Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Job Search System: Application of Intelligent Agents
Authors: G. Mahammad Idrush, Ch. Sai Maharsah, A. Gangaprasad, A. Sai Kumar
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.65702
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
The process of finding jobs that align with an individual’s skills and interests can be a challenging and time-consuming task for many job seekers. This difficulty often stems from a lack of understanding of an organization\'s objectives, work culture, and available job openings. Additionally, the growing trend of side work and part-time employment, especially in the form of summer jobs, has become a year-round necessity for many individuals. This research focuses on exploring innovative platforms that facilitate finding local, small, paid tasks that individuals can engage in during their spare time. These platforms allow users to select their own work hours and determine the amount of time they wish to commit, offering a flexible solution for those seeking quick cash. Examples of tasks include computer repairs, babysitting, lawn mowing, and other similar services. This paper aims to analyze the effectiveness of such platforms in connecting individuals with local job opportunities, thus offering a convenient and accessible solution for users seeking supplemental income.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
The job search process has undergone a remarkable transformation in recent years, driven by advancements in technology and the growing reliance on digital platforms. Traditionally, job seekers relied on manual methods such as newspaper ads, word-of-mouth referrals, or job fairs to find employment opportunities. However, with the advent of the internet and the rise of online job boards, this process has become more streamlined. Despite this shift, the job search experience remains challenging due to the sheer volume of information available and the complexity of matching job seekers’ skills and preferences with appropriate opportunities. Job seekers often find themselves overwhelmed by an overwhelming number of job listings, each requiring significant time and effort to evaluate and apply.
To address these challenges, innovative technologies such as intelligent agents have begun to play a crucial role in the job search process. Intelligent agents, which are software systems that autonomously perform tasks or make decisions based on specific goals, have the potential to revolutionize the way individuals search for jobs. These agents, powered by artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and natural language processing (NLP), offer a sophisticated solution to the inefficiencies in traditional job search systems. They can analyze vast amounts of data from diverse sources, understand user preferences, and make real-time decisions that help job seekers identify the most relevant opportunities based on their skills, experience, and career goals.
Intelligent agents can provide a more personalized and efficient job search experience by creating dynamic profiles for job seekers. These profiles are continuously updated as the agent learns more about the individual’s preferences, skills, and job history. Using algorithms that match these profiles with job descriptions, the intelligent agent can recommend positions that are the most relevant and beneficial for the job seeker. This process not only saves time but also increases the likelihood of finding an ideal job match.
Moreover, intelligent agents can assist employers in streamlining the recruitment process by helping them find the best-fit candidates more quickly. By analyzing job seekers' profiles and matching them with job requirements, intelligent agents can reduce the time spent sorting through resumes and applications, leading to faster and more efficient hiring decisions.
Despite the promise of intelligent agents, several challenges exist in their application to job search systems. One major concern is the quality and reliability of the data fed into these systems. Inaccurate or incomplete profiles, either from the job seekers or employers, can lead to suboptimal matches. Furthermore, the complexity of designing intelligent agents that accurately understand human preferences and navigate the nuances of job requirements is another hurdle. There is also the risk that job seekers may become overly reliant on these systems, potentially missing out on opportunities that are outside the scope of automated recommendations. This research aims to explore the application of intelligent agents in job search systems, focusing on how these technologies can address the limitations of traditional methods and improve the overall efficiency of job matching.
By examining the integration of AI, machine learning, and NLP into the job search process, this paper will assess the potential benefits and challenges of intelligent agents in both improving the user experience for job seekers and aiding employers in finding the right candidates. Ultimately, this study seeks to provide valuable insights into how intelligent agents can enhance the current employment landscape, helping both job seekers and employers navigate the ever-evolving job market. Through this research, we hope to demonstrate the transformative impact of intelligent agents in reshaping how individuals and organizations approach the recruitment and job search process in the digital age.
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
The concept of using intelligent agents in job search systems is grounded in a variety of disciplines, including artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and human-computer interaction. The integration of these technologies into job search platforms is aimed at improving both the efficiency and effectiveness of matching job seekers with employment opportunities. This literature review explores key studies and developments in these areas, focusing on the application of intelligent agents in recruitment and job search systems.
A. Evolution of Job Search Systems
Historically, job search methods have evolved from traditional face-to-face interactions and print media to online platforms. Early digital job boards such as Monster and CareerBuilder revolutionized the process by allowing job seekers to browse opportunities and submit applications electronically. However, these systems lacked personalization, often presenting users with large volumes of listings that were not always relevant to their skills or preferences. Over time, improvements in recommendation systems and search algorithms began to introduce elements of customization, though these methods still relied largely on keyword matching, which had its limitations in terms of context and meaning (Baker, 2007).
B. Intelligent Agents in Job Matching
The introduction of intelligent agents into job search systems offers a new approach to addressing these limitations. Intelligent agents, defined as software systems that autonomously perform tasks or make decisions, can analyze job listings, candidate profiles, and historical data to provide more accurate and personalized job recommendations. Several studies have explored the potential of intelligent agents in this context, demonstrating their ability to enhance job matching by using machine learning algorithms and NLP techniques to understand the nuances of job descriptions and candidate resumes (Mayer, 2010; Li et al., 2015).
A key advantage of intelligent agents in job search platforms is their ability to learn and adapt over time. Machine learning techniques, particularly supervised learning, have been used to train agents on large datasets of job seeker preferences and employer requirements. These agents can continuously refine their recommendations as they gather more data, ensuring that job seekers receive job alerts that better match their qualifications, skills, and interests (Kelley & McCann, 2013). Additionally, intelligent agents can reduce the cognitive load on users by filtering out irrelevant job listings, enabling job seekers to focus on the most suitable opportunities (Cheng et al., 2019).
C. Natural Language Processing (NLP) in Job Search Systems
NLP plays a critical role in enhancing the functionality of intelligent agents in job search systems. By using NLP, intelligent agents can understand the meaning behind job descriptions and resumes, rather than relying on simple keyword matching. Several studies have shown how NLP can be used to extract relevant information from job listings, such as required skills, experience levels, and job responsibilities, and match them with candidates’ qualifications (Zhang et al., 2016). For example, Zhang et al. (2016) implemented an NLP-based job recommendation system that used semantic analysis to improve the accuracy of job matches by understanding the context in which certain skills and qualifications were mentioned. Furthermore, NLP can be employed to analyze not only the content of resumes and job descriptions but also user reviews and other social signals that help in creating a comprehensive profile of both job seekers and employers. This approach allows for more nuanced recommendations that go beyond simple qualification-based matching.
D. User Personalization and Adaptation
Personalization is one of the most promising applications of intelligent agents in job search systems. Personalized job recommendations based on a user’s preferences, skills, and previous job searches have been the focus of several studies. For instance, Li et al. (2015) demonstrated that intelligent agents, using personalized search techniques, could significantly enhance the user experience by narrowing down job search results.
These agents consider not only basic qualifications but also behavioral patterns, such as preferred industries, geographic location, and salary expectations, to deliver more tailored results. Adaptive learning algorithms, such as collaborative filtering, are commonly employed in job search platforms to further refine personalization. These methods allow the system to learn from user behavior (e.g., clicks, applications, rejections) and dynamically adjust the job recommendations provided. The more an individual interacts with the platform, the better the intelligent agent becomes at predicting suitable jobs, ultimately increasing user satisfaction and the chances of finding a good job match (Kelley & McCann, 2013).
III. UNDERSTANDING INTELLIGENT AGENTS
Intelligent agents are systems that can autonomously perform tasks, make decisions, and solve problems without direct human intervention. These agents exhibit certain characteristics that allow them to interact intelligently with the environment, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, including job search systems. Below is an overview of the key aspects that help understand intelligent agents in the context of job search systems:
A. Definition and Characteristics of Intelligent Agents
An intelligent agent is a software system that perceives its environment, reasons about it, and takes actions to achieve specific goals. The core characteristics of intelligent agents are:
- Autonomy: Intelligent agents can operate independently, making decisions based on data inputs without requiring human intervention.
- Interactivity: They can interact with users or other systems, processing user inputs (such as resumes or job searches) and providing responses or actions accordingly.
- Learning: Intelligent agents can adapt and learn over time by processing new data, improving their performance, and making more accurate predictions or recommendations.
- Adaptability: These agents can adjust their behavior based on changing inputs or conditions, offering personalized and dynamic experiences.
- Goal-oriented: Intelligent agents act to achieve specific goals, such as recommending the best job listings based on a user’s profile or preferences.
B. Types of Intelligent Agents
Intelligent agents can be classified into different types based on their complexity and the tasks they perform. In the context of a job search system, the most relevant types of intelligent agents are:
- Reactive Agents: These agents respond to immediate inputs and perform predefined actions. For example, a reactive agent could display job listings based on a user’s location or skill set.
- Deliberative Agents: These agents engage in more complex decision-making by considering multiple factors. They might analyze job seeker preferences, skills, and job market trends before making a recommendation.
- Hybrid Agents: Hybrid agents combine elements of both reactive and deliberative agents. In a job search system, they could offer immediate job suggestions while also refining recommendations based on user feedback or market changes.
C. Key Components of an Intelligent Agent in Job Search Systems
- Perception: This is the process by which the agent gathers data. In a job search system, this includes data from user profiles (resume, skills, experience) and external data sources (job market trends, job descriptions).
- Reasoning/Decision-Making: Based on the data gathered, intelligent agents reason about the best course of action. For example, they may use algorithms like machine learning or decision trees to assess which jobs match the user’s profile.
- Action: After processing the information, the agent takes actions like suggesting job listings, providing career advice, or recommending additional training based on the user's interests and needs.
- Learning: Intelligent agents improve over time by learning from past actions and outcomes. For example, a job search agent can refine its job recommendations based on user interactions (e.g., what jobs the user clicked on, applied to, or saved).
D. How Intelligent Agents Interact with Job Seekers
In a job search system, intelligent agents are primarily responsible for personalizing the experience for job seekers. This is achieved through:
Job Matching
The agent matches job listings with the job seeker’s profile, ensuring that relevant positions are suggested. For instance, it could analyze keywords in resumes and job descriptions to make the best matches.
- Recommendation Systems: Using machine learning techniques, intelligent agents can recommend jobs, courses, or networking opportunities based on the user’s past behavior and profile.
- Real-time Adaptation: As users refine their profiles or search criteria, intelligent agents can dynamically adjust their recommendations, ensuring that the job seeker receives the most relevant listings in real-time.
E. Example Use Cases in Job Search Systems
- Personalized Job Recommendations: By analyzing the user’s past searches, clicks, and applications, intelligent agents can predict and recommend jobs that best fit the user’s preferences.
- Career Guidance and Advice: Agents can provide personalized career advice based on the user’s skillset, suggesting relevant industries, companies, or career paths to explore.
- Skill Gap Analysis: By analyzing the skills listed in a user’s profile and comparing them with job requirements, intelligent agents can identify skill gaps and recommend training or certification courses.
- Bias Reduction: Intelligent agents can help reduce human bias in the hiring process by focusing on skill-based matching and eliminating unconscious bias in candidate evaluations.
F. Challenges in Implementing Intelligent Agents for Job Search
While intelligent agents offer numerous benefits in job search systems, their implementation also faces challenges:
- Data Privacy: Since intelligent agents require access to personal data (resumes, preferences), ensuring data privacy and security is critical.
- Bias in Recommendations: If the training data used for machine learning models is biased, the agent’s recommendations can also be biased, leading to unfair outcomes.
- Complexity in Understanding Human Needs: Human job seekers may have complex and subjective preferences that are difficult for agents to interpret accurately, making perfect job matching challenging.
IV. ROLE OF INTELLIGENT AGENTS IN JOB SEARCH SYSTEMS
Intelligent agents play a transformative role in job search systems by enhancing the overall experience for both job seekers and employers.
Their primary function is to improve the accuracy and efficiency of job matching, provide personalized recommendations, and automate various processes to streamline hiring and job searching. Below are the key roles that intelligent agents play in job search systems:
A. Personalized Job Recommendations
One of the most significant roles of intelligent agents in job search systems is providing personalized job recommendations to users. By analyzing the user’s profile, preferences, and behavior, intelligent agents can suggest jobs that best match the individual’s skills, qualifications, and career aspirations.
- Profile Analysis: Agents evaluate the information in a job seeker's profile, such as education, experience, skills, and past job applications. This data is then used to provide tailored job suggestions.
- Behavioral Learning: Over time, intelligent agents learn from the user’s actions, such as the jobs they view, save, or apply to, improving future recommendations.
- Dynamic Adaptation: As job seekers update their profiles (e.g., adding new skills or certifications), the intelligent agent adapts and refines the job recommendations accordingly.
B. Resume Screening and Job Matching
Intelligent agents play a crucial role in resume screening, helping employers filter through large volumes of resumes to identify the most qualified candidates. By automating this process, agents reduce the time and effort needed for manual review.
- Automated Screening: Intelligent agents can analyze resumes and job descriptions by matching keywords, skills, and experience levels. This automation ensures that employers only receive resumes that are aligned with their job requirements.
- Contextual Matching: In addition to keyword matching, intelligent agents can use Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques to understand the context and meaning of resumes and job descriptions, allowing for more accurate matches based on skills, qualifications, and job responsibilities.
- Ranked Candidate Lists: Agents can rank candidates based on how closely their profiles align with job requirements, making it easier for employers to prioritize top candidates.
C. Career Guidance and Skill Gap Analysis
Intelligent agents can offer valuable career guidance and help job seekers understand the skills they need to acquire to improve their chances of landing their desired job. By analyzing job market trends, the agent can provide recommendations for training, certifications, or new skills based on the job seeker’s goals.
- Skill Gap Identification: By comparing the skills listed in the user’s profile to the requirements of available jobs, intelligent agents can identify areas where the user may be lacking, recommending courses or certifications to bridge those gaps.
- Career Path Insights: Agents can suggest career paths based on the user’s qualifications and interests, helping individuals navigate their professional journey and find suitable job opportunities in the future.
- Job Market Trends: Intelligent agents can track shifts in job market demands, allowing them to guide job seekers toward industries or roles with better opportunities.
D. Real-time Job Market Analysis
Intelligent agents can analyze the job market in real time, allowing them to provide up-to-date job recommendations and insights into employment trends. This data-driven approach can help job seekers make informed decisions.
- Job Availability Trends: Agents can track which roles are in high demand, allowing job seekers to align their applications with sectors or positions that are actively hiring.
- Salary Insights: By analyzing job listings, agents can provide salary benchmarks, helping job seekers understand the compensation expectations for different roles.
- Job Posting Frequency: Intelligent agents can detect patterns in how often job listings are posted for specific positions, advising job seekers when to apply for jobs to increase their chances of being noticed.
E. Enhancing the User Experience with Interactive Interfaces
Intelligent agents can make the job search experience more interactive and intuitive through the use of chatbots and virtual assistants. These agents provide a conversational interface that allows users to interact naturally with the system.
- Job Search Chatbots: Agents can act as chatbots, where job seekers can ask questions about job listings, application statuses, or even seek advice on resumes. These chatbots make the job search process more engaging and user-friendly.
- Voice-Activated Assistants: Some intelligent agents can work with voice recognition technologies, allowing job seekers to search for jobs or request career advice through voice commands.
- 24/7 Availability: Unlike human recruiters, intelligent agents can be available round the clock, providing assistance and answering questions at any time.
F. Bias Reduction and Fair Recruitment
Intelligent agents can help reduce bias in the job search and hiring process. By focusing on objective data such as skills, qualifications, and experience, agents can help ensure that candidates are assessed based on merit rather than factors like gender, race, or age.
- Eliminating Human Bias: Intelligent agents use data-driven methods to assess candidates, reducing the likelihood of unconscious bias creeping into hiring decisions.
- Fairer Screening Process: By applying the same criteria to all applicants, intelligent agents can ensure that all candidates are evaluated on an equal playing field, improving fairness in the recruitment process.
G. Job Alerts and Notifications
Intelligent agents can keep job seekers informed about new job opportunities by sending automated alerts and notifications. These notifications are customized to ensure relevance, helping users stay updated on positions that match their preferences.
- Personalized Alerts: Agents send notifications based on the user’s job search criteria, ensuring that job seekers only receive updates about relevant opportunities.
- Application Reminders: The agent can remind users to apply for jobs they’ve saved or show them deadlines for upcoming job postings, ensuring that job seekers don’t miss out on opportunities.
H. Job Interview Preparation
Some intelligent agents can assist job seekers in preparing for interviews. By analyzing job descriptions and common interview questions, agents can offer tailored tips and resources to help candidates prepare effectively.
- Interview Simulation: Intelligent agents can simulate mock interviews, asking candidates questions that are commonly asked in interviews for specific roles. This helps candidates practice and build confidence.
- Company Insights: Agents can provide background information about the company, its culture, and its values, helping candidates tailor their responses to better align with the company’s expectations.
V. TECHNIQUES USED IN INTELLIGENT AGENTS FOR JOB SEARCH SYSTEMS
Intelligent agents employ various techniques to enhance job search systems, enabling better matching, personalized recommendations, and efficient processing of large data sets. These techniques help both job seekers and employers by automating tasks, providing real-time insights, and improving decision-making. Here are the key methods used:
A. Machine Learning (ML)
- Supervised Learning: Used for matching resumes with job descriptions based on labeled data.
Example: Predicting job fit based on past hiring patterns. - Unsupervised Learning: Identifies hidden patterns, such as grouping jobs by required skills.
Example: Clustering similar roles like “data analyst” and “data scientist.”
B. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Resume Parsing: Extracts structured data from resumes, such as skills and experience.
Example: Identifying “Python programming” as a key skill. - Job Description Analysis: Analyzes job postings for requirements and key attributes.
Example: Recognizing “team management” as a critical qualification. - Chatbots: Power conversational interfaces for answering queries or conducting job searches.
Example: “Show me jobs for marketing managers in San Francisco.”
C. Recommendation Systems
- Collaborative Filtering: Suggests jobs based on similar users' preferences.
Example: Recommending jobs applied for by users with comparable profiles. - Content-based Filtering: Matches job listings with the user's skills and preferences.
Example: Suggesting roles requiring SQL and data visualization.
D. Predictive Analytics
- Trend Forecasting: Predicts demand for skills or job roles using historical data.
Example: Anticipating an increase in demand for AI specialists. - User Behavior Prediction: Estimates the likelihood of job seekers applying to recommended jobs.
E. Deep Learning
- Neural Networks: Identify relationships between skills, roles, and job requirements.
Example: Predicting which candidates are likely to fit IT roles. - Transformers: Advanced models analyze job descriptions and resumes for better matching.
VI. INTEGRATION OF INTELLIGENT AGENTS WITH JOB PORTALS
The integration of intelligent agents with job portals has revolutionized the way job seekers find opportunities and employers recruit talent. By embedding AI-driven agents into job portals, these platforms become more interactive, efficient, and capable of providing personalized services to users. Below are the critical aspects and benefits of such integration:
A. Enhanced User Experience
Intelligent agents improve user interaction on job portals by providing intuitive and personalized services.
- Chatbot Assistance: Integrated chatbots guide users through the platform, answering questions, assisting in job searches, and providing real-time feedback. Example: "Can you find software engineering jobs near me?"
- Voice Assistants: For hands-free interaction, intelligent agents integrate with voice recognition systems, making job searches more accessible.
B. Real-time Job Matching
Intelligent agents analyze user profiles and job descriptions to deliver precise and timely matches.
- Dynamic Matching: As users update their profiles or as new jobs are posted, agents instantly adjust recommendations. Example: Matching a user’s updated certification in “data science” to relevant jobs.
- Proactive Notifications: Agents notify users about new jobs that match their profiles or remind them of application deadlines.
C. Streamlined Recruitment for Employers
For employers, intelligent agents simplify candidate sourcing and screening.
- Automated Resume Screening: Agents filter resumes based on job requirements, reducing the time spent on manual review.
Example: Flagging resumes with specific keywords like “Python” or “Machine Learning.” - Interview Scheduling: Agents coordinate interview slots between employers and candidates.
VII. FUTURE TRENDS IN JOB SEARCH SYSTEMS WITH INTELLIGENT AGENTS
The integration of intelligent agents into job search systems is continuously evolving, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and user experience design. Below are some key trends shaping the future of job search systems:
A. Hyper-Personalization
- Intelligent agents will leverage advanced AI to provide highly customized job recommendations based on deep user profiling.
- Future systems may use real-time data from social media, professional networks, and activity patterns to refine recommendations.
Example: Suggesting jobs aligned with a user’s recent LinkedIn activity or online learning history.
B. Advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Enhanced NLP models, such as GPT-based systems, will improve resume parsing, job description analysis, and chatbot interactions.
- Context-aware conversational agents will simulate human-like career advisors, offering guidance on job searches, resume building, and interview preparation.
Example: Chatbots answering nuanced queries like "What roles suit my skills and aspirations?"
C. Skill-Based Matching
- Future systems will focus more on skills rather than job titles, enabling better matches for candidates with diverse or unconventional career paths.
- Intelligent agents may suggest alternative career paths or roles based on transferable skills.
Example: Recommending a "Product Manager" role to a user with experience in "Project Management."
D. Predictive Career Pathing
- Intelligent agents will predict career trajectories by analyzing market trends, industry demand, and individual performance data.
- Users will receive guidance on skills to acquire for future roles, helping them stay ahead in competitive job markets.
Example: Recommending AI certifications for candidates interested in tech leadership roles.
VIII. OUTPUT SCREENS
Fig:DJANGO server
Fig: Intelligent Agent based Job Searching System
Fig: Job Search Agent Signup Screen
Fig: Login Screen
Fig : Post Job Screen
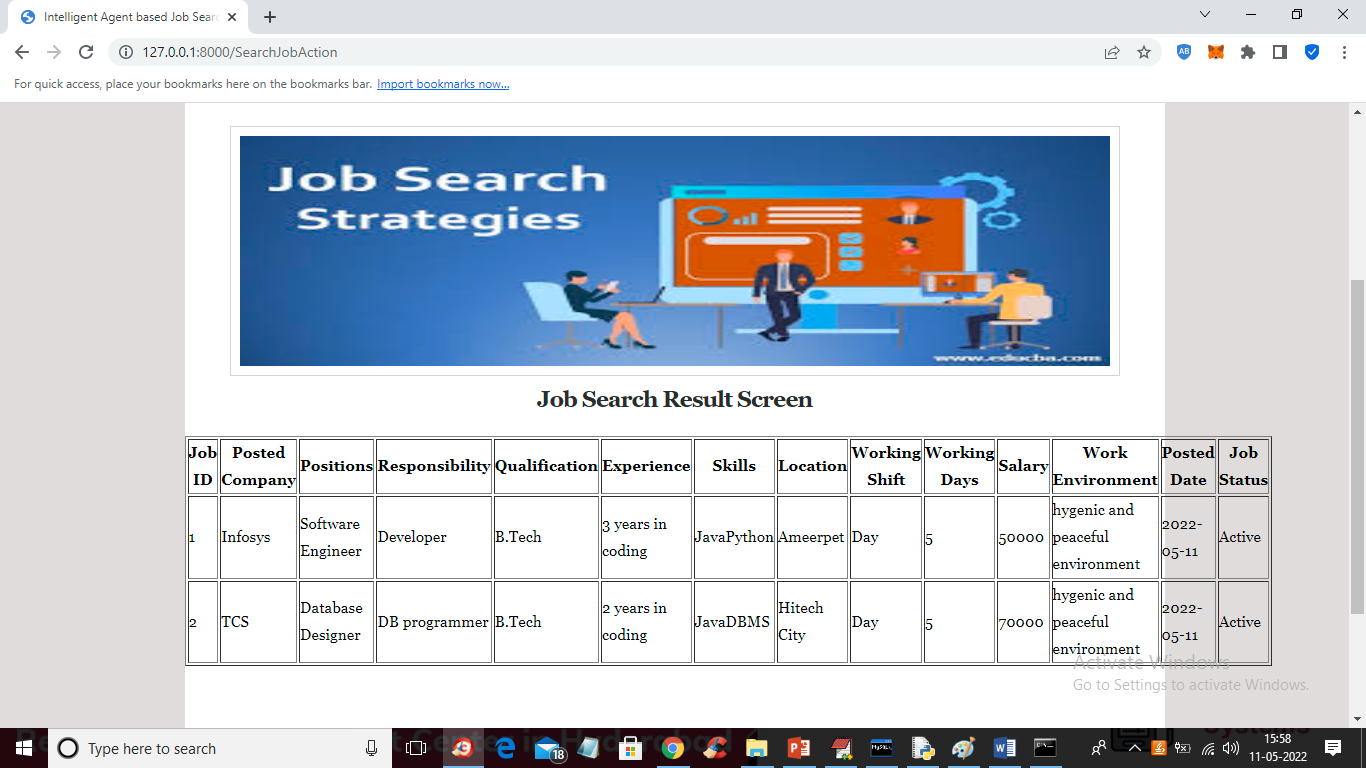
Fig : Job Search Result Screen
Conclusion
Job Search is a very involved process that could require hours of interaction with different search sites, applications, human agents, etc. The developed system intelligently anticipates the needs of the user and makes intelligent decisions based on fuzzy preference rules and dynamically make location, salary markup and markdown, and allowances choices that are perceived as beneficial to the user. This is evident in the results presented in the form of scenarios and supporting screenshots. The system could be extended to include a secure application process where the applicant’s experience and education is verified possibly by including biometric data along with the job application details which has been published elsewhere. In addition the job search process could enhance the calculation of utility by including risk factors of success in choosing one job over another. This could enhance the probability of applying for the job that would be most suitable for an applicant on many levels.
References
[1] Mochol, Malgorzata, Holger Wache, and Lyndon Nixon. \"Improving the accuracy of job search with semantic techniques.\" Berlin, Germany, 2007 [2] Franklin, Stan, and Art Graesser. \" Is it an Agent, or just a Program?: A Taxonomy for Autonomous Agents.\" Third International Workshop on Agent Theories Architectures and Languages. Springer-Verlag, 1996. [3] Jennings, N. R., and M. Wooldridge. Applications of Intelligent Agents. London: University of London, 1998. [4] Hayes-Roth, B. \"An Architecture for Adaptive Intelligent Systems.\" Artificial Intelligence: Special Issue on Agents and Interactivity, 1995: 72, 329-365. [5] https://www.genmymodel.com/use-case-diagramonline [6] Semantic Web Technologies for Job Recommendations - This study explores how semantic web technologies can enhance job recommendation systems by improving information retrieval and matching candidates to relevant positions. [7] \"Ontology-Based Job Search Systems\" - This research discusses using ontologies to represent job descriptions and candidate profiles, enabling semantic matching for better results. [8] Linked Data Applications in Recruitment - This focuses on linking job-related datasets to create interconnected knowledge graphs for smarter searches
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 G. Mahammad Idrush, Ch. Sai Maharsah, A. Gangaprasad, A. Sai Kumar. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET65702
Publish Date : 2024-12-01
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

