Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
IOT-Enabled Highway Safety Pre- Warning System
Authors: Soumya Singh, Shalini Maurya, Samta Kumari, Dr. Sureshwati , Dr. Shivani Dubey
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.65824
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
The increasing number of road accidents and the need for efficient traffic management systems have led to significant research in advanced technologies aimed at enhancing highway safety. The Internet of Things (IoT) presents a promising solution for real-time monitoring and preemtive safety measures on highways. This paper proposes an IoT-enabled Highway Safety Pre-Warning System designed to provide early warnings to drivers about potential hazards, such as accidents, roadblocks, or sudden weather changes. The system utilizes a network of interconnected sensors, cameras, and communication devices placed strategically along highways to collect and transmit data related to traffic conditions, road quality, vehicle speed, and environmental factors. The information is then processed through a central server and communicated to vehicles, traffic management centers, and emergency responders in real-time. The goal of the system is to reduce the likelihood of accidents and improve response times to incidents, ultimately enhancing the overall safety and efficiency of highway traffic. Key components of the system include vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication protocols, predictive analytics, and dynamic alert mechanisms. This paper also discusses the challenges, such as data privacy, system scalability, and integration with existing infrastructure, as well as the potential impact of this IoT-enabled safety system on reducing fatalities and improving traffic management. The architecture of the proposed system includes roadside units (RSUs) equipped with a range of sensors—such as cameras, radar, and LIDAR—to monitor traffic conditions, detect road obstructions, and measure environmental parameters like fog, rain, or ice. These units communicate with onboard units (OBUs) in vehicles through vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication protocols. The system gathers real-time data on traffic flow, vehicle speed, and road conditions and processes it through an advanced analytics platform to predict potential risks and provide early warnings to drivers. Additionally, the system incorporates predictive algorithms that use historical data and machine learning models to anticipate traffic patterns and accident hotspots. By providing warnings such as \"slow down,\" \"accident ahead,\" or \"road closed,\" the system can significantly reduce the risk of collisions caused by sudden changes in traffic conditions. Furthermore, emergency services and traffic management centers are notified in real-time, enabling faster response times and efficient incident management. The paper also explores the integration of this IoT-enabled system with existing traffic infrastructure, including challenges related to data privacy, interoperability between different vehicle brands and road systems, and the need for a standardized communication framework. Scalability and the long-term sustainability of deploying such systems across highways are also examined, as well as the potential impact on reducing fatalities, improving traffic flow, and minimizing the economic costs of accidents. In conclusion, the IoT-enabled Highway Safety Pre-Warning System represents a significant leap forward in proactive traffic management, combining advanced sensors, real-time communication, and data analytics to enhance road safety, reduce accidents, and optimize highway traffic flow. The system holds the potential to transform highway safety, providing safer, smarter, and more efficient travel for all road users.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Highway safety is a critical issue worldwide, as road traffic accidents are a leading cause of injury and death, with millions of lives affected every year. Rapidly increasing vehicle numbers, rising traffic congestion, and varying road conditions compound the risks on highways, where high speeds and limited reaction time can make minor hazards escalate into severe accidents. Traditional safety measures, such as static road signs, speed limits, and patrol enforcement, offer limited, often delayed, responses to dynamic road conditions, highlighting the need for more proactive, responsive safety solutions. The advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) has introduced new possibilities in highway safety by enabling smart, interconnected systems that can gather, process, and communicate data in real time. An IoT-enabled highway safety pre-warning system aims to leverage these advancements by deploying a network of sensors, edge devices, and communication technologies to continuously monitor road conditions, traffic patterns, and potential hazards.
This interconnected system can detect adverse conditions—such as sudden braking, obstacles on the road, adverse weather, or traffic congestion—and deliver timely alerts to drivers, significantly improving reaction time and reducing the risk of accidents. The system also has the potential to streamline traffic flow, thereby reducing congestion and associated economic costs.
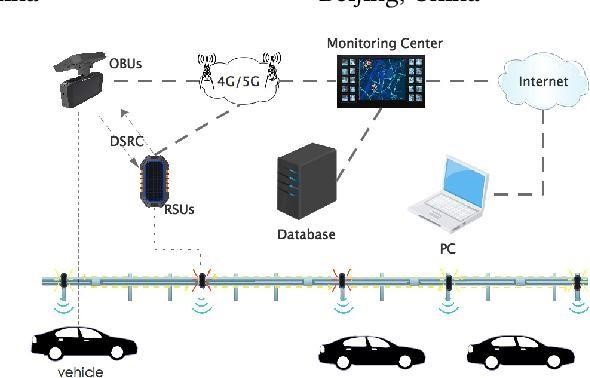
The design and implementation of an IoT-enabled highway safety prewarning system involve several core components: real-time data collection through a network of sensors (e.g., for weather, motion, and object detection), data processing on edge devices and cloud platforms, and a communication infrastructure that enables vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) interactions. These elements work together to create a dynamic safety network that operates across diverse highway conditions, ensuring that relevant data can be quickly analysed, interpreted, and acted upon. Predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms play a pivotal role in identifying potential hazards and forecasting risky situations based on data patterns, thereby enabling the system to provide preemptive alerts rather than reactive responses. The development of this system, however, faces technical and operational challenges. Effective real-time communication is reliant on stable, highspeed networks (e.g., 4G/5G), and gaps in network coverage can reduce system efficacy. Additionally, sensor accuracy can be affected by extreme weather, visibility issues, or physical obstructions, potentially impacting data reliability. Data security and privacy also present significant concerns, as the system collects and transmits large volumes of potentially sensitive data. Moreover, integrating this technology with existing highway and traffic management infrastructure may require substantial adaptation and cooperation among multiple stakeholders, including transportation authorities, telecommunication providers, and emergency services.
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
A. IoT Applications in Highway Safety
IoT technologies have shown significant potential in enhancing highway safety by enabling continuous monitoring and dynamic responses to real-time hazards. Studies by Zanella et al. (2014) and Al-Sakran (2015) highlight IoT’s role in creating "smart" road infrastructure capable of communicating critical safety data to drivers, improving reaction times and reducing accident risks.
B. Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication
V2X communication is essential for timely hazard detection and data sharing in IoT-enabled systems. Campolo et al. (2017) and Gozalvez (2016) discuss the benefits of DSRC and cellular V2X (C-V2X), noting that both provide reliable data exchange, with 5G enhancing responsiveness for real-time safety alerts. However, latency remains a challenge, especially in highspeed highway scenarios.
C. Predictive Analytics for Hazard Detection
Machine learning models have proven effective in predicting hazards by analyzing traffic data patterns. Kumar et al. (2018) and Zhu et al. (2019) demonstrate that algorithms like neural networks can forecast potential risks, allowing for preemptive alerts. Despite their benefits, these models require high computational resources, making edge-cloud integration critical for real-time processing.
D. Edge and Cloud Computing for Real-Time Processing
Edge computing reduces data latency by processing information close to the source, while cloud platforms support deeper analytics and data storage. Shi et al. (2016) and Satyanarayanan (2017) highlight that combining edge and cloud computing enables responsive, scalable highway safety systems, though this approach demands robust infrastructure for seamless performance.
E. Challenges in IoT-Enabled Highway Safety Systems
Key challenges include sensor reliability, data security, and network limitations. Alam and El Saddik (2017) address sensor accuracy issues in adverse weather, and Roman et al. (2018) emphasize the need for strong encryption to secure sensitive data. Amadeo et al. (2016) point out that current network limitations underscore the need for 5G to support low latency applications in real-time highway safety.
F. Summary and Research Gaps
While IoT-enabled highway safety systems hold significant potential for reducing accidents and improving safety, challenges remain in sensor reliability, data security, and network performance.
Further research should address these limitations, particularly by advancing V2X standards, improving sensor robustness, and ensuring data privacy.
III. METHODOLOGY
A. System Design and Architecture
- Requirements Analysis: Identify specific requirements for real-time data collection, hazard detection, communication, and alert mechanisms. Key factors include sensor accuracy, data transmission reliability, and latency limits.
- Component Selection: Select suitable hardware and software components, including sensors (for weather, motion, and object detection), edge devices (e.g., Raspberry Pi, Arduino), and cloud service providers (e.g., AWS IoT, Azure IoT) to facilitate data processing and storage.
- System Architecture: Develop an architecture that combines edge and cloud computing for data processing. The architecture should allow for low-latency data processing at the edge and advanced analytics and storage on the cloud, ensuring rapid data flow and effective alert dissemination.
B. Data Processing and Analytics
- Cloud-Based Advanced Analytics: Utilize cloud services to perform more complex data analytics, including pattern recognition and machine learning (ML) modelling. Store historical data in the cloud to train ML algorithms that can predict hazardous situations.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Develop predictive models to analyse traffic flow, detect anomalies, and anticipate hazards based on historical and real-time data. Algorithms may include decision trees, support vector machines (SVM), and neural networks, which can identify patterns in traffic flow, weather changes, and vehicle behaviour.
C. Data Collection and Sensor Deployment
- Sensor Selection: Choose sensors based on their ability to capture data relevant to highway safety, such as weather conditions, traffic flow, vehicle speed, and road obstacles. Commonly used sensors include LIDAR, cameras, infrared sensors, temperature and humidity sensors, and accelerometers.
- Sensor Placement: Strategically deploy sensors along highways, focusing on high-risk areas like intersections, curves, and entry/exit ramps. Install sensors on both roadside units and vehicles to enable comprehensive data collection.
D. Alert Mechanisms and User Interface Design
- In-Vehicle Alerts: Design in-vehicle alert systems (e.g., dashboard displays, audio notifications) to deliver timely warnings directly to drivers.
- Roadside and Mobile Alerts: Deploy digital signage along highways to display alerts to all approaching drivers. Additionally, develop a mobile application for real-time alerts and notifications, allowing nonconnected vehicles to access system warnings.
- Alert Timing and Priority Levels: Implement a priority system for alerts, where high-risk hazards (e.g., sudden obstacles, severe weather) trigger immediate notifications, while lower-risk issues (e.g., moderate congestion) are displayed with lower priority.
E. Application of Iot-enabled highway safety pre warning system
1) Real-Time Hazard Detection and Driver Alerts
- Accident Prevention: The system’s primary application is to detect hazards, such as sudden obstacles, accidents, or stalled vehicles, and provide immediate alerts to drivers, allowing them to react promptly. For example, a vehicle involved in an accident can automatically trigger alerts to nearby vehicles, reducing secondary collisions.
- Weather-Related Warnings: By integrating weather sensors, the system can detect adverse weather conditions like fog, heavy rain, or icy roads. It can then alert drivers about potentially dangerous conditions ahead, enabling them to adjust their speed and driving behavior.
- Traffic Congestion Alerts: The system can monitor real-time traffic density and detect sudden slowdowns or congestion, providing drivers with rerouting suggestions to avoid traffic jams and maintain steady highway flow.
2) Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) and Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V)
Communication
- Enhanced Situational Awareness: V2I and V2V communication allow vehicles to share information about speed, location, and road conditions with each other and roadside infrastructure. This cooperative system improves situational awareness, as drivers and autonomous vehicles receive real-time information about road hazards beyond their line of sight.
- Adaptive Signal Control and Traffic Management: V2I communication can assist highway authorities in implementing adaptive traffic signals based on real-time data. Traffic control centers can use V2I
- data to optimize traffic signals, minimize wait times, and reduce congestion at highway intersections and exits.
- Cooperative Adaptive Cruise Control (C-ACC): IoT-enabled prewarning systems support C-ACC systems, where vehicles communicate to adjust their speeds cooperatively, reducing braking, and sudden stops. This results in smoother traffic flow, reduced congestion, and improved fuel efficiency.
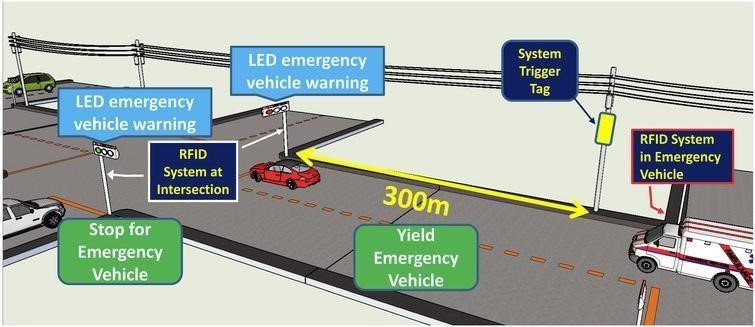
3) Smart Incident and Emergency Response
- Automated Emergency Notifications: The system can notify emergency responders in real-time about highway incidents, such as accidents, stalled vehicles, or hazardous weather. For instance, if an accident occurs, the system can transmit precise location data and traffic details, enabling faster and more targeted emergency response.
- Lane Blockage Alerts: In the event of a stalled vehicle or road blockage, the system can notify drivers and reroute traffic, allowing emergency responders to reach the scene more quickly and ensuring drivers avoid dangerous lane changes.
- First Responder Coordination: Using IoT data, emergency services can coordinate multiple responders, such as ambulances, fire trucks, and tow services, by providing them with optimized routing based on real-time traffic conditions and incident location.
4) Traffic Flow Optimization and Congestion Management
- Dynamic Speed Limits: IoT data on real-time traffic density, road conditions, and weather can be used to adjust speed limits dynamically. Variable speed limits based on current conditions allow for safer driving speeds and help prevent accidents due to sudden slowdowns.
- Peak-Time Traffic Management: By analyzing traffic patterns during peak hours, the system can predict and manage congestion points on highways, providing insights to implement timed entry ramps or restricted zones to alleviate congestion.
5) Data-Driven Policy and Infrastructure Planning
- Traffic Pattern Analysis: The data collected through the IoT-enabled pre-warning system provides detailed insights into traffic patterns, congestion hotspots, and accident-prone areas. Policymakers and urban planners can use this data to implement targeted improvements, such as adding lanes, increasing signage, or redesigning high-risk intersections..
- Policy Development and Regulatory Compliance: The system’s data can assist in developing traffic safety policies based on observed driver behaviour and accident trends. For instance, if specific speed limits or warning signs are less effective in certain areas, authorities can adjust regulations to better meet safety needs.
6) Support for Autonomous Vehicle Operations
- Enhanced Safety for Autonomous Vehicles (AVs): The pre-warning system provides real-time data on road conditions and hazards, supporting autonomous vehicles by enabling proactive responses to sudden changes in traffic or environmental conditions.
- Predictive Safety and Collision Avoidance: Data on surrounding vehicles and road infrastructure allows AVs to anticipate and avoid potential collisions, creating a safer environment for both autonomous and traditional vehicles.
7) Public Safety Awareness and Driver Education
- Awareness Campaigns: Insights from the system can help authorities launch awareness campaigns focused on areas with frequent accidents or common risky behaviours, educating drivers on how to avoid specific hazards.
- Enhanced Driving Assistance for Specific Conditions: In areas with frequent hazards, such as sharp turns or frequent wildlife crossings, the system can provide enhanced guidance to help drivers navigate these areas safely.
IV. ADVANTAGES
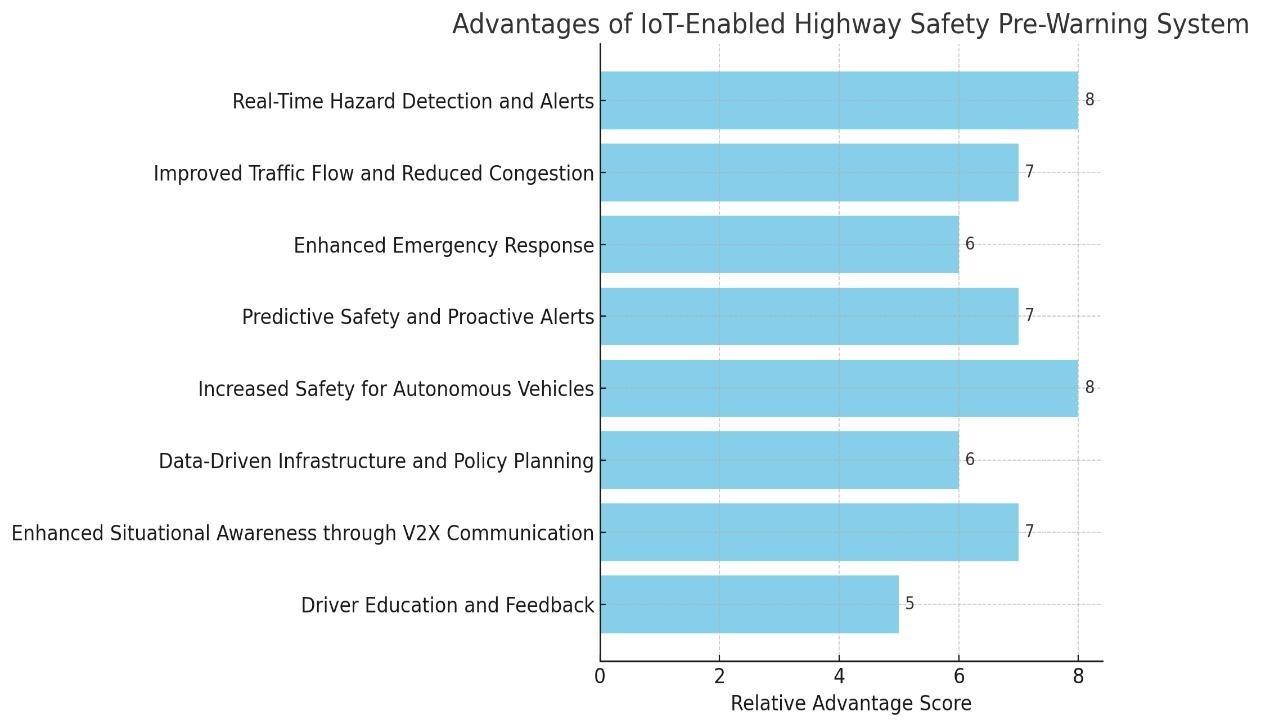
- Real-Time Hazard Detection and Alerts: Provides immediate warnings to drivers about potential hazards such as accidents, obstacles, or adverse weather, improving reaction times and reducing accident risks.
- Improved Traffic Flow and Reduced Congestion: Real-time monitoring and adaptive rerouting help manage traffic density, prevent bottlenecks, and maintain smoother traffic flow on highways.
- Enhanced Emergency Response: Automated alerts to emergency services ensure faster incident reporting and quicker response times, potentially reducing the severity of accident outcomes.
- Predictive Safety and Proactive Alerts: Predictive analytics anticipate hazards before they fully develop, enabling proactive driver warnings and reducing the chance of collisions.
- Increased Safety for Autonomous Vehicles: Supports autonomous driving by providing real-time data on road conditions, enabling AVs to respond proactively to sudden traffic changes and improve overall road safety.
- Data-Driven Infrastructure and Policy Planning: Provides valuable data on traffic patterns, accident hotspots, and road conditions, helping policymakers make informed decisions about infrastructure improvements and traffic regulations.
- Enhanced Situational Awareness through V2X Communication: Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication allows vehicles and infrastructure to share data, increasing situational awareness and allowing drivers to anticipate unseen hazards.
- Driver Education and Feedback: Real-time feedback on driving behaviour, along with insights from hazardous areas, promotes safer driving habits and increased awareness among drivers.
V. CHALLENGES AND LIMITATIONS
A. Connectivity Issues
- Limited Coverage in Remote Areas: IoT systems rely on constant communication between devices, but remote or rural highway areas may lack reliale cellular or Wi-Fi networks, affecting the system’s performance.
- Signal Interference: Weather conditions, geographic terrain, and infrastructure like tunnels or bridges can disrupt communication, leading to gaps in data transmission.
B. Scalability Concerns
- Integration with Existing Infrastructure: IoT-enabled systems need to be integrated with current road infrastructure, which might be outdated or incompatible with modern technologies.
C. Data Overload and Processing
- High Volume of Data: IoT systems generate vast amounts of data, which can be challenging to manage and analyze in real-time. Filtering relevant information from this data is a significant challenge.
- Latency: Delays in data processing can lead to slower response times, which is critical for safety systems that need to act immediately in case of accidents or hazardous conditions.
D. Cybersecurity and Privacy
- Vulnerabilities to Hacking: IoT systems are often vulnerable to cyberattacks, which could compromise safety features by interfering with the warning system, causing incorrect alerts or failures.
E. Power and Energy Consumption
- Sustainability of IoT Devices: Many IoT devices used in highway safety systems require continuous power, and maintaining power supply in remote locations or using battery-powered devices can be difficult and costly.
F. Cost of Implementation
- High Initial Investment: Implementing an IoT-enabled safety system requires a significant initial investment in sensors, infrastructure, and technology development, which may be a financial burden for governments and organizations.
G. Sensor Accuracy and Reliability
- Sensor Failure: Sensors may malfunction or become inaccurate over time due to environmental factors like dirt, weather, or physical damage, leading to false warnings or missed alerts.
- Environmental Factors: Extreme weather conditions (e.g., fog, rain, snow) can affect the reliability of sensors and cameras, reducing the system’s ability to detect potential hazards.
H. User Adoption and Trust
- Driver Reluctance: Drivers might not trust the IoT-enabled warning systems, either due to unfamiliarity with the technology or concerns about its accuracy and reliability.
- Dependence on Technology: Over-reliance on automated safety systems may lead to reduced vigilance from drivers, which could increase risk in case the system fails or gives false alarms.
I. Legal and Regulatory Issues
- Standards and Compliance: There may be a lack of uniform standards for the installation and operation of IoT-enabled systems across regions, which can complicate widespread implementation.
- Liability Concerns: In the event of a system failure or inaccurate warning, determining legal liability could be complex, as it involves multiple stakeholders (government bodies, private companies, and technology providers).
J. Environmental Impact
- E-Waste: The widespread use of IoT devices can contribute to electronic waste (e-waste), which may have long-term environmental impacts if not managed properly.
- Resource Consumption: The production and operation of IoT devices may contribute to the consumption of raw materials and energy, raising concerns about sustainability.
VI. FUTURE PROSPECT AND TRENDS
A. 5G and Advanced Connectivity
- Enhanced Communication Speed and Reliability: The deployment of 5G networks will significantly improve the speed and reliability of communication between IoT devices, allowing for faster data transmission and real-time alerts. This will reduce latency, a critical factor in safety systems where immediate response is necessary.
- Edge Computing Integration: With 5G's capabilities, edge computing can be further implemented in highway safety systems. Processing data at the source (near the IoT devices) will reduce the burden on central servers, enabling quicker response times and less reliance on centralized cloud systems.
B. AI and Machine Learning for Smart Data Processing
- Predictive Analytics: Machine learning algorithms will enhance the ability to predict accidents or dangerous situations before they happen by analysing historical and real-time traffic data, weather conditions, and vehicle behaviour. AI can enable more accurate hazard identification and reduce false alarms.
C. Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication
- Connected Vehicles: The future of IoT-enabled highway safety will heavily rely on V2X communication, where vehicles communicate not only with each other but also with infrastructure (V2I), pedestrians (V2P), and networks (V2N). This communication will allow vehicles to receive real-time warnings and take preemptive actions to avoid accidents.
D. Smart Road Infrastructure
- Smart Highways: Future highways will become smarter, equipped with IoT sensors embedded in the road itself. These smart roads will detect traffic conditions, environmental factors (e.g., temperature, fog, ice), and vehicle performance in real-time. They can adjust road signs, activate speed limits, or even change traffic lanes in response to conditions.
E. Advanced Data Analytics and Cloud Computing
- Big Data Analytics: As IoT systems generate large amounts of data, advanced analytics powered by cloud computing will be essential for analysing trends, detecting anomalies, and making predictions about traffic behaviour and safety risks.
F. Blockchain for Security and Transparency
- Enhanced Security: Blockchain technology could play a key role in securing data exchanged between IoT devices in highway safety systems. By providing an immutable record of transactions, it would prevent tampering and ensure that safety-critical data, such as warning signals or vehicle status, remains accurate and trustworthy.
G. Energy-Efficient and Sustainable IoT Devices
- Energy Harvesting: Future IoT systems may incorporate energy harvesting technologies (e.g., solar, vibration-based, or thermoelectric generators) to power roadside sensors and devices. This would reduce the need for battery replacements and help make these systems more sustainable in the long run.
H. Enhanced User Experience and Adoption
- Driver Interaction with IoT Systems: Future IoT-enabled systems may focus on improving the user interface between drivers and the safety pre-warning systems. For example, augmented reality (AR) can be used in vehicle dashboards to display warnings and information about road conditions in real-time..
I. Global Standardization and Policy Development
- Standardized Protocols: As IoT-based highway safety systems evolve, there will be a greater push for global standards in communication protocols, data formats, and safety requirements. This will ensure interoperability across devices, regions, and countries.
Conclusion
The integration of IoT-enabled highway safety pre-warning systems presents a transformative opportunity to enhance road safety, mitigate accidents, and optimize traffic management. Through the use of interconnected devices, sensors, and real-time data analytics, these systems can provide timely warnings to drivers about potential hazards, weather conditions, traffic congestion, and accidents, significantly reducing the risk of collisions and improving overall road safety. However, the widespread implementation of such systems comes with several challenges, including issues related to connectivity, data overload, cybersecurity, and the cost of deployment. Addressing these obstacles requires advancements in 5G connectivity, edge computing, AI-based data processing, and robust cybersecurity frameworks. Moreover, ensuring the interoperability of these systems with existing road infrastructure and the increasing presence of autonomous vehicles will be crucial for their successful integration.
References
[1] B. S. S. R. Anjaneyulu, et al. (2019). \"IoT-Based Traffic Management and Safety System for Smart Highways.\" International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology, 8(5), 3194-3200. This paper discusses the use of IoT devices for traffic management and road safety, providing a foundation for IoT applications in smart highway systems. [2] G. S. R. R. Kumar, et al. (2017). \"IoT-based Intelligent Transportation System for Highway Safety.\" International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science, 8(7), 1326-1330. This article explores how IoT sensors and systems can improve safety on highways by monitoring traffic conditions and providing real-time alerts. [3] M. H. Rahmani, et al. (2016). \"Smart IoT-Enabled Traffic Management System for Road Safety.\" IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 3(4), 373-379. o This journal paper presents a comprehensive analysis of Iot-based traffic management systems that can improve road safety through dynamic warning systems. [4] A. Ghosh, et al. (2019). \"Real-time IoT-enabled Traffic Accident Detection and Warning System for Smart Highways.\" Procedia Computer Science, 152, 56-63. [5] Focuses on a real-time accident detection and warning system using IoT technology, discussing both technical and safety aspects. [6] V. Shinde, et al. (2020). \"IoT-based Pre-Accident Warning System for Smart Cities.\" International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research, 9(4), 266-272. [7] Analyses a smart pre-warning system that uses IoT to predict and warn drivers about possible accidents, based on traffic data and environmental factors. Conference Papers [8] J. S. Lee, et al. (2020). \"IoT-Based Highway Safety Pre-Warning System for Autonomous Vehicles.\" Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Smart Sensors and Systems (ICSSS), 1-5. o Discusses how IoT-based systems can integrate with autonomous vehicles to enhance safety on highways, with an emphasis on pre-warning mechanisms. [9] M. B. S. Mohd, et al. (2018). \"Implementation of IoT for Road Safety Monitoring and Warning System in Highway Traffic.\" IEEE International Conference on Robotics, Automation and Mechatronics (RAM), 1-6. o This paper addresses the deployment of IoT-based systems for monitoring road conditions and issuing warnings to prevent accidents on highways. Books [1] B. Siciliano, et al. (2016). Springer Handbook of Robotics. Springer. Although primarily focused on robotics, this handbook contains chapters that address IoT technologies and their integration into transportation safety systems. [2] A. Zanella, et al. (2014). Internet of Things: A Hands-On Approach. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform. o This book provides an overview of IoT technologies and their application to various fields, including transportation safety. Reports and White Papers [1] ITU (International Telecommunication Union). (2020). \"Smart Road Safety: Leveraging IoT for Safer Highways.\" ITU’s report explores the role of IoT in improving road safety and provides an overview of existing and future IoT-based highway safety systems. [2] IEEE Smart Cities Initiative. (2021). \"Smart City Solutions for Safe and Sustainable Transportation.\" This white paper discusses how IoT systems contribute to safety and sustainability in smart cities, with a section dedicated to highway safety. Web Resources [1] Gartner Research. (2023). \"The Future of IoT in Transportation: Advancing Safety with Smart Systems.\" Provides insights into how IoT is shaping transportation systems, particularly focusing on safety and traffic management technologies. [2] The European Commission. (2022). \"IoT Solutions for Traffic Management and Safety in the EU.\" A policy document discussing the EU’s approach to using IoT to enhance highway safety and address challenges in traffic management.
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Soumya Singh, Shalini Maurya, Samta Kumari, Dr. Sureshwati , Dr. Shivani Dubey. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET65824
Publish Date : 2024-12-09
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

