Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Interaction of Technology and Space in an Interactive Museum
Authors: Sarishti Kukreja, Vandana Sehgal, Anjaneya Sharma
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.50267
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
This Project aims to put focus on the technological boom in today’s museums. There is a shift of visitors visiting in the Museums from traditional one to Interactive one as they feel much connected with the exhibits and their overall journey. Interactive Museums are replacing the old type of museums by incorporating not only sight but hear and touch also which makes one’s journey exciting and engaging. Due to the change in user’s need, Technology is becoming dominant and advance in almost every sector amongst which Museum is one part of it and becoming technological advance day by day. The research is based on the Interaction of Technology and Space in an Interactive Museum. Through the literature studies it is found out what are the upcoming latest technologies and that are already being used in Museums outside India as this sector in India is still behind if we compare with other countries but our country is also adapting technology very fast in the Institutional sector, Technologies like Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, Artificial Intelligence, Projection Mapping, Binaural technology, Holograms, Robotics, Other Interactive exhibits like Laser Maze, Illusion of Museums. With the above mentioned Technologies I have concluded the spatial requirement of each technology and its type in the Museum Sector.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
In today’s world Technology is playing important role in almost every sector amongst which Museum is one sector. When we talk about technological advance museums then it is understood that the Museum is Interactive in nature. There are 3 types of Museums namely i) Traditional in which traditional method of experiencing exhibition implied a series of displays accompanied by long and boring texts, which inevitably left the visitor feeling as dazed and confused ii) Interactive Museums offers pictures, videos and interactive software’s to display artefacts. Here, exhibits are interactive in nature; user tends to spend much more time on that particular exhibit as the exhibit tends to develop emotions of the user iii) Virtual Museums are Non physical, Off-site museum experiences. When a person is unable to reach a particular museum due to any constraints specially museum in other countries, it is not easy to visit different countries then this virtual type of museums can solve the purpose of watching museum online by sitting at your home. This technology allows user to see the space in 360 degree so that the whole enclosure is perceived. There is a transition from traditional type to Interactive type of Museums, As pointed out by Shri Sreenivasan- the Metropolitan Museum of Art’s chief Digital Officer on an interview to Gilbert “Museums no longer need to compete with each other because they are losing their visitors to the technologies, games and social media consumed by the modern society; those institutions have to find out ways to embrace the fact that Smartphone’s, tablets, smart watches and other digital devices are everywhere and take advantage of the fact that people use them no matter when or where. People ask me what our biggest competition is…It’s not the Guggenheim ; It’s not the Museum of Natural History – It’s Netflix , It’s candy crush and most recently Pokémon Go.” and many others. (Roberto Vaz) From above mentioned conversation it is clear that why museums are providing with new scenarios of Interactive Technologies. Technological advance Museums can become interactive with maximum use of senses (Vision, Touch, Sound, Smell, Taste) in exhibits; more are the number of senses involved more engaging is the user journey. Spatial Experience is a visual experience formed by principal of arranging element of space with -Media material as elements & Principles of Mechanics and Modern Technology to give a Beautiful Experience. To understand the experience, First we need to understand the Space required for each technology (with special reference to exhibits).
II. LITERATURE SURVEY
There are some renowned technologies that have been most active in Contemporary Museums and are Interactive. These are listed as following:
- Multimedia
- Illusion
These 2 are the broader categories that have been prominently used in any Interactive Museums. Further, Multimedia Technology is sub divided into following exhibits:
A. Multimedia
- Audio / Visual
a. HOLOGRAM
b. PROJECTION MAPPING
c. BINAURAL ECHNOLOGY
2. Interactive Displays
a. VIRTUAL REALITY ( VR )
b. AUGMENTED REALITY ( AR )
c. ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ( AI )
d. OTHER INTERACTIVE EXHIBITS ( LASER MAZE & SENSOR BASED)
Multimedia technology integrates image processing, sound processing, video processing, 3D animation technology and other processing technologies. Characteristics of Multimedia:
- Integration: Integration of multimedia including transmission, storage and presentation media devices.
- Diversity: It is used in diverse fields and in diverse ways.
- Interactivity: Human-computer interaction is the biggest feature of Multimedia.
- Controllability: Processing and controlling multimedia information and expressing it in a variety of media according to human requirements and acting on people’s multiple senses at the same time.
- Non-Linear: These characteristics will change people’s traditional sequential reading and writing modes.
- Ease of use of Information: Users can use the information according to their own need, interests, task requirements, and preferences and choose any information expressions such as pictures, texts and sounds.
a. Hologram
It’s a three-dimensional image formed by the interference of light beams from a laser or other light source. There are many types of Holograms used in various Industries but for my Research I will be covering the latest types that we can incorporate in a Museum.
- 3D Holographic Fans: These are type of Displays that produce 3D image floating in the air. It has strip of RGB LEDs attached to the blades of fan and a control unit lighting up the pixels. As the fan rotates, display produces a full picture.
These are wall mounted can have 2 or more blades. This can be installed on wall/ceiling /Pedestal/ Grid type stand. The set up have inbuilt Wi-Fi through which user can connect the device and can see 3D images on the Holographic fan blades.

- Cheoptics 360 Degree, Hologram: It is a Multi functional holographic display system that allows 3d objects to appear within a glass pyramid .Object appears to be floating freely before transparent background.

This Hologram is symmetrical in Nature and can be seen same from all the angles. Space requirement for this Technology is 10M X 10M.
- Stage Holograms: These are not true holograms, because you cannot walk around them to see every angle. Presentations can have hologram people, or large rotating hologram objects. Standard Size of booth: 4m x 2m x 2.5m (WXDXH). However it can be customised up to 5m in height, 10m in width. This does not require eye glasses, therefore number of people is not fixed, and it can vary. Lights to remain off when hologram is working. Red and blue glass option gives more impressive 3D effects that make object appear to float. Special technology is applied to these people so that their characters appear to be facing and talking directly to each member of the audience.
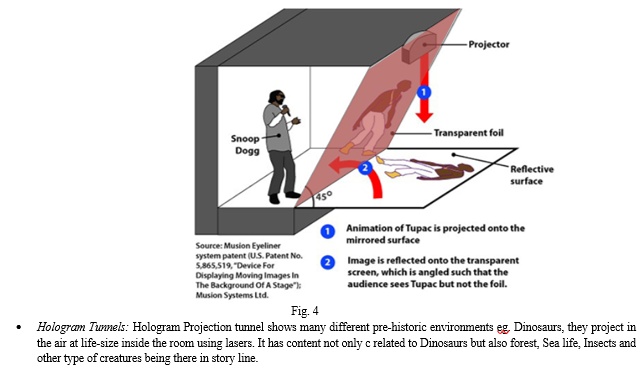

b. Projection Mapping
Projection Mapping allows existing surfaces to become alive with virtual content that can be viewed by users .Can be used to highlight existing features within historical buildings, brings to life specific shapes and structures. Alternative to screens is existing facades, Water surfaces, Undulating landscape mounds etc.
We can Analyse Projection Mapping through 5 Parameters:
C P S M A,
CONTENT = The Visuals that are Projected.
PROJECTION HARDWARE = The Equipment that is doing Projection.
SURFACE = The physical space projected onto.
MAPPING = The Technical aspects of Operating the projection on the Surface.
AUDIO = The music and sound designed in sync with visuals.
Projectors are of 2 types: Standard and Large Venue, Generally Large Venue projectors are used in Projection Mapping on spatial elements or on screens.
Rough Guide for Projection Hardware:
- 5’ X 5’ product display – 1 standard Projector
- Corporate event staging – 1-2 large venue projectors
- 3000 sq. ft. wall – 2-3 large venue projectors
- 15 story skyscraper – 10-40 large venue projectors or 2 top end large venue projectors.
- Surface: The darker the surface for projection, less effective is the illusion. Black, Grey and glass surfaces do not work with Projection surfaces. It is best on White, Matt and Non-Reflective surfaces. Best on surfaces who do not have much level difference, So watching is uniform. However, there are techniques to make even difficult surfaces work for Projection mapping.
- Throw Ratio of a Projector: For any given projector, the width of the image (W) relative to the throw distance (D) is known as the throw ratio D/W or distance over width. So for example, the most common projector throw ratio is 2.0. This means that for each foot of image width, the projector needs to be 2 feet away or D/W = 2/1 = 2.0.
c. Binaural Technology
It adds an Immersive layer to Audio. This creates an Immersive experience that allows museum visitors to feel like they are part of exhibit. Allows Visitors to hear in 3D. Like Space has 3 dimensions as Length, Width and Height, It seems that a person is in 3D sound space. When move, the sound he hear changes as well corresponding to the position of his ears. Instead of traditional commentary by experts about specific objects, this audio experience is hosted by professionals in their own words.
Technical Aspects:
- 2-4 audio Channels
- Sound is captured identically to the way we hear the world.
- It is possible to localize if the sound comes from Left, Right, Front, behind, above or below.
- Very realistic sound
- Impression of being at the place of recording.
- Immersive sound
- Headphones are necessary
- It can be used in theatres also as in example it has been used in Pittsburgh new music ensemble.

d. Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality (VR) is a computer-generated environment with scenes and objects that appear to be real, making the user feel they are immersed in their surroundings. This environment is perceived through a device known as a Virtual Reality headset or helmet. VR set-ups can be of Different size and nature.
- VR Station: It is the small cubical like station with 1 person standing inside without any Movement with the head gear experiencing himself in Virtual environment. Minimum size of cubical is 1.5M X 1.2M.
- VR room (Person with Movement): Requires moving area with VR setup along with Head gear. Minimum sizes require is 2M X 2M minimum areas but more area is always better, upto 3M X 3M
- Person with Sitting: Requires seating space in any form with movement of hands. Space required is 2M X 1.5M / person.

e. Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR) is the integration of digital information with the user's environment in real time. Unlike virtual reality (VR), which creates a totally artificial environment, AR users experience a real-world environment with generated perceptual information overlaid on top of it. It uses a Smartphone or tablet to alter the existing picture, via an app. The user stands in front of a scene and holds up their device. It will show them an altered version of reality. This technology can be Flexible with space, Technology can be used in an open corridor and it can be used in an enclosed room depending upon the type of Exhibit.

f. Artificial Intelligence
AI is intelligence demonstrated by machines as opposed to the natural intelligence displayed by humans and animals. Dubai’s Museum of the Future has added a new member to its staff – Ameca, an AI-powered humanoid robot, which interact with visitors at the futuristic museum. Also answering visitor’s queries, providing directions, greeting them.

g. Other Interactive Exhibits
The laser beams above the floor are connected to sensors that play sounds. As walked through the lasers, the connection to the sensor gets break down which plays a note. As we walk through we create own sound track. Light from one side of the tunnel is beamed continually onto sensors which are sensitive to light at the other side. While the sensor detects the laser light, no sound is played. But if the laser light gets blocked by walking through the laser beam, the sensor detects the lack of light and triggers a computer to play a note.
There are 2 type of Laser Maze set-ups- Temporary and Permanent. Temporary Laser beam set-up. Framework is made of PVC pipes over which laser lights with inbuilt sensors are hanged.

This set up is made up in Rectangular room of dimension: 8’ x 20’ x 8’ (W x L x H). The player enters the dark room through a door. The game path is blocked by bright red laser beams. He can select his level of difficulty on a touch screen. By pressing the start button, a countdown begins and game gets started. The gamers wait for their turn outside the laser room. Waiting area has a LED screen so that players can watch from outside and can make their own strategies. Different configurations can be made. Both Horizontal and Vertical lasers can be the part of the exhibit within the same configuration.









 \
\



Conclusion
Space required for exhibit under each Technological parameter, According to Literature Study: S.No. Type of Technology Size (Min. Dimensions) Remarks 1. HOLOGRAM 1a. 3D Holographic fans 1 blade = 420mm dia. 2 blade = 500-700mm dia Depth = 600mm Module based. These modules can combine to form large panel for producing 3d images 1b. Cheoptics 360 degree • Desktop • M150 • M300 • M500 W X H X D mm • 430 X 1570 X 430 • 1500 X 2430 X 1500 • 3600 X Var. X 3600 • 5600 X Var. X 5600 Room space required for M500 IS 10m X10m 1c. Stage Holograms W X D X H mm • 4000 X 2000 X 2500 Can be customised to height & width of 5m & 10m 1d. Hologram Tunnels L X W X H • 20m X 3.5m X 3m 2.5m out from the wall 1e. Hologram Enclosures Table enclosure W X D • 4.2m X 5m Space enclosure • 19m X 14m - 2. PROJECTION MAPPING 2a. Thumb rule Thumb rule: 1’ image width = Projector needs to be 2’ away. Ratio W/D ,1:2 (Not always as there are lenses that can be adjusted to change the size of image without increasing much distance between projector and screen. Control room of area 60-70sq.m required Computer or laptop and its supporting equipment\'s with amplifier for sound. 3. BINAURAL TECHNOLOGY Minimum area required for a person is 1sq.m Head phones required 4. VIRTUAL REALITY • 1 module for 1 person • Person with movement • Person with sitting • 1.5m x 1.2m for a VR station • 2m X 2m minimum area but more area is always better. 3mX3m max. area • 2m X 1.5m / person Minimum area required for a person standing without movement. Person moving with VR setup 5. AUGMENTED REALITY Required hardware: • Phone • Tablets with inbuilt apps 6. LASER MAZE Rectangular room W X L X H • (2.5 X 6.1 X2.5m) Min. dimensions required for each chamber Can have different chambers 7. ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (ROBOTICS) • Size depends upon the type of Artificial Intelligence required for the space Can be a machine Can be a machine in human form 8. ILLUSION 8a. Ames Room • Area = 15sq.m approx. 8b. Infinity Room • 4600mm x 4600mm x 2500mm (sizes taken from case studies) Eg. Yayoi Kusama (Victoria Micro gallery , London) No definite size of an infinity room. It can be rectangular/ hexagon as seen in other cases 8c. Vortex Tunnel • Bridge 6 m in Length • Bridge width 1m • MS railing with 5-6 Aluminium rings 3m in height Illusion with LED lights on curved surface of tunnel
References
[1] Anderson, Katherine. “The Canada Science and Technology Museum.” Society for the History of Technology (July 2018).
[2] Art Science Museum, Singapore.
Copyright
Copyright © 2023 Sarishti Kukreja, Vandana Sehgal, Anjaneya Sharma. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET50267
Publish Date : 2023-04-10
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

