Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Internet of Things in Disaster Management
Authors: Vaibhavi Mahesh Badade, Prof. Sonal Chanderi
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.64640
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
In recent years, natural failures including floods, landslides, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and wildfires have come to be increasingly Ubiquitous, These events, frequently worsened with of human activities like deforestation, immoderate chemical use, heavy use of gasoline production, and international warming, those problems result in sizable loss of existence and belongings damage global, fortunately, technological improvements have furnished valuable tools for know-how and mitigating the risks associated with these screws-ups. The Internet of Things (IoT), with its various competencies, has appeared as a promising solution for catastrophe management. Wi-fi sensor networks (WSNs) and IoT platforms can establish centralized facts systems to reveal environmental situations. Through sensor information evaluation, we will discover capability risks in real time. When unusual readings are detected, the device can cause signals, ship SMS messages, and make calls to exact contacts. These signals offer statistics about the threat factor, its location, and suggested movements. Using uploading actual-time statistics to cloud servers and issuing alerts through various communication channels, this machine ambitions to reinforce communities with critical data, thereby enhancing their disaster response and preparedness.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Natural and human-caused disasters pose a regular threat to groups around global. Those events, consisting of earthquakes, floods, fires, accidents, and acts of terrorism, can cause extreme harm, harm and loss of residents, and devastated economies. Latest tragedies such as the Nepal Earthquake (2015), Mexico Earthquake (2017), California Wildfires (2017-2023), Kerala Floods (2018), Cyclone Odisha (2019), the Ukrainian warfare (2022), and Turkey & Earthquake (In February 2023) show how devastating this will be. Thousands and thousands of humans are directly or not directly affected by those activities, wherein caution and practice are often constrained. Disaster management has traditionally depended on a rescue technique, but this confirms inadequate. Lack of standard expertise and superior technologies prevent well-timed warnings and proactive measures. To relieve these devastating results, we flow towards a more proactive method. This involves investing in early warning structures that utilize superior sensor networks and information analysis to pick out ability risks and trouble well-timed indicators. Education and cognizance campaigns empower individuals with the expertise and gear to count on and respond to disasters, even as network preparedness endeavors construct resilience through drills, evacuation plans, and hoarding of essential components. One promising solution for proactive disaster management lies inside the Internet of Things (IoT). The IoT Foresees a destiny where regular items are geared up with sensors that can collect statistics and transmit that information, creating a community of interconnected devices that reveal environmental situations, infrastructure integrity, and ability threats. Via exploiting this era, we will create green catastrophe management structures with numerous key benefits like real-time statistics collection, Early warnings and alerts, progressed aid allocation, greater coordination, and so on. Even as IoT offers considerable capacity, a few challenges need to be addressed. Ensuring the safety and integrity of facts collected with the aid of IoT gadgets is essential. Applying large-scale sensor networks calls for study infrastructure and efficient data control solutions. Imposing and preserving IoT systems requires a professional team of workers in areas like data evaluation and network management. Notwithstanding these challenges, studies and development are actively exploring revolutionary packages of the IoT era in catastrophe control. One instance is the improvement of a prototype IoT-primarily based system focused on detecting atmospheric modifications. This machine makes use of sensors to acquire information sensed with the aid of atmospheric adjustments and upload it to the cloud in actual time, and that difficulty signals via numerous channels such as SMS or telephone calls. By strengthening communities with important statistics, such structures can significantly beautify catastrophe reactions and preparedness. Investing in IoT studies and improvement, coupled with powerful implementation strategies, can save the lives of many residents and belongings throughout failures. As failures end up more common and intense, leveraging the strength of IoT is important for constructing a more tenacious future. The goals are as follows:
- Accentuate the capacity of IoT for proactive disaster management: The paragraph emphasizes that IoT generation offers a promising solution for enhancing catastrophe control via providing real-time facts collection, early warnings, stepped-forward useful resource allocation, and greater coordination.
- Cope with hurdles and destiny instructions: It recognizes the challenges related to IoT implementation, inclusive of protection, scalability, and information necessities. It additionally highlights the ongoing studies and improvement efforts to address those challenges and explore modern packages.
- Inspire investment in IoT: The paragraph encourages funding in IoT studies and improvement to construct greater resilient groups and save the lives of humans and animals.
- Emphasize the significance of IoT for a long-lasting future: It shows that as screw-ups turn out to be greater common and excessive, leveraging the electricity of IoT is vital for constructing a greater resilient future.
II. METHODOLOGY
IoT (Internet of Things) performs a vital role in disaster control by offering real-time facts collection, evaluation, and communique skills. The general technique involves:
A. Sensor Network Deployment:
- Strategic Placement: Sensors are methodically placed in areas vulnerable to disasters (e.g., floodplains, earthquake zones, wildwirelesser inclined regions).
- Sensor Types: diverse types of sensors are used to monitor environmental parameters (e.g., temperature, humidity, air high- quality, water levels, seismic activity).
- Connectivity: Sensors are linked to the net through the usage of numerous communique technologies (e.g., mobile network, LoRaWAN).
B. Statistics Collection and Transmission:
- Actual-time monitoring: Sensors constantly collect records and transmit them to a principal server or cloud platform.
- Information Aggregation: records from more than one sensor are aggregated and processed to become aware of developments and anomalies.
C. Facts analysis and selection support:
- Set of rules improvement: Algorithms are developed to analyze sensor information and perceive potential hazards (e.g., growing water ranges, unusual seismic hobby).
- Early warning structures: While thresholds are exceeded, the machine triggers indicators to applicable governments and groups.
- Choice support equipment: Advanced analytics and visualization tools help choice-makers verify the state of affairs and plan responses.
D. Emergency Response Coordination:
- Communication Channels: IoT platforms facilitate real-time communique among emergency responders, authorities corporations, and the public.
- Use Resource Allocation: Information-pushed insights assist optimize the allocation of sources (e.g., personnel, gadgets) to affected regions.
E. Put up-catastrophe assessment and recuperation:
- Damage Assessment: IoT sensors can be used to assess the quantity of harm to infrastructure and belongings.
- Recovery Planning: Statistics collected for the duration and after screw-ups can tell heading efforts and lengthy-time period resilience-making plans.
As shown in Fig.2. an IoT-based totally catastrophe control gadget utilizing an Arduino microcontroller as its critical processing unit. The machine encompasses Wi-Fi sensors, inclusive of a flood sensor, mild-dependent resistor (LDR) sensor, and accelerometer, to acquire environmental information. This record is transmitted to a cloud platform via a Wi-Fi or GSM module, enabling real-time monitoring and evaluation.
The collected records are processed using the Arduino microcontroller, and the effects are displayed on a liquid crystal display. Additionally, the machine can ship alerts or notifications to a cell telephone via the GSM This allows for well-timed conversation and response to capacity hazards. The device’s components are painted together in a coordinated way. The sensors gather statistics, The Arduino approaches them, and the conversation modules transmit the facts to the cloud and mobile devices. This interconnectedness allows the gadget to provide valuable knowledge and signals for disaster control functions.
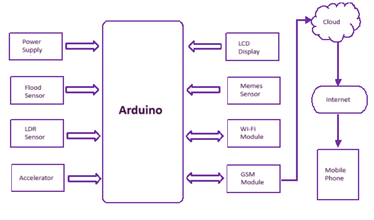
Fig. 1. Block diagram of Disaster management system
III. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
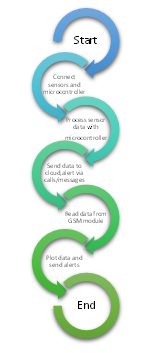
Fig. 3. Flow of Disaster Management System
As we recognized IoT structures can help to shield humans and the environment from natural failures. By using sensors to monitor situations like climate and water stages, we can offer early warnings and help citizens prepare and respond successfully provided the picture shows the workflow of an IoT gadget that is designed for catastrophe management. This machine makes use of a combination of sensors, a microcontroller, cloud connectivity, and a GSM module to gather, system, and examine information related to environmental situations.
This manner starts with the relationship of diverse sensors to a microcontroller. Those sensors are intentionally deployed to collect records on parameters including temperature, humidity, strain, fuel ranges, water degrees, and seismic hobby. The microcontroller, acting as the gadget's mind, gets and techniques the sensor data, figuring out patterns, abnormalities, or threshold crossings that could imply a potential disaster. As soon as the statistics have been processed, its miles transmitted to a cloud-primarily based platform for storage, analysis, and visualization. This allows for centralized information control and allows faraway monitoring of the state of affairs. If the facts show a crucial occasion, including a fast growth in temperature or water tiers, the gadget can trigger indicators to the citizens, along with sending SMS messages, making telephone calls, or activating sirens. Those signals may be directed to applicable government, emergency services, or the affected populace regions. To facilitate communique, the system incorporates a GSM module, which permits connectivity to cell networks. This permits the transmission and reception of statistics, such as SMS messages and contact calls.
The amassed statistics also can be visualized on a dashboard or map, providing a real-time evaluation of the scenario and assisting in choice-making. Based totally on the expected statistics, additional signals can be sent if essential, along with evacuation warnings or instructions for locating shelter. The system keeps screening information and replies to changing conditions until the catastrophe is alleviated or resolved.
IV. CHALLENGES AND FUTURE DIRECTION
The modern-day answers for catastrophe management are appropriate, however, we can cause them to be even better. We will use predict failures and make decisions on particular events that may arise. We also can make the structures easier to use and paintings higher with different emergency tools. This can help us be even extra organized for failures. This section highlights the primary problems and barriers confronted with the aid of current IoT-primarily based answers for catastrophe management structures.
A. Demanding situations
- Social-Media with Synchronized Emergency Communications: Microposting platforms like Facebook and Twitter should provide united protection function for regions liable to screw-ups, much like the “safety take a look at” characteristics used during the Nepal earthquakes. This would permit humans in affected regions to speedy percentage their vicinity and protection reputation with loved ones.
- Run-Time Analytics: Failures are often unpredictable and hard to govern. This means that we need to govern. This means that we need to make brief choices if we want to respond effectively to residents. A brand-new kind of technology called “tough actual-time analytics” can help us try this. These days, a few researchers counselled two algorithms that may be used to make selections in actual time, even though there are troubles with the system. Those algorithms might be very useful for catastrophe management.
- Cost Effectiveness: Many researchers are trying to make IoT systems less expensive and more efficient. They want to get the most out of these structures even as spending less on hardware and software. Disaster management may be very critical ang might save lives. So, groups around the arena must spend money on developing new technology to make those systems even good deal. The studies that have been accomplished thus far haven’t focused plenty on fee effectiveness. Therefore, that is something that desires to be considered in the future.
- Data Analytics: One of the largest troubles with modern-day IoT answers for disaster management is that they investigate records from distinct places and times. These facts may be in one-of-a-kind codecs and have exceptional meanings, making it hard to work with.
- Standardization: The current answers for disaster control do not continually observe the same standards for data and methods. This could be a hassle, specifically when managing specific types of failures. Whilst it might be hard to create one general for all failures, it is vital to have unusual requirements for protection, conversation, and identity. Those standards ought to be advanced as IoT generation grows and new answers are created.
B. Future Direction
The IoT era has already made considerable progress in disaster management, but its capability is a long way from being spent. As we flow ahead, we will expect sever ai interesting tendencies inclusive of greater sensor capabilities, AI-powered analytics, integration with other technology, community-based IoT moral concerns, etc.
Here are few regions for destiny research in IoT-primarily based catastrophe management structures:-
- Value: It’s miles essential to make IoT solutions for disaster control finances-friendly so they may be used more extensively. This indicates preserving the value of manufacturing and selling these devices as little as feasible. That is crucial for deploying a large number of IoT sensor modules.
- AI-Powered Analytics: AI-powered systems can analyze IoT data to predict failures and their consequences. This allows emergency responders to make quick and informed choices.
- Moral issues: It's essential to shield the privateness of facts amassed by using IoT devices, specifically during disasters. Besides, we want to make sure that everyone has get right of entry to and benefits from IoT generation, however in their historical past or where they stay.
- Real-Time Processing: Essential for IoT gadgets used in catastrophe management to procedure facts in real time. This means that the gadgets need a purpose to technique facts quickly and exactly that will respond to converting conditions. At the same time as a few current solutions keep in mind actual-time processing, all IoT-primarily based disaster management structures prioritize this capability
- Structuring of facts: It is essential for IoT gadgets utilised in catastrophe control to have a uniform facts layout. This could make it simpler to system the facts and decrease the workload at the structures that deal with the statistics.
Conclusion
An IoT-based disaster control gadget, exploiting superior strategies, can notably reduce the lack of human lives and harm to critical services cause by both herbal and human-made failures. Through implementing this machine, we will method every will method every catastrophe with a proactive and versant mindset. IoT-enabled catastrophe management structures offer early caution abilities for the spread of hazards, consisting of floods, fires, landslides, earthquakes, and different capability perils. Given the catastrophic effects, those structures can play a critical position in finding patients and coordinating rescue efforts. This newsletter explores the to be had IoT technology for catastrophe management and its suitability for deployment in numerous crisis eventualities. One potential software entails the use of finances-pleasant wi-fi sensor networks to discover floods, sparks, forest fires, and landslides alongside coastal areas. The main goal of this study is to provide an exhaustive evaluation of IoT-based disaster control structures, such as past research contributions and future studies guidelines to address the demanding situations associated with those structures. Through information on the abilities and limitations of IoT technology, we can increase extra powerful and resilient catastrophe management procedures.
References
[1] https://www.researchgate.net/publication/353333160_Disaster_Management_System_using_IoT [2] Authors: Sushma L Bhosle, Soubhagyalaxmi DB, Swetha T, Veena PD. [3] Extensive article covering the war, with sections on its background, timeline, military operations, casualties, and humanitarian impact. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Russo-Ukrainian_War [4] https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322995334_Role_of_Internet_of_Things_in_disaster_management Authors: John Wellington, P Ramesh. [5] https://www.ijcrt.org/papers/IJCRTF020017 Authors: Prof. Borhade B. M., Kajal Date, Pooja Kahane, Rutuja Rasal, Komal Aher [6] https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=8037966 Authors: Partha Pratim Ray, Mithun Mukherjee, Lei Shu. [7] M.Cioca, et al, \"SMS Disaster Alert System Programming,” in Proc. of International Conference on Digital Ecosystem and Technologies. [8] (Apr. 2015). Nepal Earthquake: Eight Million People Affected, UN Says. Accessed: October 13, 2024. [Online]. Available: www.bbc.com/news/worldasia- 32492232. [9] World Disaster Report. Accessed: October 13, 2024. [Online]. Available: http://www.ifrc.org/world-disasters-report-2014/data [10] https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320620108_Disaster_management_using_Internet_of_Things Authors: Shubham Kumar, Supratim Auddy, Subrata Pal, Himadri Nath Saha. [11] Varghese, A. J., Thomas Jolly, A., Peter, A., Rajeev, B. P., Sajitha, K. S., & George, D. E. (2019). IoT-based Disaster Monitoring and Management System [12] For Dams (IDMMSD). 2019 1st International Conference on Innovations in Information and Communication Technology (ICIICT). doi:10.1109/iciict1.2019.8741464. [13] Cyclone Fani Makes Landfall in India, Millions Evacuated. BBC News, May 3, 2019. Accessed: October 13, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.bbc.com/ [14] Earthquakes in Turkey & Syria (In February 2023). Accessed: October 13, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.bbc.com/news/topics/cq0zxdd0y39t [15] Diagram refer by https://www.ijcrt.org/papers/IJCRTF020017 Authors: Prof. Borhade B. M., Kajal Date, Pooja Kahane, Rutuja Rasal, Komal Ahe
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Vaibhavi Mahesh Badade, Prof. Sonal Chanderi. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET64640
Publish Date : 2024-10-16
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

