Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
A Review on IOT based Virtual Doctor Robot
Authors: Ms. Sakshi. P. Jadhav, Ms. Manasvi. R. More, Ms. Vidya. A. Kumbhar, Ms. Mayuri. K. Patil, Prof. Mr. S. A. Shinde
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.65561
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
The “Virtual Doctor Robot” project aims to develop an intelligent healthcare assistant capable of providing preliminary medical advice and diagnosis through an AI-driven Chabot interface. This system integrates natural language processing (NLP) to interact with users in a conversational manner, gather symptoms, and offer potential diagnoses or recommended further medical consultation. This innovation aims to enhance healthcare accessibility, especially in undeserved areas, reduce the burden on medical professionals, and streamline routine consultations. The system continuously learns from patient interactions, improving accuracy over time. While not a replacement for human doctors, virtual doctor robot offers significant potential to augment healthcare services, reduce patient wait times, and assist in preventive care by providing timely medical advice. In this discusses the technical framework of the virtual doctor robot, its capabilities, limitations, and potential future improvements. It also addresses the ethical considerations, data privacy concerns, and the challenges of integrating such technologies into mainstream healthcare.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Person-to-person contact during the epidemic was very dangerous for the specialist, medical staff, and patient. In each area, specialist are often expected to be present in medical clinics and crisis centers. Therefore, it is impossible for me to attend every single one and to be available at every location at the desired time. Doctors are usually needed to work at every hospital and emergency centre every now and then. But it is not feasible for every doctor to be available at every place at desired time. A Virtual Doctor System that enables an expert to essentially roam about any clinic space and have spoken conversation with patient helps with this problem. Such robots are used in healthcare settings to ensure assistance and to reduce individual-to-individual interaction. This may be accomplished by reducing the danger that the pandemic poses to clinical staff members and many other individuals who hold operational positions within the company. For professionals, this method has a number of benefits, including: In activity theatres, doctors will walk around. Through video chats, specialist will remotely see clinical records. Various rooms will be visited by specialists. The professional will control the mechanism using an IOT based. The mechanism controller receives the management orders given online. The device’s Wi-Fi controller controls it. To help solve this issue we here develop a virtual doctor robot that allows a doctor to virtually move around at a remote location at will and even talk to people at remote location as desired. This robot provides a whole lot of advantages for doctors:
- Doctors ability to be at anyplace anytime
- Doctors can move around in operation theatres
- Doctors can move around the patient with eas
- Doctors can see medical reports remotely via video calls
- Doctors can move around in other rooms
The system makes use of a robotic vehicle with 4wheel drive for easy navigation. The robot also includes a controller box for circuitry and a mounting to hold tablet. The tablet is used to hold live video calls. The doctors can use an IOT based panel to control the robot. The control commands sent online are received by the robot controller. The robot controller operates over wi-fi internet. The received commands are received in real time and the robot motors are operated to achieve the desired movement commands. Also the root has other functions including battery status alert to remind of battery charging on time.
A. Problem Statement
In many remote and underserved areas, access to healthcare facilities and professional medical advice is limited due to geographical barriers, lack of infrastructure, or scarcity of medical professionals. This leads to delayed diagnosis and treatment, which can worsen health conditions and increase mortality rates. Additionally, in urban areas, the high cost of healthcare and overcrowded hospitals make routine checkups difficult to access promptly.
B. Objective
-
- Remote Consultations: Facilitate remote medical consultations, allowing patients to receive healthcare without the need for physical visits, thus increasing accessibility and convenience.
- Instant Symptom Analysis: Provide immediate assessment and recommendations based on the patient's reported symptoms, leveraging advanced AI algorithms and medical databases.
- Patient Education: Offer reliable information and guidance on health conditions, preventive measures, and treatment options to empower patients in making informed health decisions.
- Medication Management: Assist patients in managing their medications by providing reminders, interactions warnings, and guidance on proper usage.
- Data Collection and Monitoring: Collect and analyze patient data over time to monitor health conditions, track treatment effectiveness, and identify potential health risks.
- Integration with Health Systems: Seamlessly integrate with existing electronic health records (EHR).
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
- Divya Ganesh “AutoImpilo: Smart Automated Health Machine using IoT to improve Telemedicine and Telehealth”. The purpose of the paper, according to Divya Ganesh,[1] is to create an automated system that can quickly link to the healthcare providers like hospitals or physicians in order to stop the spread of illness and lower the rising rates of death in regions
- During the COVID-19 Outbreak, “an IoT-based Healthcare Platform for Patients in ICU Beds,” Itamir De Morais Barroca Jr. IoT appears as a promising paradigm because it offers the scalability necessary for this objective, facilitating ongoing and accurate global health monitoring. Based on this backdrop, the authors’ earlier studies suggested an IoT-based healthcare platform to provide remote monitoring for patients in a life-threatening condition.
- Kashif Hameed, “An Intelligent IoT Based Healthcare System Using Fuzzy Neutral Network, “The term “remote delivery of healthcare services” refers to telemedicine. Telemedicine provides a lot of advantages, but it also has some drawbacks. Providers and payers as well as regulators are aware that there are certain murky regions that are difficult to monitor. Over the next ten years, the sector will expand rapidly, but it will also provide both practical and technical hurdles.
- “An IoT-based system for automated health monitoring and surveillance in post pandemic life is called COVID-SAFE Invoking” - Seyed Shahim Vedaei. The Internet of Things (IoT) may assist in providing a remote diagnosis before reaching hospitals for more effective treatment in a smart healthcare system. Develop an Internet of Things (IoT) e-health system based on Wireless Sensor Networks to continually monitor patients' state of health for diabetic patients. Blood glucose data may be transferred through wearable sensors to physicians or cellphones (WSN).
- Sumit Paul., IoT integrated with the health wearables can overcome the need of visiting hospitals for primary health issues. This also reduces the medical expenses for patients significantly. In addition, the doctors can prescribe necessary medications by observing the patient’s health stats over time through an application. Detailed analysis of the signals was obtained with respect to variations in physical and environmental activities to understand the functioning of the sensors used.
- Prajoona Valsalan, in this paper, a portable physiological checking framework is displayed, which can constantly screen the patient’s heartbeat, temperature and other basic parameters of the room. We proposed a nonstop checking and control instrument to screen the patient condition and storethe patient information’s in server utilizing Wi-Fi Module based remote correspondence.
- Md Anowar Hossain, “ the majority of medical personal wanted to control their assistant robot over the internet”. Another paper named as FASTele –A TeleEchography portable robot system can be used by any paramedic for an emergency purpose. There have been some methods on the PMS (Patient Monitoring System), advanced healthcare, smart healthcare, digital thermometer, Non-contact Infrared Thermometer.
- B.Sundari, the integration of multisensory inputs promotes the involvement of associative cortices that play a key role in learning and consequently in neuronal plasticity and recovery. While only a few studies compared neurocognitive therapy to other rehabilitative approaches, some promising work suggested that it can significantly improve upper-limb function, ability to perform activities of daily living and quality of life compared to conventional task-oriented training.
- Kaviya kumar, an intelligent network infrastructure that is dynamically enhanced and extended by edge nodes, which are generated e as the backbone for IoRT applications. The IoRT combines autonomous robotic systems with the IoT/IoT, intelligent connectivity, distributed and federated edge/cloud computing, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Digital Twins (DT), Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLTs), Virtual/Augmented Reality (VR/AR), and swarm technologies.
- Ankit Patel, with the advent of Internet of Things (IoT), robots are integrated as a ‘thing’ and establish connections with other things over the Internet. It clearly indicates the long-term benefits of human being in healthcare sector, medical emergencies, e-health, etc. using robotics and IoT. Also, the phase of adoption, interaction, challenges for future is to be discussed. As IoT having features of reconnect with different entities like apps, devices and people interaction, which gives the better solution for healthcare and medical industry
III. METHODOLOGY
1) Project Definition and Requirements Define the goal of the virtual robot. What is the robot supposed to do? This could include tasks interaction with virtual environments. Specifications:
Identify the specific functions, hardware , and software requirements. This could include programming languages, simulation platforms Constraints: Establish any limitations (e.g., computational power, time, hardware limitations, or specific virtual environment features).
2) Design Phase Conceptual Design:
Design a model of the robot, including its capabilities and functions. Decide whether it will be autonomous or remotely controlled, and what sensory inputs and outputs it will have. Simulation Environment: Choose the appropriate simulation software.
3) Software Architecture and Development Choice of Programming Languages:
Determine which languages or frameworks you will use to program the virtual robot. Common choices include: C++ (for performance-critical operations in robotics).
Performance Metrics: Measure performance using Control System: Develop or integrate the control algorithms. Communication Protocols: Define the communication methods between the robot’s components
4) Testing and Debugging Simulation Testing:
Run the robot in a virtual environment to simulate real-world tasks. Ensure the robot’s sensors respond as expected. criteria like accuracy, speed, energy efficiency, or task completion rate. Debugging: Check for control errors, sensor malfunctions, or algorithmic inconsistencies.
IV. BLOCK DIAGRAM
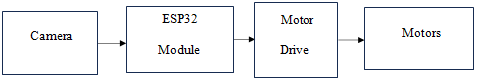
Fig . (1): Block diagram of ESP32 Module to control the Motor
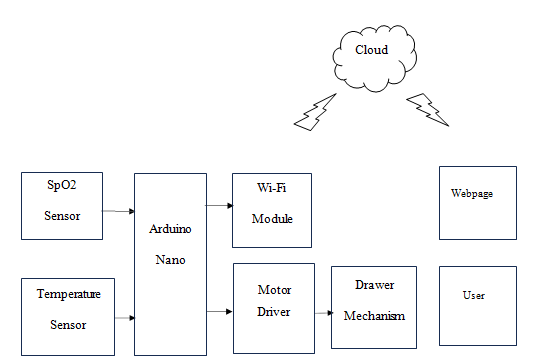
Fig. (2): Block Diagram of Monitor the Patient health and Control the Drawer Mechanism through IoT.
1) Fig. (1): Block diagram of ESP32 module to control the motor:
The robot control and video streaming system consist of ESP32 module. It can used to stream the live video of patient on the operators mobile. Also operator can send the command to the ESP32 module to control the motors and move the robot in required position. The motor driver is used to control the motors of robot.
2) Fig. (2): Block diagram of monitor the Patient health and control the drawer mechanism through IoT
- The system is used to monitor the patient health and control the drawer of medicines through IoT. The system is built around the Arduino Nano. The SpO2 sensor is used to read oxygen level and heart rate of the person. It is connected to finger tip. Its output is given to Arduino board. It will read the data continuously.
- Temperature sensor is used to read body temperature of the person. Its output is connected to Arduino Nano. Wi-Fi module is used to provide internet access to the website using IoT. The automatic drawer opening and closing system is used to medicate the patient. For this purpose the motor mechanism is used to open and close the drawers. It can be controlled through the website using IoT.
Conclusion
Using IoT based virtual doctor robot, the burden of the doctor can be reduced during the busy schedule. The waiting time of the patient can be reduced primary patient monitoring and patient caring assistance with daily activities is achieved. For user friendly, we designed “Doctor Robot” with manual and autonomous control system From anywhere any world will be able to shown the all patient data without touching the patient through IoT system and make communicate video calls with the patient A virtual doctor robot can be equipped with a variety of sensors and other hardware to monitor patients vital signs, track attendance, and move around. The robot can also be controlled remotely by a doctor using and IoT based panel.
References
[1] Divya Ganesh Seshadri, “AutoImilo: Smart Automated Health Machine using IOT to Improve Telemedicine and Telehealth”, IEEE, 2021. [2] Anita Chaudhari, Jeet Thakur and Pratiksha Mhatre, “Prototype for Quadruped Robot Using IOT to Deliver Medicines and Essentials to Patient”, International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology, 2021. [3] Divya Ganesh Gayathri Seshadri, Semathi Sokkanarayanan, “Automatic Health Machine for COVID-19 and other Emergencies”, 13th International conference on communication system and networks, 2021. [4] World Health Organization (WHO): The world health report 2016, Geneva, Switzerland, PP.8/9/2016. [5] WHO Report of the WHO-China Mission on coronavirus Disease 2019(COVID-19); WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [6] Liu, Y; Gayle, A.A.; Wilder-Smith, A.; Rocko, J. The reproductive number of COVID-19 is higher compared to SARS coronavirus. J. Travel med.2020, 27, 1-4. [7] Jonathan Malkin, jeff Bilmes Department of Electrical Engineering, The voice Controlled Robot Arm Brandi House, bhouse, jsm,bilmes@ee.washington. CHI 2009, Boston, USA. [8] Khan, Z.H.; Khalid, A.; Iqbal, J. Towards real. [9] International Journal of Research in Engineering an Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 2320-9364, ISSN(Print): 2320-9356 www.ijres.org Volume 10 Issue 4 | 2022 | PP. 24-26 www.ijres.org 24 | Page Internet of Things in Virtual Doctor Robot. [10] Pabitra Kumar Bhunia, Monalisa De, Poulami Mondal, “ An IOT based Remote Intelligent Health Monitoring and Management System for Mankind During COVID-19 Situation ”,Department of computer science and engineering,IJERT,2021.
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Ms. Sakshi. P. Jadhav, Ms. Manasvi. R. More, Ms. Vidya. A. Kumbhar, Ms. Mayuri. K. Patil, Prof. Mr. S. A. Shinde. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET65561
Publish Date : 2024-11-26
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online