). Human resource experts have been uncomfortable for some time presenting the financial statements of organizations that have always
excluded the most important and valuable asset - the human resource (Walker, 1995). An attempt to include human resources in financial statements was first reported in Schwan's 1970 study. The study revealed a pioneering human asset accounting effort by RG Barry Corporation in its financial statement assets (see table 1). From 1968, this company has established an investment accounting system to provide personnel administration to its managers. This system was later extended to office and factory personnel. The system takes into account the real costs for the employer, who must guarantee a regular return on investment and which should not be lost for human reasons due to underemployment (Davis, 1995).
A similar attempt to disclose employee information in New Jersey Bell's financial statements was also reported. Another attempt was made by Peter Drucker on the work of Michael Schiff. In his research, Schiff proposed a company's financial statements
that people will present as an "asset", ie sales and marketing forces as investments as they really are (Walker, 1995).
B. Definitions Of Human Resource Accounting
- The American Association of Accountants (AAA) defines HRA as follows: "HRA is a process of identifying and measuring employee data and reporting this information to interested parties".
- Flamhoitz defines HRA as “the consideration of people as an organizational tool. This includes measuring the costs organizations incur to recruit, select, hire, train and develop their workforce. It is also about measuring the economic value of people to the organization.”
- According to Stephen Knauf, “HRA is the measurement and quantification of human organizational inputs such as recruitment, training, experience and commitment”.
C. Development Of Human Resources Accounting
The development of HRA as a systematic and detailed academic activity according to Eric G. Flamholtz began in the 1960s. He divides the development into five phases. These are:
- First phase (1960-66) -
This marked the beginning of academic interest in the field of HRA. However, the focus for the time being has been on the derivation of the HRA concept from other studies such as the economic theory of capital, psychological theories of leadership effectiveness, the emerging concept of human resource as different from personal relationship or human, as well as the degree of the good will of the company.
2. Second phase (1966-1971) -
Greater emphasis was placed on the development and validation of various human resource accounting models. These models covered the costs as well as the monetary and non-monetary value of human resources. The goal was to develop tools that would help the organization more realistically assess and manage its human resources/assets. One of the first studies here was by Roger Hermanson, who as part of his Ph.D. examines the problem of measuring the value of human assets as an element of goodwill. Inspired by his work, scientists have undertaken several research projects to develop the concept and methods of human resource accounting.
3. Third phase (1971-76) –
This period was characterized by a widespread interest in human resource accounting, which led to a rapid growth of research in this field. In most cases the focus has been on the issue of the application of HRA in professional organizations. RG Barry's experiences contributed greatly to this step.
4. Fourth Phase(1976-1980)-
This was a period of decline in preliminary ERS as the complex problems to be explored required much deeper empirical research than was required for earlier simple models. However, the organization was not willing to sponsor such research. They found the idea of ??the HRA interesting but were reluctant to pump out large sums of time and energy to support research.
5. Stage Five (from 1980) -
There has been a sudden resurgence in interest in human resource accounting, in part because most developed economies have moved from manufacturing to service economies and recognize the importance of human assets for their organization. Because organizational survival growth and profits were thought to depend more on the intellectual assets of the companies than on the physical assets, the need arose to measure the costs, investments and value of HR more accurately.
Different types of models have been developed that are adapted to the specific needs of the organization by integrating both tangible and intangible aspects.
An important result of this renewed interest was that, unlike in previous decades, when interests were primarily academic with practical application from the mid-1990s, emphasis was placed on greater application of human resource accounting to business management. In addition, more organizations have started using human resource accounting as part of their management and financial accounting practices.
Today, human and intellectual capital is seen as strategic resources and therefore a clear assessment of their value has become of great importance. Increased pressures on corporate governance and the corporate code of conduct requiring transparency in accounting have reinforced the need to develop methods for measuring human value.
D. Importance Of Human Resources Accounting
- Information about workforce planning - It provides useful information about the cost and value of personnel. This helps with staff planning.
- Information for Human Resources Development - Human resource accounting provides useful information that aids in the creation and implementation of human resources policies. Employees are the people who work in the organization.
- Use of Human Resources - The effective and efficient use of human resources is necessary for the success of the business. The personnel administration provides the data necessary for the correct use of human resources.
- Appropriate Placement – ??Human resource accounting provides data to help select the right person for the right position. The staff's previous experience and behavior are responsible for their placemen
- Boost morale and motivation - It helps manage employee and employee benefit policies.
- Attracting the best human resources – Human resource accounting helps in attracting the best quality recruitment of qualified personnel for the organization.
E. Limitations Of Human Resources Accounting
- It is not easy to evaluate human assets: there are no guidelines distinguishing the "cost" and the "value" of human resources. The existing evaluation system has many drawbacks. After valuing human resources in a specific way, many of them may leave the organization.
Human life itself is uncertain and therefore the valuation of assets in such 'blurry' conditions is not appropriate. Like physical assets, human assets cannot be owned, stored and used at the whim and pleasure of an organization. Therefore, it would not be appropriate to treat them as "assets" in the strict sense of the word. The so-called "asset" - after being rich within a company - can simply disappear, leaving the company in irreparable loss.
2. Results of the dehumanization of human resources: It is possible that the HRA leads to the dehumanization and manipulation of employees. For example, someone with a lower value may feel discouraged and this in itself can affect their competence at work.
3. Lack of evidence: The indispensable empirical evidence has not yet been found to support the hypothesis that HRA as a management tool enables better and effective management of human resources.
4. HR is full of measurement problems: There is no agreement between accountants and finance professionals about the measurement process. In what form and how should their value be included in the financial statements? To make the problems even worse, it is a matter of determining the recovery percentages. If human resources are to be developed, how should they be amortized? Should the depreciation rate be declining, constant, or rising? Should it be the same or different for the different categories of employees?
5. Workers and unions may not like the idea: There is a constant fear of union opposition. Assigning a value to employees would encourage them to seek compensation based on such an evaluation. HRA can lead to division among employees. A group of employees may be valued below their true worth as a result of management manipulative practices. Unions can combat these manipulative practices.
F. Methods For Identifying Human Resources
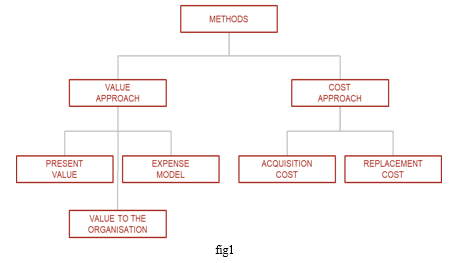
- Cost approach method In the cost approach method, we have two methods –
- Acquisition
In the cost of acquisition method, organizations capitalize all costs related to human resources (such as training, welfare and other costs) of the organization and write it off in the income statement during the entire appointment to retirement.
3. Replacement Cost Approach
This method is used to determine whether the employee should continue to work or be replaced. It takes into account the replacement costs of the staff or employee. This method also makes it possible to determine whether the appointment of employees is beneficial or not for the organization.
4. Value approach
In a value approach, we have three methods:
5. Present value
method In this method, the present value of all future employee benefits is determined as to whether the organization can afford the costs and may be able to benefit in the future from personnel costs.
6. Organizational Value Method
This method determines the organization's most valuable employee and measures whether the organization makes superior profits from that employee's services and helps to find the value of this employee.
7. Expenditure Model
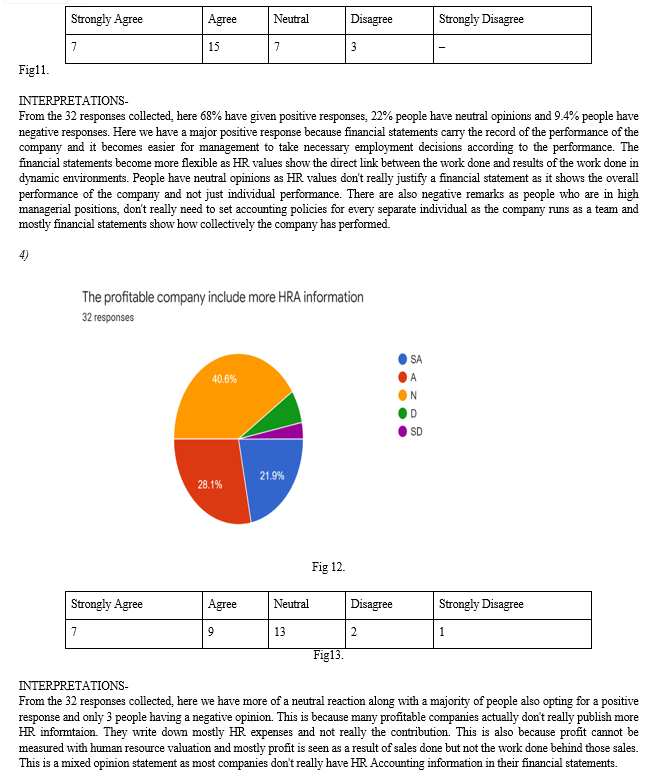
method This method divides employees into two categories: decision-making category and executive decision-making category, then determines the actual costs incurred for the two categories and determines whether it is beneficial or not for the organization.
G. Models For Identification Of Human Resource Accounting

- The Lev and Schwartz model, in the Lev and Schwartz Model, the present value of future employee benefits is determined by the following assumption: Employees are classified by age, skills and experience. The average annual income is determined per age group. Then the income until retirement of each group is determined. The later arrived value of each group must be discounted against the cost of capital. This method only takes into account employee salaries and wages and no other benefits. This method ignores the possibility of an employee leaving or other possibilities
- The Eric Flamholtz model, this model is similar to the present value model, but takes into account the fact that employees leave earlier, voluntary retirement or dismissal or death of the employee, etc.
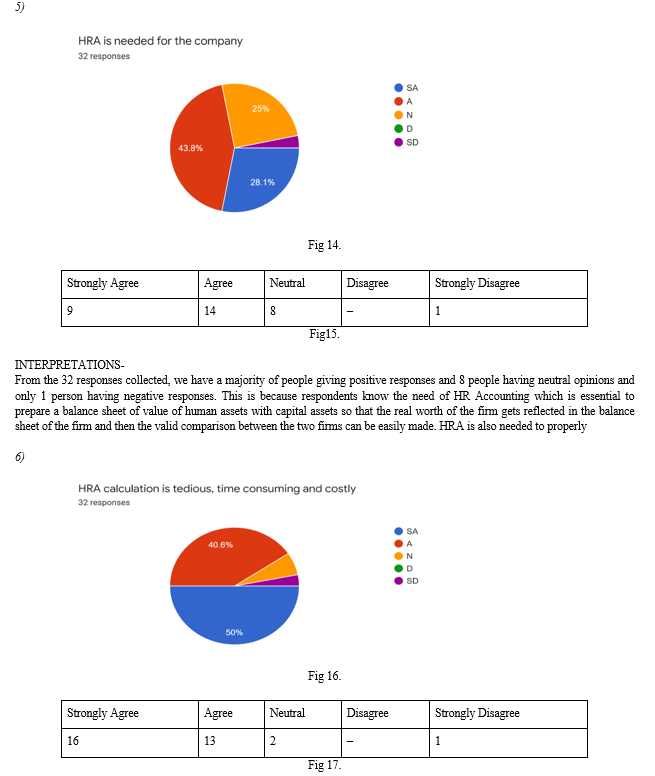
Assumptions/facts – Determine the working period of employee for the organization. Identify the period after which an employee can leave the organization the value of employees to the organization and the resulting benefits to the organization; By applying the present value method and taking into account the above facts.
3. Morse model, this model determines the gross value of the services to be provided by the employees to the organization. This method includes all employee benefits such as retirement benefits, tips, vacation pay, etc. on appropriate assumptions and then discounted to show the present value and benefits to the organization.
4. Linkert's model, this model takes into account non-monetary benefits for employees by the organization, such as job satisfaction, productivity and other non-monetary benefits.
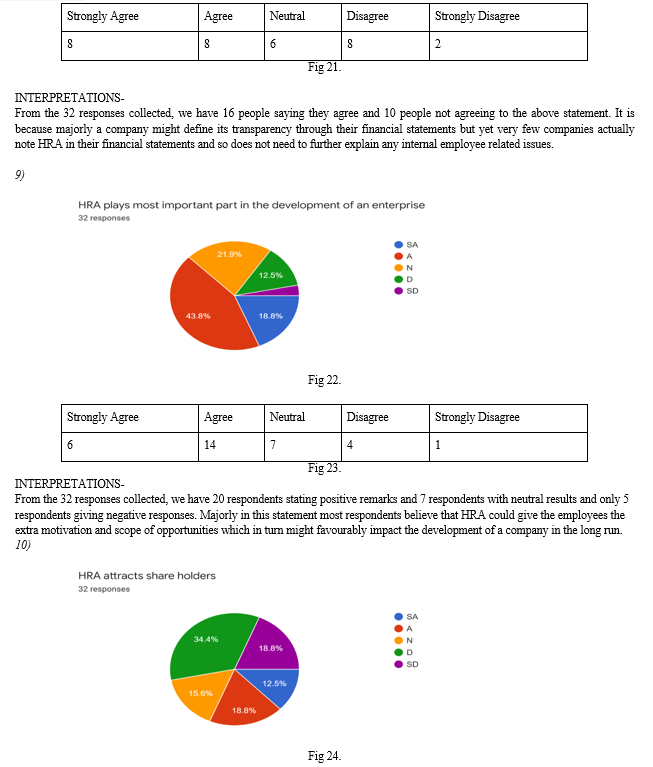
5. Organ Model, in this model, each employee's net benefits are calculated and then multiplied by his specified period of employment with the organization.
H. Evolution Of Human Resources As Assets
The past decade has seen a shift from product-based start-ups to services. The product-based startup industry is now nearly exhausted and the focus is now on service-based startups. As a result, the demand for human resources has increased. As before, there were more product-based startups, physical assets like factories, machines, etc. were paramount. On the other hand, now that the evolution is towards service, the knowledge and attitude of employees has become more important. Human resources have proven to be very important to the company as it is solely responsible for the efficient use of all physical and financial resources. Better would the quality of a company's staff be the management and use of its resources. Therefore, human resources contribute to the total assets of the company. Some companies fail to manage their human resources effectively through conventional accounting methods resulting in the new feature called human resource accounting.
The basic definition of human resource accounting would be to identify the human resource data of the organization, to measure the data in terms of cost and value. Communication of this information to the interested party. Human resources are essential and only with the help of human resources can physical and financial resources be used effectively. Human resources should be added to the balance sheet while human resources are considered as an asset.
When we talk about human resources as an asset, the definition and characteristics of an asset come to mind. Also, if human resources fall under the definition of assets and have its characteristics.
Finally, with regard to the maintenance by the company, human resources must be maintained like any other physical resource. This is mainly done through various development and training programs. For example, when it comes to making its employees happy, Google believes in nothing less than the best. He prioritizes skills over experience and hires only the smartest people. Several things are different in Google's approach to HR. The most remarkable thing about the tech giant is its combination of salaries and benefits designed to keep its employees more than motivated. Moreover, nothing is enough in today's world. You have to do things that take you way above the line to beat the competition and even stand out in the HR field. This shows that even a big company like Google is very focused on employee satisfaction because they realize the potential of HR and know that it is a very important asset that also needs to be maintained just like the others.
I. Employee Morale
In this study, the level of employee satisfaction and level of commitment to the organization is treated as employee morale. Job satisfaction is the degree of satisfaction that employees feel about their work. Job satisfaction refers to the positive attitudes or emotional dispositions that people can acquire through work or through various aspects of the job. Job satisfaction can be influenced by a person's ability to perform a required task, the level of communication in an organization, and how management treats its employees.
Communication between superior and subordinate and their relationship influences job satisfaction in the organization. How subordinates perceive a supervisor's behavior can influence job satisfaction positively or negatively.
The word "commitment" means the feeling of being emotionally or intellectually committed to a particular action. It is the link between the employees and the organization. A highly engaged person feels that he is working for himself and not for anyone else. As a result, he develops a sense of responsibility and does not need an external engine for his work. Organization can be linked to the motivation of the staff and can therefore be seen as a desirable goal in itself and a hallmark of good organizational health.
Developing a high level of organizational commitment maximizes innovative and spontaneous behavior , meaning organizations don't need to go beyond attracting and retaining people in the system to achieve greater efficiency.
J. Major Problems With Human Resources Accounting
Here are the key issues to consider when implementing human resource accounting. They are as follows:
- Traditional accounting procedures, which have been used for a long time, have become acceptable standards. As a result, whenever a new accounting system is developed, it runs counter to the strengths of the traditional system, which is considered relatively objective and free from bias. Likewise, in the case of HR accounting, it is argued that it is not symmetrical with traditional means as it cannot be included in the traditional definition of a good that of a human being.
- There is little agreement on the procedure for accounting for human assets. There are proponents and critics of different approaches, such as cost and value approaches. This factor became responsible for the slow development of the concept of HRA.
- The historical cost approach to developing HRA measures uses a depreciation rate, which yields the depreciation figure charged to the income statement each year. But it is very difficult to develop standards for this. Physically and mentally, individuals grow and deteriorate at different rates. Some become more capable through work experience, others don't. Given the difficulty of predicting such changes, it is even more difficult to develop a means of depreciating an individual's value. So far, no accurate measures of depreciation of human assets have been developed.
- In the recent past it has been noted that measurements based on the HRA value are becoming increasingly accepted, with the Flamholtz approach gradually being applied. However, this approach relies heavily on measuring the contribution of an individual or group to the rating. But measuring the contribution, especially at management level, is quite a difficult task. As a result, this factor appears to be an impediment to the development of the concept of HRA.
- Another issue that remains to be resolved is the rate at which the future contribution stream must be discounted or compounded to calculate present and future value to the organization. A number of applications are available in this process.
- If an individual is to be judged normatively, Flamholtz's model expects individuals' career paths to be plotted over the length of their likely stay in the organization in light of the current organization's promotion and retirement policies. But such an exercise is tedious.
- Concerns about the effect of HRA on human behavior may have led the organization to be reluctant to use this system. Human resource accounting can lead to alienation as people may feel that they have been reduced to an industrial input. Publishing HR data can have a disastrous effect on employee attitudes.
- Physical assets can be held and traded by an organization, but human assets can and should only be used for this purpose. Physical assets have some realizable value in retirement, but human resources do not. It may include the payment of layoffs, allowances, tips and other benefits. Human resources are a valuable asset as labor improves over time given obsolescence constraints, but for a physical asset its increasing value begins to decline immediately at the time of installation.
K. Current Status Of HRA In India
HRA reports provide useful information to company management, employees and investors. In India, very few companies use HRA. In India it is not mandatory. Infosys Technologies and BPL are the main Indian companies using HRA. It is a fact that the 21st century is the era of human demand, countries where the quality of work dominates the world with a dominant technology. Forerunners in technological progress, countries like China and Japan are all the result of the performance of the workforce. Therefore, the whole world has come to realize that human resources are the real investment in business ventures that should only catch and hold the waves of success. It can be said that INFOSYS, Bharat heavy Electrical Ltd (BHEL), DR.REDDY`S and Steel Authority of India Ltd (SAIL) are always profit generators because the recognized value of quality of work and ordered maximum priority for that company yields torn fruits with the help of torn strength (quality workers) and can withstand and effectively cope with any business storm. Although HRA has brought many benefits, its development and application in various industries is not encouraging. Since the Indian Companies Act 1956 does not provide for the possibility to present HR information in financial statements. Due to the development of business and industry, some Indian companies, both public and private, value their human resources and report this information in their annual report. Companies currently publishing a human asset rating include:
- Infosys Technologies Ltd.
- Steel Authority of India Ltd (SAIL)
- Bharat Heavy Electrical Ltd (BHEL)
- Commissioning for Petroleum and Natural Gas (CGSB)
- Oil India Ltd.
- Project and equipment company from India. (PEC)
- India Engineers Limited
- Indian Minerals and Metals Trading Corporation (MMTC)
- Electric India Ltd
- Hindustan Ltd Shipyard
- Cement Company of India. (ICC)
- Tata Engineering and Locomotive Works
- Southern Petrochemicals Industries Corporation Ltd SPIC)
- Associated Cement Company Ltd ACC)
- National Thermal Power Corporation Ltd (NTPC).
L. The Table Below Shows The HRA Information Disclosed By Some Companies
|
ORGANIZATION NAME |
HRA INTRODUCED IN YEAR |
ODEL USED DISCOUNT PRICE |
. |
|
BHEL |
1974-75 |
LEV & SCHWARTZ MODEL |
12 |
|
SAIL |
1984-85 |
LEV & SCHWARTZ MODEL |
14 |
|
MMTC |
1982-83 |
LEV & SCHWARTZ MODEL |
12 |
|
CGSB |
1981-82 |
LEV & SCHWARTZ MODEL |
12.25 |
|
NTPC |
1984-85 |
LEV & SCHWARTZ MODEL |
12 |
|
INFOSYS 96 |
LEV |
1995 & SCHWARTZ MODEL |
2007-2008 |
|
12.96 INFOSYS |
LEV |
& SCHWARTZ MODEL |
14.97 |
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
- Alexander, Michael O (1971)1 describes an application of a HR Accounting system at a public accounting firm, Touche Ross and Company. The rationale was that a public accounting firm is human resource intensive and represents an ideal proving ground for the application of human resource accounting concepts. As a result of calculating the investment in each employee in terms of outlay and opportunity costs, four human resource reports were generated: The cost of time analysis report, a summary of human resource investments report, a statement of human resource flows report, and contribution report. The researcher concluded that the HR Accounting application provided Touche Ross with information that led to a reassessment of its traditional approach.
- Elias, Nabil (1972)2 conducted an experiment to determine whether the additional human asset information provided by a HR Accounting system would make a difference in an investment decision. In the experiment, human assets are treated as aggregates of service potentials available for the expected operations of the firm from its internal members. The researcher has used historical cost method for the experiment. The result of the experiment was that the inclusion of human asset data did favourably affect the investment decisions of certain subject groups.
- D.M.C. Jones (1973)4 conducts a study on the topic,” Accounting for Human Assets”. In this paper researcher explains that an accounting system should record in money terms every financial or economic fact which affects the income or financial position of the organisation. The resources available to management include physical resources, financial resources, reputation, and the human resources within the organisation. The study signifies the importance of Human Resource Accounting in management decisions by concluding that if an accounting system fails to record and present relevant information on any of these resources it can be regarded as inadequate as a source of information for control and decision-making.
- The Report of the Committee on Human Resource Accounting (1973)5 formed by the American Accounting Association mentioned that the purpose of HRA is to improve the quality of financial decisions made both internally and externally concerning an organisation. The HRA data widens the scope of decision making with respect to internal decisions as it permits the consideration of a large set of variables and improves the basis on which the variables are considered in decision-making. The report specified that the availability of quantitative data on human resources should permit their impact to be readily incorporated in the decision-making structure. It confirms that an HRA system would improve decision making by allowing consideration of a wider number of variables. It also mentioned that the external users, particularly investors, could benefit from HRA through the provision of information on the extent to which the human assets of the organization have been increased or diminished during the period.
- Jaggi, Bikki L. (1976)6 stated that human resource accounting is not concerned with humans performance, but its primary concern is the performance of the employees’ services. The study also points out that the employee service resources which have the potential to provide economic benefits to the firm for more then one period can be treated as assets.
- Pekin Ogan (1988)7 designed a field experiment to assess the impact of HR Accounting information on layoff decisions made by the managers. The findings of the study is that HR Accounting information does make a difference in personnel layoff decisions and enables managers to increase their level of confidence regarding decisions taken.
- Gupta (1988)8 conducted a research study to examine the nature of possible impact of HRM data on decision making by management. This study revealed that the internal as well as external users of HR data considered information regarding human assets and changes thereof as valuable aids to management.
- Steven H. Appelbaum, Jamie Hood (1993)9 states that in conventional accounting, the costs associated with human resources have always been treated as expenses and have been written off annually in the financial statement. The researcher explores the value of human resources as measured by the present worth of potential services that could be rendered to the firm if the individual maintained membership throughout the expected service life. The study also examines the firm’s responsibility to shareholders with regard to reporting human resource investments objectively in financial statements.
- Malik (1993)10 carried out a research study for assessing the impact of HRA information on decision making. In judging the behavioural impact of HRA on managerial decision making, three personnel decision areas were chosen- (i) Turnover of human resources, (ii) Lay-off of human resources, and (iii) Selection of human resources. This study substantiated the earlier notion that the quantified information in the realm of human resources could help the personnel managers in reducing their level of uncertainty in decision making.
- Chris Dawson (1994)12 explains how a simulation methodology was used to explore the relationship between two prescriptive models of HR Accounting, the replacement cost model and the stochastic rewards valuation model. The researcher investigates not only the operationalization of the two models, but also the reasoning used by managers in determining the data. This study highlights the general benefits and limitations of simulation methodologies and how they relate to prescriptive and descriptive approaches to the study of management.
- Geoff Turner (1996)13 made an effort to find out whether HR Accounting is a whim or wisdom. The study states that HR Accounting has encountered two main barriers to entry into mainstream accounting. These were a) that employees do not qualify as assets and b) and inability to establish a meaningful system of measurement. In the context of current accounting concepts the first of these barriers is discussed establishing the legitimacy of the paradigm. The researcher has examined the accepting methods of measuring the value of assets and concluded that the present value, using added value as a base, is most useful for the majority of enterprises. The study suggests that in an ever changing accounting environment, the opportunity to recognize human resource assets and liabilities in the financial statements should be taken into consideration.
- Bo Hansson (1997)14 examines the pricing of knowledge- based firms compared with firms that are less dependent on human resources taking HR Accounting into consideration. The results of the study indicate that investors are not able to distinguish personnel investments form expenses, leading to an underestimation of earnings and return. Therefore the researcher suggests that investors need accounting information on human resources to help improve investment decisions.
- Narayankutty (1997)15 in his doctoral dissertation showed the magnitude of HR investment in Cochin port Trust and examined the efficiency levels of its human resources on the basis of their contribution and the investment made in human resources. This study revealed that the human resources of the enterprise were not proper utilised by the management and also concluded that the contribution of human resource to the operational efficiency of the concern was low as compared to the value of its human resource.
- Eric G. Flamholtz, Maria L. Bullen, Wei Hua (2002)17 discusses about a historical perspective and future implications of HR Accounting. This paper provides an overview and history of HR Accounting with the objective of promoting both continued academic research and organisational applications. The history of HR Accounting illustrates how academic research can generate improvement in management systems. The author suggests the implications of measuring human capital for financial reporting and managerial uses.
- S. Viramani and Bhiloda (2002)18 conducted a study in Gujarat Electricity board to assess the impact of the incentive schemes on the employees’ motivation and hence their organisational commitment. The study revealed the perception of the employees that the majority of the employees would not earn the incentive amount due to the scheme conditions. They felt that the scheme was not employee friendly and hence the result of the scheme was unhappiness amongst the employees and hence motivation.
- Patra R., Khatik S.K, & Kohle. M (2003)19 made an analysis on HR Accounting practices and values of a profit making heavy engineering public sector company, Bharat Heavy Electrical Limited (BHEL). Lev & Schwartz model of HR valuation has been used by this company. In the study the tools like T-test has been used to validate the results obtained. They have examined the correlation between the total human resources and personnel expenses for their fitness and impact on production and found that HR Accounting valuation was very much important for decision-making in order to achieve the organisation’s objectives and improve the sales.
- Foong, K., Yorston, R., & Gratton, L. (2003)21 describe the rationale for resisting these disclosures by entrepreneurs. The disclosure of HR information may act as a proof for wealth creation and hence this may result in increased bargaining power for both unions and employees. The critical accounting theory supports these findings. According to critical accounting theory, accounting numbers quantify the events and are used to subjugate the labour by the firm owners.
- Eric G. Flamholtz, Rangapriya Kannan-Narasimhan, Maria L. Bullen (2004)22 reviews the state of the art of the development of HR Accounting. In this paper the authors assess the contributions and categorise them according to studies which (1) underscore the importance of reporting human resource assets on the financial statements, (2) present empirical evidence, case and field studies on the various methods of reporting human resource assets and implementing HR Accounting in various organisations. The researchers analysis different methods for measuring human resources and demonstrates the usefulness of HR Accounting in Human resource management decision-making. This paper also identifies bottlenecks to the growth of HR Accounting and controversies related to this. The researchers suggest recommendations for future research and development in HR Accounting.
- Herman A. Theeke (2005)24 seeks to present the positions and conclusions of scholars to support a proposition that the asset approach to HR Accounting has failed and offers an alternative “liability approach” to account and report human resources. This study provides an argument and rationale to demonstrate that a liability paradigm would be compatible with normal accounting and reporting procedures.
- Parameswaran and Jothi (2005)25 observed in their study that the quantitative information about the value of human resources generated by the HRA system influences the top management in taking decisions regarding the adequacy of human resources. Again, based on these insights, the decisions regarding recruitment and selection of personnel were taken.
- Ananda Samudhram, Bala Shanmugam, Kevin Lock Teng Low (2008)28 makes an attempt to provide a model for reporting human capital on balance sheets. The researchers has developed an analytical framework that links the expenditures on human capital to the resulting long-term benefits and thus provides a model for reporting human capital on balance sheets. The expenditures related to human capital are subdivided into four categories, based on the expenditure-long-term benefits relationships. The finding was a subclass of expenditures occurs those are within the control of the organisation and provide economic benefits over several periods. And so these expenditures can be capitalised. The study also examines the financial accounting and strategic managerial accounting implication of intangibles.
- Shraddha Verma, Philip Dewe (2008)29 explores perceptions and practices in the area of valuing human resources. This study focuses on the importance of valuing human resources, current measurement practices, barriers to measurement and the progress expected in this area. A survey questionnaire is used to identify and describe perceptions and practices in valuing human resources in three types of UK organisations like traditional companies, knowledge intensive companies and local authorities. The findings of the study were that the majority of respondents regarded the measurement of human resources as important to their organisation. And a little or moderate progress was expected in measurement practices in future due to lack of organisational support, uncertainties as to what should be reported, lack of precision in current measurement practices and sensitivities around what should be reported.
- Herman and Mitchell (2008)31 illustrated the way to report under a human capital liability concept which corresponds with the conventional accounting structure of contingent liabilities; scrutinise the fiscal influences of these reporting on market assessment, internal scheduling and investigate extents of human resource liabilities. His study also observes that based on appraisals of fiscal influences of human resource liability reporting, the investigation rationally widens the findings to back the projected concept. The study concludes that the investigation offers backing for the possibility and necessity to take up a human resource liability concept for valuing, reporting and organising human capital. A careful review of the previous literatures relating to HR Accounting indicates that majority of the studies were focused towards the concepts of HR Accounting, different models of HR Accounting, HR Accounting and Decision making, HR Accounting practices in India, Benefits of HR Accounting, HR Accounting practice in different Indian companies etc. But only a very few literatures were available focusing research towards relationship between HR Accounting and organisational performance.
None of the research work has been done in the angle of identifying the necessity of HR Accounting in different industries. Thus, this research work intends to find out the company in which HR Accounting is inevitable.
III. PROFILE OF THE SELECTED RESEARCH FIELD
|
SR.NO |
Particulars |
Page no. |
|
3.1 |
Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited |
38-40 |
|
3.2 |
Oil and Natural Gases Corporation |
41-42 |
For this study, the researcher selected two public sector companies. These are BHARAT HEAVY ELECTRICALS LIMITED and OIL AND NATURAL GAS CORPORATION.
The researcher picked these companies because they use the Lev and Schwartz model of HUMAN RESEARCH ACCOUNTING and determine the value of human resources for more transparent financial reporting.
A. Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited. (Bhel)

- Introduction
Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited is an Indian government-owned engineering and manufacturing company based in New Delhi, India. It belongs to the Ministry of Heavy Industry, Government of India. Founded in 1956, BHEL is the largest manufacturer of power generation equipment in India.
2. Date.
BHEL was established in 1956 in the heavy electrical equipment industry in India. Heavy Electricals (India) Limited merged with BHEL in 1974. When established in 1956, BHEL was designed as a simple production power supply with technological assistance from the Soviet Union. In the 1980s, it was at the forefront of thyristor technology. In 1991, BHEL became a public company. Over time, it has developed its ability to produce a variety of electrical, electronic and mechanical equipment for various sectors including transmission, transportation, oil and gas and other related industries. However, the bulk of the company's revenue still comes from the sale of power generation equipment such as turbines and boilers. In 2017, equipment supplied by BHEL accounted for about 55% of the total installed power generation capacity in India. The company also supplies Indian Railways with electric locomotives and defense equipment such as Super Rapid Gun Mount (SRGM) naval weapons and simulators for the Indian Armed Forces, produced in conjunction with the Ordnance Factory Board.
3. Operations.
BHEL deals with the design, engineering, production, construction, testing, commissioning and maintenance of a wide range of products, systems and services for the key sectors of the 'economy. energy, transmission, industry, transport, renewable energies, oil and gas and defence. It has a network of 16 production units, 2 repair departments, 4 regional offices, 8 service centers, 8 foreign offices, 15 regional centers and 7 joint ventures. Infrastructure that enables the implementation of more than 150 projects in India and abroad. The company was able to supply 20,000 MW of power equipment to meet the growing demand for power generation equipment. BHEL maintained its market leadership position in the energy sector in 2015-16 with a market share of 74%. Improved focus on project implementation enabled BHEL to record the highest commissioning/synchronization of 15,059 MW power plants in domestic and international markets in 2015-16, a 59% increase over 2014-15. In FY 2015-16, BHEL surpassed its installed base of 170 GW of electrical equipment with a record high of 15,000 MW in one year.
It has also been exporting energy and industrial products and services for over 40 years. BHEL's global references are distributed in more than 76 countries on six continents. The total installed capacity of BHEL's overseas power plants in 21 countries, including Malaysia, Oman, Iraq, United Arab Emirates, Bhutan, Egypt and New Zealand, exceeds 9,000 MW. Their physical exports range from turnkey projects to after-sales services.
4. Human Resources Initiative
Human Management As an organization that has made a significant contribution to economic growth, BHEL is a solid company dedicated to ensuring the growth and development of its employees, and
BHEL is a human-centered PSU with a solid over fifty years of engineering excellence. greatly contributed to the development of the country as a whole. BHEL, an integrated power plant equipment manufacturer, is one of the largest engineering and manufacturing companies in the field of design, engineering, production, construction, testing, the commissioning and maintenance of products, systems and services for a number of key sectors of the economy. .] was the initiator. Through these experiences, the organization aims to meet the expectations of its employees in the short and long term.
Although the organization is striving to earn more awards for itself, it certainly does not leave its employees behind, as all of its achievements rest on its employees. Interestingly, the employee satisfaction index of the organization is equal to 7 on a 10-point scale, which is commendable in modern conditions.
B. Oil And Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC)

- Introduction.
The Oil and Natural Gas Corporation is an oil and gas exploration and production company owned by the Indian government. It belongs to the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas of the Government of India. Its head office is in New Delhi. Operations are overseen by the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas.
2. Date.
ONGC was established on August 14, 1956 by the Government of India. It is involved in the exploration and exploitation of hydrocarbons in 26 sedimentary basins in India and owns and operates over 11,000 kilometers of pipelines in the country. Its international subsidiary ONGC Videsh currently implements projects in 17 countries.
3. Operations
ONGC Videsh Limited (OVL) is an international subsidiary of ONGC. It was renamed on June 15, 1989. The main task of ONGC Videsh is to search for oil and gas deposits outside India, including exploration, development and production of oil and gas. There are currently 38 projects in 17 countries. Its oil and gas production increased from 0.252 MMT O+OEG in 2002/03 to 8.87 MMT O+OEG in 2010. ONGC holds a 100% equity interest in ONGC Videsh Limited. India Petroleum Corporation Limited (HPCL) is an Indian petroleum and natural gas company headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra. India holds about 25% market share and strong marketing infrastructure among public sector enterprises (PSUs). The Oil and Natural Gas Corporation holds a 51.11% stake in HPCL and the rest is split between financial institutions, the state and other investors.
The company ranked 367th in the 2016 Fortune Global 500 list of the world's largest companies. Before ONGC acquired a majority stake in HPCL, the former was not on the Fortune Global 500 list and the latter was HPCL.
4. Human Resources Initiative
Today, ONGC is India's flagship company; and a dedicated team of around 33,000 professionals working around the clock to make this possible. It is this effort that is reflected in ONGC's aspirations and performance indicators. The company has adopted progressive policies for scientific planning, acquisition, use, training and team motivation. Everyone is important at ONGC, every mind is important. ONGC is unique as a company with in-house service capabilities in all areas of oil and gas exploration and production and related oil and gas services. Needless to say, it was done by the men and women behind the car. Our executive profile is based on over 18,000 scientists, engineers and technically experienced professionals, mostly from leading universities/institutions in India and abroad. These include geologists, geophysicists, geochemists, drilling engineers, reservoir engineers, petroleum engineers, production engineers, engineering and maintenance contractors, financial and human resources and IT professionals.
IV. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
|
SR.NO. |
Particulars |
Page no. |
|
4.1 |
Introduction |
44 |
|
4.2 |
Need of the study |
44-45 |
|
4.3 |
Relevance of the study |
45 |
|
4.4 |
Assumptions |
45-46 |
|
4.5 |
Objectives of the study |
46 |
|
4.6 |
Statement of Hypothesis |
46-47 |
|
4.7 |
Working definitions of terms used |
47 |
|
4.8 |
Scope of the study |
47 |
|
4.9 |
Classes of respondents |
47 |
|
4.10 |
Universe and sample size |
48 |
|
4.11 |
Sources of data collection |
48 |
|
4.12 |
Method of data collection |
48 |
|
4.13 |
Review of important and relevant literature on study |
48 |
|
4.14 |
Knowledge contribution likely outcomes |
48 |
|
4.15 |
Limitations of the study |
49 |
A. Introduction
Human Resource Accounting is one of the most important aspects of accounting in any business involving employees who are the main backbone of a company. Almost all the large sized organisations have a separate HRD department. Business organisations need to understand the new conceptual framework of human resource accounting. Initially the organisations were manufacturing based, so were giving more importance to the physical assets like plant, machinery, material etc. But over time the economy witnessed a transition from manufacturing to service based economies where knowledge, skill, talent, efficiency, ideas, energy and quality of the employees are established to be of greater significance. In this knowledge driven economy, the total worth of the organisation depends mainly on the calibre, motivation and competence of the human resources.
B. Need of the study
The following reasons are why HR Accounting is important and the need of this study-
- Helps management in employment and utilisation of human resources in a cost-effective manner;
- Helps management in deciding promotion, demotion, transfers, retrenchment, and VRS schemes.
- Provide a basis for planning about human resources.
- Helps in identifying key employees and their cost and benefits.
- Aid in making budgets or forecasts.
- Help management in directing employees in improving their performance.
C. Relevance of the study
- Academic relevance: The above study provides an insight to the use of accounting to measure the positive effects of human resource in a company.
- Research Relevance: The following research will be an effort to understand the importance of human resource accounting in major Public sector companies.
- Government Relevance: The following study will be helpful in ascertaining various government policies regarding Human Resource Accounting.
- Corporate Relevance: The research will bring to the forefront the various corporate structures involved in the framework of Human Resource Accounting.
- Investor Relevance: Since we know investment and financing are the two main prospects of starting and building or expanding their business, this research will show how Human Resource Accounting results makes it easier for such investing decisions to be taken in future by all parties involved in a company.
D. Assumptions
- Human resources provide benefits to an organisation in a fashion similar to the manner in which financial and physical resources provide benefits.
- The benefits associated with both conventional assets and human resources have value to the organisation because these benefits contribute in some way to the accomplishment of the organisational goals.
- Since the usual accounting definition of an asset involves the right to receive economic benefits in the future, human assets are appropriately classified as accounting assets.
- It is theoretically possible to identify and measure human resource cost and benefits within an organisation.
E. Objectives of the study
- To analyse the importance of employees as an asset of the company.
- To study the impact of HR Accounting in the organisation.
- To study how the balance sheet is affected by HR Accounting.
- To study the objectives of HR Accounting.
- To describe the significance of HR Accounting.
F. Statement of Hypothesis
H1- There is no significant impact of Human Resource Accounting on overall performance on organisations.
H2- There is a significant impact of Human Resource Accounting on overall performance on organisations.
G. Working Definitions of terms used:
HR – HUMAN RESOURCE
HRA – HUMAN RESOURCE ACCOUNTING
ROI – Return on Investment
H. Scope of the study:
a) The study focuses on HR Accounting value, Morale and ROI of 2 companies from the Indian Public Sector.
b) It focuses on finding out the industries in which Human Resource plays a significant role and those industries which can harness the benefit of Human Resource Accounting by implementing it.
c) The study has covered skilled, technical and management level employees.
I. Classes Of Respondents To Be Contacted
Employees of ONGC AND BHEL and along with random sampling.
J. Universe and Sample Size
The following study will include a random sample universe of permanent employees of 2 different Public Sector Industries, who have been in office for more than 1 year. The sample size will be around 50-100 employees from the above universe.
K. Sources of data collection:
The data to be collected for this study will be random sampling and online references from various related content.
L. Method of data collection:
Primary data collection will be done through questionnaires submitted to the above sample size and secondary data will be collected from the online references through research of relevant data from relevant studies.
M. Review of important and relevant literature on the study:
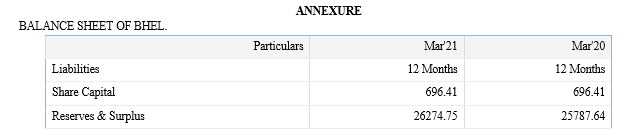
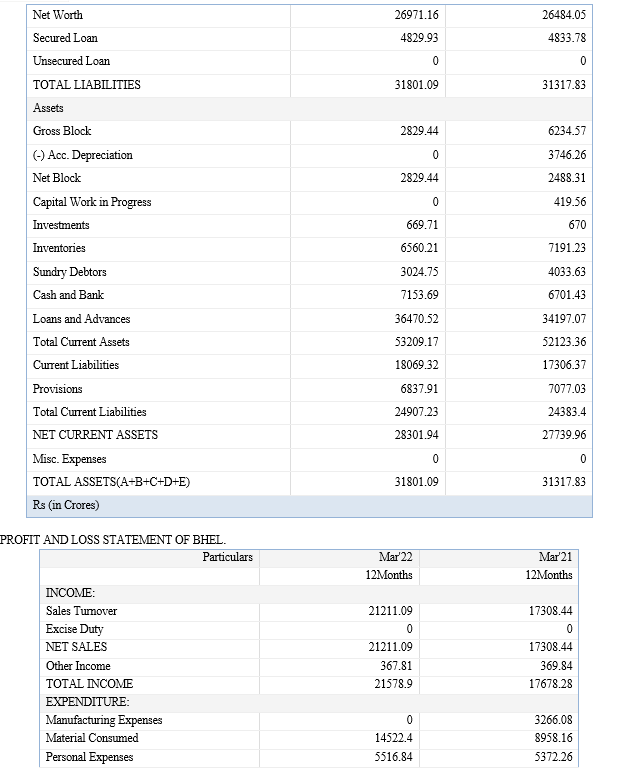
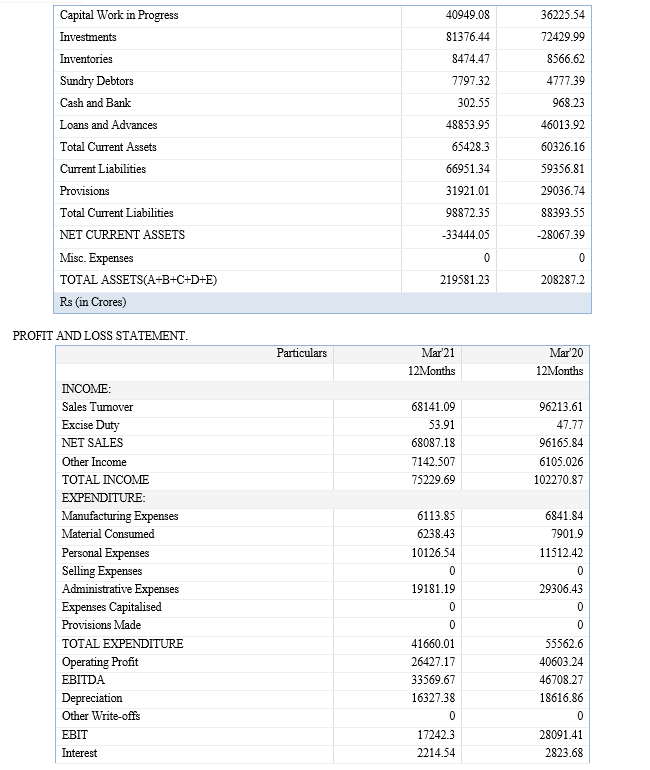
The above mentioned research literature has been done in the wake of how important human resource as an asset in a company is and the relevant data has been referred from various HR Accounting study conducted as an analysis of the changes to the balance sheet when HR Accounting is carried out.
N. Knowledge contribution likely outcomes:
The importance of HR Accounting, on how if we study them as an Asset for the company.
O. Limitations of the study
- The major limitation will be collecting samples of 50 employees data among a data universe of BHEL and ONGC due to time constraint.
- There is no confident data available on how the HR Accounting effects the final reports of a company.
V. ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION OF DATA
|
SR.NO. |
Particulars |
Page no. |
|
5.1 |
Introduction |
51 |
|
5.2 |
Data analysis and interpretation |
51-72 |
A. Introduction
The collection of data has been a very important step as both the primary and secondary data collected for this study has been gathered from annual reports of the public companies, journals related to the research topic, company websites and company portals and last from the primary data collected through the questionnaire provided by the researcher. Both the primary and secondary data has been collected in accordance with the outline laid down for the research. After the data is arranged and tabulated the researcher proceeds for analysis and interpretation of data. There are various methods of analysis of data. Analysis and interpretation are many times done in comparison. These comparisons may be at a fixed time or between two time periods. The most important of these methods of analysis and interpretation are methods which are helpful in establishing functional relationships and forecasting.
In this chapter the researcher has identified HR Accounting Value of organisations, Morale of employees in the organisation and ROI of the organisations in different industries using the primary and secondary data collected. These data are analysed through various statistical tools to understand the interrelationship between these three variables and to identify the impact of HR value and morale on company’s ROI in various industries and to find out whether HR value influences balance sheet and whether high HR value in a company will result in high employee morale. This chapter also analyses the major benefits which companies will acquire by following HR Accounting valuation.





A. Introduction
This chapter provides a clear overview of the work carried out by the researcher during the study. This chapter intends to present the hypothesis test, summarize the research result, draw a conclusion, and give suggestions and recommendations based on the results. This chapter brings together the entire thesis to address the research problem and research questions, provides theoretical and practical implications, and contributes to closing research gaps
This chapter is about how HRA would give an organization a correct vision towards the way forward , but most organizations do not value their plans and human resources to implement HR are at a very early stage, so they must focus more on both theory and practice. Therefore, considering the importance of HRA, proper initiative should be taken by the government and companies together, as well as professional boards at the national and international level, regarding the formulation of special accounting standards and valuation models on the measurement and value report. of HR.
B. Hypothesis Testing
Based on the analysis and interpretation of the data, here are the observations.
H1- There is no significant impact of Human Resources Accounting on the general performance of organizations.
H2- There is a significant impact of human resource accounting on the overall performance of organizations.
- By analyzing the collected data and reviewing the financial statements of the selected public companies, we can arrive at the situation that there is a significant impact of Human Resource Accounting on the overall performance of organizations. Through the elaborated questionnaire, we obtained a majority of positive answers regarding the questions asked. We had a specific set of questions that were intended to specifically understand the pervasive impact of HRA and the researcher got positive answers.
- When we review the financial statements we can see that there has been an impact on the net amounts of the companies, this is also due to the expenses recorded related to the cost incurred to manage human resources. The value of human resources is also recorded in the accounting books just like other physical possessions. Human Resources cost assessment, budgeting and reporting help the organization to accurately document its assets and therefore is a very monetary part of every business association. A financial report of any organization depends entirely on the cost of the labor that works in that organization. Although it is not exact if the HRA values ??are added, we can summarize that the impact of HRA has been positive.
- In the end, we see that there is a significant impact of HRA on the overall performance of the company, since HRA helps to generate the qualitative value and morale of the employee and we can notice that if these values ??represent a positive result, there is always an overall result. . improvement in company performance.
- We rule out hypothesis 1 and accept hypothesis 2. Certainly, if an organization is adopting HRA in their organization, there will be an overall impact on the organization, this is because management will make better decisions regarding human resources and how to use them. optimal for them. is achieved. Ultimately, this will affect the efficiency of employee performance and will be beneficial in rewarding said employees and thus boosting morale and performance.
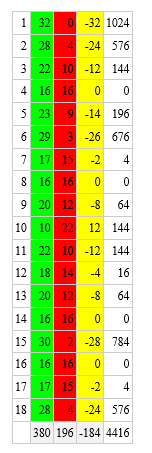
- Conducting the T-Test for the following observations to prove the first hypothesis nul and the second one significant:
- The t-test was conducted by the researcher on the basis of the data collected through primary source as goggle forms and circulated among a class group of 32 respondents. Among all the responses there were two classes of answers, positive and negative. We conducted the t test according to the following data shown below:
In the following table we can mark the positive responses as green (x) and the negative responses as red (y). In the 3rd column which is denoted by the color yellow, is (y-x). In the 4th column which is denoted by the color white is the square roots of (y-x) i.e. (y-x) ².
The formula for the t-test is t=
C. Justification of Objectives
- Analyze the importance of employees as an asset of the company.
The definition of an asset includes having future service potential or being owned by the company and organized by the company itself. Well speaking of future service potential, HR definitely possesses this characteristic as they cannot show their total service in one accounting year. When it comes to business ownership, the American Accounting Association defines an asset as an "economic resource devoted to business purposes within a specified accounting entity, and are aggregates of potential service available or beneficial to expected operations." This shows us that the main concern is economic importance. Here too it satisfies the definition.
2. Study the impact of HR Accounting on the organization.
The impact of HRA on the organization itself is very important. Human resource accounting provides a company with the values ??of employees on a qualitative scale. This means that you can determine if an employee is performing at the optimal level or not. This means that an organization can change HR policies, which could affect performance from how the company wants it to be done.
3. Study how the balance sheet is affected by Human Resources Accounting
Human resources are not shown as assets on the Balance Sheet because it is not possible to express them in monetary terms. Anything that cannot be expressed in monetary terms is not recorded in the accounting books. In the HRA approach, human resource-related expenses are reported as assets on the balance sheet, unlike the traditional accounting approach that treats a company's human resource-related costs as expenses on the income statement that reduce profits. .
4. Describe the importance of Human Resources Accounting.
Human resource accounting is the measurement of the cost and value of people to the organization. The importance of HRA can be seen through accounting that considers human resources as an asset and all financial expenses on human resources such as salaries, training, etc. are recorded in the accounting books. This means that the result of HRA can help improve the financial position of a company, since if the employees are well served in the HRA assessment, the performance of the company increases, which is a significant impact of resource accounting. humans.
D. Findings and Suggestions.
Now let's take a look at the current situation of human resource accounting. Although there has been a lot of literature and attention, there has been little real research in the area of ??human resource accounting. For human resource accounting to be a useful tool, it is necessary to determine whether the information provided by such a system makes a difference in the decision-making of management or investors. In the case of ONGC and BHEL, it could be seen that it did affect their decisions regarding their human resources. ONGC and BHEL management felt that the information provided from their system made a difference, because it quantifies this information and puts it on an equal footing with conventional financial information. The benefits of their system have never been empirically proven, but only reflect the perceptions of management.
Another statement that goes along with the question of does it have any impact or not is, if it does have an impact, is it beneficial or detrimental? This question must be answered both from the perspective of the organization and the people who are accounted for in said system.
This issue still needs to be addressed in field studies. The basic idea of ??when a company is trying to give value to employees is found threatening to many people. People fear that this measurement value is an estimate of what their personal worth is. This really results from a misunderstanding of what human resource accounting is trying to do. In the current economic scenario, most of the systems that are being implemented are based on cost measurements and do not attempt to reflect the economic value of an employee for the company; These methods are used because they are relatively simple and because an operational method has been used to value human resources. has not yet been developed. This concern should be addressed in future studies to determine its impact on organizations.
E. Conclusion
In today's age where technology, finance and information become ubiquitous, the success or failure of a company is determined by the quality of human resources. But companies are considering the amount spent on improving human resources as an expense and not an investment. In the drive to minimize cost, try to reduce employee expenses such as training and development, incentives, fringe benefits, etc.
These are not expenses but investments that will bring benefits in the future. Therefore, measuring the value of Human Resources will be very useful for internal decisions and for external representation of the quality, caliber and strength of the human resources that the company possesses.
The quality of human resources in a company can be determined by its book value of human resources. When the value of Human Resource Accounting is high in some industries, morale is also high and has resulted in better performance and vice versa. But in some industries, the HR Accounting value does not have a significant influence on morale and shows that the increase in the HR Accounting value need not result in an increase in morale for all industries. But in certain industries that are HR-oriented, where success depends primarily on employee performance, the increased value of HR Accounting has resulted in better financial performance. So, the study concludes that ONGC and BHEL, which are predominantly HR oriented, can follow HR accounting valuation practices which can bring huge benefits and for other industries it is optional and they can adopt it after performing cost analysis. -benefit.
At the end of the investigation, the researcher would like to conclude that this study had tried to anticipate the imminent impact of Human Resources Accounting in companies and managed to show it. Through the financial statements that were analyzed, we can see that even if the HRA is not mentioned in the P/L or Balance Sheet, employees will perform at a higher level if their values ??are extracted and treated as an asset. asset and not as an expense. . It can also be seen that even if there is little contribution of these values ??in terms of the monetary aspect, the acquired values ??can be a boost or a motivation to have a much more optimal perspective towards performance and it increases the morale of these employees, which in turn in turn can prove effective in the results of the work done and, in the end, these same high-performing employees can be adequately compensated with the amount of value they actually bring to compensation.
F. Additional scope of the study
As human resource accounting has not yet been introduced in many companies, it is still in a growth stage; therefore, much research is required in this field. The researcher has identified some topics for future research which are detailed below: A study to develop a usable system and procedures for human resource accounting valuation. Study to establish a relationship between the Accounting value of HR of an organization and economic parameters such as the share price and perform a comparative analysis of them with the Economic added value. Impact of the HR Accounting assessment on decision-making related to HR management. Impact of the HR Accounting valuation on the perception of investors to invest in the company. A study on the disclosure methodology of HR Accounting in the company's
VII. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
It is a pleasure to thank all those who made this project work possible. The successful completion of this project is possible only due to support and cooperation of my teachers, friends and well-wishers. I would like to extend my sincere gratitude to all of them.
I am highly indebted to the project guide Dr. Santosh Marwadikumbhar, my classmates and the staff of Symbiosis College of Arts and Commerce for their encouragement, guidance and support.
I also take this opportunity to express gratitude to my parents for their support and co-operation in completing this project. Finally, I would express my gratitude to all those who directly and indirectly assisted me in completing this project.

References
[1] Job performance and employee engagement: An Explorative study”. Issues in Business Management and Economics, 4 (1). [2] A study on human resource accounting , by Kavitha. C Inevitability of hra in indian industries. By P. Smitha [3] Afiouni, F. (2007). “Human Resource Management: A Road Map toward Improving Organizational Performance”. Journal of American Academy of Business, 11(2). [4] Ajay Kr. Singh and Nisha Gupta. (2010). “Contribution based measurement of Human asset for Strategic Decision making using human capital informationsystem”. , 2(1). [5] Ajay Kumar Singh. (2000). “Accounting Information System for Human Response Management” Delhi Business Review, 1(2). [6] Ajay Singh, Kr., & Lavanya Rastogi. (2001). “Human Value Added”. Delhi Business Review, 2(1). human resources: an analytical framework”. Journal of Intellectual Capital, 9(4). [7] www.bhel.com [8] www.data.gov.in [9] www.economictimes.indiatimes.com [10] www.moneycontrol.com [11] www.ongcindia.com [12] www.statisticstimes.com [13] www.tradingeconomics.com [14] www.valueresearchonline.com [15] www.wikipedia.com. [16] www.investopedia.com [17] https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/bharat-heavy-electricals-ltd/profitandlose/companyid-11831.cms [18] https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/oil-and-natural-gas-corporation-ltd/balancesheet/companyid-11599.cms [19] https://www.google.com/search?q=significance+of+human+resource+accounting&sxsrf=ALiCzsYZ78O1Q_kiuymx95uFJTE9dRbcNA:1653469126654&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwj7ysO_pPr3AhUDUGwGHcm7AhQQ_AUoAnoECAEQBA&biw=1536&bih=722&dpr=1.25 [20] https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/02686909610131657/full/html [21] https://eduvark.com/ongc-balance-sheet-179634.html [22] https://www.amity.edu/gwalior/ajm/pdf/human_resource.pdf [23] https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Human-Resource-Accounting-Practices-in-ONGC-An-Singh-Kumar/257f71ae862748ef823c2dc88914567c0385ba45
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Randeep Gogoi, Dr. Santosh Marwadikumbhar. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET58022
Publish Date : 2024-01-13
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

