Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Intelligent Helmet for Bike Rider’s Safety
Authors: Mrs. P. Madhuri , Lakshmi Raja Vaisali Marepalli, Konakanchi Sri Radha Madhavi, Boga Sneha Sri, Mandala Akshethra
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.60162
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
The intelligent helmet introduced in the paper aims to bolster rider safety, especially in areas like India with high rates of motorcycle accidents. By incorporating features like alcohol detection and accident identification, it addresses common causes of accidents such as driver negligence or impairment. Integrated with the bike\'s ignition system, it prevents ignition activation if the rider is intoxicated, thus averting potential accidents. In case of an accident, the helmet autonomously alerts registered numbers or authorities, providing precise GPS location data for swift response. Additionally, it monitors real-time vehicle speed and triggers SMS alerts if speed limits are exceeded, aiming to prevent accidents caused by speeding. Through RF technology, the helmet ensures seamless connectivity with the bike\'s systems, facilitating efficient data transmission and significantly enhancing rider safety.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
An intelligent helmet system for motorcycles to enhance rider safety. It prioritizes helmet enforcement before starting the bike, using GSM and GPS to track accidents and aid in prompt medical assistance. Integrated features include alcohol and accident detection modules to mitigate common causes of road mishaps, crucial in countries like India with rising motorcycle usage and accidents. Recognizing the urgency for proactive safety measures, the system incorporates sensors like limit switches and breath analyzers, alongside GPS and GSM technology, to ensure helmet compliance, detect alcohol, and alert authorities in case of accidents. Emphasizing timely medical intervention, it seeks to bridge the gap between accidents and aid through swift GPS-based notifications. By addressing these key aspects of motorcycle safety, the working model aims to significantly reduce accidents and fatalities, fostering safer road environments. Leveraging advanced technologies, it proactively tackles factors contributing to motorcycle accidents, ultimately enhancing rider safety and decreasing road fatalities.
A. Literature Survey
The literature survey reviews studies on smart helmet technologies and two-wheeler safety concerns. Smith et al. (2018) and Johnson (2020) explore the evolution of smart helmets, highlighting sensor integration for enhanced safety. Brown (2017) and Garcia (2019) emphasize the vulnerability of two-wheeler riders, advocating for real-time monitoring and proactive safety measures. Patel et al. (2020) and Clark (2018) discuss IoT applications in two-wheeler safety, proposing integration with communication systems for hazard alerts. Wong (2016) and Kim (2021) focus on sensor technologies, emphasizing sensor fusion methodologies for accurate detection of rider behavior and accidents. Anderson et al. (2019) & Carter (2020) present prototypes of intelligent helmets with accident detection and emergency response systems. Gaps identified include standardized data analysis protocols, integration with vehicle systems, and user interface design. Future directions include enhancing reliability and real-time responsiveness, as highlighted by Mitchell (2022) & Foster (2021). Overall, the literature underscores the need for further research to address gaps and improve the effectiveness of intelligent helmet systems for enhanced two-wheeler safety.
B. Formulation of the Problem
The problem statement addresses the pressing safety concerns confronting two-wheeler riders, encompassing motorcyclists and scooterists, amidst the perils of sudden braking, collisions, and distractions on the road. In response, the working model endeavors to develop an intelligent helmet system leveraging advanced technologies to bolster rider safety comprehensively. Central to this endeavor is the identification of key challenges:
Accident prevention is addressed through sensor integration, while distracted driving is countered with features discouraging smartphone usage and issuing hazard alerts. Emergency response capabilities are enhanced with automatic distress signal transmission, and proper helmet compliance is ensured through a smart locking mechanism. Fatigue detection mechanisms prompt timely breaks, and improved navigation and real-time weather updates fortify rider safety.
C. Objectives
The Intelligent Helmet aims to enhance motorcycle rider safety through four primary objectives.

Firstly, it detects helmet usage using image processing algorithms from helmet-mounted cameras. Secondly, it integrates a breathalyzer sensor to detect alcohol levels, triggering alerts or vehicle disablement if thresholds are exceeded. Thirdly, the system tracks vehicle speed using GPS or speed sensors, issuing warnings if limits are surpassed. Lastly, it employs accelerometers to detect accidents, automatically notifying emergency contacts with GPS location data. The system architecture includes a microcontroller for data integration, wireless modules for communication, and a user interface for real-time feedback. Power considerations and ethical/legal standards are crucial in the working model's implementation, ensuring continuous operation and user privacy.
II. HARDWARE USED
- Limit Switch: Detects the presence of the helmet on the rider's head, ensuring that the bike cannot be started unless the helmet is worn, thus enhancing safety.
- Alcohol Gas Sensor: Integrates into the helmet to detect alcohol consumption by the rider, preventing ignition if the alcohol level exceeds a certain threshold, promoting responsible riding behavior.
- GSM Module: Enables the helmet to send alerts and notifications to emergency contacts or authorities in case of accidents, facilitating prompt medical assistance and improving emergency response.
- GPS Module: Tracks the location of the rider in real-time, allowing the system to send accurate location details to emergency services in the event of an accident, aiding in swift response and rescue operations.
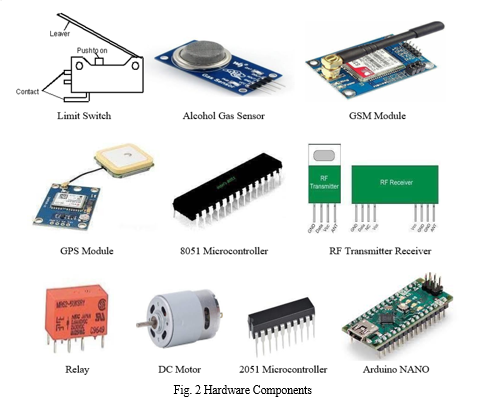
5. Microcontroller 8051: Controls the various functions and sensors of the intelligent helmet system, processing data and executing algorithms to ensure seamless operation and safety enforcement.
6. RF Transmitter Receiver: Facilitates wireless communication between the helmet and the bike's control system, enabling features such as helmet detection and automatic ignition control.
7. Relay: Acts as a switch to control the power supply to the bike's ignition system based on inputs from sensors like the limit switch and alcohol gas sensor, ensuring safe operation.
8. DC Motor: Potentially used in mechanisms such as automatic helmet locking systems, where the motor locks or unlocks the helmet based on the status of safety checks performed by the system.
9. AT89C2051 Microcontroller: Provides the intelligence and processing power needed for the helmet's safety features, implementing algorithms for helmet detection, alcohol sensing, and accident detection.
10. Arduino NANO: Offers a flexible and easy-to-use platform for prototyping and developing the intelligent helmet system, allowing for rapid iteration and customization of features to enhance rider safety.
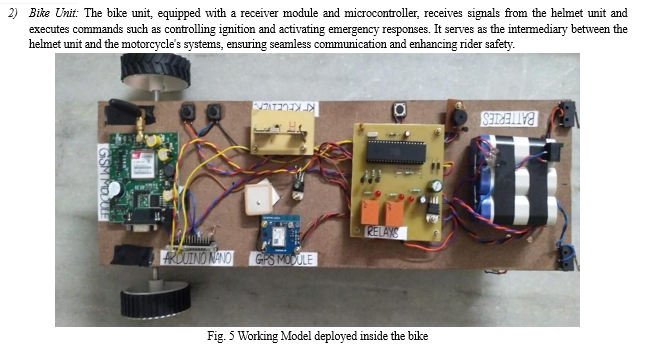
III. WORKING
The helmet system aims to bolster motorcycle rider safety through a multifaceted approach that integrates advanced sensors and technology into helmets.
The intelligent helmet system integrates vital features to enhance safety for two-wheeler riders. To enforce helmet usage, a transmitter-receiver mechanism ensures that the bike cannot be started without the rider wearing the helmet. The transmitter in the helmet communicates with a receiver in the bike, managed by the AT89C2051 Microcontroller, which, upon signal reception, activates a mechanism to turn off the motor, prohibiting bike operation until the helmet is worn.
Addressing the risk of alcohol consumption while riding, an MQ2 alcohol gas sensor in the helmet triggers LED indicators upon detection of alcohol, signaling intoxication. This information is relayed to the bike's receiver, alerting the rider and potentially disabling the vehicle to prevent accidents caused by impaired judgment.
Additionally, speed control is vital for maintaining safe riding conditions. A 5V relay acts as a speed control mechanism, activating a warning beep if the vehicle exceeds a preset speed limit. This prompt alerts the rider to reduce speed and avoid potential accidents.
Accident detection is paramount for rider safety. Limit switches on the motorcycle detect accidents by monitoring changes in vehicle dynamics. Activation of these switches triggers alerts; in minor accidents, a lower beep sound prompts the rider to assess the situation, while in major accidents initiate emergency protocols.
In such cases, the GPS module determines the vehicle's precise location, processed by the Arduino microcontroller. A distress signal, including location information, is transmitted to preconfigured emergency contacts via the GSM module. This rapid response system ensures prompt assistance, potentially saving lives in critical situations. Overall, the integrated features of the intelligent helmet system synergize to enhance rider safety and prevent accidents on the road.
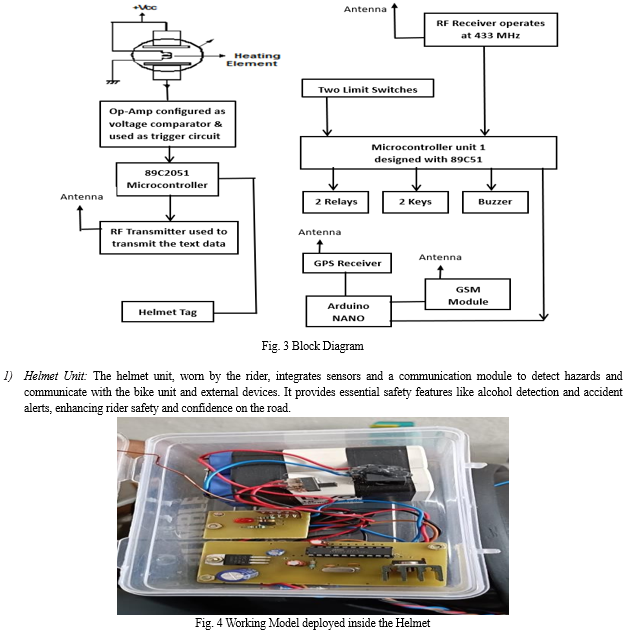
Overall, the intelligent helmet system functions as a comprehensive safety mechanism, combining proactive measures like helmet enforcement and alcohol detection with reactive responses to speed violations and accidents, thereby creating a safer environment for motorcycle riders.
IV. RESULTS
The working model incorporates several features aimed at enhancing the safety of riders. Here's a description of the results and observations based on the outlined functionalities:
- Helmet Detection and Ignition Control: The system effectively ensures that the vehicle's ignition starts only when the helmet is worn correctly and securely clipped. This feature significantly promotes helmet usage among riders, thereby reducing the risk of head injuries in case of accidents.
- Alcohol Detection and Vehicle Control: The inclusion of an alcohol sensor within the helmet is a crucial safety measure. By detecting alcohol levels, the system can prevent the operation of the vehicle if the rider is under the influence, thus minimizing the likelihood of accidents caused by impaired judgment and reflexes.
- Overspeed Alert: The continuous buzzer alert for over speeding serves as a timely warning to the rider, prompting them to adjust their speed and adhere to safe limits. This feature helps prevent accidents resulting from excessive speed, which is a common cause of two-wheeler accidents.
- Accident Detection and Emergency Response:
a. Small Accident Notification: In the event of a minor collision or impact, such as another vehicle touching or bumping into the two-wheeler, the system triggers a small beep sound. This serves as an alert to the rider to assess the situation and take necessary action.
b. Major Accident Notification: If the two-wheeler is involved in a major accident, characterized by significant impact or damage, the system activates a continuous beep sound and automatically stops the vehicle's movement. Simultaneously, the system initiates an emergency response protocol by sending messages to the concerned family, nearby police station, and nearby hospital. These messages contain detailed location information, including a Google Maps link, enabling prompt assistance and medical intervention.

Overall, the working model demonstrates effective integration of technology to enhance rider safety on two-wheelers, addressing key risk factors such as helmet non-compliance, alcohol impairment, over speeding, and accident detection. The observed functionalities indicate the potential to significantly reduce the incidence and severity of accidents involving two-wheelers, thereby contributing to road safety.
V. ADVANTAGES, DISADVANTAGES, APPLICATIONS
A. Advantages
The working model offers a multifaceted approach to enhancing rider safety through innovative technology integration.
- Risk Reduction: The integration of advanced safety features like alcohol detection and speed control minimizes the risk of accidents and injuries by proactively mitigating potential hazards on the road.
- Improved Visibility: The incorporation of LED lights and real-time updates on traffic conditions enhances rider visibility, reducing the risk of accidents caused by poor visibility conditions.
- Emergency Response: Integration of accident detection systems and GPS tracking enables rapid notification of emergency services, facilitating prompt medical assistance and rescue operations.
- Data Collection and Analysis: The ability to collect and analyze data related to rider behavior and road safety metrics offers valuable insights for improving safety outcomes and informing policy decisions.
- Customizable Features: Customizable settings and options empower riders to optimize their safety equipment according to their unique preferences and requirements.
- Safety Features: A comprehensive array of safety features, from helmet-based alcohol detection to real-time monitoring capabilities, promotes safer riding practices and enhances overall road safety.
- Real-time Monitoring: Continuous tracking of critical safety parameters enables immediate intervention in emergencies or hazardous situations, enhancing rider awareness and responsiveness.
- Communication and Connectivity: Integration of communication technologies facilitates efficient data exchange and information sharing, improving coordination among stakeholders and enhancing rider protection.
- Integration with IoT and Future Tech: Leveraging IoT platforms and emerging technologies ensures relevance and effectiveness in addressing evolving safety challenges and opportunities in two-wheeler transportation.
B. Disadvantages
Despite its promising safety features, the working model faces certain challenges and limitations that may impede its widespread adoption and effectiveness.
- Cost: The working model's high cost, attributed to advanced safety technologies and communication modules, may hinder widespread adoption due to affordability concerns.
- Complexity and Reliability: The interconnected nature of the system components poses challenges in ensuring reliability and performance under various conditions, risking technical malfunctions and compromising safety.
- Privacy Concerns: The integration of sensing and communication technologies raises privacy concerns regarding data collection, storage, and sharing, potentially infringing on riders' privacy rights.
- User Acceptance and Comfort: The alteration of aesthetics and comfort due to electronic components may lead to resistance from riders accustomed to traditional helmets, impacting adoption rates.
- Dependency on Technology: Reliance on advanced technologies introduces a dependency that poses risks in scenarios like limited network coverage or technical failures, potentially compromising safety.
C. Applications
The working model holds diverse applications across various sectors, promising to revolutionize rider safety and redefine standards in two-wheeler protection.
- Motorcycle and Bicycle Safety: The intelligent helmet working model enhances rider safety by integrating advanced safety features tailored for motorcycle and bicycle riders, reducing accidents and injuries on the road.
- Urban Commuting: With improved visibility and real-time monitoring, the working model enhances safety for two-wheeler riders navigating congested urban environments, promoting efficient and safe commuting practices.
- Sports and Adventure Activities: Tailored safety features like impact sensors and GPS tracking make the intelligent helmet working model valuable for enhancing rider protection during sports and adventure activities, enabling informed decision-making in challenging terrain.
- Industrial Safety: In industrial settings, the working model's features such as proximity sensors and hazard detection systems improve worker safety on two-wheeler vehicles, reducing accidents and enhancing workplace safety.
- First Responder Assistance: The intelligent helmet working model facilitates swift and effective assistance from first responders by streamlining communication and providing precise location tracking during emergencies, potentially saving lives in critical situations.
- Healthcare and Rehabilitation: By offering real-time monitoring and remote support, the working model aids in healthcare and rehabilitation efforts, benefiting patients recovering from injuries or undergoing rehabilitation both at home and in clinical settings.
- Military and Defence: In military applications, the working model enhances rider safety and operational effectiveness during tactical operations and reconnaissance missions, contributing to mission success and personnel protection in diverse environments.
Conclusion
The Intelligent Helmet working model focuses on enhancing rider safety through two key mechanisms, enforcing helmet usage and detecting alcohol consumption. If either safety rule is violated, the system prevents bike operation, ensuring adherence to safety protocols. In the event of accidents, the system swiftly notifies the police station of the rider\'s location via SMS, facilitating prompt medical assistance for victims. Although successfully developed and tested as a prototype, further modifications are necessary for optimal functionality. Despite being constructed with locally available components to minimize costs; enhancements are essential to meet operational requirements and ensure reliability. The working model underscores the potential of low-cost embedded systems in bolstering vehicle safety and reducing accidents, showcasing the effectiveness of innovative solutions in addressing critical safety concerns on the road. With continued refinement and implementation, the Intelligent Helmet working model can significantly enhance rider safety and contribute to overall road safety initiatives.
References
[1] Ali, Mohammad, et al. \"Predictive prevention of loss of vehicle control for road way departure avoidance.\" Intelligent transportation systems, IEEE transactions on 14.1(2013)- 56-68. [2] Chan, Ching-Yao. \"On the detection of vehicular crashes -system characteristics and architecture. \"Vehicular Technology, IEEE Transaction on 51.1(2002):180-193. [3] Jesudoss A, Vybhavi R and Anusha B, “Design of Smart Helmet for Accident Avoidance”, International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing, April 4-6, 2019, India. [4] Mr G Vinod and Mr Sai Krishna, “Smart Helmet”, International Journal of Engineering Sciences & Research Technology, April 2008. [5] Wu, Xinye, et al. \"Research on vehicle rollover and control. \"Advanced Computer Control (ICACC), 2010 2nd International Conference on.vol.2. IEEE, 2010.
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Mrs. P. Madhuri , Lakshmi Raja Vaisali Marepalli, Konakanchi Sri Radha Madhavi, Boga Sneha Sri, Mandala Akshethra . This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET60162
Publish Date : 2024-04-11
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

