Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Insurtech's Role in Enhancing Healthcare Insurance Accessibility and Efficiency in India
Authors: Dr. M. Sumathy, Ms. Bharathi. M
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.65519
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Insurance Technology (Insurtech) is transforming healthcare this paper explores how innovative technologies such as digital on boarding, automated claims processing, wearable health trackers, and predictive analytics are reshaping the industry. These advancements have not only streamlined processes but also brought insurance services to underserved areas, offering personalized solutions that significantly enhance customer satisfaction. Technologies like telemedicine, block chain for secure transactions, and AI-driven risk analysis are playing a transformative role in improving transparency, speeding up claims processing, and delivering tailored insurance products. These developments are creating a more inclusive and efficient insurance system. However, challenges such as data privacy concerns, regulatory hurdles, and low levels of digital literacy remain obstacles to fully realizing the sector\'s potential. This study also highlights trends in InsurTech funding in India, the increasing demand for health-focused insurance products, and the role of technology in improving policyholder engagement. InsurTech is poised to redefine healthcare insurance in India, driving operational excellence, expanding coverage, and enhancing service quality. The study offers insights into Insurtech and how to reshape healthcare insurance in India.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
InsurTech, or insurance technology, is significantly reshaping healthcare insurance in India by addressing inefficiencies and improving customer satisfaction. Integrating digital tools such as telematics, data-driven insights, and automation is transforming the life insurance sector and enhancing health-related coverage. A study by Kaur and Singh (2023) found that InsurTech innovations in policy management and customer service management are strong predictors of customer satisfaction in India’s life insurance sector, a trend likely to extend to healthcare insurance as well (Kaur & Singh, 2023). Additionally, the rise of InsurTech startups is playing a critical role in expanding insurance access, particularly in underserved regions where traditional models fail to provide adequate coverage (Suryavanshi, 2022). Another study highlights the adoption of telematics and data analysis as critical for improving risk assessment in healthcare insurance, as these technologies reduce information asymmetry and moral hazard, resulting in more personalized and cost-effective policies (Malik et al., 2022). This convergence of technology is expected to revolutionize healthcare insurance in India by making policies more transparent, accessible, and efficient. However, the journey is not without its challenges. Issues related to data privacy, regulatory compliance, technological infrastructure, and digital literacy pose significant hurdles that need to be addressed to fully realize the potential of insurtech in the healthcare insurance domain. This article explores the versatile impact of insurtech on healthcare insurance in India, exploring into the technological innovations driving this change, the benefits for consumers, the challenges faced by the industry, and the future outlook of this dynamic sector. Through this research aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how insurtech is reshaping healthcare insurance and paving the way for a more inclusive and efficient healthcare system in India. Sumathy et al. (2023)
II. REVIEW OF LITERATURE
Kiwanuka and Sibind(2024) examined the influence of digital literacy and InsurTech adoption on insurance inclusion in Uganda, with a specific focus on whether InsurTech adoption mediates the relationship between digital literacy and insurance inclusion. Using a cross-sectional and quantitative correlational approach, the researchers gathered data from 391 individuals who had accessed insurance products through digital platforms, such as mobile phones and computers. To analyze the hypothesized relationships, Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modelling (PLSEM) was employed.Moreover, the study provided novel insights by establishing that InsurTech adoption mediates the link between digital literacy and insurance inclusion. This implies that while digital literacy directly enhances insurance inclusion, it also indirectly contributes to inclusion by promoting the adoption of InsurTech platforms.
Archillies Kiwanuka and Athenia Bongani Sibind (2023) aimed to explore the role of various dimensions of insurance literacy in predicting insurance inclusion in Uganda. The focus of their research lies in the individual components of insurance literacy—knowledge, skills, attitude, and behavior—and how these factors influence the adoption and usage of insurance products. Their approach was correlational and cross-sectional, involving data collected from 400 individuals who had enrolled in insurance schemes.
By employing hierarchical multiple regression analysis, the study sought to determine the predictive power of each component of insurance literacy on insurance inclusion.
Kaur, Pavanpreet and Singh, Maninder (2023) the study examines how the adoption of InsurTech in the life insurance sector, driven by the Fourth Industrial Revolution (IR 4.0), influences customer satisfaction. Using data from 304 life insurance policyholders in north-western India, the research applies Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modelling (PLS-SEM) and Importance-Performance Map Analysis (IPMA) to assess the impact of InsurTech on customer satisfaction. Findings indicate that InsurTech adoption positively influences customer satisfaction, with customer service management and policy management being key predictors. Improving online distribution and customer service management were identified as areas that can further enhance satisfaction.
III. OBJECTIVES
To analyze the impact of InsurTech innovations on the accessibility of healthcare insurance service delivery.
IV. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This study will employ a qualitative research methodology (Bharathi et al., 2023). Qualitative research aims to provide a comprehensive explanation of a phenomenon through extensive data collection, emphasizing the significance of detailed analysis (Susanto, Ari, 2022). For this study, secondary data were used from articles, journals, Indian Insurtech, IRDA, and various websites.
V. DISCUSSION
A. Brief Overview of the Insurtech Sector in India
The InsurTech sector in India has developed as a lively and quickly evolving section of the larger financial technology (fin-tech) ecosystem. Insurtech combines innovation with traditional insurance practices, utilizing sophisticated technologies to improve operational efficiency, improve customer experience, and broaden the range of insurance services available to consumers and businesses alike.
B. Growth and Evolution
In the last decade, India has seen an increase in insurtech firms and activities aimed at challenging the traditional insurance business. These companies use digital platforms, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and block-chain to automate procedures including policy issuance, claims processing, and consumer involvement. The Indian insurtech market is characterized by a wide spectrum of participants, including startups, existing insurers undergoing digital transformation, and insurer-technology collaborations. This ecosystem encourages innovation, competition, and the creation of specialized insurance products that address a wide range of consumer demands.
C. Technological Innovations
Insurtech firms in India use AI and machine learning algorithms for predictive analytics, underwriting automation, and personalized customer insights.
These technologies help insurers to better analyze risks and provide tailored insurance solutions based on individual data and behavior patterns.
Block-chain technology is being researched to improve data security, streamline claims processing, and promote transparent insurance transactions. Block-chain reduces fraud risks and increases confidence between insurers and policyholders by generating immutable data and smart contracts.
In 2023, global Insurtech funding experienced an increased compared to 2022, while India remained relatively robust with a stable share of Insurtech investments.
Figure 1: The funding level of InsurTech in India (2018–2023)
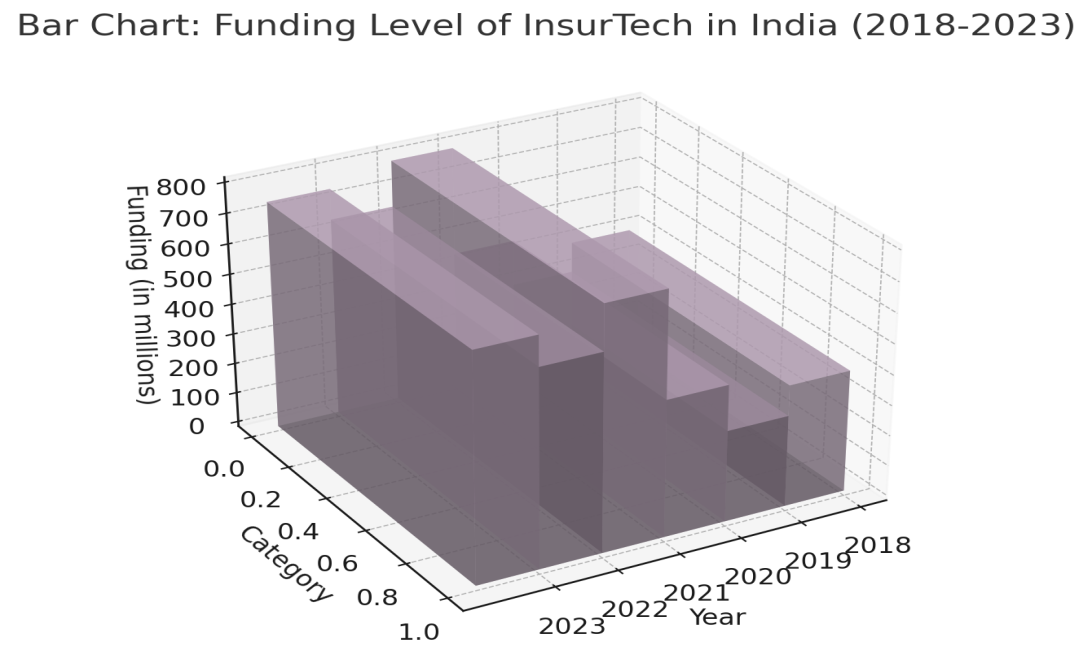
Source: Indian-Insurtech.com
Figure 1 shows a 3D bar chart representing the year-wise funding levels in the InsurTech sector in India from 2018 to 2023. The height of each bar corresponds to the total amount of investment in that particular year. The figure highlights a significant peak in funding in 2021, followed by stable and steady growth in 2022 and 2023. The visual representation helps convey the increasing investor confidence and growing market for InsurTech in India during these years.
Figure 2: Funding distribution by year (2018–2023)
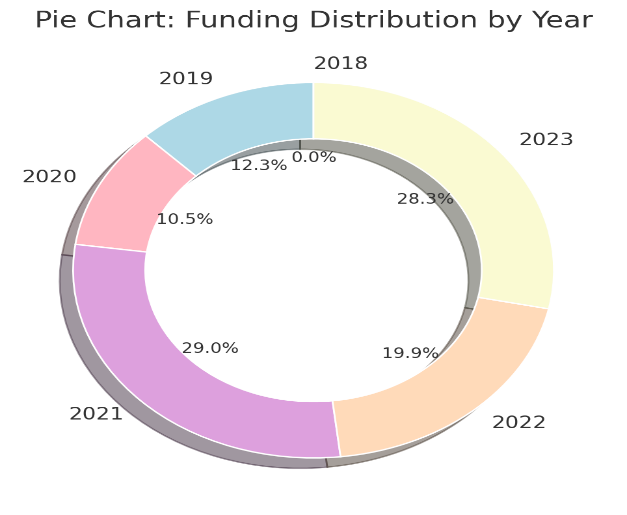
Source: Indian-Insurtech.com
Figure 2 illustrates a donut chart that breaks down the distribution of InsurTech funding across the years 2018 to 2023. The chart visually indicates the percentage of total funding that each year represents within this period. It shows that 2021 contributed the highest share of funding (29.0%), indicating the peak of investment activity during these six years. Subsequent years, 2022 and 2023, are seen maintaining a substantial portion of the total funding (19.9% and 20.8%, respectively), reflecting continued stability and interest from investors in the sector after the surge in 2021. The chart provides a clear and quick reference for understanding the distribution of investment flows over time.
1) The spike in InsurTech funding in 2021 can be attributed to several key factors:
The spike in InsurTech funding in 2021 can be attributed to several factors. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated digital transformation across industries, including insurance, driving a surge in demand for digital solutions. Consumers increasingly sought online insurance products, and innovations like AI-driven claims processing and underwriting gained traction, attracting significant investment. Regulatory bodies in India, such as IRDAI, also encouraged innovation, boosting investor confidence. Additionally, the global boom in FinTech and InsurTech during 2021 contributed to this spike, with India benefiting as an emerging market. The growth potential of the Indian insurance market, with its large population and relatively low insurance penetration, further enticed investors, making 2021 a pivotal year for InsurTech.
Figure 3: Exploring Equity Funding in India's Insurtech Sector
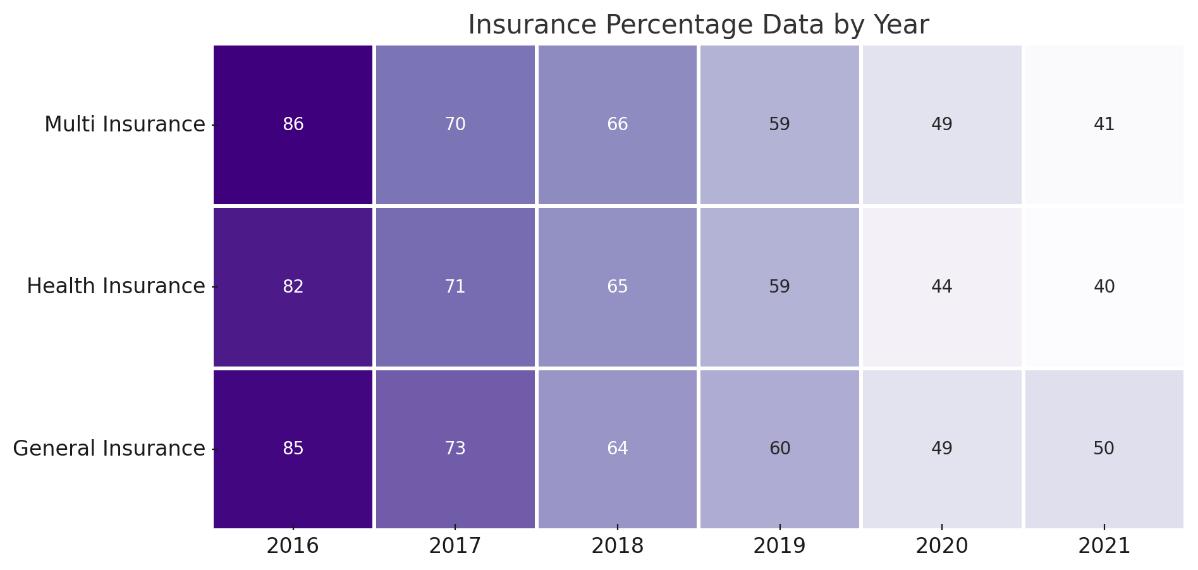
Source: Indian-insurtech.com
Figure 3 visualizes the insurance percentage data for three insurance categories: Multi-Insurance, Health Insurance, and General Insurance, from 2016 to 2021. The data shows that multi-insurance experienced a significant decline, reaching its lowest point in 2020, followed by a slight recovery in 2021. Meanwhile, Health Insurance consistently increased over the same period, indicating a growing demand for health-related insurance products. General Insurance remained stable from 2016 to 2020, before experiencing a sharp increase in 2021, reflecting heightened consumer interest and policy changes in the sector. The darker colors represent higher insurance percentages for each category.
2) To analyze the Insurtech innovations in India improve accessibility and efficiency in healthcare insurance service delivery and management.
Healthcare insurance plays a crucial role in providing financial protection against medical expenses, ensuring access to quality healthcare services without the burden of high costs. In India, healthcare insurance is particularly significant due to the high out-of-pocket expenses for medical treatments, the growing incidence of lifestyle-related diseases, and the economic disparities among the population. By offering coverage for hospitalization, surgeries, and other medical needs, healthcare insurance helps mitigate financial risks, promotes preventive care, and contributes to overall health and well-being in the Indian context.
Insurtech, the fusion of insurance and technology, is revolutionizing the healthcare insurance landscape in India. By leveraging advanced technologies, insurtech companies are enhancing the accessibility and efficiency of service delivery and management. Here’s an analysis of how these innovations are making a significant impact:
3) Digital On-boarding and Policy Issuance
Online Platforms: Insurtech companies use digital platforms to simplify the process of purchasing insurance. Customers can compare policies, get quotes, and purchase plans online without the need for physical paperwork.
Automated Underwriting: AI and machine learning algorithms assess risk and underwrite policies quickly and accurately, reducing the time taken for policy issuance.
4) Claims Processing
Automated Claims Management: Insurtech solutions automate the claims submission and processing workflow. This reduces the time taken to settle claims, enhances transparency, and minimizes human errors.
Block chain Technology: Block-chain ensures secure and transparent transaction records, facilitating faster and fraud-resistant claims processing.
5) Telemedicine and Remote Healthcare Services
Virtual Consultations: Insurtech platforms often include telemedicine services, enabling policyholders to consult doctors remotely. This is especially beneficial in rural and underserved areas.
Digital Health Records: Maintaining electronic health records (EHRs) allows for seamless sharing of patient data among healthcare providers, improving diagnosis and treatment efficiency.
6) Wearable Technology and Health Monitoring
Health Tracking Devices: Insurtech integrates with wearable devices that monitor vital health metrics. This data helps in personalized insurance plans and proactive health management.
Preventive Care: Continuous health monitoring promotes preventive care, reducing the incidence of severe health conditions and associated insurance claims.
7) Customer Engagement and Support
Chatbots and AI Assistants: AI-powered chatbots provide 24/7 customer support, answering queries, guiding policyholders through processes, and resolving issues quickly.
Mobile Apps: Dedicated mobile apps allow policyholders to manage their insurance policies, file claims, and access healthcare services on the go.
8) Enhanced Data Analytics
Predictive Analytics: Insurtech utilizes big data and predictive analytics to identify trends, forecast risks, and tailor insurance products to meet customer needs more effectively.
Fraud Detection: Advanced data analytics help in identifying fraudulent claims and activities, ensuring the integrity and sustainability of insurance operations.
9) Regulatory Compliance and Reporting
RegTech Solutions: Regulatory technology (RegTech) solutions assist insurtech companies in complying with complex regulatory requirements. This ensures adherence to legal standards and reduces the risk of penalties.
10) Impact on accessibility and efficiency
Insurtech innovations in India are significantly enhancing both the accessibility and efficiency of healthcare insurance services. Digital platforms and mobile apps have extended the reach of insurance services to remote and undeserved areas, overcoming geographical barriers that previously limited access. This accessibility is further augmented by the integration of telemedicine, which allows policyholders to consult healthcare providers remotely, reducing the need for physical visits and overcoming logistical challenges.
Insurtech has revolutionized the efficiency of service delivery and management in several ways. Automated processes for policy issuance and claims management streamline operations, reducing paperwork, minimizing errors, and accelerating turnaround times. AI and machine learning algorithms enhance these processes by automating underwriting decisions and facilitating faster claims processing, thereby improving service responsiveness and customer satisfaction. Moreover, the use of advanced data analytics in insurtech enables personalized insurance products and predictive modeling. Insurers can analyze vast amounts of data to tailor coverage options based on individual risk profiles and healthcare needs. This not only optimizes resource allocation but also enhances the affordability and relevance of insurance products for a diverse range of policyholders. Overall, Insurtech’s impact on accessibility and efficiency in healthcare insurance in India is profound, fostering greater inclusivity, reducing operational costs, and ultimately improving the overall quality of healthcare coverage available to the population.
Conclusion
Insurtech has ushered in a new era for healthcare insurance in India, marked by unprecedented advancements in accessibility and efficiency. By harnessing digital platforms, automation, and data analytics, insurtech companies are not only simplifying insurance processes but also expanding coverage to previously underserved populations. This transformation not only enhances customer satisfaction but also drives operational excellence, making healthcare insurance more responsive to the diverse needs of policyholders across the country. As insurtech continues to innovate, its role in shaping the future of healthcare insurance in India remains pivotal, promising continued improvements in accessibility, efficiency, and overall quality of service delivery and management.
References
[1] Kiwanuka, Archillies& Sibindi, Athenia. (2024). Digital Literacy, Insurtech Adoption and Insurance Inclusion in Uganda. Journal of Risk and Financial Management. 17. 119. 10.3390/jrfm17030119. [2] Pavanpreet, Kaur., Maninder, Singh. (2023). Exploring the impact of InsurTech adoption in Indian life insurance industry: a customer satisfaction perspective. The TqmJournal, doi: 10.1108/tqm-06-2023-0186 [3] Archillies Kiwanuka and Athenia Bongani Sibind (2023) Insurance Literacy: Significance of Its Dimensions for Insurance Inclusion in Uganda, Economies 2023, 11(2), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/economies11020033. [4] Kaur, Pavanpreet& Singh, Maninder. (2023). Exploring the impact of InsurTech adoption in Indian life insurance industry: a customer satisfaction perspective. The TQM Journal. 10.1108/TQM-06-2023-0186. [5] Urvashi, Suryavanshi. (2022). The Insurtech Revolution in Insurance Industry: Emerging Trends, Challenges and Opportunities. International journal of management and development studies, 11(08):12-19. doi: 10.53983/ijmds.v11n08.002 [6] Susanto, Ari. (2022). Digital transformation of the insurance industry: The potential of insurance technology (insurtech) in indonesia. Journal of humanities, social sciences and business (jhssb). 2. 54-62. 10.55047/jhssb.v2i1.375. [7] Sakshi, Malik., Rosy, Dhall., Anjani, Singh, Tomar. (2022). InsurTech in insurance. International Journal of Health Sciences (IJHS), 5276-5287. doi: 10.53730/ijhs.v6ns3.7083 [8] Sumathy, M., & Bharathi, M. (2021). A study on level of awareness and satisfaction of financial inclusion services among the select public sector bank customers in Coimbatore district. EPRA International Journal of Research and Development (IJRD), 6(9), 288–298. https://doi.org/10.36713/epra2016 [9] Sumathy, M., & Bharathi, M. (2021). A study on factors affecting concerns and obstacles in the effective implementation of financial inclusion practices of select public sector banks (PSBs) in Coimbatore district. EPRA International Journal of Research and Development (IJRD), 6(9), 282–287. https://doi.org/10.36713/epra2016 [10] Shallini, V., Sumathy, M., & Bharathi, M. (2024). A study on the impact of PMJDY and PMFBY on farmers\' financial inclusion in India. Research Explorer: A Blind Review & Refereed Quarterly International Journal, 12(42), April–June. Available from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/381708838_A_STUDY_ON_THE_IMPACT_OF_PMJDY_AND_PMFBY_ON_FARMERS\'_FINANCIAL_INCLUSION_IN_INDIA
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Dr. M. Sumathy, Ms. Bharathi. M. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET65519
Publish Date : 2024-11-25
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

