Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Impact of Influencer Marketing and User-Generated Content on Millennials Purchase Decisions
Authors: Javin Kohli, Dr. Rajeev Gupta
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.61376
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
In the digital era, influencer marketing and user-generated content (UGC) have significantly transformed marketing strategies, particularly affecting millennials\' purchasing decisions. This research delves into the impact of these digital marketing strategies on millennials, focusing on the importance of trust, authenticity, and the integration of influencer marketing with UGC. Influencers, due to their perceived credibility and relatability, play a pivotal role in shaping consumer behavior, but their influence depends heavily on the authenticity of their endorsements. Similarly, UGC contributes to shaping consumer perceptions through genuine expressions of consumer experiences, highlighting the value of transparency and community in digital marketing. The study employs a mixed-methods approach, analyzing the responses of millennials to influencer marketing and UGC, and presents an integrated view of how these strategies influence purchasing decisions. The findings underscore the necessity for brands to forge authentic partnerships with influencers, emphasize storytelling, and actively engage with and promote UGC to resonate with millennials. Integrated marketing campaigns that effectively blend the persuasive power of influencers with the authenticity of UGC have been shown to generate curiosity, trust, and excitement among millennials, although skepticism remains a challenge due to concerns over authenticity. This research contributes to the evolving landscape of digital marketing strategies, offering insights into the complex web of influences that shape millennials\' consumer behavior. It highlights the need for marketers and brands to navigate the intricacies of trust, authenticity, and community engagement in a digital context, providing a roadmap for effectively leveraging influencer marketing and UGC to engage the millennial audience.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
A. Overview of Influencer Marketing and UGC.
In contemporary digital landscapes, the realm of marketing has undergone a paradigm shift propelled by the omnipresence of social media platforms. Among the various marketing strategies that have gained prominence, influencer marketing and user-generated content (UGC) have emerged as powerful tools, particularly in shaping the purchasing behavior of millennial consumers. This dissertation embarks on a comprehensive exploration of the multifaceted impact that influencer marketing and user-generated content have on millennials' decision-making processes when it comes to making purchases.
Born in the era spanning from the early 1980s to the mid-1990s, the millennial generation stands out for its deep-rooted relationship with technology and unparalleled digital savvy. This group, often referred to as digital natives, has woven platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and YouTube seamlessly into their everyday routines, using these channels not just for fun, but also as key tools for finding information and uncovering new products. Against this backdrop, the rise of influencer marketing has been notable. This strategy capitalizes on the influence of people with large digital audiences to endorse goods or services, signifying a notable transformation in contemporary marketing strategies.
Influencer marketing captivates audiences by seamlessly blending authentic, relatable content with traditional advertising. Influencers, distinct from traditional ad figures, build personal brands and establish sincere relationships with their audience. This authenticity transforms them in the eyes of millennials from mere advertisers to valued, trustworthy peers who provide guidance and advice across life's many facets, including consumer choices. The clever fusion of branded content within an influencer's personal story offers a distinct mix of genuine engagement and promotional appeal, proving to be a powerful strategy for swaying buying behaviors.
Additionally, the emergence of user-generated content (UGC) has significantly altered how consumers interact with brands. UGC encompasses all forms of content, including reviews, photos, and videos, crafted by users rather than by the brands themselves. Social media has evolved into a vibrant arena where individuals freely share their product experiences, opinions, and creative takes. Driven by a quest for authenticity and the influence of peer endorsements, millennials in particular regard UGC as an essential resource for information gathering prior to making purchases.
This dissertation seeks to unravel the intricate interplay between influencer marketing, user-generated content, and the process of decision making used by millennials. Examining the psychological underpinnings of influencer influence and the significance of user-generated content on customer perceptions, we aim to elucidate the nuanced ways in which these digital marketing strategies shape millennials' attitudes and behaviors in the realm of commerce.
The first chapter of this dissertation will delve into the theoretical frameworks that underpin influencer marketing and user-generated content. Drawing from communication theories, social psychology, and consumer behavior models, we will establish a conceptual foundation to comprehend the mechanisms through which influencers and user-generated content exert their influence on millennials.
The subsequent chapter will undertake an exhaustive examination of the current scholarly work on influencer marketing and user-generated content. This review will meticulously evaluate prior research, pinpointing any existing gaps in knowledge and establishing a foundation for our research approach. Through the integration of existing studies, our goal is to construct a solid theoretical basis that will guide the empirical research that follows.
In the third chapter, we will present our research methodology, outlining the approach taken to gather and analyze data. By adopting a mixed-methods strategy that merges both qualitative and quantitative research methodologies, our aim is to thoroughly capture the intricate nuances of how millennials react to influencer marketing and user-generated content. This comprehensive approach allows for a deeper understanding of the varied and complex ways in which this demographic engages with and is influenced by these modern marketing phenomena. Surveys, interviews, and content analysis will serve as primary tools to uncover the intricacies of this dynamic relationship.
The fourth chapter will present the findings of our empirical research, offering insights into the key determinants that influence millennials' purchasing decisions. We will explore themes such as authenticity, trust, and relatability and elements that determine the effectiveness or ineffectiveness of these online marketing approaches.
The final chapter will synthesize the findings, draw conclusions, and propose implications for marketers, brands, and future research endeavors. By elucidating the transformative impact of influencer marketing and user-generated content on millennials' purchase decisions, this dissertation aspires to contribute to the evolving landscape of marketing strategies in the digital age.
B. Understanding Influencer Marketing and User-Generated Content through Theoretical Lenses
In the digital age, influencer marketing and user-generated content have emerged as pivotal elements of the marketing landscape, significantly altering how brands interact with their audiences. The relevance of these marketing strategies stems from their profound impact on consumer behavior, leveraging the pervasive reach and interactive nature of digital platforms. Having grown up in the digital era, millennials are not only prolific users of social media but also exhibit distinct consumer behaviors influenced by digital content and online personalities.
The focus on millennials is particularly significant because of their role in reshaping market dynamics and setting trends that influence broader consumer behaviors. Their comfort with technology, preference for digital communication, and reliance on social media for information make them a unique target for marketers. Influencer marketing and user-generated content effectively capitalize on these traits by delivering personalized, authentic, and engaging content directly through channels that millennials trust and frequent.
The goal of this chapter is understand the frameworks that underpin influencer marketing and user-generated content, providing a comprehensive understanding of their mechanisms of influence on consumer behavior among millennials. By examining principles from communication theories, social psychology, and consumer behavior models, the chapter seeks to elucidate the intricate ways through which influencers and user-generated content sway millennials' attitudes, preferences, and purchasing decisions. This exploration is crucial for developing effective marketing strategies that resonate with this influential demographic, ensuring that brands can effectively engage with millennials in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
C. The Rise of Influencer Marketing and User-Generated Content
Influencer marketing involves utilizing individuals who have substantial followings online, termed influencers, to advertise products or services to their followers. These influencers might include bloggers, personalities on social media, or experts in a particular field who have established trust and credibility among their audience. Conversely, User-Generated Content (UGC) refers to all types of content, including photos, videos, reviews, or endorsements, produced by users rather than companies or professional creators.
Both influencer marketing and user-generated content have seen significant evolution alongside the rise of social media platforms. Social media provided individuals with the tools to easily create and share content, democratizing the online space. This shift empowered ordinary users to become influential voices within their communities, leading to the rise of influencers and the widespread creation of user-generated content.
These digital phenomena hold particular importance for millennials due to several factors. Firstly, millennials value authenticity in their interactions with brands. They are more likely to trust recommendations from their peers or individuals they perceive as genuine, such as influencers who share relatable content or personal experiences. Influencer marketing and user-generated content allow brands to tap into this desire for authenticity by aligning themselves with trusted voices within the millennial demographic.
Secondly, millennials are highly engaged with digital platforms, spending a significant portion of their time online. Influencer marketing and user-generated content provide entertaining and personalized content experiences that resonate with millennials' digital-centric lifestyles. Additionally, millennials tend to rely heavily on peer opinions and recommendations when making purchasing decisions.
In conclusion, influencer marketing and user-generated content have evolved alongside social media platforms and hold particular significance for millennials due to their emphasis on authenticity, digital engagement, and reliance on peer opinions. Brands that effectively leverage these digital phenomena can establish meaningful connections with millennial consumers and drive impactful marketing outcomes.
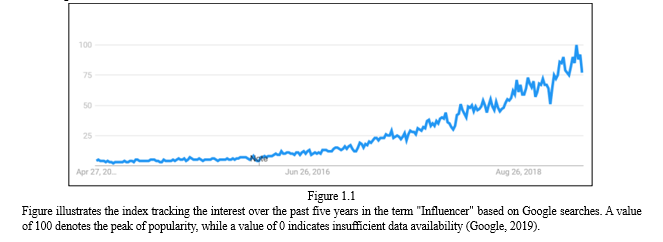
D. Theoretical Frameworks Overview
Communication theories are vital for grasping how information is shared and received in the realm of influencer marketing. The Two-step Flow Theory indicates that information travels from mass media to opinion leaders, who then pass it on to a broader audience. Within influencer marketing, influencers serve as these opinion leaders, influencing their followers' perceptions and actions. Meanwhile, the Uses and Gratifications Theory suggests that people proactively search for and utilize media to meet certain desires, such as entertainment or information. In influencer marketing, this means that followers interact with influencers' content to fulfill their desires for entertainment, motivation, or advice on products.
Social Psychology theories provide insights into how influencers can shape attitudes and behaviors. Social Proof theory suggests that individuals look to others' behaviors to guide their own actions, leading to the phenomenon of "social proof" where people are influenced by the actions of others. In influencer marketing, influencers demonstrate product usage or endorsement, serving as social proof to their followers. Social Identity
Theory proposes that individuals' self-concept is influenced by their group memberships. Influencers often cultivate specific identities or lifestyles that resonate with their audience, leading followers to adopt similar attitudes and behaviors to align with the group identity promoted by the influencer.
Consumer Behavior Models offer frameworks for understanding the consumer journey influenced by digital content. The AIDA framework (Attention, Interest, Desire, Action) describes the phases a consumer goes through from becoming aware of a product to making a purchase decision. In influencer marketing, influencers capture attention through engaging content, generate interest by showcasing products or experiences, stimulate desire by highlighting benefits or lifestyle associations, and ultimately drive action through calls to action or promotional codes.
For illustration, diagrams or models can be used to visually represent these theories. For instance, the AIDA model funnel visually depicts the consumer journey, starting with a broad audience at the top (Awareness) and narrowing down to actual purchasers at the bottom (Action). Similarly, diagrams can be used to illustrate the flow of information in the Two-step Flow Theory or the influence of social proof in decision-making processes. These visual aids enhance understanding and provide a framework for implementing theoretical concepts in influencer marketing strategies.
E. Mechanisms of Influence
Credibility and Trust play pivotal roles in influencer marketing, particularly among millennials. Influencers often build credibility through consistent and authentic content creation, establishing themselves as trustworthy sources of information and recommendations. When content feels authentic and unbiased, millennials are more likely to trust the information presented, leading to increased engagement and brand loyalty.
Social and Psychological Engagement serves as a powerful mechanism of influence among millennials in influencer marketing. The interactive nature of social media platforms allows for real-time engagement through likes, comments, and shares. These engagements not only authenticate the content but also cultivate a feeling of community and inclusion among followers. Millennials are drawn to content that elicits emotional responses and facilitates connections with like-minded individuals. Therefore, influencers who prioritize meaningful engagement with their audience can significantly impact millennials' attitudes and behaviors towards brands.
Personalization and Identification are key drivers of consumer behavior among millennials in influencer marketing. Personalized content tailored to individual preferences and interests resonates more strongly with millennials, leading to higher levels of engagement and brand affinity. Moreover, millennials often identify with influencers who share similar values, lifestyles, or experiences, leading to a sense of connection and trust. When influencers authentically align with millennials' identities and aspirations, they become more influential in shaping their consumer choices and brand perceptions.
F. Case Studies and Examples
- Case Study 1: Glossier's Influencer Marketing Strategy
Glossier, a cosmetics company, is renowned for its effective influencer marketing strategies. The brand partners with influencers who reflect their core values of natural beauty and genuineness. By tapping into the influencers' trustworthiness and rapport, Glossier successfully connects with millennial consumers who prioritize honesty and relatability. Beauty bloggers and Instagram influencers produce content featuring Glossier items in their daily routines, attracting significant engagement via likes, comments, and shares. Utilizing social proof and a tailored approach, Glossier builds a dedicated community of millennial patrons who resonate with the brand's welcoming message and visual style.
2. Case Study 2: Airbnb's User-Generated Content Strategy
Airbnb's strategy for user-generated content encourages guests to post their travel stories, including photos and reviews, on social media platforms. This method leverages the social proof theory by highlighting genuine travel experiences from actual users. Millennials, who seek unique and personalized travel experiences, are drawn to Airbnb's platform, where they can discover hidden gems and connect with local hosts. Through engagement metrics such as shares and tags, Airbnb harnesses the power of user-generated content to inspire and influence millennial travelers. Additionally, Airbnb's emphasis on community and belonging resonates with millennials' desire for authentic and meaningful experiences.
Analyzing these case studies through theoretical lenses, we can see how they effectively engage millennial audiences. Glossier's influencer marketing strategy aligns with the Two-step Flow Theory by leveraging influencers as opinion leaders who disseminate brand messages to their followers.
The authenticity and relatability of Glossier's user-generated content foster trust and credibility among millennials, leading to increased engagement and brand loyalty. Similarly, Airbnb's user-generated content strategy embodies the social proof theory by showcasing real travelers' experiences and recommendations.
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
Building upon the theoretical foundations laid in the first chapter, the second chapter of this dissertation undertakes a thorough examination of existing literature on influencer marketing and user-generated content (UGC). This comprehensive review aims to critically assess prior studies, identify gaps in the current body of knowledge, and lay the groundwork for our research methodology. Through synthesizing existing research, our objective is to construct a robust theoretical framework that will inform the subsequent empirical investigation, providing a nuanced understanding of the impact of these digital marketing strategies on millennials' purchasing decisions.
- Exploring Consumer Motivations for Creating User-Generated Content
(Terry Daugherty, July 2013)
This exploratory study, encompassing 325 participants, investigates the consumer consumption and creation of user-generated content (UGC) within the context of Web 2.0 technologies. The findings affirm a robust relationship between attitude and behavior, highlighting the mediating role of attitude in influencing both UGC consumption and creation. Notably, ego-defensive and social functions emerge as primary motivators for UGC creation, suggesting individuals engage in content creation as a means of self-presentation, ego protection, and a desire for social connection within online communities. While the study provides valuable insights, gaps exist in the depth of attitudinal exploration, consideration of contextual factors impacting attitudes, and the examination of the long-term sustainability of attitudes and behaviors in the evolving online media landscape. Addressing these gaps could refine the study's applicability and contribute further to our understanding of UGC dynamics.
2. User-Generated Content and Social Media
(Luca, 2015)
This chapter undertakes a comprehensive review of the impact of user-generated content (UGC) and social media on diverse aspects of user behavior and decision-making. It reveals a robust causal relationship between UGC and significant economic and social outcomes, utilizing varied methodologies such as regression discontinuity and field experiments. The study emphasizes direct collaboration with platforms under investigation, leveraging unique datasets to uncover nuanced insights into the multifaceted consequences of UGC, spanning domains from restaurant choices to voting behavior. While shedding light on factors influencing UGC quality, such as promotional content and peer effects, the chapter also highlights non-pecuniary incentives as tools to stimulate contributions. However, the exploration suggests gaps in understanding user motivations, the contextualization of UGC impact across diverse populations, and a deeper examination of privacy concerns and ethical considerations. These identified gaps pave the way for future research to enrich our understanding of the dynamic interplay between UGC and societal dynamics.
3. The Impact of User-Generated Content on Customer Purchase Intentions of Online Shoppers
(Gabelaia, Feb 2023)
The literature review unfolds against the backdrop of a dynamic marketing landscape, emphasizing customer-centric strategies, authenticity, and transparency as integral elements. Recognizing the pivotal role of content marketing in capturing customer attention, the review underscores the necessity for precise campaign execution to achieve expected returns on investment. Audience engagement and content prioritization emerge as potent strategies for fostering relationships and authority to ensure customer retention. In the context of the evolving cyber-culture, businesses integrate artificial intelligence strategically, while staying attuned to changing trends allows marketers to capitalize on new opportunities. User-generated content (UGC) is identified as a contemporary communication method, lauded for its role in building brand trustworthiness due to its easy maintainability and cost-effectiveness. The research's core objective is to probe the relevance of UGC in shaping the purchase intentions of online shoppers and discern the primary factors influencing online purchase decisions.
Employing a quantitative research method with distinct target audiences—online shop owners and shoppers—the analysis unveils a divided attitude towards UGC between these groups. While UGC is found to positively impact brand awareness, its overall effectiveness remains unclear, necessitating further research to elucidate the intricate relationship between UGC and customer purchasing decisions. This review thus illuminates the study's contributions, while also pinpointing gaps that warrant additional exploration to enhance the understanding of UGC's impact in the online retail landscape.
4. Do user-generated content and micro-celebrity posts encourage generation Z users to search online shopping behavior on social networking sites—the moderating role of sponsored ads.
(Shetu, 2023)
This study delves into the nuanced dynamics of online purchasing behavior among Generation Z on social networking sites, with a particular focus on the impact of user-generated content (UGC) and micro-celebrity posts. The investigation extends to scrutinizing the mediating role of user search intent, introducing moderation through sponsored ads. Utilizing self-administered questionnaires and cross-sectional studies, the research targets university students of Generation Z in Dhaka, Bangladesh, employing systematic random sampling across six institutions. The dataset comprises 565 standardized questionnaire samples. The findings reveal statistically significant direct, indirect, and mediation relationships associated with user-generated content. Similarly, micro-celebrity posts exhibit statistically significant direct and indirect relationships, although the mediation relationship is deemed insignificant. Notably, users' search intention emerges as strongly correlated with online purchasing behavior, accentuating the crucial role of sponsored ads in the moderation analysis. The application of the stimulus-organism-response (S-O-R) paradigm to explore online purchasing preferences of Generation Z in Bangladesh adds a unique dimension to the study. While offering implications for future research, the study also acknowledges its limitations, underscoring its contribution to understanding the complex interplay of factors influencing the online buying decisions of Generation Z consumers in the context of Bangladesh.
5. Impact Of User Generated Content On Consumer Purchase Intention
(Maksimova, 2018)
This dissertation aimed to fulfill three primary objectives: to explore the nature of User-Generated Content (UGC), examine the factors influencing consumer buying decisions, and identify how UGC impacts these purchase intentions. This investigation was part of a larger effort to outline the impact of UGC created by Facebook users specifically in relation to Company X. The study was conducted in two key stages—initially through secondary research utilizing a variety of sources, followed by primary research using a quantitative approach via a survey. The survey, carried out in April 2018 among customers from Company X's database, showed a clear pattern: people tend to trust UGC, and their willingness to buy is significantly affected by the opinions or reviews of previous buyers. These outcomes offer valuable guidance for Company X, underscoring the importance of effectively managing UGC on platforms such as Facebook to build consumer trust and sway buying behavior.
6. The effect of influencer marketing on the buying behavior of young consumers
(Verplancke)
In the contemporary landscape of beauty and fashion marketing, the symbiotic relationship between companies, social media influencers, and their predominantly young audience is a pivotal focus. This study delves into the intricate dynamics of influencer marketing, aiming to unravel how beauty and fashion companies strategically leverage social media platforms through influencers to shape consumer behavior, particularly among adolescents and young adults. The research questions explore the nuances of influencer strategies and their impact on the purchasing decisions of this digitally savvy demographic. Through qualitative research, incorporating insights from influencers, brands, and followers, the study unveils a multifaceted landscape where brands hold substantial sway over young consumers. The findings emphasize the influential power of authentic connections between followers and influencers, shedding light on the intricate balance between paid partnerships and genuine product endorsements, ultimately guiding brands in their pursuit of effective influencer marketing strategies.
7. How do Instagram influencers affect the consumer buying behaviour of Gen-Z?
(Wansi, 2012)
The Influencer Marketing Agency (IMA) has evolved from a fashion inspiration platform into a global influencer marketing powerhouse, connecting brands with influential bloggers, vloggers, and social media personalities worldwide. Despite their
expertise in engaging Millennials, born from 1980-94, the agency recognized a knowledge gap regarding Generation-Z (born from 1995-2010), whose consumer influence is steadily growing. To address this, the research question focused on understanding how Instagram influencers impact the consumer buying behavior of Gen-Z. Through comprehensive desk research encompassing the roots of influencer marketing, the rise of Instagram, and the agency's business strategy, coupled with field research involving one-on-one interviews with Gen-Z members, key insights emerged. The agency is advised to prioritize authenticity in influencer selection, continually educate marketing teams about Gen-Z's preferences, stimulate creativity among influencers, and craft meaningful campaigns that align with social issues. Ultimately, Instagram influencers serve as catalysts, capturing Gen-Z's attention and guiding them on their consumer buying behavior journey.
8. Effect of Influencer Marketing On Young Indian Adults
(Prakash, 2018)
The research paper investigates the attitudes and awareness of young Indian adults (18-25) towards influencer marketing, aiming to understand its impact on purchasing decisions. Utilizing quantitative methods, the study reveals the target group's high awareness and positive perception of influencer marketing, emphasizing its usefulness in product decisions. Trust and credibility emerge as crucial factors, highlighting the significance of influencers in shaping consumer choices. However, the study lacks a detailed exploration of influencer types, potential drawbacks, and a comprehensive comparison with traditional marketing. Future research could address these gaps for a more nuanced understanding of influencer marketing dynamics and implications.
9. Celebrity endorsements: Influence of a product-endorser match on Millennials' attitudes and purchase intentions
(McCormick, 2016)
This study explores how the congruence between a product and its celebrity endorser influences millennial consumers' attitudes towards advertisements and their intent to purchase. It found that millennials showed little intent to purchase products endorsed by unfamiliar celebrities, yet these endorsements led to favorable advertisement evaluations.
- Findings: The congruence between a product and its celebrity endorser plays a significant role in shaping millennials' purchase intentions and attitudes towards advertisements.
- Limitations: The research focuses solely on the impact of celebrity endorsements and may not fully account for other forms of influencer marketing or UGC.
10. Facebook advertising's influence on intention-to-purchase and purchase amongst Millennials
(Duffett, Jul 16, 2015)
Investigating the behavioral attitudes of millennials in South Africa towards Facebook advertising, this study assessed how these attitudes, along with usage and demographic variables, influence their intention-to-purchase and actual purchase behaviors.
- Findings: Advertising on Facebook positively influences millennials' intention-to-purchase and purchase behaviors, with log-on duration, profile update frequency, and ethnic orientation enhancing perceptions of Facebook advertising.
- Limitations: The study's geographic focus on South Africa may limit the generalizability of its findings to millennials in other regions. Further, it primarily examines Facebook and might not fully represent the impact of other social media platforms or influencer marketing strategies.
11. Swipe to Buy? Examining the Influence of Instagram and TikTok on Millennials' Fast Fashion Purchases
(Y Qayyum, 2024)
The research explores how User-Generated Content (UGC) impacts millennials' purchasing decisions, with a specific emphasis on the fast fashion industry. It investigates the influence of platforms such as Instagram and TikTok on shaping millennials' attitudes towards fast fashion brands and subsequent purchasing behaviors.
- Findings: The study highlights the significant role of influencer marketing and UGC in shaping millennials' attitudes towards fast fashion brands and their subsequent purchasing behaviors.
- Limitations: The focus is largely on fast fashion, which might not entirely capture broader purchasing decisions across other product categories.
12. Impact of Online Consumer Reviews on Consumer Purchase Intention and Buying Decision Among Millennials
(S Arockia Shiny, 2023)
The research delves into analyzing the influence of online reviews on millennials' intentions to purchase and their final buying decisions. Specifically, it examines how peer opinions shared through online reviews affect millennials' perceptions of products or services and their subsequent purchase intentions.
- Findings: Online reviews are found to significantly impact millennials' perceptions and purchase intentions, emphasizing the power of peer opinions in the digital age.
- Limitations: The study may not fully account for the varying credibility of online reviews and how millennials discern this.
13. Exploring the Influence of YouTube Videos on Purchase Intentions among Millennial Consumers in Tasikmalaya City
(Nugraha, 2023)
Investigates how UGC on YouTube affects the purchasing intentions of millennials, with a case study in Tasikmalaya City.
- Findings: YouTube content plays a crucial role in informing and persuading millennials, thereby significantly affecting their purchase decisions.
- Limitations: The geographical focus on Tasikmalaya City may limit the generalizability of the findings to other regions or globally.
14. The Impact of Social Media Influencers on Purchase Intention and the Mediation Effect of Customer Attitude
(Rahman, 2022)
This study examines how social media influencers affect the purchase intentions of millennials, with a focus on the mediating role of customer attitudes towards brands and products. The research explores various social media platforms and considers different types of influencers, including micro and macro-influencers.
- Findings: Findings suggest that influencers significantly impact millennials' purchase intentions, particularly when consumers have positive attitudes towards the promoted products. The credibility and relatability of influencers play crucial roles in shaping consumer attitudes and purchase decisions.
- Limitations: The study mainly focuses on specific categories of products, such as fashion and beauty, which might not apply to other sectors. Additionally, the research was conducted in a limited geographical area, which may affect the generalizability of the results to a broader population.
15. User-Generated Content and Its Impact on Consumer Behavior: A Cultural Perspective (Dang, 2021)
This paper investigates the role of (UGC) on consumers from a cultural perspective, analyzing how cultural differences affect the perception and impact of UGC on millennials' purchase decisions. The study contrasts Western and Eastern cultural contexts to understand how cultural values and norms shape the effectiveness of UGC.
- Findings: The research finds that UGC significantly influences millennials' purchasing behavior, with variations across different cultures. In Western cultures, consumers value authenticity and personal experiences shared in UGC, while in Eastern cultures, the collective opinion and group consensus in UGC have a more substantial impact on purchase decisions.
- Limitations: The study's cultural comparison is broad, and the findings may not fully represent all nuances within each cultural context. Additionally, the research focuses on millennials, potentially overlooking generational differences in the perception and influence
In this dynamic landscape of digital marketing, influencer marketing has come out to be as one of the critical discipline, enabling companies to promote their brands more directly and effectively than traditional advertising methods. This literature review explores various facets of influencer marketing, focusing on perspectives from brand owners, influencers, and consumers, as well as delving into the principles of influence and the result of (UGC) on consumer behavior.
a. Influencer Marketing: A Tripartite Perspective
- Brand Owner Perspective: Digital communication through influencer marketing allows brand owners to achieve communication goals, develop consumer engagement, enhance brand image and attitudes, and generate traffic to reach wider audiences, especially on social media. Choosing influencers who match the brand's identity and target demographic is essential for the effectiveness of these campaigns. (Bakker, 2018; Brown & Hayes, 2008)
- Influencer Perspective: Influencers, based on their popularity and follower count, engage in paid partnerships with brands. The number of followers is a key criterion for their selection, influencing the reach and potential success of brand partnerships. It is imperative for influencers to choose brands that align with their values to maintain credibility and trustworthiness among their followers (Bakker, 2018).
- Consumer Perspective: In the consumer decision-making process, influencers play a significant role in encouraging purchases. Consumers recognize influencer marketing as paid advertising but prioritize credibility and trust in following influencers. This highlights the importance of authentic influencer-brand alignments in influencing consumer decisions (Hein, 2017).
b. Principles of Influence in Influencer Marketing
Cialdini (2007) identifies six principles of influence that are particularly relevant to influencer marketing: reciprocity, consistency, social proof, authority, scarcity, and liking. These principles help explain how influencers affect consumer engagement and decision-making, offering insights into crafting effective influencer marketing strategies.
c. The Impact of Follower Size on Influence
Influencers can be categorized into micro, mid, and macro influencers based on their follower counts. While a larger audience may enhance an influencer's reach, engagement levels, characterized by likes, comments, and shares, often vary inversely with follower size. Micro influencers, in particular, tend to have higher engagement rates and influence on brand recommendations, underscoring the complex dynamics between follower count, engagement, and influencer effectiveness (Conick, 2018; De Veirman et al., 2017; Hall, 2016).
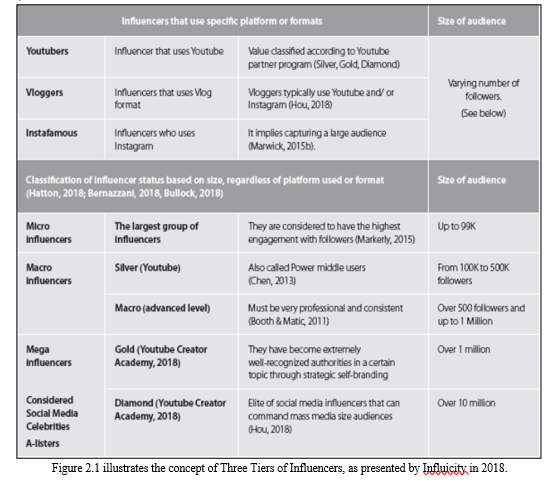
d. The Role of User-Generated Content in Marketing
The Global 2020 Cloudinary UGC Study highlights the increasing creation and impact of UGC in marketing. A significant rise in UGC creation, coupled with a strong consumer preference for visual content, underscores its importance in influencing purchase decisions. Platform preferences and generational differences in UGC consumption further emphasize the need for marketers to tailor their strategies to meet the nuanced demands of diverse consumer segments.
In conclusion, influencer marketing represents a vital tool for brands to engage with consumers in a more personal and credible manner. The principles of influence, along with the strategic use of UGC, play critical roles in shaping consumer behavior and preferences. As this field continues to evolve, understanding the interplay between influencers, brands, and consumers will be essential for crafting effective digital marketing strategies.
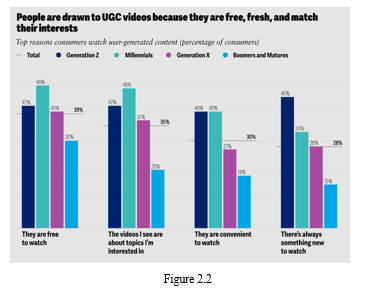
Engaging millennials with influencer marketing and (UGC) enormously impacts their purchasing decisions. Video games serve as one avenue to reach this demographic, but leveraging social media, particularly through content creators, holds even greater sway. These creators, beyond mere entertainers, morph into trusted advisors for their followers, who rely on them for product recommendations and reviews, ultimately shaping their purchasing choices (referencing figure 3). About half of millennials attest that UGC videos aid them in discovering new products or services, with nearly 40% expressing a heightened inclination to purchase after viewing a creator's review. This trend can be attributed to the organic integration of advertising within creators' content, often appearing as product reviews or usage within their niche. Approximately 40% of millennials find it challenging to discern when user-created videos are sponsored or contain advertisements. Essentially, millennials willingly embrace this form of advertising when it originates from a trusted influencer or content creator, highlighting the profound impact of influencer marketing and UGC on their purchase behaviors.
III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The research methodology functions as a structured plan for the upcoming study, aiming to unravel the influence of influencer marketing and (UGC) on the purchase decisions of millennials. The primary focus is on comprehending how these marketing strategies impact the choices made by millennials when it comes to making purchases. This section will outline the specific methods and techniques employed for data collection and analysis, providing details on sample size and sampling techniques tailored to this investigation.
A. Research Objectives
- To analyze the perceived credibility and trustworthiness of influencers among millennials and its impact on their purchase decisions.
- To quantify the differential effects of these marketing strategies on various stages of the consumer decision-making process, including awareness, consideration, and actual purchase decisions.
- To evaluate the cognitive and emotional responses of millennials to integrated Influencer Marketing and UGC campaigns.
B. Research Design
The research design employs a cross-sectional survey methodology, gathering data at a specific moment to evaluate the ongoing impact of influencer marketing and user-generated content (UGC) on consumer attitudes and perceptions in the digital marketing landscape.
Sample size and sampling technique :
- Sample size: The sample size will be around 82 consumers. The ideal sample population will have the desired characteristics: Millennials that actively use digital marketing platforms and services will be the best target audience for the study on influencer and UGC marketing. These millennials often are very active on social media and are in touch with the latest trends. There are characteristics are.
- Seeking Authenticity
- Diverse demographics
- Value social proof
- Are socially connected
- Community Driven Consumers
2. Sample Technique
Using both convenience and stratified sampling in this research has its advantages. Convenience sampling makes it easy to reach participants, which is handy when it's tough to connect with them otherwise. On the other hand, stratified sampling helps ensure that different groups within the population are well-represented. By combining these methods, we strike a balance between practicality and inclusivity, making it more likely that our findings will be relevant and cover a variety of perspectives.
Type of questionnaire
In this study, I'm using Likert scale and multiple-choice questionnaires. The Likert scale helps gauge the intensity of participants' opinions quantitatively, while multiple-choice questions offer predefined options for a more structured understanding of preferences and experiences. This combo allows for a well-rounded exploration of both quantitative trends and qualitative insights.
The reasoning behind determining the sample size, selecting the sampling technique, and opting for a specific questionnaire format is as follows:
a. Sample Population Rationale: The sample size for this study is set at approximately 81 consumers, targeting millennials who actively engage with digital marketing platforms and services. This demographic is chosen due to its pronounced presence on social media and keen awareness of current trends. The ideal participants possess characteristics such as a genuine desire for authenticity, diverse demographic backgrounds, a strong inclination towards social proof, active social connections, and a community-driven consumer mindset. By focusing on this specific sample population, the study aims to capture nuanced insights into the impact of influencer and user-generated content marketing within a demographic that is highly receptive to these digital marketing strategies.
b. Sample Technique Rationale: A dual sampling approach combining convenience and stratified methods is adopted for its unique advantages. Convenience sampling facilitates easy participant access, especially beneficial when connecting with the target audience might otherwise be challenging. Simultaneously, stratified sampling ensures a more representative sample by accounting for the diversity within the millennial population. This combined strategy strikes a balance between practicality and inclusivity, enhancing the likelihood of obtaining findings that are not only practical and feasible but also broadly applicable, covering a spectrum of perspectives within the targeted demographic
c. Type of Questionnaire Rationale: The research employs a combination of Likert scale and multiple-choice questionnaires to gather a comprehensive understanding of participants' opinions and preferences. The Likert scale offers a structured and quantifiable measure of the intensity of respondents' attitudes, providing a valuable quantitative dimension for analysis.
Simultaneously, multiple-choice questions offer a predefined set of response options, enabling a more structured exploration of specific choices and preferences. This dual approach ensures a nuanced exploration of both quantitative trends and qualitative insights, enriching the depth and breadth of the collected data and facilitating a more thorough examination of the research objectives.
d. Data Collection Technique
For this research, an integrated survey approach will be employed, utilizing both Likert scale and multiple-choice questionnaires to gather comprehensive insights into the impact of influencer marketing and user-generated content on the purchase decisions of millennials. The survey instrument will be distributed digitally, leveraging online platforms to efficiently reach the target millennial audience. The integrated survey approach will encompass questions aligned with the research objectives, providing a mix of quantitative data for statistical analysis and qualitative insights to enhance the understanding of millennials' consumer decision-making processes.
To ensure a well-rounded and representative sample, a combination of convenience and stratified sampling techniques will be employed. Convenience sampling will facilitate easy access to participants, particularly vital when connecting with the digitally active millennial population, while stratified sampling will guarantee diverse representation across different demographic strata. This dual approach aims to strike a balance between practicality and inclusivity, contributing to the relevance and applicability of the research findings.
IV. DATA ANALYSIS
In this chapter, we explore influencer marketing dynamics and its impact on millennials' purchasing decisions. We focus on how millennials perceive influencer credibility and trustworthiness and how this influences their buying behavior. With the rise of social media, influencers play a pivotal role in marketing strategies, making it essential to understand their relationship with consumer behavior. Through detailed analysis, we aim to uncover the complexities of this relationship, including trust, frequency of influencer-influenced purchases, and perceived genuineness. Our research seeks to provide empirical insights into influencer effectiveness among millennials, identifying conditions that either persuade or dissuade buyers. This chapter investigates both direct influencer impact on purchases and underlying factors moderating this influence, offering a comprehensive view of influencer credibility's role in shaping consumer behavior.
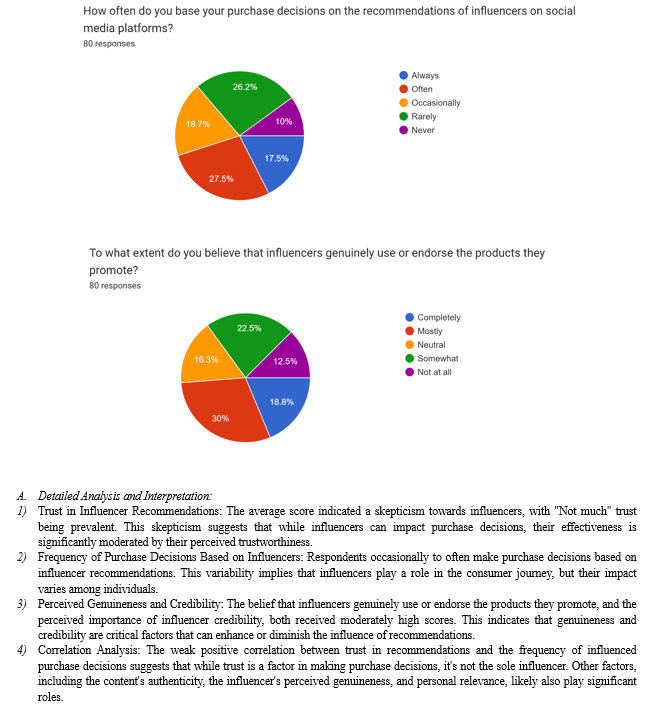


- Awareness of New Products Through Influencer Marketing or UGC:
- The distribution suggests that a significant portion of respondents occasionally (25.93%) or rarely (22.22%) become aware of new products through influencer marketing or user-generated content (UGC).
- While often (20.99%) and always (16.05%) are also notable percentages, it's evident that these channels are important but not exclusive sources of product discovery for the respondents.
- The fact that 14.81% claim never to become aware through these channels indicates there's still a segment of the audience less influenced by influencer marketing or UGC.
2. Movement from Awareness to Consideration Stage:
- A significant proportion of respondents (32.50%) feel neutral about moving from awareness to consideration based on influencer or UGC recommendations.
- However, there's a notable portion who find it likely (21.25%) or very likely (18.75%), suggesting a positive impact on consideration stage decisions.
- Conversely, a considerable percentage also find it unlikely (16.25%) or very unlikely (11.25%), indicating skepticism or resistance to this transition.
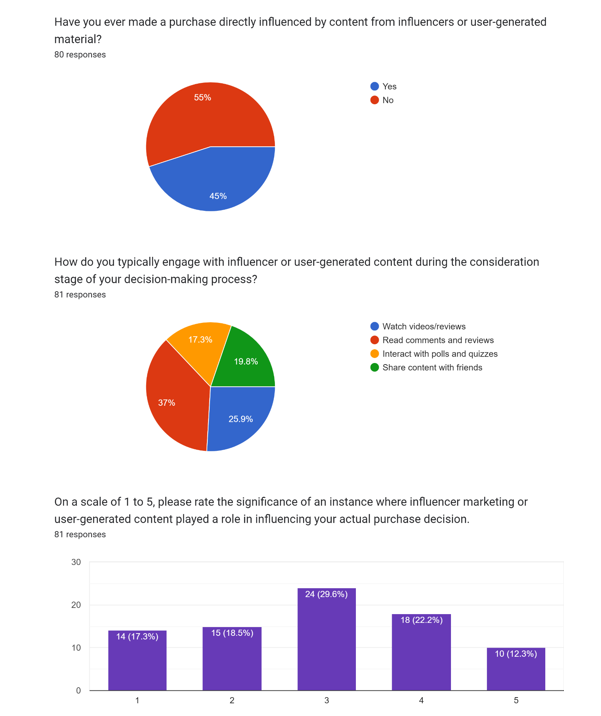
3. Direct Purchases Influenced by Influencers or UGC:
- Almost half of the respondents (45%) claim to have made purchases directly influenced by influencers or UGC.
- This indicates a substantial impact on consumer purchasing behavior, highlighting the effectiveness of these channels in driving conversions.
4. Engagement with Content During Consideration Stage:
- Reading comments and reviews (37.04%) and watching videos/reviews (25.93%) are the most common ways respondents engage with influencer or UGC during the consideration stage.
- Sharing content with friends (19.75%) and interacting with polls and quizzes (17.28%) are also notable, though to a lesser extent.
- This suggests that peer opinions and detailed product evaluations play significant roles in influencing decision-making during the consideration stage.
5. Significance of Influencer Marketing or UGC in Purchase Decisions:
- The ratings range from 1 to 5, with a higher concentration of responses around the mid-range (3).
- This indicates a moderate level of influence of influencer marketing or UGC on purchase decisions for the respondents.
- While some respondents rated it higher (4 or 5), indicating significant influence, there were likely others who rated it lower, reflecting varied perceptions of its importance in their purchase decisions.
Hypothesis for objective 2
Null Hypothesis (H0): There is no association between becoming aware of products through influencer marketing or UGC and making a purchase directly influenced by such content.
Alternative Hypothesis (H1): There is an association between becoming aware of products through influencer marketing or UGC and making a purchase directly influenced by such content.
Since the first question has multiple categories (Never, Rarely, Occasionally, Often, Always), we'll simplify the categories to "Aware through Influencers/UGC" (combining Occasionally, Often, Always) and "Not Aware through Influencers/UGC" (combining Never, Rarely) for a clearer analysis. This approach makes the Chi-square test more straightforward and meaningful.
Row totals:
Aware: 45% (direct purchase influenced by influencers or UGC)
Not Aware: 55% (direct purchase not influenced by influencers or UGC)
Column totals:
Yes: 25.93% (awareness of new products through influencer marketing or UGC)
No: 74.07% (not aware of new products through influencer marketing or UGC)

D. Interpretation:
The chi-square statistic of 1.94 with a p-value of 0.164 suggests that we do not reject the null hypothesis at the conventional alpha level of 0.05. This outcome indicates insufficient evidence to assert a significant link between product awareness through influencer marketing or user-generated content (UGC) and making purchases directly influenced by such content, according to the data analyzed.
The single degree of freedom (df) aligns with what is anticipated from a simplified 2x2 contingency table analysis. This setup helps in examining the expected distribution of responses, presuming there is no correlation between becoming aware of products via influencers/UGC and engaging in purchases influenced by this exposure.
E. Conclusion:
The analysis suggests that, within the limitations of this dataset and the specific categorization applied, the impact of becoming aware of new products or services through influencer marketing or UGC on making direct purchases is not statistically significant. This could indicate that while influencers and UGC play a role in the awareness stage, other factors might be more decisive in driving actual purchase decisions.
Objective 3:
In this study, our objective is to evaluate the cognitive and emotional responses of millennials towards integrated Influencer Marketing and User-Generated Content (UGC) campaigns. We seek to understand how millennials perceive and engage with marketing initiatives that combine influencer endorsements with user-generated content on various platforms. By examining both cognitive and emotional responses, we aim to gain deeper insights into the effectiveness of these integrated campaigns in capturing millennials' attention, generating positive associations, and ultimately influencing their purchasing behaviors. Through rigorous analysis, we endeavor to uncover the nuances of millennials' reactions to such campaigns, shedding light on the interplay between cognitive processing and emotional resonance in the context of modern marketing strategies.
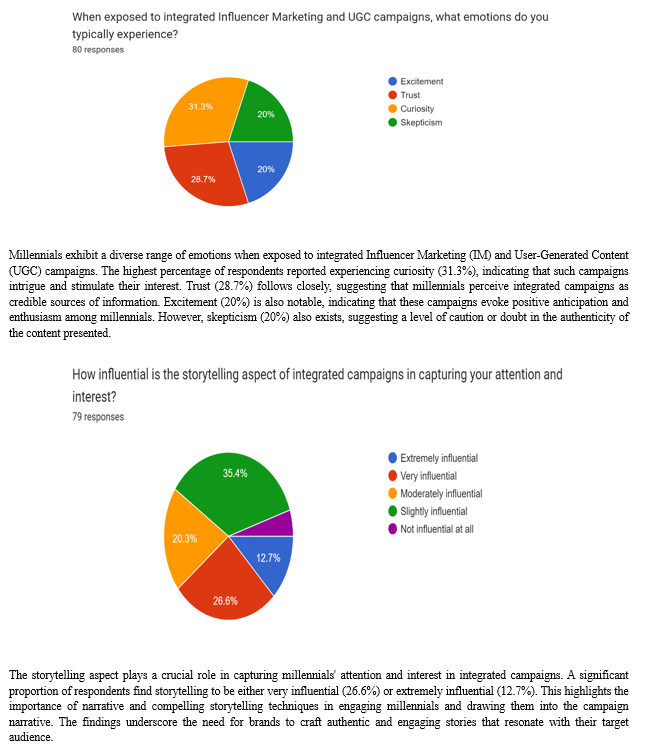
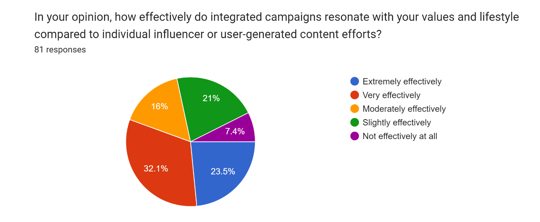
Integrated campaigns are perceived to resonate effectively with millennials' values and lifestyle. A majority of respondents believe that these campaigns resonate either very effectively (32.1%) or extremely effectively (23.5%) with their values and lifestyle. This suggests that integrated campaigns have the potential to align with millennials' preferences, interests, and beliefs, enhancing their engagement and receptiveness to the content presented. However, a notable proportion also perceives moderate (16%), slight (21%), or no (7.4%) resonance, indicating room for improvement in tailoring campaigns to diverse audience segments.
The transformative impact of influencer marketing and user-generated content (UGC) on the purchasing decisions of millennials represents a pivotal shift in contemporary marketing strategies. This exploration synthesizes findings from an in-depth analysis, drawing conclusions and outlining implications for marketers, brands, and future research endeavors. The digital landscape, characterized by its dynamic interaction between consumers and brands through social media platforms, has ushered in a new era where credibility, authenticity, and personal connection are paramount.
V. FINDINGS
A. Trust and Authenticity: The Cornerstones of Influence
The digital age has elevated the importance of trust and authenticity in marketing strategies. Influencer marketing and UGC have emerged as powerful tools, leveraging these elements to impact millennials' purchasing decisions significantly. Influencers, by virtue of their relatability and perceived closeness to their followers, have the potential to sway consumer behavior in ways traditional advertising cannot. However, this influence is contingent upon their credibility and the authenticity of their endorsements. Millennials, a demographic deeply entrenched in digital culture, exhibit a discerning approach to influencers, valuing genuineness over sheer popularity.
The skepticism towards influencers underscores a broader trend among millennials: the desire for authentic, transparent marketing practices. Influencers who genuinely use and endorse products, demonstrating a real connection with what they promote, are more likely to influence purchasing decisions positively. This dynamic has prompted a reevaluation of how brands engage with influencers, emphasizing the need for authentic partnerships that resonate with the target audience's values and interests.
B. User-Generated Content: A Catalyst for Engagement
UGC represents another facet of the digital marketing paradigm, offering a platform for consumers to share their experiences, opinions, and creative expressions related to products and services. This form of content has a profound impact on millennials, who often turn to UGC as a trustworthy source of information before making purchasing decisions. The personal nature of UGC, coupled with its ability to foster community and shared experiences, makes it a potent tool for influencing consumer behavior.
The engagement with UGC, particularly in the consideration stage of the purchasing journey, highlights its significance in the decision-making process. Millennials engage with comments, reviews, and videos to gain insights into products, relying on peer opinions and detailed evaluations to inform their choices. This engagement underscores the need for brands to facilitate and encourage the creation of UGC, providing platforms where consumers can share their experiences and interact with each other.
C. Integrated Marketing Campaigns: Blending Influencer Marketing and UGC
The integration of influencer marketing and UGC within comprehensive campaigns presents a nuanced approach to engaging millennials. These campaigns, which blend the persuasive power of influencers with the authenticity of user-generated content, have the potential to generate curiosity, trust, and excitement among millennials. However, the presence of skepticism highlights the critical need for authenticity and genuine storytelling within these campaigns.
Storytelling emerges as a key element in capturing the attention and interest of millennials, with narrative-driven content demonstrating the ability to engage and resonate deeply with this demographic. The effectiveness of integrated campaigns, therefore, hinges on the ability of brands to craft authentic and compelling stories that reflect the values, interests, and lifestyles of the target audience.
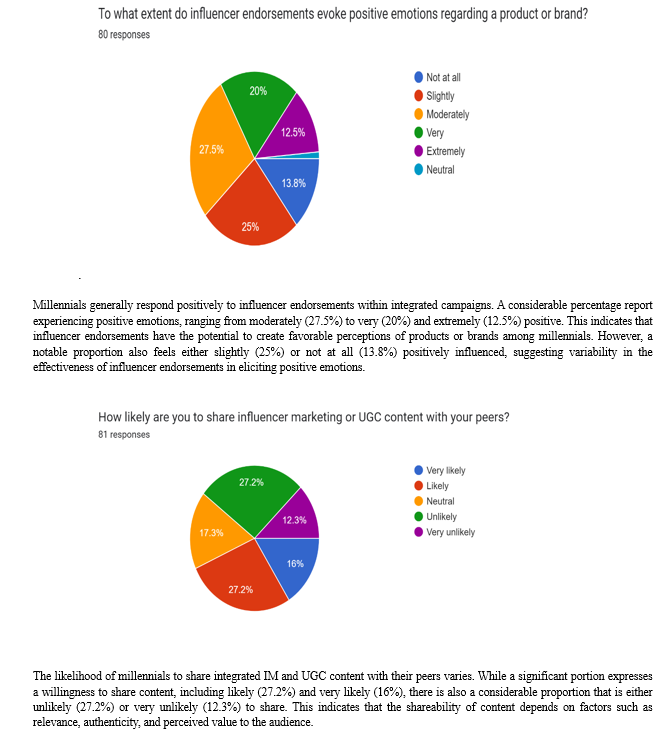
D. The Role of Emotion and Peer Influence
The emotional responses elicited by influencer endorsements and UGC within integrated campaigns reveal the complex interplay of factors influencing millennials' purchasing decisions. Positive emotions, such as trust and excitement, indicate the potential of these endorsements to create favorable perceptions of products or brands. However, the variability in responses suggests that the effectiveness of influencer endorsements is not universal, emphasizing the importance of selecting influencers who genuinely connect with the audience.
Peer influence, as demonstrated through the sharing behavior of millennials, plays a significant role in the dissemination and impact of integrated campaigns. The willingness to share content reflects the perceived relevance, authenticity, and value of the campaign, highlighting the importance of creating content that encourages peer-to-peer interaction and amplification.
E. Tailoring Campaigns to Resonate with Millennials
The findings underscore the importance of tailoring campaigns to align with the values, preferences, and lifestyles of millennials. Integrated campaigns that resonate effectively with this demographic's values are more likely to engage and influence purchasing behavior. This alignment necessitates a deep understanding of the target audience, requiring brands to engage in continuous research and dialogue with millennials to ensure that marketing efforts are relevant and impactful.
F. Implications for Marketers and Brands
Brands and marketers encounter the challenge of managing the intricacies of influencer marketing and User-Generated Content (UGC) in an environment where genuineness and trust are crucial. To connect effectively with millennials, brands should:
- Establish Genuine Relationships: Choose influencers whose principles reflect those of the brand and who have an authentic rapport with their followers. Genuine relationships boost credibility and trust, which are essential for influencing buying behavior.
- Focus on Storytelling: Employ story-driven content to captivate millennials, using storytelling to forge engaging, genuine campaigns that strike a chord with the desired demographic.
- Promote User-Generated Content: Create spaces and opportunities for customers to share their stories and viewpoints. Interacting with and highlighting UGC can strengthen brand authenticity.
VI. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The satisfaction that accompanies that the successful completion of any task would be incomplete without the mention of people whose ceaseless cooperation made it possible, whose constant guidance and encouragement crown all efforts with success. I would like to thank Amity University for giving me the opportunity to undertake this project. I would like to thank my faculty guide Mr Rajeev Pathak who is the biggest driving force behind my successful completion of the project. He has been always there to solve any query of mine and also guided me in the right direction regarding the project. Without his help and inspiration, I would not have been able to complete the project. Also I would like to thank my batch mates who guided me, helped me and gave ideas and motivation at each step.
Conclusion
The findings underscore the paramount importance of trust and authenticity in influencer marketing and UGC strategies. Influencers, by virtue of their relatability and perceived authenticity, wield considerable influence over millennials\' purchasing decisions. However, this influence is heavily contingent upon their credibility and the genuine nature of their endorsements. It becomes clear that for influencer marketing to be effective, influencers must embody the values and interests of their audience, fostering a genuine connection that transcends mere product promotion. Similarly, UGC has emerged as a critical factor in shaping consumer perceptions, serving as a platform for authentic expression and shared experiences. The engagement with UGC reflects a broader desire among millennials for marketing practices that prioritize transparency, authenticity, and community. This trend highlights the necessity for brands to not only encourage the creation of UGC but to actively engage with it, integrating consumer voices into their marketing narratives. Integrated marketing campaigns, which meld the influence of credible influencers with the authenticity of UGC, present a potent strategy for engaging the millennial audience. The success of these campaigns hinges on their ability to resonate with the values, preferences, and lifestyles of millennials, emphasizing the critical role of storytelling and emotional engagement in creating meaningful connections.
References
[1] Dang, L. N. (2021). User-Generated Content and Its Impact on Consumer Behavior: A Cultural Perspective. [2] Duffett, R. (Jul 16, 2015). Facebook advertising\'s influence on intention-to-purchase and purchase amongst Millennials . Internet Res. [3] Gabelaia, I. (Feb 2023). The Impact of User-Generated Content on Customer Purchase Intentions of Online Shoppers. LNNS, Volume 640. [4] Luca, M. (2015). User-Generated Content and Social Media. Handbook of Media Economics. [5] Maksimova, D. (2018). IMPACT OF USER GENERATED CONTENT ON CONSUMER PURCHASE INTENTION . [6] McCormick, K. (2016). Celebrity endorsements: Influence of a product-endorser match on Millennials\' attitudes and purchase intentions. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services. [7] Nugraha, F. (2023). Exploring the Influence of YouTube Videos on Purchase Intentions among Millennial Consumers in Tasikmalaya City. [8] Prakash, B. (2018). Effect of Influencer Marketing On Young Indian Adults. [9] Rahman, J. S. (2022). The Impact of Social Media Influencers on Purchase Intention and the Mediation Effect of Customer Attitude. [10] S Arockia Shiny, P. S. (2023). Impact of Online Consumer Reviews on Consumer Purchase Intention and Buying Decision Among Millennials. [11] Shetu, S. N. (2023). Future Business Journal. [12] Shetu, S. N. (2023). Do user-generated content and micro-celebrity posts encourage generation Z users to search online shopping behavior on social networking sites—the moderating role of sponsored ads. Future Business Journal. [13] Shetu, S. N. (2023). Do user-generated content and micro-celebrity posts encourage generation Z users to search online shopping behavior on social networking sites—the moderating role of sponsored ads. Future Business Journal. [14] Terry Daugherty, M. S. (July 2013). Exploring Consumer Motivations for Creating User-Generated Content. 16-25. [15] Verplancke, N. G. (n.d.). The effect of influencer marketing on the buying behavior of young consumers . [16] Wansi, J. (2012). How do Instagram influencers affect the consumer buying behaviour of Gen-Z? [17] Y Qayyum, O. W. (2024). Swipe to Buy? Examining the Influence of Instagram and TikTok on Millennials\' Fast Fashion Purchases.
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Javin Kohli, Dr. Rajeev Gupta. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET61376
Publish Date : 2024-04-30
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

