Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Unveiling the Power of Big Data: Insights into Big Data Analytics, Applications, and Advancements
Authors: Anusha A. K. R. S., Jenefa Joy A. B.
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.63520
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
In the era of digital transformation, the exponential growth of data from multifaceted origins has fundamentally revolutionized decision-making and strategic planning across global industries. Big Data, distinguished by its immense volume, rapid velocity, diverse variety, and critical veracity, introduces unprecedented opportunities alongside formidable challenges. This journal explores the foundational concepts, methodologies, and applications of Big Data and analytics. It delves into the types and characteristics of Big Data, examines sources and collection methods, outlines analytical steps and tools, and addresses the inherent challenges. Through comprehensive analysis, this journal aims to provide insights into leveraging Big Data for informed decision-making, innovation, and competitive advantage in various sectors.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Big Data typically refers to datasets that are so large and complex that traditional data processing software often cannot manage them effectively. These datasets can include both structured data (like numbers, dates, and strings that fit into traditional databases) and unstructured data (like text, images, and videos).
Big Data Analytics involves applying sophisticated analytical techniques to vast and varied datasets that encompass structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
II. BIG DATA AND ITS TYPES
A. Big data
The term Big Data refers to huge volumes of data, both structured and unstructured, that cannot be stored and processed by any traditional data storage or processing units. Big data can be analyzed to gain insights that enhance decision-making and provide confidence for strategic business initiatives.
The term Big Data was coined by Roger Magoulas back in 2005. The term 'Big Data' was in use since the early 1990s. Although it is not exactly known who first used the term "big data," most people credit John R. Mashey, who worked at Silicon Graphics at the time, is credited with popularizing the term.
B. Types of Big data
Big data is classified in three ways:
- Structured Data
- Structured data adheres to a pre-defined data model and is therefore straightforward to analyze. It conforms to tabular format with relationship between the different rows and columns.
- Example: Excel Files, SQL Databases, Credit Card Numbers
2. Semi-Structured Data
- Semi-structured data is a form of structured data that does not adhere to the traditional tabular structure. Semi-structured data contains tags or other markers to separate sematic elements and enforce hierarchies of records and fields within the data.
- Example: Email, XML, TCP/IP packets, object-oriented databases
3. Unstructured Data
- Unstructured data is a form of data that has many forms and which does not follow conventional data models.
- It is hard to store and manage unstructured data.
- Example: Web Pages, Customer Reviews, Weather Forecast Report, Media Data, IoT Sensor Data, Text Files, Power Point Presentations.
III. CHARACTERISTICS OF BIG DATA
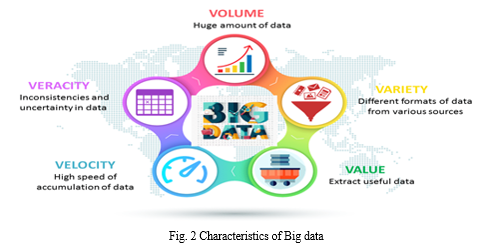
Big Data has 7V's characteristics. They are described below:
- Volume: It refers to huge amount of data generated every second from sources such as, cell phones, credit cards, social media, sensors, images, videos, etc.
- Variety: It refers to the diversity and range of different data types, including Semi-structured data, unstructured data, and raw data.
- Velocity: It refers to the speed at which companies receive, store, and manage data – For example, the specific number of search queries or social media posts received within a day, hour or other units of time.
- Veracity / Validity: It refers to the degree of accuracy or reliability that the data has to offer for the intended use. The data is fundamental in business developments.
- Value: It refers to the amount of valuable, reliable, and trustworthy data that needs to be stored, processed, and analyzed to find new perceptions and insights.
- Volatility / Variability: It refers to the changing nature of data that companies seek to capture, manage, and analyze. For example, in sentiment or text analytics, changes in the meaning of keywords or phrases.
- Visualization: It refers to the challenges to visualize big data. Technical challenges are faced by current big data visualization tools due to limitations of in-memory technology and poor scalability, functionality, and response time.
IV. SOURCES OF BIG DATA
The bulk of big data generated comes from the following primary sources:
- Human-Generated Data
Predict Consumer Preferences, Changing Trends
- Blogs
- Reviews
- Facebook Posts
- Instagram Posts
- Linked-in Posts
- Twitter Tweets
- YouTube Videos
- Transactional Data – Online Purchase
- Databases
2. Machine-generated Data
- Server Logs
- Weather Forecast Data
- Stock Exchange Data – Time-Series Data – Observe Trends
- Sensor Data
- Traffic Data
- Security Camera Data
- Military Surveillance Data
3. Human and Computer-generated Data
- Cloud Data – Real-time Data, Structured and Unstructured Data
- Machine Learning data sets
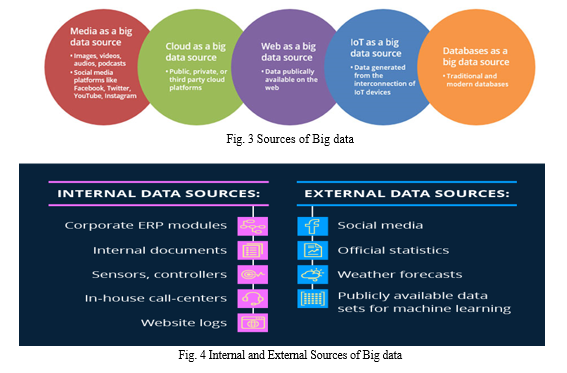
a. Media as Big Data Source: The most popular source of big data is media as it provides valuable insights on consumer preferences and changing trends. Media includes social media and generic media. It includes Google, Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Instagram, as well as generic media like images, audios, videos, and podcasts.
b. The Web as Big Data Source: The World Wide Web ensures for its diverse usability.
c. Cloud as Big Data Source: Cloud storage accommodates unstructured and structured data and provides business with real-time information and on-demand insights.
d. IoT as Big Data Source: Machine-generated content or data created from IoT establish a valuable source of big data. The data is usually generated from the sensors that are connected to the electronic devices. IoT is now gaining momentum and includes big data generated from computers, smartphones, and also from every device that can emit data. With IoT, data can now be obtained from medical devices, vehicular processes, video games, meters, cameras, household appliances, and the like.
e. Database as Data Source: Databases can provide for the extraction of insights that are used to drive business profits. Popular databases include MS Access, DB2, Oracle, SQL, and Amazon Simple.
f. Transactional Data as Data Source: Transactional data are gathered when a user makes an online purchase (product, time of purchase, payment method).
g. Time series Data as Data Source: Time series data help in observing trends. Example: Stock exchange data
V. CHALLENGES WITH BIG DATA
Big data poses several challenges in spite of huge benefits. The challenges include new privacy and security concerns, accessibility for business users, and choosing the right solutions for your business needs. To make the most of the incoming data, organizations will have to address the following:
- Data Collection, Storage, and Processing: Collecting and processing data becomes more difficult as the amount of data grows. Organizations must make data easy and convenient so that it enables easy usage by data owners of all skill levels to use.
- Data Quality: With so much data to maintain, organizations have to spend so much time for maintaining data without duplicates, errors, absences, conflicts, and inconsistencies.
- Data Security: As the amount of data grows, the privacy and security concerns increases rapidly. Organizations will need to put in lot of efforts for compliance and put constricted data processes in place before they take advantage of big data.
- Maintenance Cost: Non-optimal infrastructure and outdated technologies make big data maintenance expensive.
- Scalability: The system may reach scalability limit quickly and may be insufficient hardware infrastructure. The simplest solution is upscaling, i.e. adding more resources to the system. Upscaling may be difficult under certain conditions.
- Finding Right Tools: New technologies for processing and analyzing big data are developed all the time. A big challenge for companies is to find out which technology works best for them without introducing new risks and problems.
- Visualization: Data visualization of complex reports may be messy.
VI. BIG DATA ANALYTICS AND ITS TYPES
Big Data Analytics is the use of advanced analytic techniques against very large, diverse data sets that include unstructured, semi-structured, and structured data, from different sources, and in different sizes from terabytes to zettabytes.
Big data analytics comprises techniques to examine big data to uncover information -- such as correlations, hidden patterns, market trends, and customer preferences -- that can help organizations make informed business decisions.
Big data analytics provides benefits such as effective marketing, new revenue opportunities, customer personalization, and improved operational efficiency. With an effective strategy, these benefits can provide competitive benefits over rivals.
A. Types of Big data Analytics
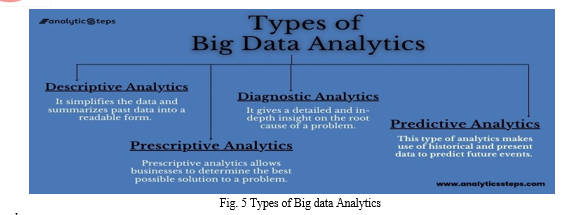
- Descriptive Analytics: It looks at past data to examine, understand, and describe something that’s already happened. It simplifies the data and summarizes the past data into a readable form.
- Diagnostic Analytics: It gives a detailed and in-depth insight on the root cause of a problem.
- Predictive Analytics: It uses historical and present data to predict future events.
- Prescriptive Analytics: It identifies specific actions that an individual or organization should take to reach future targets or goals. It allows businesses to determine the best possible solution to a problem.
Examples
- A bakery might use its data to realize the demand for bread bowls increases in the winter — which means you don’t need to discount the prices when demand is high.
- An increase in cyberattacks might mean you need to take proactive precautionary measures.
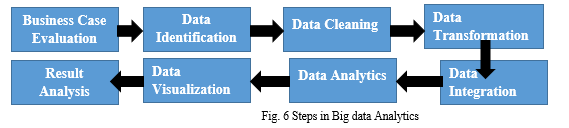
VII. STEPS IN BIG DATA ANALYTICS
- Business Case Evaluation: The first step in big data analytics lifecycle starts with a business case, which describes the goals and objectives behind the analysis.
- Data Identification and Data Collection: In this step, a wide-ranging variety of data sources are identified. Data professionals collect data from a vast variety of sources. Often, it is a mix of unstructured and semi-structured data.
- Data Preparation and Data Processing: Data is prepared and processed after it is collected and stored in a data warehouse or data lake, data professionals must organize, configure, and partition the data properly for analytical queries. Detailed data preparation and processing yields higher performance from analytical queries.
- Data Cleaning / Data Filtering / Data Scrubbing: Data is cleansed to improve its quality. Data professionals scrub the data using scrubbing tools or data quality software. Now they look for any errors or inconsistencies, such as duplications or formatting mistakes, and organize and tidy up the data. All of the identified data from the previous stage is filtered here to remove corrupt, missing, and inconsistent data.
- Data Transformation / Data Wrangling / Data Munging: Data transformation is the process of converting data from one format or structure into another.
- Data Analytics: The collected, processed and cleaned data is analyzed with analytics and statistical tools to discover useful information.
- Data Visualization: Data visualization is the graphical representation of discovered information and data. By using visual elements like charts, graphs, plots, maps, tables, etc., data visualization tools provide an accessible way to see and understand trends, outliers, and patterns in data. Our eyes are drawn to colors as well as patterns. By visualizing charts, trends and outliers can be easily identified. Data visualization helps to tell stories by representing data into a form which is easier to understand, highlighting the trends and outliers. The data and the visuals should work together.
- Result Analysis: This is the last step of the Big Data analytics lifecycle, where the final results of the analysis are made available to business stakeholders who will take action.
VIII. BIG DATA ANALYTICS TOOLS
Several tools are available for big data analytics. Some of the popular tools include the following:
- Apache Hadoop
- Hadoop is a Java-based, free, open-source platform that is being used to store and analyze big data.
- It also offers cross-platform support for its users.
- It can process both structured and unstructured data from one server to multiple computers.
- It is highly flexible and can be easily implemented with MySQL and JSON.
- It offers quick access via Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS).
- Today, it is the best big data analytic tool and is popularly used by many tech giants such as Amazon, Microsoft, IBM, etc.
2. Apache Hive
- Hive is an open-source data warehousing tool for managing big data.
- It manages large datasets stored in Hadoop’s HDFS or other compatible file systems.
- It supports SQL-like queries called HiveQL for data analysis.
- It is interoperable with other big data tools.
- It is a scalable and efficient data warehousing solution.
3. MongoDB
- MongoDB is a free, open-source platform and a document-oriented (NoSQL) database that is used to store a high volume of data.
- It is a schema-less database and can hold varieties of documents inside.
- It is used on datasets that change frequently.
- It supports many programming languages such as Python, Jscript, and Ruby.
- It is written in C, C++and JavaScript.
4. MapReduce
- MapReduce is a distributed execution framework within the Apache Hadoop Ecosystem and is Java-based.
- It takes away the complexity of distributed programming by exposing two processing steps that developers implement: 1) Map and 2) Reduce.
- In the Mapping step, data is split between parallel processing tasks.
- Transformation logic can be applied to each piece of data.
- After transformation, the Reduce phase aggregates data from the Map set.
- In general, MapReduce uses Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) for both input and output. However, some technologies such as Sqoop, allow access to relational systems.
5. Apache Cassandra
- Cassandra is an open-source NoSQL distributed database which is used to fetch large amounts of data.
- It supports all forms of data i.e. unstructured, semi-structured, structured data and allows users to change as per their needs.
- It is capable of delivering thousands of operations every second and can handle petabytes of resources with nearly zero downtime.
- It offers high scalability and availability without compromising speed and performance.
- It is fault-tolerant. In case of any node failure, the failed node will be replaced without any delay.
- It was created by Facebook back in 2008 and was published publicly.
6. Apache Spark
- Spark can analyze large amounts of data.
- Spark is used for real-time processing via Spark Streaming.
- Spark allows users to run in their preferred language. (JAVA, Python, etc.)
- It can run on Mesos, Kubernetes, or the cloud.
7. Apache Storm
- Storm an open-source, distributed real-time big data processing system.
- Storm has no language barrier.
- Storm processes data even if the node gets disconnected.
- Storm is highly scalable. It maintains performance level even if the load increases.
- It is fast. The speed of Apache Storm is faultless and can process up to 1 million messages of 100 bytes on a single node.
- A storm is a robust, user-friendly tool used for data analytics, especially in small companies.
- Some of the most remarkable names are Twitter, Zendesk, NaviSite, etc.
8. Apache Kafka
- Apache Kafka is an open-source, distributed event store and stream-processing platform.
- It was developed by the Apache Software Foundation written in Java and Scala.
- The project aims to provide a unified, high-throughput, low-latency platform for handling real-time data feeds.
- It is used for fault-tolerant storage.
9. Talend
- Talend is an open-source big data integration platform
- It facilitates data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) tasks.
- It supports various data sources.
- It offers an intuitive graphical interface.
- It supports extensive data transformation capabilities.

IX. BENEFITS OF BIG DATA ANALYTICS
The importance of big data lies not in the quantity of data a company possesses, but in how effectively it utilizes this data. Each company leverages data uniquely; the more efficiently a company uses its data, the greater its potential for growth. By analyzing data from any source, a company can find answers that enable it to:
- Cost Savings: Big Data tools like Hadoop and cloud-based analytics can provide cost advantages for businesses when storing large amounts of data. These tools also help in identifying more efficient ways of conducting business.
- Time Reductions: The high speed of tools like Hadoop and in-memory analytics allows businesses to quickly identify new data sources, enabling immediate data analysis and rapid decision-making based on the insights gained.
- Understanding Market Conditions: Through big data analysis, companies can gain deeper insights into current market conditions. For instance, by analyzing customers' purchasing behaviors, a company can identify the most popular products and tailor its offerings accordingly, gaining a competitive edge in the market.
- Business Competence: Using insights derived from big data, you can compete with big businesses by identifying best business strategies, strategic decisions, predicting risks, and improving customer satisfaction.
- Managing Online Reputation: Big data tools enable sentiment analysis, providing insights into what people are saying about your company. By monitoring and improving your business's online presence, these tools can help enhance reputation management efforts.
- Using Big Data Analytics to Enhance Customer Acquisition and Retention: Customers are the cornerstone of any successful business. Without a strong customer base, achieving success becomes challenging. Moreover, in today's highly competitive landscape, simply acquiring customers is not enough; retaining them is equally crucial. Failure to understand customer needs and preferences can lead to offering subpar products or services, resulting in customer attrition and negative business outcomes. Big data analytics empowers businesses to observe and analyze various customer-related patterns and trends. By closely monitoring customer behavior, businesses can identify opportunities to enhance customer loyalty and satisfaction.
- Using Big Data Analytics to Solve Advertisers' Problems and Offer Marketing Insights: Big data analytics can transform business operations, including the ability to meet customer expectations, adapt the product line, and ensure that marketing campaigns are powerful and effective.
- Big Data Analytics: As a driver of innovations and product development, another huge advantage of big data is the ability to help companies innovate and redevelop their products.
- Improve pricing - Using big data improves your pricing.
- Identify Local preferences – Big data allows you to focus on local preferences.
- Increase Sales and Loyalty - Using big data helps you increase sales and loyalty.
- Improve customer service – Big data improves customer service by analyzing customer responses.
- Increase efficiency - Using big data increases your efficiency.
- Hire right employees - Using big data ensures you hire the right employees.
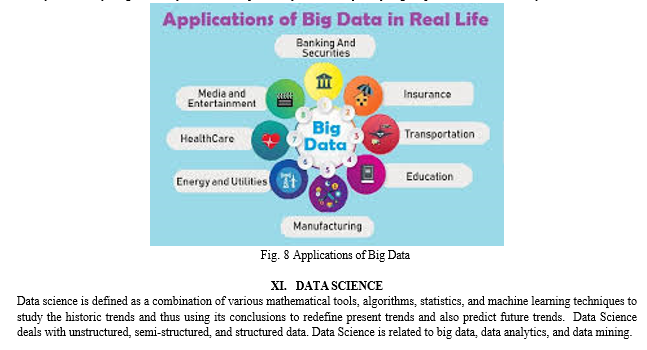
X. APPLICATIONS OF BIG DATA
Big Data is being the most wide-spread technology that is being used in almost all business sectors.
- Tracking Customer Shopping Behavior and Spending Habit: Big retail stores like Amazon, Flipkart, Walmart, Big Bazar etc. track data of customer’s spending habit (in which product customer spent, in which brand they spent, how frequently they spent), shopping behavior, customer’s most liked product, most searched / sold product so that they can keep those products in stock and fix production/collection rate of that product.
- Recommendation: Big retail stores track customer spending habit, and their shopping behavior to provide a product recommendation to the customer. E-commerce sites like Amazon, Walmart, and Flipkart does product recommendation. By tracking the products a customer is searching for, businesses can utilize this data to recommend similar products that align with the customer's interests and preferences. YouTube shows recommended video based on user’s previously liked, watched video type. Relevant advertisements are shown during video running based on the content of the video.
- E-commerce: Big data analytics is used to predict customer preferences, trends, and optimize prices.
- Financial and Banking: Financial and banking sectors extensively use Big data technology. Big data analytics enables banks to comprehensively grasp customer behavior by analyzing inputs such as investment patterns, shopping trends, motivations to invest, and personal or financial backgrounds. Retail banks leverage data extensively to gain insights into how customers utilize their accounts and to identify potential security risks. By employing big data analytics, banks can enhance customer satisfaction, minimize risks, and mitigate fraudulent activities.
- Healthcare: With the help of predictive analytics, medical professionals and health care personnel are now able to provide personalized healthcare services to individual patients. Patient records, treatment plans, prescription etc. can be analyzed to provide better healthcare.
- Smart Traffic System: Data on traffic conditions from various sources, including roadside cameras, entry and exit points of the city, and GPS devices in vehicles (such as Ola and Uber cabs), is collected and analyzed. This data enables the recommendation of less congested routes, reducing travel time and minimizing traffic congestion. Additionally, optimizing routes helps to decrease fuel consumption, contributing to environmental sustainability.
- Secure Air Traffic System: At various places of flight (like propeller) sensors are present. These sensors capture data like the speed of flight, moisture, temperature, and other environmental conditions. An environmental parameter within the flights is set up and varied based the results of data analytics. By analyzing machine-generated data from flights, it is possible to estimate the duration for which the machine can operate flawlessly before requiring replacement or repair.
- Education Sector: Organizations offering online educational courses use big data to search candidates interested in specific course. If someone searches for YouTube tutorial video on a subject, then online or offline course provider organization on that subject send advertisement online to that person about the course.
- Energy Sector: Smart electric meters record power consumption every 15 minutes and transmit this data to a server for analysis. Through this data, it becomes possible to estimate the periods of low power demand across the city. Utilizing this system, manufacturing units or households can be advised to operate heavy machinery during off-peak hours, typically at night when power demand is lower, leading to reduced electricity bills.
- Media and Entertainment Sector: Companies providing media and entertainment services, such as Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Spotify, analyze data collected from their users. This includes information on the types of videos and music, users are watching or listening to the most, as well as the duration of time users spend on the platform. This data is then analyzed to lead the development of the next business strategy.
- Virtual Personal Assistant: Big Data Analytics aids virtual personal assistant tools (such as Google Assistant in Android, Siri in Apple devices, and Cortana in Windows) in providing answers to various user queries. For example, if a user asks, "Should I need to take my rain coat with me today?" the tool gathers data including the user's location, current season, and the prevailing weather conditions. It then analyzes this data to assess the probability of rain and delivers a suitable response.
- Risk Management: Big Data Analytics provides essential insights into consumer behavior and market trends, enabling businesses to evaluate their position and progress effectively. Predictive analytics can anticipate upcoming risks, supported by prescriptive analytics and other statistical analysis techniques, allowing for proactive risk mitigation strategies.
- Government: The vast Aadhaar data is analyzed and stored to find things like the number of youth in the country. This helps government to devise new schemes to target the majority of the population. Government can use big data analytics to segment population and to reduce frauds.
- Cyber Security: Big data analytics is used to prevent cybercrimes by analyzing the patterns and trends in cybercrimes.
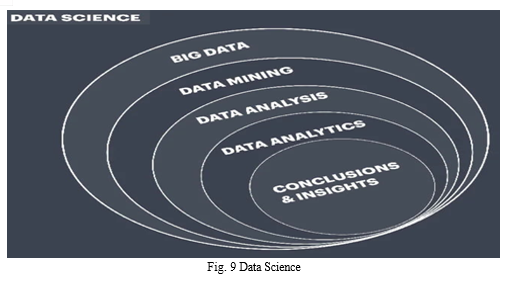
A. Key Functions of Data Science
Data science involves the following key functions:
- Data Wrangling: The process of cleaning and organizing data to be more readily used.
- Statistical Modeling: The process of running data through different models—such as regression, classification, and clustering models, among others—to identify relationships between variables and gain insight from the numbers.
- Programming: The process of writing computer programs and algorithms in a variety of languages—such as R, Python, and SQL—that can be used to analyze large datasets more efficiently than through manual analysis.
B. Functions of Data Scientist
Data Scientists perform the following functions
- Gather data and pinpoint data sources.
- Analyze vast quantities of data, encompassing both structured and unstructured formats.
- Develop solutions and formulate strategies to address business challenges.
- Combine diverse algorithms and modules to uncover trends and patterns.
- Utilize a variety of data visualization techniques and tools to present findings effectively.
- Explore emerging technologies and tools to devise innovative data strategies.
- Facilitate discussions and evaluate the viability of AI/ML solutions for enhancing business processes and achieving desired outcomes.
C. Skillset of Data Scientist
Data Analysts require the following skills:
- Data Analysis skills
- Data Visualization skills
- Mathematical skills
- Problem solving skills
- Programming skills
- Big data technology
- Database Management skills
- Machine Learning with Artificial Intelligence
- Deep Learning with Natural Language Processing
Conclusion
The field of Big Data and Big Data Analytics represents a transformative force across various industries, driven by its ability to handle vast volumes of data, diverse data types, and its application of advanced analytical techniques. This journal has explored several key aspects of Big Data and Big Data Analytics. 1) Types and Characteristics: Big Data encompasses structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, originating from sources such as sensors, social media platforms, and transaction records. Its defining characteristics —Volume, Velocity, and Variety—underscore its complexity and the challenges it poses for traditional data processing methods. 2) Sources: The sources of Big Data are diverse and expansive, ranging from machine-generated data streams to human-generated content on social media platforms. These sources contribute to the exponential growth of data, creating opportunities for organizations to extract valuable insights. 3) Tools and Techniques: Advanced tools and techniques such as machine learning algorithms, data mining, natural language processing, and predictive analytics are essential in making sense of Big Data. These tools enable organizations to uncover patterns, trends, and correlations that facilitate informed decision-making and strategic planning. 4) Applications: The applications of Big Data and Big Data Analytics are broad and impactful. Industries leverage these technologies for purposes including customer segmentation, personalized marketing, operational efficiency improvements, healthcare diagnostics, and fraud detection. The ability to derive actionable insights from Big Data empowers organizations to innovate, optimize processes, and gain a competitive edge in their respective markets. In summary, while Big Data presents challenges related to data management, privacy, and scalability, its potential to revolutionize business operations and drive innovation cannot be overstated. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities and applications of Big Data Analytics, shaping the future of data-driven decision-making across industries worldwide.
References
[1] Hassan Aldarbesti, Abbas Al-Refaie, et al, Big Data Analytics: A Literature Review Paper, IEEE Access, 2021. [2] Samah Mohamed, Ahmed Abdel-Basset, et al, A Survey on Big Data Analytics: Challenges, Open Research Issues, and Tools, Future Generation Computer Systems, Science Direct, 2021. [3] Iqbal H. Sarker, Jiayu Shang, et al, Big Data Analytics for Cyber-Physical Systems: A Survey, ACM Computing Surveys, 2020. [4] Neda Alavi, Mostafa Jafari, et al, Big Data Analytics in E-commerce: A Comprehensive Review and a Framework for Future Research, Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 2021. [5] Yalini Chandrasekaran, Saravanan Subramanian, et al, Machine Learning and Big Data Analytics for Healthcare: A Comprehensive Survey, Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 2020. [6] Iqbal H. Sarker, Jiayu Shang, et al, Big Data Analytics for Cyber-Physical Systems: A Survey, ACM Computing Surveys, 2020. [7] S. Sathiya Kumaran, K. Thangavel, et al, Challenges and Opportunities in Big Data Analytics: A Review, Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2023. [8] Sarah Faisal, Imran Sarwar Bajwa, et al, Ethical Issues in Big Data Analytics: A Comprehensive Review, IEEE Access, 2023. [9] Mohit K. Chandra, Raghvendra Kumar, et al, Security Challenges in Big Data Analytics: A Systematic Review, Information Systems Frontiers, 2022. [10] Priyanka Gupta, Vikram Goyal, et al, Scalability Challenges in Big Data Analytics: A Survey, Journal of Big Data, 2022. [11] Abeer Al-Mutairi, Khaled Alutaibi, et al, Legal and Regulatory Issues in Big Data Analytics: A Review, Future Generation Computer Systems, 2023.
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Anusha A. K. R. S., Jenefa Joy A. B.. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET63520
Publish Date : 2024-06-30
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

