Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
IOT: Smart Home for Aged
Authors: V. Venkata Ramanjaneylu, B. Vaishnavi, B. Aravind , Ch. Manideep
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.65766
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
In the rapidly advancing digital age, the elderly population often faces challenges adapting to modern smart home technologies, which can limit their independence and safety. These challenges are even more pronounced for individuals with sensory impairments, such as those who are deaf or hard of hearing. To address these issues, this project proposes an IoT-Enabled Smart Home System tailored for aged individuals, integrating innovative solutions that enhance accessibility, convenience, and safety. The system leverages Internet of Things (IoT) technology to create a connected ecosystem of devices that automate daily tasks and provide personalized assistance. Key features include a smart doorbell system that replaces traditional sound-based alerts with alternative sensory notifications like vibrations or light signals, ensuring accessibility for hearing-impaired users. Additionally, the system integrates health monitoring sensors, automated lighting, and cloud-based connectivity to enable real-time remote management by caregivers or family members. By using a cloud-based control network, IoT devices, and user-friendly interfaces, the smart home enhances the quality of life for elderly users by improving safety, promoting independence, and reducing caregiver burden. This innovative approach demonstrates the potential of IoT to transform traditional homes into inclusive environments that cater specifically to the needs of the aging population, offering a scalable and impactful solution for modern smart living.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
As the global population ages, there is an increasing need to create environments that cater to the unique needs of elderly individuals, particularly those with physical and sensory impairments. Simple tasks, such as managing household appliances, recognizing visitors, or responding to alerts, can become challenging for the elderly, especially for those with hearing or vision difficulties. The rapid advancements in technology offer an opportunity to bridge these gaps and enhance the quality of life for seniors by creating smart, connected living spaces. The IoT-Enabled Smart Home for the Aged project aims to address these challenges by integrating Internet of Things (IoT) technology into the homes of elderly individuals. This smart home system is designed to provide enhanced safety, convenience, and accessibility, promoting independence and reducing the reliance on caregivers. By automating everyday tasks and providing real-time monitoring and alerts, the system ensures that elderly individuals can live more comfortably and securely in their own homes. One of the key features of this system is its ability to provide notifications to hearing-impaired users through alternative sensory methods, such as vibrating wristbands or visual signals, replacing traditional sound-based alerts like doorbells. This innovative solution ensures that elderly individuals, regardless of their sensory limitations, can stay informed about visitors and emergencies. In addition, the system integrates health monitoring devices, smart appliances, and remote management capabilities via cloud-based platforms, enabling caregivers and family members to stay connected and respond promptly to any concerns. The objective of this project is to demonstrate the potential of IoT technology in creating a smart home environment that caters specifically to the needs of aged individuals, allowing them to live more independently and safely. By combining cutting-edge technology with thoughtful design, this IoT smart home system provides a holistic solution that addresses the accessibility, health, safety, and social engagement challenges faced by the elderly.
II. CHALLENGES FACED BEFORE
Before the development of the IoT-Enabled Smart Home System for elderly individuals, several significant challenges existed in ensuring the safety, comfort, and independence of aged individuals, particularly those with sensory impairments or mobility limitations. These challenges included:
A. Difficulty in Adapting to Modern Technology
- Technological Gaps: Many elderly individuals face challenges in adapting to advanced technologies due to a lack of familiarity with modern gadgets, complicated interfaces, or fear of technology. This makes it difficult for them to use common smart home devices or even control basic household appliances.
- Complex User Interfaces: Existing smart home devices often have complex user interfaces that are not designed with elderly users in mind. This complexity can cause frustration and hinder adoption among seniors.
B. Hearing Impairments
- Traditional Sound-Based Alerts: Many home automation systems rely on sound-based alerts (such as doorbells or alarms), which are ineffective for individuals with hearing impairments. Elderly users who are deaf or hard of hearing might miss important notifications about visitors, emergencies, or security alerts, compromising their safety and comfort.
- Lack of Alternative Sensory Alerts: The absence of alternative methods (such as vibrations, light signals, or visual notifications) to replace sound-based alerts further isolates individuals with hearing impairments.
C. Safety and Security Concerns
- Home Security: Seniors, especially those living alone, are more vulnerable to security threats. Traditional security systems often require physical interaction, such as turning on alarms or locking doors, which may not be feasible for elderly individuals with mobility or cognitive impairments.
- Emergency Situations: In the event of a fall, health emergency, or fire, elderly individuals may not be able to react quickly enough or alert others. Lack of real-time monitoring systems or emergency response systems exacerbates these risks.
D. Limited Mobility and Physical Constraints
- Difficulty in Managing Household Appliances: Elderly individuals with limited mobility may struggle to perform basic tasks such as turning on lights, adjusting thermostats, or operating home appliances. This can lead to feelings of dependence on caregivers or family members.
- Access to Controls: Reaching and operating switches, door handles, or appliance buttons may be physically challenging for seniors with mobility issues or arthritis.
E. Health Monitoring Challenges
- Lack of Continuous Health Monitoring: Monitoring the health status of elderly individuals, such as heart rate, blood pressure, or oxygen levels, is often overlooked in traditional home setups. This lack of real-time health data can delay medical intervention in case of an emergency.
- Absence of Remote Monitoring for Caregivers: Family members or caregivers may not have immediate access to health or activity data of elderly individuals, making it difficult to respond to changes in health or address emergencies promptly.
F. Social Isolation and Engagement
- Reduced Social Interaction: Elderly individuals, especially those living alone, often experience social isolation, leading to mental health issues like depression and anxiety. The absence of easy communication tools further alienates them from family and friends.
- Limited Entertainment and Engagement: Access to entertainment options, such as watching TV, listening to music, or video calling loved ones, may be hindered by complicated interfaces or lack of integration between devices.
G. Lack of Automation and Energy Efficiency
- Manual Operation of Household Systems: Without automation, elderly individuals must manually control lighting, temperature, and other household devices, which can be physically taxing and inefficient.
- Energy Wastage: Many homes lack energy-efficient systems, and elderly users may forget to turn off appliances or lights, leading to unnecessary energy consumption and higher costs.
H. Dependency on Caregivers
- High Reliance on Others: Elderly individuals often rely heavily on family members or professional caregivers for basic tasks, such as turning on appliances, managing medication schedules, or ensuring safety. This dependency can be a source of stress and reduce their sense of independence.
- Limited Remote Assistance: Traditional systems do not allow caregivers to remotely monitor or assist elderly individuals, requiring them to be physically present to provide help.
These challenges highlighted the need for a comprehensive solution that could address accessibility, safety, health monitoring, and communication issues for the elderly. The IoT-Enabled Smart Home System was developed to overcome these limitations and provide a more independent, secure, and user-friendly living environment for aged individuals.
III. RESEARCH APPROACH
The development of the IoT-Enabled Smart Home System for elderly individuals was driven by a structured research approach to ensure that the solution effectively addresses the unique needs of this demographic, particularly those with mobility and sensory impairments. The research methodology was divided into several key phases:
A. Problem Identification and Needs Analysis
This initial phase focused on understanding the specific challenges faced by elderly individuals in traditional home environments. The approach included:
- Literature Review: An in-depth review of existing studies on IoT applications in elderly care, smart home technologies, and accessibility features. This helped to identify gaps in current solutions and understand the specific requirements of the elderly population.
- User Surveys and Interviews: Conducted surveys and interviews with elderly individuals and caregivers to gather insights into their daily challenges and expectations from smart home technologies. The feedback focused on issues like hearing impairments, mobility limitations, and security concerns.
- Stakeholder Collaboration: Engaged with healthcare professionals, caregivers, and family members to understand the essential features needed to support elderly independence and safety at home.
B. Conceptualization and System Design
Based on the research findings, a conceptual framework for the IoT-enabled smart home was developed:
- Designing for Accessibility: Focused on ensuring that the system was easy to use, especially for elderly individuals with limited technological knowledge. The design incorporated large icons, simplified interfaces, and alternative sensory notifications (vibrations, light signals) to cater to hearing-impaired users.
- Smart Device Integration: Selected appropriate IoT devices (sensors, actuators, wearable devices) and platforms (e.g., cloud computing, mobile applications) that could seamlessly integrate into the system.
- Prototyping: Developed initial system prototypes that incorporated essential components such as smart doorbells, health monitoring devices, and remote control capabilities for caregivers. These prototypes were iteratively tested with potential users to refine the design and functionality.
C. Technological Feasibility and Selection
To implement the conceptual framework, the research focused on evaluating various technological solutions:
- IoT Platform Selection: Evaluated different IoT platforms, such as MQTT, Zigbee, and Wi- Fi, to ensure seamless communication between devices. Cloud services (e.g., AWS IoT, Firebase) were considered for remote monitoring and data storage.
- Sensor and Actuator Evaluation: Identified and tested sensors (e.g., motion sensors, health monitors) and actuators (e.g., smart locks, light systems) to ensure they met the system's requirements for accuracy, reliability, and ease of integration.
- Cloud-Based Control Network: Assessed cloud computing options to facilitate data processing, storage, and remote access for caregivers and family members.
D. Development and Integration
The system was developed using an agile methodology, allowing for iterative design and testing:
- Hardware and Software Integration: Integrated various hardware components (sensors, smart devices) with software systems (mobile apps, cloud platforms) to create a cohesive and functional system.
- Testing with Elderly Users: Conducted extensive usability testing with elderly individuals to ensure that the system was intuitive, easy to use, and effective in meeting their needs. Feedback from these tests led to the refinement of the user interface and alert systems.
- Real-Time Data and Emergency Response: Implemented real-time monitoring and alert systems, including fall detection and health monitoring, ensuring that caregivers could receive notifications promptly in case of any abnormalities.
E. Evaluation and Performance Testing
To assess the system's effectiveness, the following evaluations were conducted:
- Functional Testing: Ensured that each component (e.g., health monitors, smart doorbells, lighting control) performed as expected, including testing the accuracy of health data collection and the reliability of notifications.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Engaged elderly users in real-world scenarios to evaluate the usability and responsiveness of the system. This phase included testing the system’s accessibility features (vibrating alerts, voice control) for those with sensory impairments.
- Performance Metrics: Measured the system’s response time, reliability, and overall efficiency, ensuring that it could handle multiple devices and provide timely notifications without delays.
F. Impact Assessment and Feedback Loop
In this final phase, the system’s impact on the elderly users' daily lives was assessed:
- User Feedback and Iterative Improvements: Collected ongoing feedback from elderly users, caregivers, and family members to understand their experience with the system and identify areas for improvement.
- Health and Safety Benefits: Analyzed the effectiveness of health monitoring features in detecting anomalies and preventing medical emergencies, as well as evaluating how the system contributed to improved safety and independence.
- Scalability and Future Enhancements: Explored the potential for future scalability by integrating additional features such as AI-driven health predictions, smart mobility aids, and more advanced energy efficiency systems.
The research approach ensured that the IoT-Enabled Smart Home System was not only technically feasible but also tailored to the real-world needs of elderly individuals, promoting independence, safety, and quality of life. By combining user-centered design with cutting-edge IoT technologies, this approach created a holistic and effective solution for aging in place.
IV. FEATURE EXTRACTION
The IoT-Enabled Smart Home System for elderly individuals integrates various technologies to enhance accessibility, safety, and independence. The features extracted during the development of the system were carefully selected to address the unique needs of elderly users, especially those with sensory impairments, limited mobility, and other age-related challenges. The features can be categorized into several key areas: accessibility, safety, automation, health monitoring, and communication.
A. Accessibility Features
These features ensure that elderly individuals, including those with hearing or mobility impairments, can interact with the system easily and effectively:
- Alternative Notification Methods: The system replaces traditional sound-based alerts (e.g., doorbells, alarms) with alternative sensory notifications like vibrating wristbands or visual cues (flashing lights or screen notifications), ensuring users with hearing impairments are aware of events.
- Simplified User Interface: A user-friendly mobile app interface with large icons, clear text, and intuitive navigation makes it easy for elderly users to operate smart devices, even if they are unfamiliar with technology.
- Voice-Control Integration: Voice assistants (such as Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant) allow elderly users to control devices (lights, fans, door locks) using simple voice commands, making it accessible for users with limited mobility.
B. Safety and Security Features
The system includes features designed to enhance the safety and security of elderly individuals, especially those living alone:
- Smart Doorbell with Vibrating Alert: A smart doorbell integrated with cameras and motion sensors sends vibrating alerts to a wristband or smart wearable, ensuring that users are notified of visitors, even if they cannot hear the doorbell.
- Fall Detection Sensors: Fall detection sensors integrated with wearable devices or installed around the home monitor the user’s movement patterns. If a fall is detected, the system immediately sends an alert to caregivers or family members.
- Emergency Response System: The system includes an emergency button or voice-activated commands to instantly notify caregivers or emergency services in case of health emergencies or accidents.
- Smart Locks and Surveillance: Smart locks and motion detectors provide security by allowing users to remotely control door access and monitor activity in and around the house through connected cameras.
- Gas and Smoke Detection: Smoke and gas detectors connected to the IoT network can automatically notify users and caregivers of hazardous conditions, triggering emergency alerts and activating ventilation systems if necessary.
C. Health Monitoring Features
The system incorporates various devices that continuously monitor the health and well-being of elderly individuals:
- Wearable Health Sensors: Devices like smartwatches or health bands monitor vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels, sending real-time data to the cloud for tracking and analysis.
- Health Anomaly Alerts: The system sends automatic alerts to caregivers or healthcare providers if abnormal health conditions (e.g., elevated heart rate, low oxygen levels) are detected.
- Medication Reminders: The system can send reminders for medication intake, ensuring that elderly users adhere to their prescribed schedules.
- Remote Health Monitoring: Family members or caregivers can access real-time health data through the cloud, ensuring that the elderly individual's health is closely monitored even if they are not physically present.
D. Home Automation Features
To simplify daily tasks and enhance the comfort of elderly individuals, the system includes home automation features:
- Automated Lighting: Motion sensors and ambient light sensors automatically control lighting, ensuring that lights are turned on when movement is detected or adjusted based on the time of day or ambient light levels.
- Temperature Control: Smart thermostats adjust home temperature based on user preferences or environmental conditions, providing comfort without manual intervention.
- Voice-Activated Appliance Control: Users can control various household appliances (such as fans, lights, or air conditioning) using voice commands or through the mobile app for convenience.
- Automated Energy Management: The system optimizes energy use by automatically turning off unused appliances and adjusting the temperature based on user activity, promoting energy efficiency and reducing costs.
E. Communication and Social Engagement Features
The system promotes communication and social engagement, combating isolation and promoting mental well-being:
- Video Calling Integration: The system includes video calling devices that allow elderly users to stay in touch with family members and friends. Automated calls can be initiated when family members are available, reducing feelings of loneliness.
- Social Interaction Reminders: The system can provide reminders for social activities or prompt users to engage in communication with loved ones, promoting mental and emotional well-being.
- Entertainment Access: Smart TVs or connected devices provide easy access to entertainment, such as streaming services, music, and video content, ensuring that the elderly can stay mentally engaged and entertained.
F. Remote Monitoring and Control Features
Caregivers and family members can remotely monitor and assist elderly individuals through these features:
- Cloud-Based Control: The system is connected to the cloud, allowing caregivers or family members to remotely control devices, monitor health data, and receive alerts about any unusual activity or emergencies.
- Mobile App for Caregivers: A dedicated mobile app for caregivers provides real-time access to health data, environmental conditions, and emergency alerts, enabling proactive care even from a distance.
- Activity Monitoring: The system tracks daily activities and sends updates to caregivers, helping them ensure that the elderly individual is safe, active, and following a regular routine.
G. Energy Efficiency and Environmental Control Features
The system promotes sustainability and environmental responsibility:
- Smart Energy Metering: The system includes smart energy meters that track and optimize the consumption of electricity, helping to reduce energy costs and ensure efficient power usage.
- Solar Energy Integration: In future iterations, the system could integrate with solar panels and battery storage systems to enable self-sustaining energy management, reducing dependency on external power sources and lowering costs.
H. Customization and Scalability Features
The system is flexible and adaptable to meet the individual needs of elderly users:
- Personalized Alerts and Preferences: Users can customize alert methods, the sensitivity of sensors, and other settings to match their unique needs, such as adjusting vibration intensity or changing notification methods.
- Scalable Design: The system’s modular design allows for easy expansion. Additional devices, such as more sensors or health monitors, can be added as needed, ensuring that the system evolves with the user’s changing requirements.
These features were extracted and integrated into the IoT-Enabled Smart Home System to create a comprehensive solution that enhances the safety, health, and comfort of elderly individuals while promoting independence and reducing reliance on caregivers. Each feature was designed with user- centered principles to ensure ease of use, accessibility, and long-term sustainability.
V. OUTPUT
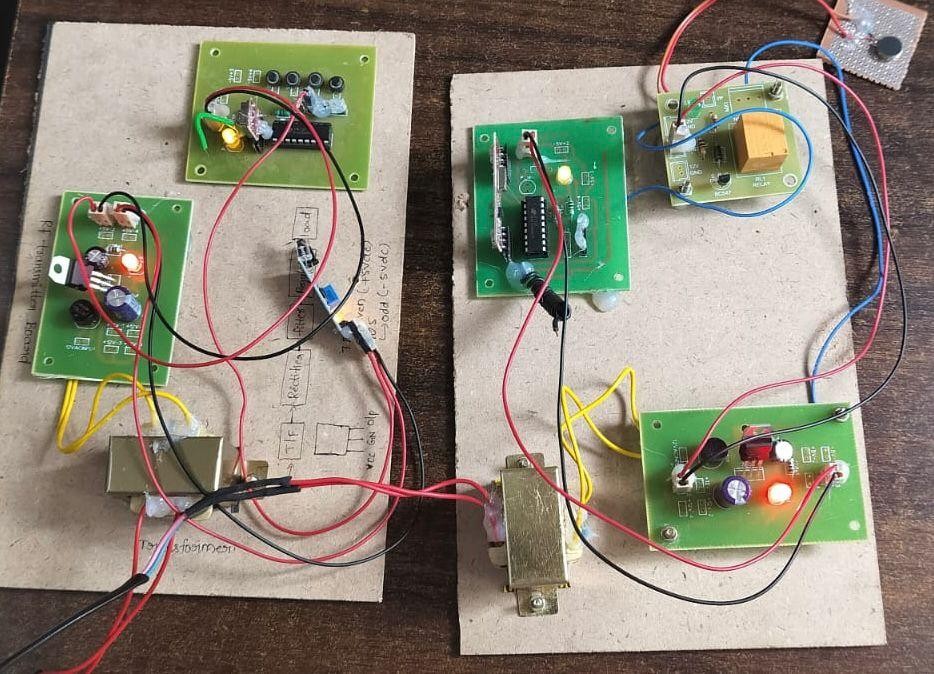
Fig : Prototype Circuitry for IoT-Enabled Smart Home System
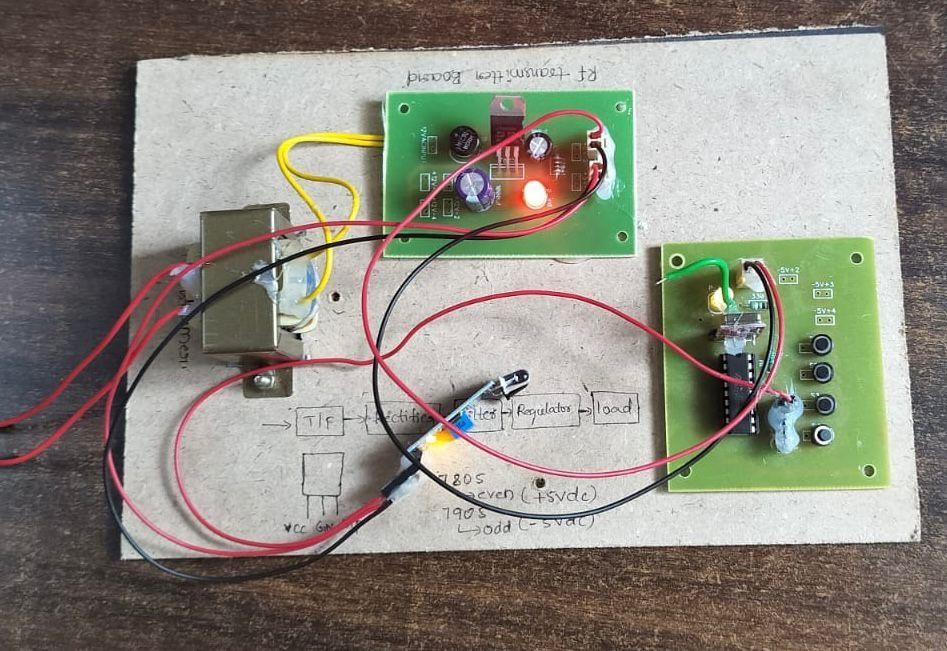
Fig : Prototype Circuitry for IoT-Enabled Smart Home System
VI. ADVANTAGES
The IoT-Enabled Smart Home System offers a range of benefits that enhance the safety, comfort, independence, and overall quality of life for elderly individuals. Some of the key advantages include:
A. Improved Safety and Security
- Real-Time Alerts: The system sends immediate notifications in the case of emergencies (such as falls, smoke detection, or gas leaks), allowing caregivers or emergency services to respond quickly.
- Smart Surveillance: Integrated motion detectors and smart cameras provide continuous monitoring of the home, ensuring that the elderly individual is safe and not at risk of intrusions or accidents.
- Remote Monitoring: Caregivers and family members can monitor the elderly individual remotely, providing peace of mind that assistance can be summoned whenever needed.
B. Enhanced Health Monitoring
- Continuous Health Tracking: Wearable devices track vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels, allowing healthcare providers and family members to monitor health status in real time.
- Fall Detection: Sensors can detect falls and instantly notify caregivers or emergency contacts, improving response times in critical situations.
- Medication Reminders: The system sends automated reminders for medication intake, helping elderly individuals stick to their prescribed routines and avoid forgetting critical medications.
C. Increased Independence
- Automated Home Control: Elderly individuals can control lighting, appliances, doors, and other devices through voice commands or mobile apps, making it easier to interact with the home environment without needing assistance.
- Mobility Assistance: Features like voice-activated appliances and smart door locks help elderly individuals manage their environment, reducing the need for help with routine tasks.
- Customizable Features: The system can be adjusted to suit individual preferences, such as changing the intensity of vibrations or notifications, making it adaptable to different users.
D. Improved Comfort
- Automated Environment Adjustments: The system automatically adjusts lighting, temperature, and other environmental factors based on the user’s preferences or time of day, enhancing comfort without manual effort.
- Energy Efficiency: The system helps conserve energy by turning off unused appliances or adjusting heating and cooling settings, lowering utility costs while maintaining comfort.
E. Social Engagement and Communication
- Video Calling: Integrated video calling allows elderly individuals to stay in touch with family members and friends, reducing social isolation.
- Social Reminders: The system can remind users to interact with loved ones or participate in social activities, promoting mental health and social engagement.
- Entertainment Access: Elderly users can easily access entertainment content (e.g., music, videos) through the system, keeping them mentally engaged and entertained.
F. Scalability and Flexibility
- Modular Design: The system’s architecture allows for easy expansion, meaning new devices (such as additional sensors, health monitors, or appliances) can be added as needed, ensuring long-term viability.
- Adaptability: As the user’s needs evolve, the system can be modified with additional features or changes, providing lasting value over time.
G. Reduced Caregiver Burden
- Remote Assistance: Caregivers can monitor the elderly individual from a distance, reducing the need for constant physical visits while ensuring that any issues are promptly addressed.
- Automation of Routine Tasks: Routine tasks like turning on lights, adjusting thermostats, or monitoring health can be automated, reducing the workload for caregivers.
Conclusion
The IoT-Enabled Smart Home System represents a significant advancement in supporting elderly individuals to live more safely, comfortably, and independently in their own homes. By integrating smart technologies, the system offers enhanced safety through real-time monitoring and alerts, improves health tracking with wearable devices, and provides convenience through home automation. The ability to remotely monitor and manage the environment reduces caregiver burden while ensuring elderly individuals can maintain their autonomy and well-being. Additionally, the system\'s scalability and flexibility make it adaptable to the evolving needs of elderly users, while its energy efficiency and cost-saving features offer long-term sustainability. The system also fosters social engagement and mental well-being by facilitating communication and providing entertainment options. Ultimately, the IoT-Enabled Smart Home System not only addresses the challenges faced by elderly individuals but also opens up new possibilities for more personalized and proactive care. With further refinement and widespread adoption, this system can contribute to the creation of safer, more supportive environments for aging populations worldwide.
References
[1] ”Senior resource for aging in place”, 2011 [Online]. Available: http://www.seniorresource.com/ageinpl.htm [2] M. Hazas, J. Scott, and J. Krumm, ”Location-aware computing comes of age,” IEEE Computer, Vol. 37, No. 2, pp. 95-97, Feb. 2004. [3] M.D. Rodriguez, J. Favela, E.A. Martinez, and M.A. Munoz, ”Locationaware access to hospital information and services,” IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, Vol. 8, No. 4, pp. 448-455, Dec. 2004. [4] D. J. Cook, M. Schmitter-Edgecombe, and P. Dawadi, Analyzing ac- tivity behavior and movement in a naturalistic environment using smart home techniques, IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, vol. 19, no. 6, pp. 18821892, Nov 2015. [5] S. Helal, W. Mann, H. El-Zabadani, J. King, Y. Kaddoura, and E. Jansen, The gator tech smart house: a programmable pervasive space, Computer, vol. 38, no. 3, pp. 5060, March 2005. [6] Brumitt, Barry and Meyers, Brian and Krumm, John and Kern, Amanda and Shafer, Steven, EasyLiving: Technologies for Intelligent Environments, 2000, [Online], Available: https://www.microsoft.com/enus/research/publication/easyliving-technologies-intelligent- environments/ [7] A. Harter, A. Hopper, P. Steggles, A. Ward, and P.Webster, ”The anatomy of a context-aware application,” Proceedings of the 5th annual ACMIIEEE international conference on Mobile computing and networking, pp. 59-68, 1999. [8] K. N. Ha, K. C. Lee and S. Lee, ”Development of PIR sensor based indoor location detection system for smart home,” 2006 SICEICASE International Joint Conference, Busan, 2006, pp. 2162-2167. doi: 10.1109/SICE.2006.315642 pages 12-29, [9] Y. Li, M. Liu and W. Sheng, ”Indoor human tracking and state estimation by fusing environmental sensors and wearable sensors,” 2015 IEEE International Conference on Cyber Technology in Automation, Control, and Intelligent Systems (CYBER), Shenyang, 2015, pp. 1468-1473. doi: 10.1109/CYBER.2015.7288161
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 V. Venkata Ramanjaneylu, B. Vaishnavi, B. Aravind , Ch. Manideep. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET65766
Publish Date : 2024-12-05
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

