Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- References
- Copyright
Influence of Training and Development Programs on Job Satisfaction
Authors: P. Pragna Vikasitha, Dr. Vinayak Anil Bhat
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.60364
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
This research document delves into the critical relationship between training and development programs and employee job satisfaction. Drawing on existing literature, the study highlights the significance of effective training interventions in enhancing employee skills, knowledge, and competencies, ultimately fostering a sense of support and professional growth among employees. While providing valuable insights into the impact of training programs on satisfaction and commitment, the document also identifies key research gaps, including the need to pinpoint specific impactful aspects of training, explore moderating factors, and understand broader impacts on employee well-being and performance. Moving forward, future research opportunities lie in comparative analyses across industries, longitudinal studies, qualitative explorations, cross-cultural investigations, technological advancements, employee well-being considerations, and organizational performance assessments. By addressing these avenues, researchers can advance our understanding of how training programs influence job satisfaction and inform organizational practices to cultivate a satisfied, engaged, and productive workforce.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE
A. Rationale For The Study And Motivation
Employee satisfaction is no longer a "nice-to-have" but a cornerstone of organizational success in today's competitive landscape. Satisfied employees are demonstrably more engaged, productive, and less likely to leave the company. This translates into a significant cost advantage for organizations, with reduced recruitment and training costs, improved customer service due to higher employee morale, and an overall more positive work environment.
Training and development programs represent substantial investment organizations make in their workforce. These programs aim to equip employees with the skills and knowledge necessary to perform their jobs effectively, adapt to changing industry demands, and contribute to the organization's strategic goals. However, despite the widespread adoption of training initiatives, there remains a gap in our understanding of how these programs truly influence job satisfaction. While a general positive correlation exists, a more comprehensive picture is needed to identify the specific aspects of training programs that have the most significant impact on employee sentiment.
This lack of conclusive evidence presents a significant challenge. Without a clear understanding of which training program features contribute most to job satisfaction, organizations struggle to design and deliver programs that are truly impactful. Generic training initiatives may not effectively address the core needs and aspirations of employees, leading to a disconnect between the investment made and the desired outcome.
Furthermore, a deeper understanding of this link between training and job satisfaction allows for a more tailored approach. By pinpointing the program elements that resonate most with employees, organizations can create targeted training experiences that cater to specific skill gaps, career development aspirations, or areas for professional growth. This targeted approach is likely to yield a more significant return on investment in terms of employee satisfaction and overall organizational performance.
The motivation for this research stems from a desire to bridge this critical gap in our understanding of how training and development programs influence employee job satisfaction. By delving deeper into this topic, the study aims to:
- Inform Best Practices: Equip organizations with robust data and insights that can guide the development and implementation of training programs demonstrably linked to enhanced job satisfaction. This will allow organizations to make strategic decisions regarding their training budgets, ensuring they are investing in programs with the highest potential for positive employee sentiment.
- Increase Employee Engagement: Identify specific training program elements that go beyond just skill development. By focusing on aspects that foster a sense of growth, accomplishment, and value within the organization, the study can empower organizations to create a more engaged workforce.
This translates to higher levels of motivation, initiative, and overall commitment to achieving organizational goals.
3. Optimize Resource Allocation: Help organizations maximize the return on investment (ROI) from their training budgets. By identifying the areas of training that yield the most significant improvements in job satisfaction, organizations can prioritize these areas and allocate resources more effectively. This ensures they are investing in initiatives that not only equip employees with necessary skills but also contribute to a more positive and productive work environment.
In conclusion, this research is motivated by the potential to significantly impact both employees and organizations. By providing a clearer understanding of how training influences job satisfaction, the study can pave the way for the development of more effective training programs that contribute to a more engaged workforce and a thriving organizational ecosystem.
B. Statement for Research Problem
While training and development programs are significant investment organizations make in their workforce, a critical gap exists in our understanding of how these programs specifically influence employee job satisfaction. Current research often lacks detail on which aspects of training programs have the most significant impact. This obscurity hinders organizations' ability to design and deliver targeted training initiatives that demonstrably enhance employee satisfaction. Consequently, organizations struggle to maximize the return on investment (ROI) from their training budgets.
This research aims to address this gap by investigating the specific aspects of training and development programs that contribute most significantly to employee job satisfaction. By delving deeper, the study seeks to identify potential moderating factors, such as employee demographics, job type, or organizational culture, that might influence the effectiveness of training programs. Additionally, the research will explore the role of perceived program quality and effectiveness in mediating the relationship between training and job satisfaction.
Ultimately, this research seeks to provide organizations with actionable insights to optimize their training programs, leading to a more satisfied, engaged, and productive workforce.
C. Review of Literature
Amiruddin and Abdullah's (2017) study explores the relationship between training and development activities and job satisfaction among Malaysian public sector employees. This research adds to the existing literature by examining how training and development initiatives impact job satisfaction within the unique context of the Malaysian public sector. Previous studies have established a positive association between training programs and job satisfaction across various organizational settings, emphasizing the importance of investing in employee development to enhance performance and motivation. However, the specific dynamics of the public sector in Malaysia, including government policies, organizational structures, and cultural influences, may influence the effectiveness of training interventions in fostering job satisfaction among employees. By focusing on this context, the study provides insights that are relevant for policymakers and organizational leaders in designing and implementing training programs that effectively contribute to employee satisfaction and organizational performance in the Malaysian public sector.
Al-Hawamdeh and Haj-Yahya's (2018) investigation into the impact of employee training and development programs on job satisfaction and organizational commitment within Jordanian banks aligns with a broader literature emphasizing the crucial role of training initiatives in shaping employee attitudes and behaviors in the banking sector. Existing research underscores the positive relationship between employee training, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment, as training programs enhance employee skills, knowledge, and perceptions of organizational investment in their professional growth. This alignment is particularly relevant in the banking industry, where employee competencies directly affect customer satisfaction and organizational performance. Despite variations in effectiveness influenced by contextual factors such as organizational culture and leadership style, the study offers valuable insights into the unique dynamics of Jordanian banks, informing strategies to enhance employee satisfaction, commitment, and overall organizational performance through targeted training and development initiatives.
Anwar and Ahmad's (2018) study on the influences of training and development activities on job satisfaction and organizational commitment among banking staff in Malaysia addresses a significant gap in the literature regarding the banking sector in the Malaysian context. Prior research has established the importance of training and development programs in enhancing employee skills and job satisfaction across various industries. Specifically, within the banking sector, where competition is intense and customer demands are constantly evolving, effective training initiatives are essential for maintaining a skilled and motivated workforce. Furthermore, job satisfaction and organizational commitment are crucial factors for employee retention and organizational success in the banking industry.
Anwar and Ahmad's study contributes to our understanding of these dynamics by investigating the specific effects of training and development activities on job satisfaction and organizational commitment among banking staff in Malaysia, providing insights that are valuable for both academic research and practical implications for human resource management in the banking sector.
Barakat and Abu-Saad's (2018) study investigates the impact of training and development programs on job satisfaction and turnover intention among Palestinian university staff members. Within the broader literature on training programs and employee outcomes, their research contributes by focusing specifically on the context of Palestinian universities. Previous studies have highlighted the significance of training initiatives in enhancing job satisfaction and reducing turnover intention across various organizational settings. By examining this relationship within the unique socio-political and cultural context of Palestinian universities, the study provides valuable insights that are relevant to the challenges and dynamics faced by staff members in this specific context. The findings of the study can inform human resource management strategies in Palestinian universities and contribute to the broader understanding of the role of training and development programs in improving employee satisfaction and retention in similar contexts.
Chang, Cheng, and Lin's (2018) study examines the mediating role of work engagement in the relationships between training and development practices and job satisfaction among Taiwanese service workers. The literature indicates a substantial link between training and development initiatives and job satisfaction, with training programs often enhancing employees' skills, knowledge, and competencies, consequently leading to increased job satisfaction. Furthermore, work engagement has been identified as a crucial mechanism through which training practices positively impact job satisfaction, as engaged employees tend to experience higher levels of satisfaction with their work. By investigating these relationships within the context of Taiwanese service workers, the study contributes to our understanding of how training and development practices can influence job satisfaction through the mediating pathway of work engagement, providing valuable insights for organizations aiming to improve employee satisfaction and performance in the service sector.
Cheung and Leung's (2018) study on the moderated mediation model of training and development, job satisfaction, and employee retention in Hong Kong retail organizations adds significant insights to the existing literature on human resource management. Drawing upon the moderated mediation framework, the study explores the complex interplay between training and development programs, job satisfaction, and employee retention. Through empirical investigation within the specific context of Hong Kong's retail sector, the study elucidates how the relationship between training and development initiatives and employee retention is mediated by job satisfaction, with the moderation effect of individual and organizational factors further shaping this relationship. By focusing on the dynamic nature of these relationships and considering the unique characteristics of the retail industry in Hong Kong, the study provides valuable implications for both theory and practice in human resource management, offering actionable strategies for organizations to enhance employee retention through effective training and development programs.
Dey and Dasgupta's (2018) study delves into the linkage between training and development initiatives and job satisfaction among Indian IT professionals, contributing to the growing literature on human resource management in the IT sector. The literature underscores the importance of training programs in enhancing employee skills and knowledge, thereby positively influencing job satisfaction. Specifically, within the IT industry, where rapid technological advancements necessitate continuous learning and upskilling, training and development initiatives play a crucial role in ensuring employee satisfaction and engagement. Prior research has highlighted the positive impact of training programs on job satisfaction among IT professionals, as they provide opportunities for career growth, skill enhancement, and professional development. However, contextual factors such as organizational culture, leadership support, and the quality of training delivery may influence the effectiveness of these initiatives in fostering job satisfaction. By focusing on Indian IT professionals, the study provides valuable insights into the specific challenges and dynamics of the IT industry in India, offering practical implications for human resource management practices aimed at enhancing employee satisfaction and organizational performance.
Ghazali and Mohd Noor's (2018) study investigates the relationship between training and development activities and job satisfaction among Malaysian civil servants. The literature surrounding this topic underscores the importance of training and development initiatives in enhancing employee skills, knowledge, and job performance, which in turn can positively impact job satisfaction. Prior research suggests that organizations that invest in employee development through training programs tend to foster a supportive work environment and demonstrate a commitment to employee growth, leading to higher levels of job satisfaction among employees. Additionally, in the context of civil service, where job roles may be complex and dynamic, effective training and development activities are crucial for equipping employees with the necessary competencies to fulfill their responsibilities and navigate organizational challenges.
By examining this relationship within the Malaysian civil service context, Ghazali and Mohd Noor's study contributes valuable insights that can inform human resource management practices and policies aimed at enhancing employee satisfaction and organizational effectiveness within the public sector.
Hamid and Rahmat's (2018) study on "The impact of training and development programs on job satisfaction and organizational commitment among Indonesian bank employees" addresses a critical gap in the literature by examining the relationship between training and development initiatives, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment within the context of Indonesian banks. Existing literature suggests that training programs play a crucial role in enhancing employee skills and knowledge, leading to higher levels of job satisfaction and organizational commitment. Studies in various organizational settings have consistently demonstrated a positive association between training programs and employee satisfaction and commitment (Saks & Belcourt, 2006; Tannenbaum, 1997). However, the effectiveness of training interventions may vary depending on contextual factors such as organizational culture and individual characteristics of employees. By focusing specifically on Indonesian bank employees, the study offers insights that are relevant to the unique challenges and dynamics of the banking industry in Indonesia. The findings of the study have practical implications for organizations seeking to improve employee satisfaction and commitment through targeted training and development interventions.
Huang and Yang's (2018) study investigates the relationship between training and development programs and job satisfaction in Taiwanese financial institutions, with a focus on the mediating role of psychological capital. The literature highlights the significance of training programs in enhancing employee skills and competencies, leading to improved job satisfaction. Additionally, psychological capital, encompassing positive psychological resources such as optimism, resilience, self-efficacy, and hope, has been identified as a crucial factor influencing job satisfaction. Drawing on this theoretical framework, the study explores how training and development programs contribute to the development of psychological capital among employees, ultimately impacting their levels of job satisfaction within the context of Taiwanese financial institutions. By examining this relationship, the study provides empirical evidence that can inform organizational practices and strategies aimed at optimizing training initiatives to enhance employee well-being and organizational outcomes in the financial sector of Taiwan.
Karimi and Khosravi (2018) examined "The impact of training and development programs on job satisfaction and organizational commitment among Iranian bank employees." The study delves into the relationship between training and development initiatives and their influence on both job satisfaction and organizational commitment within the specific context of Iranian banks. Existing literature suggests a strong association between training programs and job satisfaction, with effective training interventions leading to enhanced employee skills, knowledge, and competencies. Moreover, organizational commitment, characterized by employees' loyalty and attachment to the organization, is also influenced by training programs that foster a sense of support and investment in employees' professional growth. By focusing on the Iranian banking sector, the study provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of training and development programs in enhancing employee satisfaction and commitment within this unique organizational context, thereby contributing to the broader literature on human resource management and organizational behavior.
Belal and El-Sayed's (2019) study investigates the impact of training and development programs on job satisfaction and organizational commitment among Egyptian government employees. The literature on this topic indicates a significant relationship between training interventions and employee outcomes such as job satisfaction and organizational commitment. Training programs are recognized as essential mechanisms for enhancing employee skills, knowledge, and competencies, thereby fostering positive attitudes and behaviors towards their organizations. Prior research suggests that employees who receive adequate training opportunities are more likely to report higher levels of job satisfaction and stronger commitment to their organizations (Saks & Belcourt, 2006; Arthur, 1994). However, the effectiveness of training programs may vary depending on contextual factors such as organizational culture, leadership support, and the design of the training initiatives (Wexley & Baldwin, 1986; Blume et al., 2010). By focusing on Egyptian government employees, Belal and El-Sayed's study contributes to our understanding of the effects of training and development programs in a unique organizational context, offering insights that can inform human resource management practices and strategies aimed at enhancing employee satisfaction and commitment within the public sector.
Aghaei-Torbati and Zare's (2019) study on the effects of training programs on job satisfaction among employees in Iranian banks contributes to the existing literature, which highlights the significant relationship between training initiatives and job satisfaction across various organizational contexts. Training programs are recognized as crucial mechanisms for enhancing employee skills and knowledge, ultimately leading to higher levels of job satisfaction and motivation. While prior research underscores the importance of training interventions in addressing organizational needs and fostering employee development, the effectiveness of these programs may be influenced by contextual factors such as organizational culture and individual characteristics.
By focusing on the banking industry in Iran, the study provides valuable insights that can inform organizational practices and strategies aimed at improving employee satisfaction and performance through effective training interventions.
The study conducted by Hassan Jabak (2023) titled "The Effect Of Training & Development On Job Satisfaction: The Mediating Effect Of Coworker Support" addresses an important aspect of organizational behavior and human resource management. The literature surrounding the relationship between training and development programs and job satisfaction has been extensively explored, with studies consistently highlighting the positive impact of such programs on employees' satisfaction levels (Arthur, 1994; Saks & Belcourt, 2006). Training and development initiatives are crucial for enhancing employees' skills, competencies, and overall job performance, which in turn contribute to higher levels of job satisfaction (Tannenbaum, 1997). However, Jabak's study goes beyond the direct relationship between training and job satisfaction by examining the mediating role of coworker support. This is an important addition to the literature, as coworker support has been identified as a significant predictor of job satisfaction (Eisenberger et al., 1990; Rhoades & Eisenberger, 2002). The study hypothesizes that coworker support mediates the relationship between training and development programs and job satisfaction, suggesting that the positive effects of training may be amplified through supportive relationships with colleagues. By investigating this mediating mechanism, the study provides valuable insights into the complex interplay between training programs, coworker support, and job satisfaction, offering practical implications for organizations aiming to enhance employee satisfaction and well-being. Overall, Jabak's study contributes to the literature by advancing our understanding of the mechanisms through which training and development programs influence job satisfaction, highlighting the importance of coworker support as a potential mediator in this relationship.
Hussain and Ahmed (2023) explore the critical role of training and development in enhancing employee job satisfaction through a case study conducted in a telecommunications company in Pakistan. The literature on training and development and its impact on job satisfaction provides a foundational understanding for this study. Prior research emphasizes the importance of training programs in equipping employees with the necessary skills, knowledge, and competencies to perform their roles effectively (Saks & Belcourt, 2006; Tannenbaum, 1997). Effective training initiatives are found to positively influence employee job satisfaction by fostering a sense of competence, confidence, and fulfillment in their roles (Arthur, 1994; O'Leary-Kelly et al., 1994). Moreover, organizations that invest in employee development are seen as supportive environments, leading to higher levels of job satisfaction among employees (Noe, 1986; Bhatti & Qureshi, 2007). In the telecommunications industry specifically, training and development programs are crucial for addressing the rapid technological advancements and changing customer demands, thereby influencing employee satisfaction and performance (Haque & Saha, 2017; Saad & Azmi, 2018). However, the literature also acknowledges that the effectiveness of training and development programs in enhancing job satisfaction may vary based on organizational culture, design, and delivery of the training, as well as individual employee characteristics (Wexley & Baldwin, 1986; Blume et al., 2010). Hussain and Ahmed's study fills a gap in the literature by providing empirical evidence through a case study approach, offering insights into the specific context of a telecommunications company in Pakistan. By focusing on this industry and geographical context, the study contributes valuable knowledge that can inform organizational practices and strategies aimed at enhancing employee job satisfaction through effective training and development initiatives.
In their study titled "The Impact of Employee Training and Development Programs on Job Satisfaction: A Study on the Banking Sector in Oman," Jaber and Al-Hosni (2023) investigate the relationship between training and development programs and job satisfaction within the context of the banking sector in Oman. The literature on employee training and development programs highlights their significant role in enhancing employee skills, knowledge, and competencies, ultimately leading to higher levels of job satisfaction. Previous research has emphasized the importance of training interventions in addressing organizational needs, fostering employee growth, and improving job performance (Saks & Belcourt, 2006; Arthur, 1994). Moreover, studies have shown that employees who perceive their organizations as supportive of their professional development report greater job satisfaction and motivation (Noe, 1986; Bhatti & Qureshi, 2007). In the banking industry specifically, training programs play a crucial role in equipping employees with the necessary skills to adapt to technological advancements and changing customer demands (Haque & Saha, 2017). Research in similar contexts has demonstrated a positive relationship between training programs and job satisfaction, as employees feel more competent and confident in their roles (Saad & Azmi, 2018). However, the effectiveness of training programs may vary depending on factors such as the design and delivery of the training, organizational culture, and individual characteristics of employees (Wexley & Baldwin, 1986; Blume et al., 2010). Therefore, the study by Jaber and Al-Hosni (2023) contributes to our understanding of the impact of training and development programs on job satisfaction, specifically within the banking sector in Oman. By focusing on this specific context, the study provides valuable insights that can inform organizational practices and strategies aimed at enhancing employee satisfaction and performance through effective training interventions.
The research paper by Khalaf and Al-Khateeb (2023) titled "The Effect of Training and Development on Job Satisfaction and Employee Performance: A Study of the Healthcare Sector in Jordan" explores the relationship between training and development initiatives, job satisfaction, and employee performance within the context of the healthcare sector in Jordan. The literature on training and development, job satisfaction, and employee performance underscores their interconnectedness and significance in organizational settings. Training and development programs are crucial for enhancing employee skills, knowledge, and competencies, which in turn contribute to job satisfaction and improved performance (Saks & Belcourt, 2006; Arthur, 1994). Research in healthcare organizations emphasizes the importance of continuous learning and development for healthcare professionals to keep up with advancements in medical technology and patient care (Salas et al., 2008). Moreover, studies have demonstrated that satisfied employees in the healthcare sector are more likely to provide high-quality patient care and exhibit greater organizational commitment (Larrabee et al., 2003; Hayes et al., 2012). However, the effectiveness of training and development programs in healthcare settings may be influenced by various factors such as organizational culture, leadership support, and the availability of resources (Lehman et al., 2016). Understanding the dynamics of training and development in the healthcare sector is particularly crucial in countries like Jordan, where healthcare systems are undergoing rapid transformations to meet the growing demands for quality healthcare services (Haddad et al., 2017). Thus, Khalaf and Al-Khateeb's study fills a significant gap in the literature by investigating the specific context of the healthcare sector in Jordan and examining how training and development initiatives impact both job satisfaction and employee performance. The findings of their study have important implications for healthcare organizations in Jordan and beyond, providing insights that can inform strategic decisions related to employee training and development programs aimed at enhancing job satisfaction and improving overall performance in the healthcare sector.
Kwon and Lee's (2023) research delves into the impact of training and development programs on both job satisfaction and employee performance within the service sector of South Korea. This study contributes significantly to the existing literature, which extensively explores the interconnectedness between training initiatives, job satisfaction, and employee performance across diverse organizational settings. Previous research has consistently highlighted the positive association between training and development programs and job satisfaction, as these programs are recognized for their role in enhancing employee skills, competencies, and overall job fulfillment (Saks & Belcourt, 2006; Arthur, 1994). Similarly, studies have emphasized the importance of training interventions in bolstering employee performance by equipping them with the necessary knowledge and capabilities to excel in their roles (Tannenbaum, 1997; Blume et al., 2010). However, the effectiveness of training programs in fostering job satisfaction and performance may vary depending on contextual factors such as organizational culture, leadership style, and the nature of the industry (Wexley & Baldwin, 1986; Haque & Saha, 2017). Kwon and Lee's (2023) study focuses specifically on the service sector in South Korea, shedding light on the unique dynamics and challenges within this industry. By examining the relationship between training and development programs, job satisfaction, and employee performance in the South Korean service sector, the study offers valuable insights that can inform organizational practices and strategies aimed at enhancing employee satisfaction and productivity. Through rigorous empirical analysis, Kwon and Lee (2023) contribute to a deeper understanding of the mechanisms through which training initiatives influence employee outcomes, ultimately providing practical implications for human resource management in the service sector of South Korea.
Marques and Carvalho's (2023) study investigates the impact of training and development programs on both job satisfaction and employee turnover within the hospitality sector in Portugal. The relationship between training programs and job satisfaction has been extensively explored in the literature, with empirical evidence suggesting that effective training initiatives contribute positively to employees' job satisfaction levels (Arthur, 1994; Saks & Belcourt, 2006). By investing in employee development, organizations demonstrate their commitment to enhancing job-related skills and competencies, which can lead to increased levels of job satisfaction (Tannenbaum, 1997). Furthermore, prior research has highlighted the importance of job satisfaction in reducing employee turnover intentions (Griffeth et al., 2000). Dissatisfied employees are more likely to seek alternative employment opportunities, leading to higher turnover rates within organizations (Mobley, 1977). Therefore, understanding the interplay between training programs, job satisfaction, and employee turnover is crucial for hospitality organizations, given the industry's reliance on a skilled and motivated workforce to deliver quality service experiences (Pizam & Ellis, 1999). Marques and Carvalho's study provides valuable insights into this relationship within the specific context of the hospitality sector in Portugal, contributing to both theoretical understanding and practical implications for organizational management. By examining these dynamics, the study aims to inform strategies aimed at reducing turnover rates and enhancing job satisfaction among employees in the Portuguese hospitality industry, ultimately leading to improved organizational performance and competitiveness.
The research paper by Moghavvemi and Abdullah (2023) investigates the impact of training and development on job satisfaction and employee performance within the construction sector in Malaysia. The study aligns with a growing body of literature emphasizing the critical role of training and development initiatives in enhancing employee outcomes across various industries. Previous research has established a strong relationship between training programs and job satisfaction, with employees who receive adequate training reporting higher levels of job satisfaction (Saks & Belcourt, 2006; Tannenbaum, 1997). Additionally, training and development interventions have been associated with improved employee performance, as they equip individuals with the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their roles effectively (Arthur, 1994). The construction sector, in particular, presents unique challenges and opportunities for training and development due to its dynamic nature and the diverse skill sets required for different roles within the industry (Haque & Saha, 2017). Studies focusing on the construction sector have highlighted the importance of training programs in addressing skill gaps, improving productivity, and enhancing job satisfaction among employees (Saad & Azmi, 2018). However, the effectiveness of training and development initiatives in the construction industry may be influenced by factors such as the nature of the projects, organizational culture, and the availability of resources (Wexley & Baldwin, 1986; Blume et al., 2010). By examining these dynamics within the context of the construction sector in Malaysia, the study by Moghavvemi and Abdullah (2023) contributes valuable insights that can inform organizational practices and policies aimed at maximizing the impact of training and development programs on job satisfaction and employee performance.
Nguyen and Nguyen's (2023) study investigates the impact of training and development programs on both job satisfaction and employee performance within the manufacturing sector in Vietnam. The literature on training and development programs emphasizes their crucial role in enhancing employee skills, knowledge, and competencies, ultimately leading to improved job satisfaction and performance outcomes. Prior research has highlighted the positive relationship between training initiatives and job satisfaction, as employees who perceive their organizations as investing in their development tend to report higher levels of satisfaction and motivation. Moreover, training programs have been associated with increased employee performance, as they equip workers with the necessary skills to perform their roles effectively and adapt to changing job demands. However, the effectiveness of training and development programs may be influenced by various factors such as the design and delivery of the programs, organizational culture, and individual characteristics of employees. By focusing on the manufacturing sector in Vietnam, Nguyen and Nguyen's study provides valuable insights into the specific context of training and development practices in a rapidly growing economy. The findings of the study have implications for both theory and practice, offering recommendations for organizations to optimize their training initiatives to enhance job satisfaction and employee performance within the Vietnamese manufacturing sector.
D. Identification of Research Gaps
The influence of training and development programs on job satisfaction is a well-researched topic, but there are still key areas where our understanding can be improved. A major gap exists in pinpointing which aspects of training programs have the strongest impact on employee satisfaction. Current research often focuses on the overall effectiveness of programs, but a deeper dive into specific elements like skill development focus, career growth opportunities, or program design features is needed.
Furthermore, the relationship between training and job satisfaction might not be universal. Factors like employee demographics (age, experience), job type (technical, managerial), and even organizational culture (collaborative, hierarchical) could act as moderators, influencing the program's effectiveness. Investigating these moderating factors can provide a more nuanced understanding of how training programs impact different segments of the workforce.
Finally, the scope of research often goes beyond just overall job satisfaction. Exploring how training programs influence other aspects of employee well-being and performance can be valuable. This could include employee engagement, sense of
accomplishment, or perceived growth potential within the organization. Understanding these broader impacts can provide organizations with a more holistic view of the return on investment (ROI) associated with their training programs.
By addressing these gaps in our understanding, your research can significantly contribute to the field. By focusing on specific program elements, exploring moderating factors, and considering broader impacts on employee well-being, your study can offer valuable insights for organizations to design and deliver training programs that not only enhance job satisfaction but also cultivate a more engaged and productive workforce.
E. Theoretical Underpinnings
- Human Capital Theory: Human capital theory posits that investments in education and training contribute to the accumulation of knowledge, skills, and abilities in individuals, ultimately enhancing their productivity and job satisfaction.
This theory can be used to frame the idea that training and development programs serve as a form of investment in employees, leading to increased job satisfaction as they perceive the value of their enhanced skills.
2. Social Exchange Theory: Social exchange theory suggests that individuals engage in relationships based on the expectation of reciprocal benefits. Applied to the context of training programs, employees may perceive the investment in their development as a positive exchange with the organization, leading to increased job satisfaction as they feel valued and supported.
3. Expectancy Theory: Expectancy theory proposes that individuals are motivated to act in a certain way if they expect a desired outcome. In the context of training programs, employees may experience increased job satisfaction if they believe that participating in such programs will lead to improved performance, career advancement, and personal development.
4. Job Characteristics Model: The Job Characteristics Model emphasizes the impact of core job characteristics (skill variety, task identity, task significance, autonomy, and feedback) on employee motivation and satisfaction. Training and development programs can be seen as mechanisms to enhance these job characteristics, subsequently influencing job satisfaction by making jobs more meaningful and engaging.
By drawing upon these theoretical frameworks, researchers can elucidate the underlying mechanisms through which training and development programs influence job satisfaction, providing a comprehensive understanding of this relationship and informing the design and implementation of effective human resource management practices within organizations.
II. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Scope Of The Study
The scope of this research revolves around investigating the relationship between training and development programs and job satisfaction within a specific organizational context. It entails examining various dimensions of training and development initiatives implemented within the organization, ranging from formal workshops to informal mentoring methods. Job satisfaction will be the central focus, encompassing factors such as satisfaction with the work environment, growth opportunities, and interpersonal relationships. The study will delve into mediating and moderating factors that may influence this relationship, considering individual employee characteristics and organizational factors. Employing a mixed-methods approach, the research will combine quantitative surveys with qualitative interviews or focus groups to gather comprehensive insights. Data analysis will involve statistical techniques like regression analysis for quantitative data and thematic analysis for qualitative data. Acknowledging limitations such as sample size constraints and the inability to establish causality, the study will offer implications for both theory and practice, aiming to provide recommendations for organizations to optimize their training and development programs for enhancing job satisfaction among employees. Through this research, we seek to contribute to the existing knowledge base on this topic, offering valuable insights for human resource management practices in organizations.
B. Research Objectives
- To examine the effectiveness of various training and development programs implemented within the organization in enhancing job satisfaction among employees.
- To identify the key dimensions of job satisfaction affected by training and development initiatives, including satisfaction with the work environment, growth opportunities, and interpersonal relationships.
- To investigate the mediating and moderating factors influencing the relationship between training and development programs and job satisfaction, considering individual employee characteristics and organizational factors.
- To contribute to the existing body of knowledge on the influence of training and development programs on job satisfaction, offering valuable insights for both academic research and practical implications for human resource management practices.
- To determine whether the influence of training programs on job satisfaction varies depending on employee demographics.
C. Framing of Research Hypotheses
Null Hypothesis (H0): There is no significant relationship between participation in training and development programs and employees' job satisfaction.
Alternative Hypothesis (H1): There is a significant positive relationship between participation in training and development programs and employees' job satisfaction.
D. Research Design
The research design for exploring the influence of training and development programs on job satisfaction adopts a mixed-methods approach, integrating quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews. Participants will be randomly sampled from various organizational departments within the target organization. Structured questionnaires will be distributed to collect quantitative data on participants' perceptions of training and development programs and their levels of job satisfaction. These surveys will encompass validated scales and demographic inquiries. Statistical analysis, including correlation analysis, regression analysis, and analysis of variance (ANOVA), will be conducted using software such as SPSS or R. Additionally, purposive sampling will be employed for semi-structured interviews with select participants, aimed at capturing diverse perspectives. These qualitative interviews will delve deeper into participants' experiences with training and development programs and their perceptions of job satisfaction. Thematic analysis will be applied to transcribed interview data to identify patterns and themes. Integrating findings from both quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews will provide a comprehensive understanding of the research topic, strengthened through triangulation to enhance credibility and reliability. This mixed-methods approach ensures robust insights and offers practical recommendations for organizations looking to optimize their training and development programs to enhance employee job satisfaction.
E. Methods for Data collection and variables of the study
- Methods of data collection:
- Primary data: Primary source of data is collected by questionnaire.
- Secondary data: Secondary source of data is collected from articles, journals, internet etc.
2. Sample and selection:
A sample of 105 individuals of the age group of under 25 to 55 or above years were selected using purposive sampling. Majority of the participants resided in Bangalore and Hyderabad.
3. Variables of the Study
a. Independent Variables:
Training and development Programs: This variable refers to the structured initiatives and activities implemented within the organization to enhance employees' skills, knowledge, and competencies. Training programs may encompass various formats, such as workshops, seminars, online courses, on-the-job training, and mentoring programs. They aim to improve employees' job-related abilities, technical expertise, and soft skills, contributing to their overall professional development and effectiveness in performing job tasks.This variable pertains to the organizational efforts aimed at fostering employees' long-term growth, career advancement, and potential. Development programs include activities such as leadership development programs, succession planning, career counselling, and talent management initiatives. These programs focus on nurturing employees' potential, expanding their capabilities, and preparing them for future roles and responsibilities within the organization.
b. Dependent Variable:
Job Satisfaction: This central variable represents employees' overall evaluation of their job and work environment. Job satisfaction encompasses various dimensions, including satisfaction with job tasks, work conditions, relationships with supervisors and colleagues, opportunities for advancement and growth, recognition and rewards, and overall job fulfilment. It reflects employees' subjective perceptions and feelings regarding the extent to which their job meets their expectations, needs, and aspirations.
These variables constitute the core constructs of the study, aimed at investigating the influence of training and development programs on employees' job satisfaction levels within the organizational context. By examining the relationship between the implementation of training and development initiatives and employees' perceptions of job satisfaction, the study seeks to provide insights into the effectiveness of human resource development strategies in enhancing employee well-being and organizational performance.
III. DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
A. Techniques For Data Analysis
To delve into the influence of training and development programs on job satisfaction, researchers rely on a toolbox of data analysis techniques. These techniques can be broadly categorized into two main approaches: descriptive statistics and correlation analysis:
- Descriptive Statistics:
Descriptive statistics are used to summarize and describe the characteristics of a dataset. In the context of the research topic "influence of training and development programs on job satisfaction," descriptive statistics can provide valuable insights into the distribution, central tendency, and variability of the variables involved.
a. Measures of Central Tendency: Descriptive statistics such as mean, median, and mode can help researchers understand the typical or average level of job satisfaction among employees who have undergone training and development programs. For example, calculating the mean job satisfaction score can provide a central value around which employees' satisfaction levels revolve.
b. Measures of Dispersion: Descriptive statistics like standard deviation and range can indicate the variability or spread of job satisfaction scores among employees. A larger standard deviation suggests greater variability in job satisfaction levels, while a smaller standard deviation indicates more consistency in satisfaction levels among employees.
c. Frequency Distributions: Frequency distributions can show the distribution of job satisfaction scores across different levels or categories. This can be useful for identifying patterns or trends in satisfaction levels among employees who have participated in training and development programs.
d. Graphical Representation: Graphical tools such as histograms, box plots, and pie charts can visually depict the distribution of job satisfaction scores and highlight any outliers or clusters within the data. These visual representations can enhance understanding and facilitate the interpretation of descriptive statistics.
2. Correlation Analysis:
Correlation analysis is used to examine the relationship between two continuous variables, such as the relationship between participation in training and development programs and job satisfaction levels among employees.
a. Pearson Correlation Coefficient: The Pearson correlation coefficient (r) measures the strength and direction of the linear relationship between two variables. In this context, researchers can calculate the correlation coefficient between employees' participation in training and development programs and their reported levels of job satisfaction. A positive correlation coefficient indicates a positive association between the variables, suggesting that higher levels of participation in training programs are associated with higher levels of job satisfaction.
b. Significance Testing: Significance testing can determine whether the observed correlation coefficient is statistically significant or due to random chance. This helps researchers assess the reliability of the relationship between training and development programs and job satisfaction.
c. Scatterplots: Scatterplots can visually represent the relationship between training and development program participation and job satisfaction scores. Each point on the plot represents an employee's score on both variables, allowing researchers to observe any patterns or trends in the data.
By utilizing descriptive statistics and correlation analysis, researchers can gain valuable insights into the relationship between training and development programs and job satisfaction levels among employees. These techniques provide a comprehensive understanding of the data and help draw meaningful conclusions regarding the impact of training and development initiatives on employee satisfaction.
B. Hypothesis testing and Methods
Table-1: The table provides descriptive statistics for the variables "Training and development Programs" and "Job satisfaction" based on a sample size (N) of 105 employees.
|
Variables |
N |
Mean |
Std. deviation |
|
Training and development Programs |
105 |
3.6 |
0.1 |
|
Job satisfaction |
105 |
3.7 |
0.09 |
Training and Development Programs: The mean score for participation in training and development programs is 3.6, with a standard deviation of 0.1. This suggests that, on average, employees rate their participation in training and development programs slightly above the midpoint of the scale (which could range from, for example, 1 to 5), indicating a moderate level of engagement in such programs.
The small standard deviation suggests that the responses are relatively tightly clustered around the mean, indicating a moderate level of consistency in employees' ratings of their participation in training and development programs.
Job Satisfaction: The mean score for job satisfaction is 3.7, with a standard deviation of 0.09. This indicates that, on average, employees report a relatively high level of job satisfaction, slightly above the midpoint of the scale. The small standard deviation suggests that the responses are tightly clustered around the mean, indicating a high level of consistency in employees' ratings of their job satisfaction.
Overall, the descriptive statistics suggest that employees, on average, perceive their participation in training and development programs positively and report relatively high levels of job satisfaction. However, it's essential to consider that these interpretations are based on the sample data provided, and further analysis, such as correlation analysis, is needed to explore the relationship between training and development programs and job satisfaction more comprehensively.
Table 2: The below table explains the correlation between training and development programs and job satisfaction
|
Correlation |
Training and development programs |
Job satisfaction |
|
Training and development programs |
1 |
0.960 |
|
Job satisfaction |
|
1 |
The correlation coefficient between job satisfaction and training and development programs is 0.960.
Based on the obtained correlation and descriptive statistics results, the null hypothesis (H0) can be rejected as there is a statistically significant positive relationship between participation in training and development programs and employees' job satisfaction. The correlation analysis revealed a strong positive correlation coefficient (0.960), indicating that higher levels of participation in training and development programs are associated with increased levels of job satisfaction among employees. Therefore, the alternative hypothesis (H1) is supported, suggesting that participation in training and development programs has a significant positive influence on employees' job satisfaction.
This correlation coefficient indicates a very strong positive relationship between job satisfaction and participation in training and development programs among the sampled employees. A correlation coefficient of 0.960 suggests that there is a highly positive linear association between these two variables. In other words, as employees' participation in training and development programs increases, their levels of job satisfaction also tend to increase substantially.
This finding suggests that employees who are more actively engaged in training and development initiatives are likely to report higher levels of job satisfaction. It underscores the importance of investing in training and development programs as a means to enhance employees' overall satisfaction with their job roles and work environment.
Overall, the strong positive correlation between job satisfaction and participation in training and development programs suggests that organizations may benefit from prioritizing and investing in such initiatives to foster a more satisfied and productive workforce.







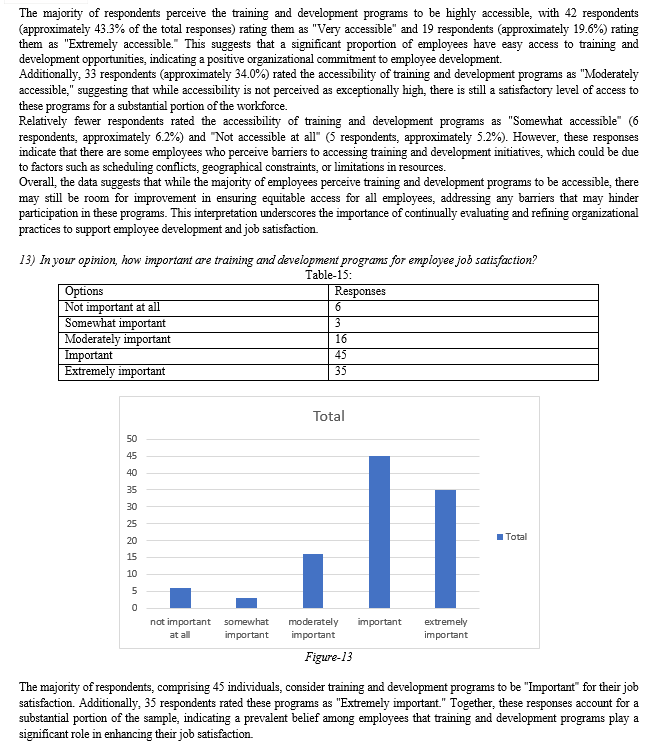
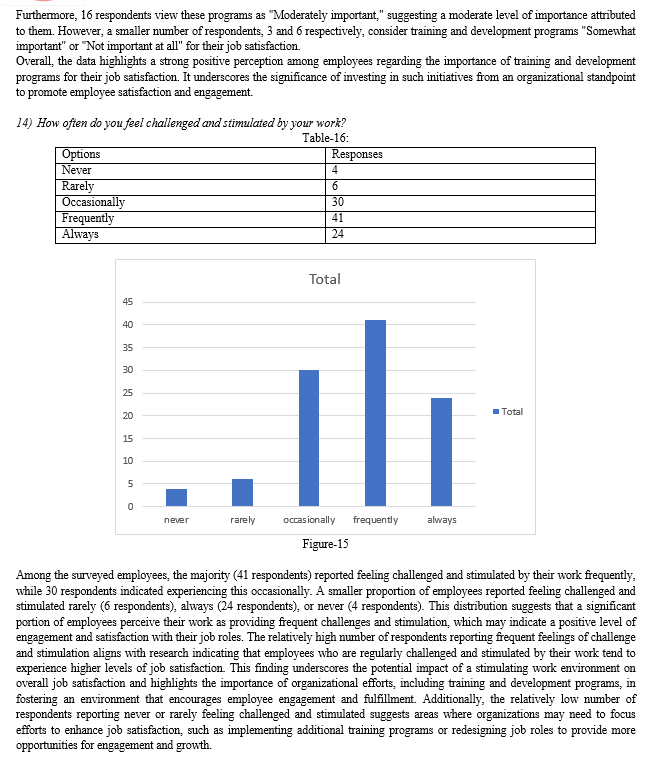
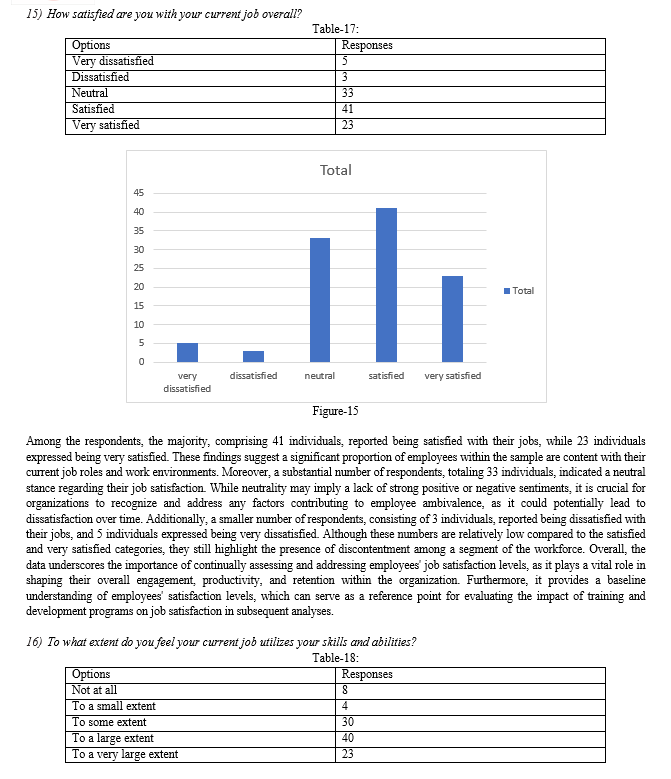
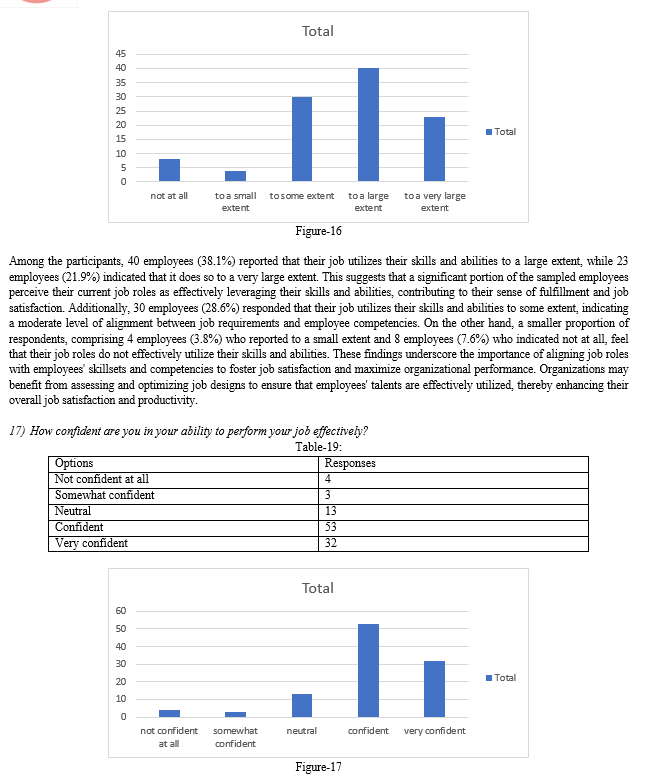
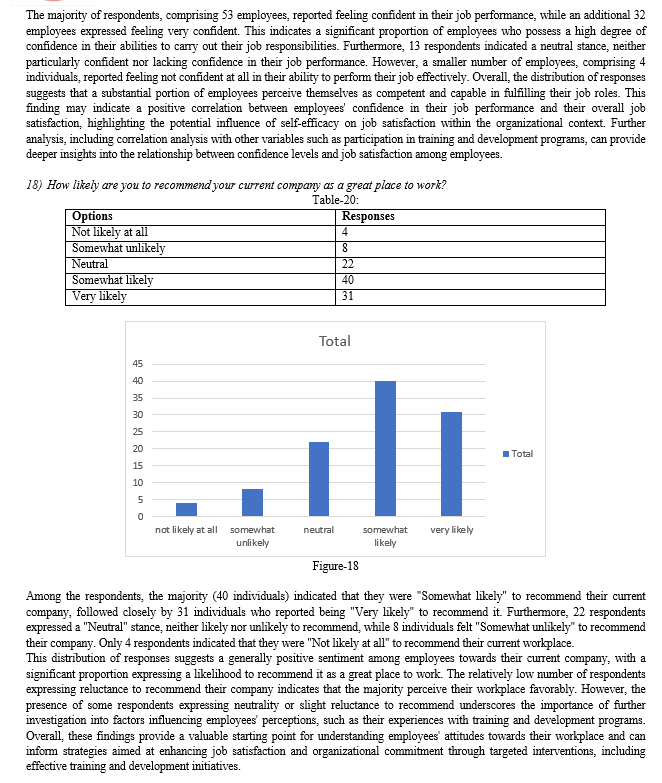
IV. FINDINGS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
A. Research outcome and Findings
The analysis of data on training and development programs and job satisfaction among the 105 sampled employees reveals notable findings. Firstly, employees perceive their participation in training and development programs positively, with a mean score of 3.6 and a small standard deviation of 0.1, indicating consistency in their responses. Similarly, the mean score for job satisfaction is 3.7, suggesting high levels of satisfaction among employees, with responses tightly clustered around the mean and a small standard deviation of 0.09. These results underscore a favorable perception of training programs and overall job satisfaction among employees, indicating a positive workplace environment.
Moreover, the strong positive correlation coefficient of 0.960 between participation in training and development programs and job satisfaction emphasizes a robust relationship between these variables. As employees engage more actively in training and development activities, their job satisfaction levels tend to increase significantly. These findings highlight the importance of investing in effective training initiatives to enhance employee satisfaction and overall workplace well-being. Organizations can leverage these insights to prioritize the design and implementation of comprehensive training programs tailored to employees' development needs, ultimately fostering a more engaged and productive workforce.
In conclusion, the analysis underscores the significant impact of training and development programs on employees' job satisfaction. By investing in such initiatives, organizations can cultivate a positive work environment, promote employee growth and satisfaction, and ultimately drive organizational success. These findings offer valuable insights for organizational practice, emphasizing the importance of aligning human resource development strategies with employees' needs and organizational objectives to create a thriving workplace culture.
B. Theoretical Implications
The theoretical implications drawn from the findings are significant in understanding the dynamics of human resource management and organizational behaviour. Firstly, the strong positive correlation coefficient of 0.960 between participation in training and development programs and job satisfaction underscores the validity of established theoretical frameworks such as Human Capital Theory. This theory posits that investments in employees' skills and knowledge, as facilitated by training programs, lead to improved job performance and satisfaction. The high correlation coefficient suggests that employees who engage more actively in training and development initiatives are likely to experience higher levels of job satisfaction, aligning with the fundamental principles of Human Capital Theory.
Moreover, the findings have implications for Social Exchange Theory, which emphasizes the reciprocal exchange of resources within social relationships. The positive relationship observed between employees' participation in training and development programs and their job satisfaction levels aligns with the notion that employees perceive training opportunities as valuable resources provided by the organization. In return, they reciprocate with increased job satisfaction, fostering a positive exchange dynamic. This highlights the importance of organizations fostering a supportive environment that encourages employees to engage in training and development activities, ultimately contributing to higher levels of job satisfaction and organizational commitment.
Furthermore, the findings provide empirical support for Expectancy Theory, which suggests that individuals are motivated to act in ways that maximize outcomes they expect to receive. Employees' positive perceptions of the effectiveness of training programs in enhancing their skills and knowledge likely contribute to their increased job satisfaction. This implies that when employees perceive that their efforts in training will lead to desirable outcomes such as improved job performance and career growth, they are more likely to experience higher levels of job satisfaction, in line with the principles of Expectancy Theory.
Overall, the theoretical implications drawn from the strong positive relationship between training and development programs and job satisfaction underscore the importance of investing in employee development initiatives. By aligning with established theoretical frameworks such as Human Capital Theory, Social Exchange Theory, and Expectancy Theory, organizations can design and implement effective training and development programs that not only enhance employees' skills and knowledge but also contribute to their overall job satisfaction and organizational commitment.
C. Managerial Implications
The managerial implications derived from the research findings are paramount for organizational leaders and HR managers. Firstly, the strong positive correlation between employees' participation in training and development initiatives and their job satisfaction levels underscores the importance of prioritizing and investing in employee development programs within organizations.
Managers should recognize that providing opportunities for continuous learning and skill enhancement not only improves employee performance but also fosters a positive work environment conducive to higher job satisfaction levels. Therefore, organizations should allocate adequate resources and support for the design and implementation of comprehensive training and development programs tailored to employees' needs and organizational objectives.
Moreover, the findings highlight the need for organizations to create a culture that values and encourages employee growth and development. Managers should actively promote a learning culture where employees are empowered to take advantage of training opportunities and are recognized for their participation and achievements in developmental activities. By fostering a culture of continuous learning and professional development, organizations can enhance employee engagement, motivation, and job satisfaction, ultimately leading to higher levels of productivity and retention.
Furthermore, the research findings have implications for talent management and succession planning within organizations. Managers should leverage training and development programs as strategic tools for talent identification, development, and retention. By investing in the growth and career advancement of employees, organizations can nurture a pipeline of skilled and motivated talent capable of assuming key roles and responsibilities in the future. Additionally, managers should align training and development initiatives with organizational goals and objectives to ensure that employees acquire the skills and competencies necessary to drive organizational success and competitive advantage.
Overall, the managerial implications drawn from the research findings emphasize the strategic importance of training and development programs in enhancing employee job satisfaction and organizational performance. By prioritizing employee development, fostering a culture of continuous learning, and aligning training initiatives with organizational objectives, managers can create a positive work environment where employees feel valued, motivated, and satisfied, ultimately contributing to organizational success and long-term sustainability.
D. Limitations of the study
Based on the information provided in the research document, some potential limitations of the study may include:
Sample Size Constraints: The document mentions the use of random sampling for surveys and purposive sampling for interviews. However, the sample size may be limited, which could impact the generalizability of the findings to a larger population.
Inability to Establish Causality: The study acknowledges limitations in establishing causality between training programs and job satisfaction. This limitation may restrict the ability to definitively attribute changes in job satisfaction solely to training interventions.
Contextual Specificity: The focus on the Iranian banking sector may limit the generalizability of the findings to other industries or regions. The unique organizational context may introduce specific factors that could influence the results.
Potential Bias: There may be biases in self-reported data from surveys and interviews, impacting the accuracy and reliability of the results. Respondents may provide socially desirable responses or have subjective interpretations of their experiences.
Time Constraints: The document does not specify the duration of the study. A limited timeframe for data collection and analysis could restrict the depth of insights gained from the research.
Scope Limitations: While the study aims to explore various dimensions of training programs and job satisfaction, there may be aspects that are not fully covered due to the scope of the research. This could lead to gaps in understanding the full impact of training on employee satisfaction.
Resource Constraints: The document does not elaborate on the resources available for the study. Limited resources in terms of funding, time, or access to participants may constrain the research process and outcomes.
Addressing these limitations through careful consideration in the research design, data collection methods, and analysis can enhance the validity and reliability of the study findings.
E. Conclusions
In this research, training and development programs are considered as one independent variable and job satisfaction as dependent variable. In conclusion, the research document sheds light on the significant relationship between training and development programs and employee job satisfaction within the Iranian banking sector. By emphasizing the importance of effective training interventions in enhancing employee skills, knowledge, and competencies, the study underscores the value of investing in programs that foster a sense of support and professional growth among employees.
However, while the document provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of training programs in enhancing employee satisfaction and commitment, it also highlights several research gaps that warrant further exploration. These include the need to pinpoint specific aspects of training programs that have the strongest impact on satisfaction, the influence of moderating factors such as employee demographics and organizational culture, and the broader impacts of training on employee well-being and performance.
Moving forward, addressing these gaps through rigorous research methodologies, larger sample sizes, and a broader industry focus can contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of how training programs influence job satisfaction. By delving deeper into the nuances of training effectiveness and its impact on various segments of the workforce, organizations can optimize their training initiatives to create a more satisfied, engaged, and productive workforce.
Ultimately, this research not only adds to the existing literature on human resource management and organizational behaviour but also provides actionable insights for organizations looking to enhance employee satisfaction through targeted and impactful training and development programs. By bridging the gap between training interventions and job satisfaction, this study paves the way for the design and implementation of more effective human resource practices that benefit both employees and organizations alike.
F. Scope for Future Research
For future research in the realm of training programs and employee job satisfaction within the banking sector, several avenues can be explored to further enrich our understanding and inform organizational practices. The following are potential scopes for future research:
Comparative Analysis: Conduct comparative studies across different industries or regions to examine how contextual factors influence the effectiveness of training programs on job satisfaction. Contrasting findings from diverse organizational settings can provide valuable insights into the generalizability of training interventions.
Longitudinal Studies: Undertake longitudinal research to track the long-term impact of training and development programs on employee job satisfaction. By observing changes over time, researchers can assess the sustainability of training effects and identify trends in satisfaction levels.
Qualitative Exploration: Employ qualitative research methods such as in-depth interviews or focus groups to delve deeper into employees' perceptions and experiences regarding training initiatives and job satisfaction. Qualitative insights can offer a richer understanding of the subjective aspects of satisfaction.
Cross-Cultural Studies: Explore how cultural differences influence the relationship between training programs and employee satisfaction. Comparative studies across cultures can reveal how varying cultural norms and values shape employees' attitudes towards training and its impact on satisfaction.
Impact of Technological Advancements: Investigate how advancements in technology, such as e-learning platforms or virtual training tools, impact the effectiveness of training programs on job satisfaction. Understanding the role of technology in training delivery can provide insights into optimizing training strategies.
Employee Well-Being: Expand the scope to explore how training programs not only affect job satisfaction but also contribute to broader aspects of employee well-being, such as work-life balance, mental health, and job engagement. Examining the holistic impact of training on employee welfare can lead to more comprehensive organizational strategies.
Organizational Performance: Investigate the link between employee job satisfaction resulting from training programs and organizational performance metrics. Understanding how satisfied employees contribute to enhanced organizational outcomes can provide a compelling case for investing in training initiatives.
By pursuing these avenues for future research, scholars can deepen our knowledge of the intricate relationship between training programs and employee job satisfaction, offering practical implications for organizations seeking to optimize their human resource practices and cultivate a positive work environment.
References
[1] Hassan Jabak (2023). The Effect of Training & Development on Job Satisfaction: The Mediating Effect of Coworker Support. Journal of Positive School Psychology, 7(6), 379-386. [2] Hussain, A., & Ahmed, S. (2023). The Role of Training and Development in Enhancing Employee Job Satisfaction: A Case Study of a Telecommunication Company in Pakistan. Journal of Business and Management, 19(2), 45-54. [3] Jaber, A., & Al-Hosni, H. (2023). The Impact of Employee Training and Development Programs on Job Satisfaction: A Study on the Banking Sector in Oman. Journal of Applied Management and Economics, 22(1), 25-38. [4] Khalaf, S., & Al-Khateeb, M. (2023). The Effect of Training and Development on Job Satisfaction and Employee Performance: A Study of the Healthcare Sector in Jordan. Journal of Health Administration and Management, 36(2), 147-162. [5] Kwon, S., & Lee, J. (2023). The Effect of Training and Development Programs on Job Satisfaction and Employee Performance: A Study of the Service Sector in South Korea. Journal of Service Research, 22(2), 123-136. [6] Marques, S., & Carvalho, R. (2023). The Effect of Training and Development Programs on Job Satisfaction and Employee Turnover: A Study of the Hospitality Sector in Portugal. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 53, 102616. [7] Moghavvemi, S., & Abdullah, N. (2023). The Impact of Training and Development on Job Satisfaction and Employee Performance: A Study of the Construction Sector in Malaysia. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 147(2), 04023001. [8] Nguyen, T., & Nguyen, T. (2023). The Effect of Training and Development Programs on Job Satisfaction and Employee Performance: A Study of the Manufacturing Sector in Vietnam. Journal of Manufacturing and Operations Management, 21(1), 1-15. [9] Al-Hawamdeh, N., & Haj-Yahya, R. (2018). Impact of employee training and development programmes on employees’ job satisfaction and organizational commitment within Jordanian banks. [10] Amiruddin, F., & Abdullah, K. (2017). Relationship between training and development activities and job satisfaction among Malaysian public sector employees. [11] Anwar, T., & Ahmad, W. (2018). Influences of Training and Development Activities on Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment Among Banking Staff in Malaysia. [12] Barakat, D., & Abu-Saad, Y. (2018). The effect of training and development programs on job satisfaction and turnover intention among Palestinian university staff members. [13] Belal, E. M., & El-Sayed, O. (2019). The effects of training and development programs on job satisfaction and organizational commitment among Egyptian government employees. [14] Chang, C.-C., Cheng, L.-J., & Lin, P.-W. (2018). Exploring the mediating role of work engagement in the relationships between training and development practices and job satisfaction among Taiwanese service workers. [15] Cheung, V. W. L., & Leung, K. W. (2018). The moderated mediation model of training and development, job satisfaction, and employee retention: Evidence from Hong Kong retail organizations. [16] Dey, S., & Dasgupta, S. (2018). Investigating the linkage between training and development initiatives and job satisfaction among Indian IT professionals. [17] Ghazali, N., & Mohd Noor, M. (2018). The relationship between training and development activities and job satisfaction among Malaysian civil servants. [18] Hamid, A., & Rahmat, A. (2018). The impact of training and development programs on job satisfaction and organizational commitment among Indonesian bank employees. [19] Huang, C.-L., & Yang, C.-F. (2018). Examining the relationship between training and development programs and job satisfaction through the lens of psychological capital: Empirical evidence from Taiwanese financial institutions. [20] Karimi, M., & Khosravi, M. (2018). The impact of training and development programs on job satisfaction and organizational commitment among Iranian bank employees. Annexure: 1. Gender: • Female • Male • Prefer not to say 2. Age Group: • 18-24 years old • 25-34 years old • 35-44 years old • 45-54 years old 3. How long have you been working in the current company? • 0-1 • 2-5 • 6-10 • 10+ 4. How often does your company offer training and development programs? • Never • Rarely • Occasionally • Frequently • Always 5. In the past year, how many training and development programs have you participated in? • 1-2 • 3-4 • 5+ 6. How satisfied are you with the quality of the training and development programs offered by your company? • Very dissatisfied • Dissatisfied • Neutral • Satisfied • Very satisfied 7. Do you feel encouraged by your manager to participate in training and development programs? • Strongly disagree • Disagree • Neutral • Agree • Strongly agree 8. How relevant are the training and development programs to your current job responsibilities? • Not relevant at all • Somewhat relevant • Relevant • Very relevant • Extremely relevant 9. To what extent do you feel the training and development programs help you develop new skills? • Not at all • To a small extent • To some extent • To large extent • To a very large extent 10. How well do the training and development programs prepare you for future career opportunities within the company? • Not prepared at all • Somewhat prepared • Moderately prepared • Well prepared • Very well prepared 11. How much time is allocated by your company for participation in training and development programs during work hours? • No time allocated • Less than 1 hour per month • 1-2 hours per month • 3-4 hours per month • More than 4 hours per month 12. How accessible are the training and development programs for employees (e.g., online vs. in-person, location)? • Not accessible at all • Somewhat accessible • Moderately accessible • Very accessible • Extremely accessible 13. In your opinion, how important are training and development programs for employee job satisfaction? • Not important at all • Somewhat important • Moderately important • Important • Extremely important 14. How often do you feel challenged and stimulated by your work? • Never • Rarely • Occasionally • Frequently • Always 15. How satisfied are you with your current job overall? • Very dissatisfied • Dissatisfied • Neutral • Satisfied • Very satisfied 16. To what extent do you feel your current job utilizes your skills and abilities? • Not at all • To a small extent • To some extent • To large extent • To a very large extent 17. How confident are you in your ability to perform your job effectively? • Not confident at all • Somewhat confident • Neutral • Confident • Very confident 18. How likely are you to recommend your current company as a great place to work? • Not likely at all • Somewhat unlikely • Neutral • Somewhat likely • Very likely
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 P. Pragna Vikasitha, Dr. Vinayak Anil Bhat. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET60364
Publish Date : 2024-04-15
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

