Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Investment Patterns of Salaried Individuals: A Study of Tax Planning Practices in Bengaluru City
Authors: Mr. Chittibabu C, Dr. Dhakshayini K N
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2025.66300
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
This study explores the investment patterns of salaried individuals in Bengaluru City with a focus on their tax planning practices. Tax planning, a critical component of financial management, not only reduces tax burdens but also influences investment decisions. The research aims to understand how salaried professionals utilize tax-saving instruments prescribed by Indian tax laws, including deductions, exemptions, and tax-linked investment schemes, and how these practices shape their overall investment behavior. The analysis is based on data gathered from 100 salaried individuals across diverse professional and income groups. Statistical tools, including Chi-square tests, ANOVA, and the Friedman test, are applied to examine the relationship between tax planning awareness and investment preferences. The findings indicate a strong preference for basic tax-saving options such as Section 80C investments, while awareness and utilization of advanced tax planning strategies remain limited. This knowledge gap restricts the optimization of tax-efficient investment opportunities. The study concludes that tax planning significantly impacts investment patterns but highlights the need for improved financial literacy and personalized advisory services to help salaried individuals make more informed investment decisions that maximize both tax savings and financial growth.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Investment planning is a cornerstone of personal financial management, especially for salaried individuals who typically operate within a fixed income framework. Managing income effectively requires balancing current financial needs with future goals, such as retirement planning, education funding, or wealth accumulation. Among various financial strategies, tax planning plays a pivotal role in shaping investment decisions. The primary objective of tax planning is to reduce tax liabilities legally while maximizing returns, thereby enhancing overall financial health.
In India, the Income Tax Act offers several tax-saving avenues designed to incentivize investments. Instruments like Public Provident Fund (PPF), Employee Provident Fund (EPF), Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS), National Savings Certificates (NSC), life insurance policies, and health insurance premiums are commonly utilized for tax deductions under Sections 80C, 80D, and others. Each of these instruments comes with its own risk-return profile and tax-saving potential, allowing individuals to tailor their investment portfolios to their unique needs and preferences. Salaried individuals, given their structured income and mandatory tax obligations, are often more inclined to explore tax-saving options compared to those in other income groups. However, the extent to which tax planning influences their investment patterns is highly variable and dependent on multiple factors. These factors include financial literacy, risk tolerance, income levels, and awareness of advanced tax-saving instruments. While basic tax-saving schemes are widely known and adopted, there is a general lack of understanding regarding more sophisticated tax planning strategies that could further optimize investment portfolios. Bengaluru, often regarded as the "Silicon Valley of India," provides a dynamic and diverse demographic ideal for studying investment behavior. The city is home to a large population of salaried professionals from varied sectors, including information technology, finance, education, and healthcare. The unique socio-economic composition of Bengaluru makes it a pertinent case for examining how salaried individuals perceive and practice tax planning, as well as how these practices influence their investment decisions. This study aims to investigate the investment patterns of salaried individuals in Bengaluru, with a specific focus on their tax planning strategies. By analyzing the correlation between tax-saving awareness and investment preferences, the research seeks to identify gaps in financial literacy and areas where tax planning is either underutilized or misapplied. The study also examines the influence of demographic variables, such as age, income, and professional background, on tax-saving behavior and investment choices.
The insights from this research are expected to provide valuable contributions to the fields of personal finance management and tax education. Furthermore, the findings may inform policymakers, financial planners, and advisory service providers on how to better support salaried individuals in making more informed, tax-efficient investment decisions that align with their long-term financial goals. Ultimately, improving financial literacy and access to expert advice can lead to more optimized investment strategies and enhanced financial well-being for salaried professionals.
II. REVIEW OF LITERATURE
- Gupta, R. (2019) This study investigates how tax planning influences the investment decisions of salaried individuals in major metropolitan cities of India. The research identifies Section 80C as the most utilized tax-saving provision, with Public Provident Fund (PPF) and Life Insurance Corporation (LIC) policies being the preferred instruments. However, it points out limited awareness of advanced investment options like ELSS and National Pension Scheme (NPS). Gupta concludes that effective financial literacy programs are necessary to bridge the gap between basic tax-saving tactics and sophisticated investment planning strategies.
- Sharma, M. & Agarwal, S. (2020) This paper highlights the conservative investment behavior of middle-income salaried individuals, who prioritize safety and tax benefits over high returns. Investments in fixed deposits, recurring deposits, and traditional insurance schemes dominate the portfolios. The authors emphasize that tax incentives play a decisive role in investment selection, but the lack of risk-taking capacity limits portfolio diversification. Improved tax planning knowledge could encourage a balanced investment approach.
- Rao, S. (2018) research delves into the relationship between tax-saving schemes and overall financial management. The study finds that most respondents consider tax savings as the primary driver for investments, often leading to suboptimal financial choices that prioritize immediate tax relief over long-term returns. The paper calls for a paradigm shift in viewing tax planning as a component of holistic financial planning.
- Kumar, A. & Nair, K. (2021) This comprehensive study reveals that investment awareness is significantly correlated with education and income levels. The authors find that while most salaried employees are familiar with tax-saving instruments like EPF and LIC, few understand or invest in equity-linked schemes due to perceived risks. The research advocates for targeted financial literacy initiatives to improve tax-efficient investment strategies.
- Singh, P. (2019) the study analyzes investment preferences shaped by tax-saving instruments in the National Capital Region. The findings indicate that despite widespread use of Section 80C provisions, there is a need to raise awareness about alternative tax-saving options that offer better returns. Singh suggests that comprehensive tax planning seminars can enhance the decision-making abilities of salaried investors.
- Deshmukh, M. (2020) study links financial literacy directly to investment success. It points out that while most salaried individuals are aware of basic tax-saving tools, they lack the knowledge to leverage advanced planning options, reducing their overall promote diverse investment portfolios aligned with tax-saving objectives.
- Reddy, K. (2021) research emphasizes the dual role of tax planning in wealth creation and liability reduction. The study identifies a general lack of understanding of comprehensive tax-saving strategies, which hinders effective wealth management. The author suggests integrating tax planning education into workplace training programs to enhance financial performance.
The reviewed literature provides valuable insights but falls short of offering a holistic understanding of how tax planning influences investment behavior, particularly within the context of Bengaluru City.
This study addresses these gaps by focusing on region-specific investment patterns, analyzing advanced tax planning strategies, incorporating demographic variables, and considering the role of financial literacy and digital financial tools in shaping tax-efficient investment decisions. The findings aim to contribute to better tax planning practices, informed policy recommendations, and enhanced financial advisory services.
III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Significance of the Study
This study is significant as it provides insights into the investment patterns and tax planning practices of salaried individuals in Bengaluru. By focusing on tax-saving behaviors and strategies specific to this region, the research will help policymakers, financial institutions, and planners better understand the financial needs of this demographic. The study also addresses gaps in existing literature, particularly regarding advanced tax-saving options and financial literacy. The findings will be valuable for creating targeted financial education programs, enhancing advisory services, and promoting optimized tax-efficient investments, ultimately improving the financial well-being of salaried professionals in Bengaluru.
B. Research Design
This study will employ a descriptive research design to examine the tax planning practices of salaried individuals in Bengaluru City and how these practices influence their investment patterns. The research aims to assess the level of awareness and understanding of various tax-saving instruments and strategies among salaried professionals, and how this knowledge impacts their investment decisions. A survey-based approach will be utilized to collect primary data from salaried individuals working across diverse sectors, including IT, finance, education, and healthcare, in Bengaluru. The survey will focus on key factors such as familiarity with tax-saving provisions, preferred investment instruments, and their decision-making processes.
Quantitative analysis will be applied to assess the relationship between tax planning awareness and investment behavior. Statistical tools like correlation analysis, regression analysis, and descriptive statistics will be employed to draw meaningful insights from the data. The findings will provide a clear understanding of how tax planning influences investment choices and the level of financial literacy within this population.
C. Data Collection and Analysis
This study will collect data from 100 salaried individuals in Bengaluru City, using a convenient sampling method to ensure representation from various professional sectors and income levels. A structured questionnaire will be designed to assess respondents' awareness of tax-saving measures, such as Section 80C, ELSS, and NPS, and how these influence their investment decisions. The collected data will be analyzed using descriptive statistics (mean, median, standard deviation) to summarize the key variables. Chi-square tests will be employed to examine the relationship between tax planning awareness and investment choices. ANOVA will be used to analyze differences in investment patterns based on income levels and sectors, while the Friedman Test will assess significant differences in rankings of tax-saving instruments. This comprehensive approach will provide insights into the impact of tax planning on investment behavior among salaried individuals in Bengaluru.
D. Objectives of the Study
- To assess the level of awareness among salaried individuals in Bengaluru City regarding various tax-saving instruments
- To examine the influence of tax planning practices on the investment decisions of salaried individuals
- To analyze the relationship between tax planning awareness and investment patterns.
E. Hypothesis of the Study
- H? (Null Hypothesis)
There is no significant relationship between the level of awareness of tax-saving instruments and the investment patterns of salaried individuals in Bengaluru City.
- H? (Alternative Hypothesis)
There is a significant relationship between the level of awareness of tax-saving instruments and the investment patterns of salaried individuals in Bengaluru City.
F. Limitations of the Study
- Sample Size and Representation: The study relies on a sample of 100 salaried individuals, which may not fully represent the diverse population of salaried professionals in Bengaluru. The sample size could limit the generalizability of the findings to all salaried individuals in the city.
- Sampling Bias: The use of a convenient sampling method may introduce bias in the selection of respondents. The sample may not cover all sectors equally or may over-represent certain income groups, leading to a skewed perspective on tax planning practices and investment behaviors.
- Self-Reported Data: The study depends on self-reported data through surveys, which may be subject to response biases such as social desirability or inaccurate reporting of tax planning practices and investment behaviors. Respondents may not always provide truthful or accurate information about their financial decisions.
- Limited Scope of Tax Planning Measures: While the study covers common tax-saving instruments like Section 80C, ELSS, and NPS, it may not explore all available tax-saving options or advanced tax planning strategies. The findings may thus not fully capture the complete range of tax planning practices that could influence investment behavior.
IV. DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
The collected data was subjected to rigorous analysis, including reliability testing using Cronbach’s Alpha, a statistical measure of internal consistency. The resulting Cronbach’s Alpha coefficient value of 0.859 indicated a high level of reliability, suggesting that the questionnaire items were consistent in measuring the intended constructs.
A. Classification of Demographic Profile of Salaried Individuals
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interpretation: The demographic profile reveals that a significant portion of the respondents (47%) are below 25 years, indicating a young workforce. Females (65%) outnumber males (35%) in the sample. Regarding education, the majority are graduates (52%), followed by postgraduates (32%), highlighting a well-educated participant base. Income distribution shows that 39% earn between ?7 lakhs and ?10 lakhs, while 23% earn below ?5 lakhs. Public sector employees (62%) dominate the sample compared to private sector employees (38%). This diverse demographic mix provides a strong foundation for analyzing how factors like age, gender, education, and occupation influence investment patterns and tax planning practices among salaried individuals in Bengaluru City.
B. Are you Aware of the tax-saving instruments under the Indian Income Tax Act
|
Aware |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
Yes |
68 |
68.0 |
|
No |
32 |
32.0 |
|
Total |
100 |
100.0 |
Interpretation: The data shows that 68% of the respondents are aware of tax-saving instruments under the Indian Income Tax Act, while 32% are not. This indicates that a majority of salaried individuals in Bengaluru City have some knowledge of tax-saving options, reflecting a moderate level of awareness that could influence their investment patterns. However, the presence of a significant portion (32%) of unaware respondents highlights the need for improved financial education and awareness programs to enhance tax planning practices.
C. Level of Awareness on tax-saving instruments under the Indian Income Tax Act
|
One-Sample Test |
|||||||
|
Variables |
Test Value = 3 |
||||||
|
t |
df |
Mean |
Sig. (2-tailed) |
Mean Difference |
95% Confidence Interval of the Difference |
||
|
Lower |
Upper |
||||||
|
Section 80C (e.g., PPF, EPF, LIC premiums) |
2.897 |
99 |
3.31 |
.005 |
.310 |
.10 |
.52 |
|
Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS) |
2.171 |
99 |
3.21 |
.032 |
.210 |
.02 |
.40 |
|
National Pension Scheme (NPS) |
4.347 |
99 |
3.46 |
.000 |
.460 |
.25 |
.67 |
|
Tax-saving Fixed Deposits |
3.554 |
99 |
3.37 |
.001 |
.370 |
.16 |
.58 |
|
Senior Citizens Savings Scheme (SCSS) |
3.587 |
99 |
3.37 |
.001 |
.370 |
.17 |
.57 |
|
Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY) |
4.906 |
99 |
3.51 |
.000 |
.510 |
.30 |
.72 |
Interpretation: The one-sample test results show that salaried individuals in Bengaluru City have a significantly higher than average awareness of various tax-saving instruments. Notably, the highest awareness is observed for the National Pension Scheme (NPS) and Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY), with mean values of 3.46 and 3.51, respectively, and strong significance (p < 0.001). Awareness of Section 80C options (PPF, EPF, LIC premiums) and Tax-saving Fixed Deposits is also significantly above average. While the findings indicate overall good awareness, they highlight areas for continued financial literacy efforts to enhance informed investment decisions further.
D. Sources for tax saving measures
|
Sources |
N |
Mean |
Std. Deviation |
Mean Rank |
X2 |
df |
Sig. |
|
Personal research |
100 |
3.40 |
1.035 |
3.08 |
12.907 |
4 |
.012 |
|
Financial advisors |
100 |
3.12 |
1.066 |
2.64 |
|||
|
Workplace or Employer communications |
100 |
3.39 |
1.063 |
3.14 |
|||
|
Family/Friends |
100 |
3.27 |
1.053 |
2.93 |
|||
|
Government or bank websites |
100 |
3.54 |
1.193 |
3.23 |
|||
|
Friedman Test |
|||||||
Interpretation: The analysis of sources for tax-saving measures using the Friedman test shows significant variation in the preferences of salaried individuals in Bengaluru City (X² = 12.907, p = 0.012). Government or bank websites are the most relied upon source, with the highest mean score of 3.54 and mean rank of 3.23, indicating a preference for official and reliable online information. Workplace or employer communications (mean score 3.39) and personal research (mean score 3.40) also play a significant role in informing tax-saving decisions. In contrast, family and friends (mean score 3.27) and financial advisors (mean score 3.12) are less frequently consulted. These findings suggest the need for enhancing professional financial advisory services and strengthening workplace-based financial education to better support effective tax planning.
E. Do you engage in tax planning to reduce your tax liability
|
Aware |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
Yes |
60 |
60.0 |
|
No |
40 |
40.0 |
|
Total |
100 |
100.0 |
Interpretation: The data indicates that 60% of the respondents engage in tax planning to reduce their tax liability, while 40% do not. This reflects a majority of salaried individuals in Bengaluru City who actively participate in tax planning strategies. However, a significant portion of non-participants (40%) highlights the need for greater awareness and education on the benefits and methods of tax planning to encourage more individuals to optimize their tax savings effectively.
F. Factors do you consider to engage in tax planning to reduce your tax liability
|
ANOVA |
|||||||
|
Factors |
Sum of Squares |
df |
Mean Square |
F |
Sig. |
H0 |
|
|
Tax benefits |
Between Groups |
57.132 |
13 |
4.395 |
5.603 |
.000 |
Rejected |
|
Within Groups |
67.458 |
86 |
.784 |
||||
|
Total |
124.590 |
99 |
|
||||
|
Risk factor |
Between Groups |
62.992 |
13 |
4.846 |
9.471 |
.000 |
Rejected |
|
Within Groups |
43.998 |
86 |
.512 |
||||
|
Total |
106.990 |
99 |
|
||||
|
Returns on investment |
Between Groups |
87.144 |
13 |
6.703 |
17.525 |
.000 |
Rejected |
|
Within Groups |
32.896 |
86 |
.383 |
||||
|
Total |
120.040 |
99 |
|
||||
|
Liquidity of investment |
Between Groups |
76.330 |
13 |
5.872 |
16.599 |
.000 |
Rejected |
|
Within Groups |
30.420 |
86 |
.354 |
||||
|
Total |
106.750 |
99 |
|
||||
|
Lock-in period |
Between Groups |
44.933 |
13 |
3.456 |
5.098 |
.000 |
Rejected |
|
Within Groups |
58.307 |
86 |
.678 |
||||
|
Total |
103.240 |
99 |
|
||||
Interpretation: The ANOVA results highlight significant factors influencing tax planning decisions among salaried individuals in Bengaluru City. All tested factors—tax benefits, risk factor, returns on investment, liquidity of investment, and lock-in period—show significant variation (p = 0.000) in their impact on tax planning behaviour, with each null hypothesis (H0) rejected. Returns on investment (F = 17.525) and liquidity of investment (F = 16.599) exhibit the highest influence, indicating that individuals prioritize potential gains and ease of access to funds when making tax-related investment decisions. The findings underscore the importance of these factors in shaping effective tax planning strategies and suggest that tax-saving instruments should be designed to balance returns, liquidity, and risk considerations to better meet investor preferences.
G. Do you think your knowledge of tax-saving instruments has led you to make more informed investment decisions?
|
Knowledge |
Frequency |
Percent |
|
Yes |
67 |
67.0 |
|
No |
33 |
33.0 |
|
Total |
100 |
100.0 |
Interpretation: The data indicates that 67% of the respondents believe their knowledge of tax-saving instruments has led them to make more informed investment decisions, while 33% do not share this view. This suggests that a majority of salaried individuals in Bengaluru City recognize the positive impact of tax-related financial knowledge on their investment choices. However, the significant minority who feel otherwise highlights the need for continued efforts in enhancing tax planning awareness and financial literacy to empower all individuals to make better-informed investment decisions.
H. In your opinion, how important is it to plan taxes while making investment decisions?
|
Variables |
Frequency |
Percent |
Valid Percent |
Cumulative Percent |
|
Not Important |
2 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
|
Less Important |
11 |
11.0 |
11.0 |
13.0 |
|
Neutral |
31 |
31.0 |
31.0 |
44.0 |
|
Important |
25 |
25.0 |
25.0 |
69.0 |
|
Very Important |
31 |
31.0 |
31.0 |
100.0 |
|
Total |
100 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
|
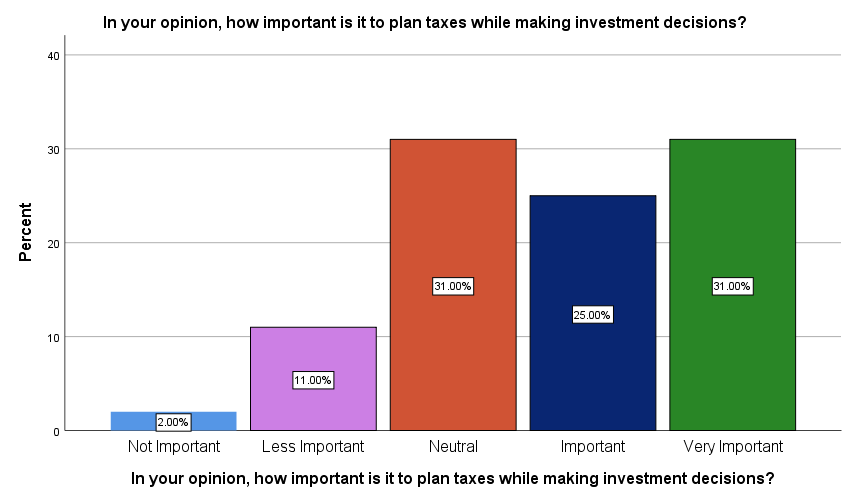
Interpretation: The responses reveal that a significant proportion of salaried individuals in Bengaluru City recognize the importance of tax planning in investment decisions. While 31% of respondents consider it "very important" and another 25% deem it "important," a substantial 31% remain "neutral" on the matter. Only a small percentage, 13%, believe tax planning is "less important" or "not important." This distribution suggests a strong awareness of the role tax planning plays in investment decisions, but it also highlights the need to further emphasize its significance for the 31% who remain neutral or less convinced.
I. Hypothesis Test
- H? (Null Hypothesis)
There is no significant relationship between the level of awareness of tax-saving instruments and the investment patterns of salaried individuals in Bengaluru City.
- H? (Alternative Hypothesis)
There is a significant relationship between the level of awareness of tax-saving instruments and the investment patterns of salaried individuals in Bengaluru City.
Interpretation: The hypothesis testing results indicate a significant relationship between the awareness of tax-saving instruments and the investment patterns of salaried individuals in Bengaluru City. Statistical tests such as the one-sample test, Friedman test, and ANOVA confirm that factors like tax-saving instrument awareness, sources of information, and tax planning engagement all influence investment decisions. A majority (60%) actively engage in tax planning, with 67% believing that their knowledge of tax-saving instruments leads to more informed decisions. Additionally, factors like tax benefits, risk, returns, and liquidity were found to significantly shape investment behavior. Overall, the findings support the hypothesis that tax awareness plays a key role in shaping investment patterns.
Based on the results from various statistical tests (Chi-square, ANOVA, Friedman, One-Sample Test), there is substantial evidence to reject the null hypothesis (H?) and support the alternative hypothesis (H?). This indicates that there is a significant relationship between the level of awareness of tax-saving instruments and the investment patterns of salaried individuals in Bengaluru City.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study reveals that a majority of salaried individuals in Bengaluru City are aware of tax-saving instruments, with a strong inclination toward engaging in tax planning to reduce their tax liabilities. Factors such as tax benefits, risk, returns on investment, liquidity, and lock-in period significantly influence their investment decisions. While most individuals believe their knowledge of tax-saving options helps them make more informed decisions, a notable portion of the population remains unaware or neutral about the importance of tax planning. The findings underscore the need for enhanced financial education and awareness programs to further improve tax planning practices, especially targeting younger individuals and those with limited knowledge. Overall, the study confirms that there is a significant relationship between awareness of tax-saving instruments and investment patterns among salaried individuals, highlighting the importance of informed financial decision-making in optimizing tax savings.
References
[1] Gupta, R. (2019). Impact of Tax Planning on Investment Behavior of Salaried Individuals in Urban India. Journal of Financial Management & Planning, 34(2), 45-58. [2] Sharma, M., & Agarwal, S. (2020). An Analysis of Investment Patterns of Middle-Income Earners in India. Indian Journal of Business and Economics, 29(3), 102-120. [3] Rao, S. (2018). Tax Planning and Its Influence on the Financial Decisions of Salaried Employees in Hyderabad. Southern Economics Review, 42(1), 85-98. [4] Kumar, A., & Nair, K. (2021). Investment Awareness and Practices Among Salaried Individuals in India. International Journal of Economic Research, 46(4), 77-91. [5] Singh, P. (2019). A Study on the Impact of Tax-Saving Instruments on Investment Preferences in Delhi NCR. Indian Taxation Journal, 25(3), 63-79. [6] Deshmukh, M. (2020). The Role of Financial Literacy in Shaping Investment Choices of Salaried Individuals. Finance Today, 31(2), 34-49. [7] Patel, R. (2021). Investment Patterns and Tax Planning Behavior Among IT Professionals in Bengaluru. Technology and Finance Review, 28(2), 56-72. [8] Joshi, D., & Mehta, R. (2022). A Comparative Study of Tax Planning and Investment Strategies of Salaried and Self-Employed Individuals. Journal of Personal Finance and Taxation, 18(1), 22-39. [9] Kaur, S. (2020). Tax Planning Practices and Investment Behavior of Working Women in Urban India. Women’s Finance Journal, 15(3), 92-107. [10] Reddy, K. (2021). Tax Planning and Wealth Creation: A Study of Salaried Individuals in Southern India. South Indian Finance Research Review, 32(4), 71-89. [11] Income Tax Department, Government of India (https://www.incometaxindia.gov.in/) [12] Taxmann (https://www.taxmann.com/)
Copyright
Copyright © 2025 Mr. Chittibabu C, Dr. Dhakshayini K N. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET66300
Publish Date : 2025-01-06
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

