Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Classroom to Google Room an Incredible Revolution in Teaching-Learning Pedagogy
Authors: S. Basheer Ahmed, Prof. K. Ratna Shiela Mani
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2021.38868
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Education 4.0 made the world of knowledge acquisition and sharing to take a diverse spin, teaching-learning fully loaded with technology. The extensive use of Smartphone and internet paved a way to include technology into teaching-learning. Inclusion of technology or internet has become obligatory and fetched ease in academic as well as non-academic learning tendencies of inclination of understanding. The instructors have the challenges to guide or edify their learners other than face-to-face means of instructions. The teachers have to be proficient in handling technology or smart tools of teaching-learning besides having command over their area of teaching. This paper focuses on the remote online teaching-learning platforms or tools that help the teachers to teach or guide their learners online and the attitudes of the teachers and the students towards the use of the remote online platforms in ELT.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
The sudden outbreak of Coronavirus made all the streams of business, health and education to look for the right alternative for continuing their services and survival, the pandemic has a fabulous impact on various sectors all over the globe, Holshue, DeBolt, & Lindquist (2020), Peng, Xu, &Li, (2020). It caused the field of education to have an absolute technical shift for its endurance. Since the current situation demands a physical distance among the individuals, no face-to-face learning is possibly carried. Thus, the technical support gears up and occupy a potential role in teaching-learning and stands as a wonderful bridge between teachers and students. Moreover, the requirements of the student community have turned into so classy as well and they find themselves to be perturbed to carry weighty books but feel comfortable in carrying phones with them and this can be used for educational purpose as an effective tool for learning, Tuncay (2016). Smartphone and social media have already become a part of life for the learners antecedently; and the teachers have been appealed to become skilled at the technical aspects especially those that are employed to instruct students, construct new knowledge and assess their understanding. The ‘ICA’ of teaching-learning led many teachers to look for various tools that can channelize their teaching to succeed in their roles. The sudden move from a traditional controlled environment to an online learning platform requires guidance, Geng, Law, & Niu, (2019) and the organizations are encouraging their teaching staff to change their attitudes towards the remote teaching-learning platforms, Mirzajani, Mahmud, Fauzi Mohd. Ayub, & Wong (2016)
Most researchers have been investigating about the alternative online teaching-learning tools, the primary research anticipations of investigators are to examine the aspects such as comprehending the learners’ mindset towards learning through online applications; their miscellaneous opinions and judgments; the criteria followed to assess learning outcomes; a mixture of strategies applied in teaching; the satisfaction expected to achieve; and the students’ performances, (Gonzalez & Louis, 2018; Sun, 2014).
To carry teaching-learning on online platforms there must be a suitable tool that can reach the teachers’ goals and learners’ needs. There should be a modification required in the pedagogy followed by the teachers. Here, the pedagogy stipulates the instructor to get excellence not only in what to teach but also in how to teach. Since the online teaching-learning tools or platforms sway their users to have a good command over them, it becomes crucial for the teachers to be proficient in handling them. Online learning is defined as remote learning that can be carried out online through electronic devices such as Laptops, Desktops, Tablets, and Smartphones, Gonzalez & Louis (2018)
II. EDUCATION 4.0
Harkins, (2008) Emphasizes Education 4.0 as an innovation in learning. It is the subsequent rejoinder of the 4th Industrial revolution which brought a major transformation in human life in general and the governance of human practices in particular. In other words, it is a progression in online technologies. The teachers act as the perfect facilitators whose roles are less in their involvement but high in making their learners involved.
The teacher has to make his learners classify their knowledge and skills rather than spoon-feed themselves to just pass the tests held academically, Hussin (2018). The teachers are the facilitators and they have to use a variety of online platforms or applications to preserve the role, they have to provide a perfect platform to their learners as per their requirements and expectations beyond their academics.
A. Remote Online Teaching-Learning Tools
Education 4.0 gave a wide range of priority to the remote online platforms for the convenience and service to the student community. There are various categories of online teaching-learning tools that come into existence to fill the gaps in teaching-learning professionally as well as academically.
B. Essential Remote Online Applications
Online applications such as Google Classroom, Online Whiteboard, GSuite, and Google Docs, Google Sheets, Google Meet, Google forms, all the social media networks such as Facebook, LinedIn, Youtube, Twitter, WhatsApp, Instagram, Telegram, Messenger, etc, and the other remote online platforms such as blogs, Skype, Webinars, Microsoft Teams, Zoom, WebEx, Quizlet, etc., are the most commonly used remote online teaching-learning platforms that preferably accomplish the maximal teaching-learning goals.
C. Research Objectives
- To identify the attitudes of the teachers towards the utilization of remote online applications in developing writing skills
- To find out the perceptions of the undergraduate level learners of the region towards the remote online platforms in developing writing practices
D. Research Questions
- What are the attitudes of the teachers towards the inclusion of remote online teaching-learning tools in ELT especially in developing writing skills?
- What are the perceptions and believes of the students of undergraduate level from various kinds towards the inclusion of remote online teaching-learning tools in ELT especially in developing writing skills?
E. Research Region and Population
The research was done through survey held in the chosen region among the research population, the chosen region is Rayalaseema situated in Andhra Pradesh of India, and this is populated with the individuals who are extensively populated with the technically advanced students who are comfortable in using smart phones, laptops and other technical gadgets. The chosen population is undergraduate level in their academic level but from varied environments such as technical, engineering, non-engineering, arts, and sciences.
F. Research Methodology
An online survey method was chosen to collect and analyze the responses of the teachers and students of region; the survey was held through online medium by using questionnaires prepared in the application called Google forms.
There were two different questionnaires prepared for teachers and students separately but the statements are aimed at the research questions.
Since, the attempt is to identify the attitudes of both the groups, the statements of the questionnaires were made partially identical and aimed at the valid responses directly towards the inclusion and expected effect of remote online social media tools into teaching and learning. The questionnaires also consist of few other statements related to personal information.
G. Survey
A survey through Google forms app was held in the region to identify the attitudes of the teachers and students towards the use of remote online teaching-learning platforms and their impression on the student community. There were 37 responses of the teachers and 80 responses from the students from various kinds of institutions such as Technical, non-technical, Govt., and self-financing colleges collected through an online survey.
III. DATA ANALYSIS
Besides the personal information, nominal data such as name, gender, age, email id, working institution etc., there was an ordinal data through five crucial statements formed in a five point Likart Scale collected through Google forms application. The statements were prepared to find out the attitudes of the teachers towards the inclusion of remote online teaching-learning platforms in developing students’ writing performances. 76 % of the respondents are the Ph.D level and 24 % are the post graduation level. It is also very clear that all of them are well qualified; their views can be considered valid and reliable. The outcomes of the responses of the teachers are analyzed below.
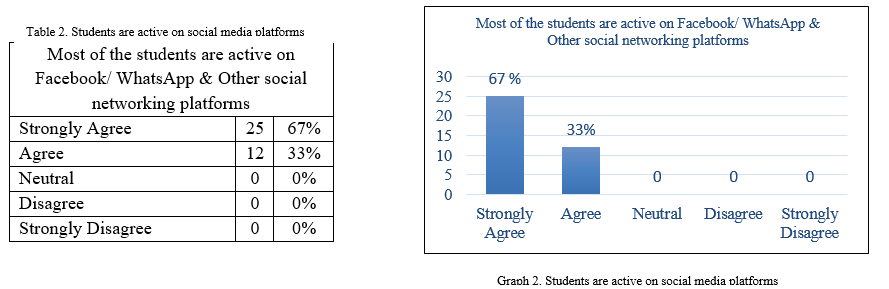
The statement most of the students are active on Facebook/ WhatsApp & Other social networking platforms is made to identify the teachers’ observation regarding the active participation of the student community on the social media platforms like Facebook and WhatsApp. The outcomes of the responses were shown in table 5 and graph 5 below, surprisingly, 67% of the respondents are strongly agreed and 33% are agreed with the statement made. This implies that almost all of them have approved that the students spare their time on social media platforms excessively.
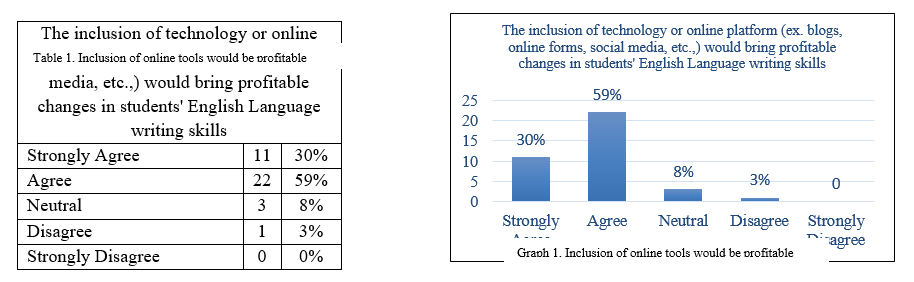
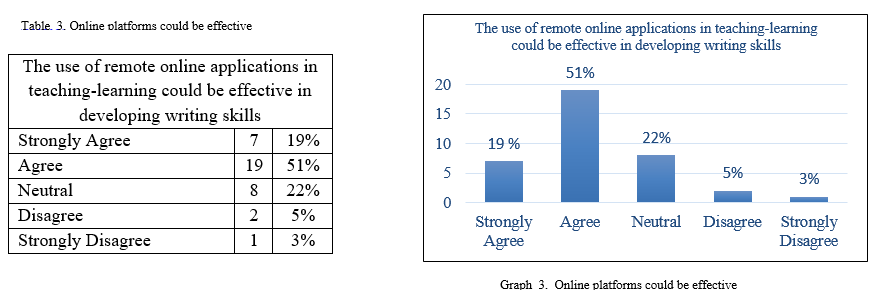
The statement 3 the use of remote online applications in teaching-learning could be effective in developing writing skills is made to find out, the teacher’s view on the use of the social media platforms to help the learners to develop their writing ability. The outcomes of the responses were shown in table 6 and graph 6 below, it is quite impressive that 19% of the respondents strongly agreed, 51% agreed, and 22% neutral to the statement and it is very clear that most of the teachers have a positive attitude towards the inclusion of social media platforms into teaching-learning language in general and writing skills in particular.
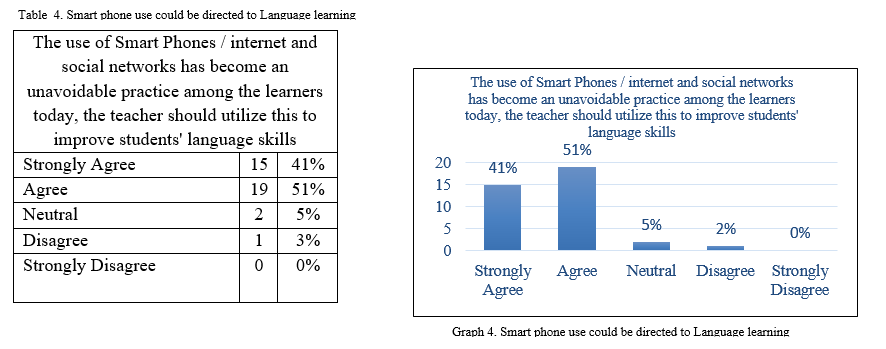
The statement 4 the use of Smart Phones / internet and social networks has become an unavoidable practice among the learners today, the teacher should utilize this to improve students' language skills is made to know if the teachers have positive impression towards the inclusion of smart phones, internet into teaching since they are unavoidable practices among the learners today. The outcomes of the responses were shown in table 7 and graph 7 below, it is very clear from the outcomes that 41% had strongly agreed, 51% agreed, and 5% neutral towards the statement and it is evident that almost all of the respondents have a positive opinion on the given statement and agreed that the use of smart phones or internet or social media platforms has become an inevitable activity among the learners and it would be advantageous if the teachers utilize the habit for teaching-learning goals that they intended to improve among their learners.
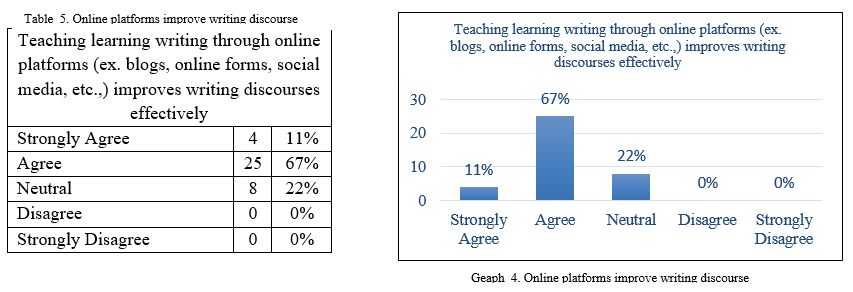
The statement 5 teaching learning writing through online platforms (ex. blogs, online forms, social media, etc.,) improves writing discourses effectively is given to identify the teachers’ attitudes towards the anticipated competence of the use of remote online teaching-learning platforms into teaching writing skills. The outcomes of the responses were shown in table 8 and graph 8 below.11% of the respondents are strongly agreed, 67% agreed, and 22% neutral towards the statement and it is very clear from the outcomes that the maximum number of respondents have a positive perception towards the inclusion that it would bring positive results and can improve the writing performances of the learners.
IV. STUDENT QUESTIONNAIRE
The survey data collected through Google form to identify the attitudes of the students towards the use of remote online teaching-learning platforms and their expected intuition on their learning outcomes is analyzed by following the descriptive statistics. There were 103 responses from the students of various kinds of institutions such as Technical, non-technical, Govt., and self-financing colleges collected through an online Google form survey questionnaire. The questionnaire includes a few statements related to the personal details such as name, age, gender, institution in which they study, and email id. The ordinal data was collected through a questionnaire prepared by following a five point Likert scale and aimed at the six crucial statements which were focused on identifying the attitudes towards the effectiveness of the use of remote online teaching-learning platforms in developing students’ writing performances.
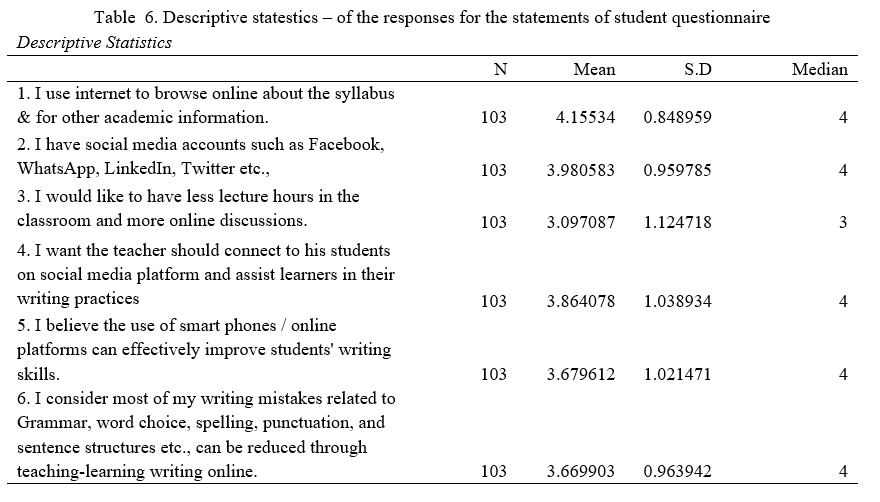
The above table shows the mean, standard deviation, and median of the responses of the students for the statements asked through student questionnaire prepared and circulated through Google form link. The interpretation of the responses is done based on the range of the mean values calculated through appropriate statistical technique; the range of the mean values can be inferred by observing the interpretation table 7 below.
Table 7. Interpretation of the range of the responses
|
Scale |
Range |
Response |
Verbal Interpretation |
|
5 |
4.21 - 500 |
Strongly Agree |
Very High |
|
4 |
3.41- 4.20 |
Agree |
High |
|
3 |
2.61- 3.40 |
Neutral |
Moderately Agree |
|
2 |
1.81- 2.60 |
Disagree |
Low |
|
1 |
1.00 - 1.80 |
Strongly Disagree |
Very Low |
The responses which are shown in table 6 are acquired through student questionnaire and can be interpreted as per the ranges shown in the table 7 to accurately identify the validity of the responses, the given statements fall between the range 3.66 - 4.15 and the SD value 4 except the statement 3 which ranges to 3.08 and SD 3, this is interpreted as the acceptance towards the use of the online teaching-learning tools in developing writing skills as well as language skills is high and the respondents have agreed to the utilization of the remote online tools in learning, the statement 3 (with mean value 3.097087) which talks about the less lecture hours and more online discussions falls in the rage of moderate level that is 2.61- 3.40 and the standard deviation is 3, it is inferred as the responses are neither agree or disagree but have a moderate level of acceptance towards the increase of online hours in place of traditional chalk and talk method of teaching-learning.
Conclusion
Since the use of online tools such as social media networks and other teaching-learning platform has turns to be an inevitable practice among the individuals of technical as well as non-technical environments, a teacher has to be well prepared and ready to organize the teaching activity via the integration of technology of online teaching-learning tools or networking platforms in teaching. The teachers have to accustom themselves to the technology as well as the management of online learning tools; the effective use of online platforms in their teaching-learning framework will make them effortlessly cater to the requirements of their learners. Awareness towards the remote online teaching-learning tools and acquiring the total competence towards the heterogeneous online applications are the need of the hour. The responses obtained through survey questionnaire are delimited to identification of the attitudes of the teachers and students of the region and are minimized to only the strait forward opinions on the notion expecting the valid judgments towards the inclusion of remote online teaching-learning applications in developing writing skills among the undergraduate level learners. The outcomes of the survey are satisfactory and present the observations of the learners and teachers positive.
References
[1] Chaiyo, Y., &Nokham, R. (2017). The effect of Kahoot, Quizizz and Google Forms on the student\'s perception in the classrooms response system. Paper presented at the International Conference on Digital Arts, Media and Technology (ICDAMT). Chiang Mai: IEEE [2] Geng, S., Law, K., & Niu, B. (2019). Investigating self-directed learning and technology readiness in blending learning environment. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 16. http://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-019-0147-0. [3] Gonzalez, D., & Louis, R. St. (2018). Online Learnng. In J. I. Liontas (Ed.), The TESOL Encyclopedia of English Language Teaching (1sted.). http://doi.org/10.1002/97811184235.eelt0423 [4] Harkins, A.M. (2008). Leapfrog principles and practices: Components of education 3.0 and 4.0. Future Research Quarterly, 24(1), 19-31. [5] Holshue, M.L., DeBolt, C., & Lindquist, S. (2020). First case of 2019 novel Coronavirus in the United States. New England Journal of Medicine, 382, 929. [6] Hussin, A.A. (2018). Education 4.0 made simple: Ideas for teaching. International Journal of Education & Literacy Studies, 6(3), 92-98. Available at: 10.7575/aiac.ijels.v.6n.3p.92. [7] Iftakhar, S. (2016). Google Classroom: What works and how? Journal of Education and Social Sciences, 3(1), 12-18. [8] Mirzajani, H., Mahmud, R., FauziMohdAyub, A., & Wong, S. L. (2016). Teachers’ acceptance of ICT and its integration in the classroom. Quality Assurance in Education, 24(1), 26-40. http://doi.org/10.1108/QAE-06-2014-0025. [9] Omar, A., Amir, Z., & Mohamad, M. (2018). Facilitating online learning: students’ online discussion strategies for a project work at a technical university in Malaysia. 3L: The Southeast Asian Journal of English Language Studies, 24(4), 102-114. Available at: 10.17576/3L-2018-2404-08. [10] Peng, X., Xu., X., & Li, Y. (2020). Transmission routes of 2019-nCoV and controls in dental practice. International Journal of Oral Science, 12, 1. [11] Tan, P., & Tan, K. (2020). In-game instructions: The extent of their usefulness in enhancing the vocabulary acquisition of ESL learners. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (iJET), 15(4), 73-89. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3991/ijet.v15i04.11647. [12] Tuncay, N. (2016), Smartphones as tools for distance education. Journal of education & institutional Studies in the World, 6(2), 20-30. [13] Zarzycka-Piskorz, E. (2016). Kahoot it or not? Can games be motivating in learning grammar? Teaching English with Technology, 16(3), 17-36.
Copyright
Copyright © 2022 S. Basheer Ahmed, Prof. K. Ratna Shiela Mani. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET38868
Publish Date : 2021-11-13
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

