Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- References
- Copyright
Master Teachers as Instructional Leaders in Public Elementary Schools in the Division of Rizal
Authors: Dr. John Marco F. Quisquino
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2022.47974
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
The study aimed to determine the instructional leadership skills and competencies of Master teachers and its effect on professional growth of teachers in the Division of Rizal during the school year 2019-2020 base reference for policy enhancement. The study found out that in general, the master teachers are highly competent as regard to instructional skills and competencies in terms of instruction, research, coaching and mentoring, and observation and supervision. Also, in general, the teachers had a great extent on their professional growth in gaining new knowledge and information as regard to teaching techniques and methodologies that they could apply it in the teaching arena. There is a significant relationship between the level of instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers with respect to instruction, research, coaching and mentoring, and observation and supervision, and the extent of professional growth of teachers, since the computed p-value is less than 0.05 thus the null hypothesis is rejected. The findings show that the instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers with respect to instruction, research, coaching and mentoring, and observation and supervision are significantly correlated with the professional growth of teachers. It can be concluded that the instructional skills and competencies of master teachers are highly competent in terms of instruction, research, coaching and mentoring, and observation and supervision. Teachers have a great extent on their professional growth in accessing to and are participating in a variety of learning opportunities that addresses their needs and preferences. Further, master teacher’s instructional skills and competencies in terms of instruction, research, coaching and mentoring, and observation and supervision were significantly related to the professional growth of teachers
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
The pandemic has had a significant impact on the education sector and provided a much-needed impetus for digitization in the whole world. It has transformed the education system drastically and has brought a paradigm shift in teaching and learning methodologies forcing educational institutions across the globe to re-imagine traditional classroom learning and transition to an online mode of teaching to provide uninterrupted access to education and knowledge. Now more than ever, is instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teacher plays a big role to the teacher in coping with this New Normal. Instructional Leadership is generally defined as the management of curriculum and instruction by a school principal and with the help of master teachers. De Lima (2018) defined instructional leadership as the ability to involve colleagues collaboratively in mutual learning and development with the main purpose of improving teaching and learning. Thus, teacher plays a significant role in the classroom settings or even in the virtual environment so that learners can achieve the desired learning outcomes. As stated in DepEd Memorandum No. 50, Series 2020 also known as the DepEd Professional Development priorities for teachers and school leaders to wit: The professional development priorities shall support the realization of the department’s goal of continuous upskilling and reskilling of teachers and school leaders that will result in better learning outcomes. The policy clearly stated that teachers and school leaders need to attend seminars and trainings that could further enhance their capabilities and knowledge on the technological advancement and current trend of our digital society. Therefore, professional training process and professional development process is one of the important factors in the educators’ use of virtual classroom practices. If the teachers have sound professional background and professional knowledge, they can effectively use the various instructional practices in the virtual classroom. Moreso, the quality of education depends on the ability, hard work and dedication of the teacher. If a teacher fails to keep himself in touch with the rapid scientific and educational developments, then he would become inefficient and ineffective. There are factors for shaping the quality of teaching. Among them, teacher training and professional development program are the main factor affecting the teachers’ practices. Likewise, in terms of instructional materials, master teachers could assist their mentees to develop teaching aides and help them in the validation. Master teachers as an instructional leader find ways to help/assist their co-teachers in carrying out their duties and responsibilities in facilitating student learning through functional lesson plans of activities and appropriate, adequate, and updated instructional materials.
Indeed, instructional leaders must be aware of the strengths and weaknesses of their teachers and plan professional-development workshops based on the needs of the teachers. Leaders who have adhered to these practices in the past have had students who have achieved more than students who have had leaders who have not done so. These observations prompted and motivated the researcher to conduct this study and further determine the instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers and its effect to professional growth of teachers in the Division of Rizal and address the problem to attain quality education. The researcher believes that the findings of the study which is the policy enhancement will greatly help masters teachers in improving and upgrading their instructional leadership skills and competencies as well as the professional growth of teachers. The present study is anchored the concept and principles of Teacher Leadership Theory by York-Barr and Duke. This theory of action for teacher leadership has seven major components. The first three focused on the teacher leaders (their characteristics, type of leadership work they engaged in and the conditions that support their work) and represented the foundations upon which teacher leadership is possible. The next three (means of leadership influence, targets of leadership influence, and intermediary outcomes of teacher leadership) suggested the path by which teachers affect student learning. The seventh component, student learning completed their theory of action on teacher leadership. Based on the theory presented, a conceptual framework is designed to give direction and emphasis to the study. The conceptual model used in the study is the Coombs’ System Approach specifically the Input - Process – Output (IPO) model system analysis. The first frame refers to the input which consists of level of instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers as assessed by the respondents in terms of instruction, research, coaching and mentoring, and observation and supervision and the extent of professional growth of teachers. The second frame refers to the process which includes the preparation and validation of questionnaire checklist; administration and retrieval of questionnaire checklist and tabulation; qualitative and quantitative data analysis and interpretation of data and further analysis of the study.
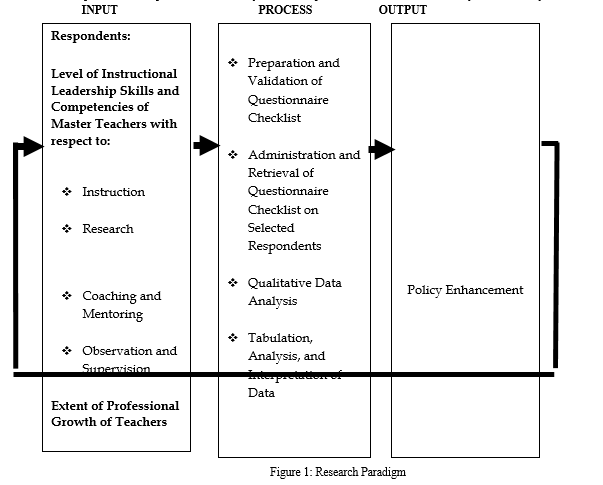
The third frame consists of the expected output of the study which is the enhancement of policy to improve the professional growth of teachers as well as the instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers. The three frames are connected by a straight line to indicate the relationship between the input, process, and output.
This study aimed to determine the instructional leadership skills and competencies of Master teachers and its effect on professional growth of teachers in the Division of Rizal during the school year 2019-2020 base reference for policy enhancement. Specifically, this study sought to answer the following sub – problems: 1) What is the level of instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers as assessed by the respondents in terms of instruction, research, coaching and mentoring, and observation and supervision? 2) What is the extent of professional growth of teachers as assessed by the respondents? 3) Is there a significant relationship between the extent of instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers and the extent of professional growth of teachers? 4) Based on the results, what policy enhancement may be developed?
This study tested the hypothesis states that there is no significant relationship between the level of instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers and the extent of professional growth of teachers.
This study is designed to benefit the following: School Heads. With the findings of the study, they would be provided with baseline information from which future directions could be based as regards managing their human resources. Master Teachers. This study provided information and knowledge that can be used by the master teachers in enhancing their instructional skills and competencies. Teachers. This study is also beneficial to the teachers for they would be given a research-based assessment of their belief, attitudes and behaviors have shaped and continuously shapes where they belong. Researchers. The future researchers will be benefiting from this study by providing them a material they can replicate in their own locale. The recommendations of this study will help them decide to conduct a similar study in the future.
The study aimed to determine the instructional leadership skills and competencies of Master teachers and its effect on professional growth of teachers in the Division of Rizal during the school year 2019-2020 base reference for policy enhancement. The respondents of the study were the master teachers from public elementary schools in the Division of Rizal. There were thirty-seven (37) out of 261 master teachers. The study used the Slovins Formula with 15% of margin of error in determining sample respondents out of the total population of the master teacher at selected public elementary schools in the Division of Rizal. Purposive sampling technique used in determining the respondents of the study.
In order for the intended readers to fully understand the paper, the research has given both the conceptual and operational definition of the terms used in this paper. 1) Competencies. This refers to the ability of master teachers to do something successfully and efficiently relevant to instruction. 2) Instructional Leadership Skills. This refers to the traits possessed by effective educational leaders to inspire action and optimism. 3) Master Teachers. A teacher who has mastered the basics of teaching, one who goes and beyond to ensure a positive learning experience for each student and who shares his knowledge with the broader learning community. 4) Professional Growth. This refers to gaining new skills and work experience that can help master teacher’s reach his/her career goal.
II. METHODOLOGY
This section presents the research design, locale, sample and sampling technique, research instrument, data gathering procedure, statistical treatment of data, and ethical consideration.
The study used the descriptive correlational research designs since the study investigated the relationship between the level of instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers and the extent of professional growth of teachers. According to Sousa (2020) descriptive correlational research design describes the variables and the relationship that occur naturally between and among them.
The study conducted in selected public elementary schools in the District of Cainta, Taytay, and Angono, Division of Rizal. The researcher selects three (3) Districts based on the population of master teachers. More so, the subjects of the study were the institutions in the three districts which are highly recognized by the Division of Rizal in different pedagogical categories, both in academic and extra-curricular activities.
The respondents of the study were thirty-seven (37) master teachers from the three (3) districts in the Division of Rizal. The study used the Slovins Formula with 15% of margin of error in determining the sample respondents per school. The non-probability sampling especially the purposive sampling technique was used in selecting the respondents who assessed the extent of professional growth of master teachers as instructional leaders.
The study utilized a researcher-made instrument. The instrument was digital driven through the google form as the major tool of the study.
The instrument was used to gather necessary data on the level of instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers as assessed by the respondents in terms of instruction, research, coaching and mentoring, and observation and supervision. Below was the four-point scale used with its corresponding verbal interpretations
|
Scale |
Range |
Verbal Interpretation |
|
4 |
3.50 – 4.00 |
Highly Competent |
|
3 |
2.50 – 3.49 |
Competent |
|
2 |
1.50 – 2.49 |
Moderately Competent |
|
1 |
1.00 – 1.49 |
Not Competent |
Data collected in this study, follows the standard operating procedures. The instrument used in the study was submitted to the adviser in order to gather initial comments and suggestions for the improvement of the questionnaire checklist. After revision of the instrument had been made, the researcher’s made instrument was validated by the experts with the reasonable background in test construction and on the topic to comment on its content for the finalization of the items to be included in the instrument. Upon completion of the content validation form, permission from the office of the principal was sought by the researchers to administer the instrument to the respondents. Then, immediate retrieval of the instrument was done.
The statistical tools used in this study were frequency and percentage distribution, weighted mean, ANOVA, and Pearson ‘r’ correlation. The researcher was strictly observing the following ethical considerations including the research participants were not subjected to harm in any ways whatsoever; the researcher prioritized the respect for dignity of research participants; full consent was obtained from the school heads of participants prior to conduct of the study; and the protection of the privacy of research participants has been ensured.
III. RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
This section briefly presents the results, analysis, and interpretation of the data gathered based on the problems presented in the research.
A. Of Instructional Leadership Skills And Competencies Of Master Teachers As Assessed By The Respondents In Terms Of Instruction, Research, Coaching And Mentoring, And Observation And Supervision
Table 1 presents the level of instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers as assessed by the respondents in terms of instruction.
Table 1
Level of Instructional Leadership Skills and Competencies of Master Teachers as Assessed by the Respondents in Terms of Instruction
|
Instruction |
Mean |
Verbal Interpretation |
|
3.76 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.63 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.65 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.52 |
Highly Competent |
|
Overall |
3.64 |
Highly Competent |
It can be gleaned from the table that the overall mean of the level of instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers as assessed by the respondents in terms of instruction is 3.64 verbally interpreted as “Highly Competent”. It may mean that the master teachers demonstrated the knowledge and understanding of the curriculum and ensure that planning and delivering differentiated instruction is their utmost concern could bring quality learning.
It implies that master teacher’s instructional competence are essential and significant tools needed for teaching and learning in order to promote teacher’s efficiency and improve learner’s performance. This is consistent with the findings of Bukoye (2019) investigated the utilization of instructional materials as tools for effective academic performance of students. The findings revealed inadequate use of instructional materials in most schools and majority of the teachers did not take cognizance of the importance derived from the use of instructional materials while teaching. Those that adopted the utilization, did not use them appropriately. No wonder the high rate of students’ failure in external examinations.
Based on the findings, the professional counsellors in the state should sensitize all heads of schools and teachers through seminars and workshops on the importance and good utilization of instructional materials. Among other recommendations, the government should endeavor to release enough funds.
Table 2 presents the level of instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers as assessed by the respondents in terms of research.
Table 2
Level of Instructional Leadership Skills and Competencies of Master Teachers as Assessed by the Respondents in Terms of Research
|
Research |
Mean |
Verbal Interpretation |
|
3.52 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.65 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.63 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.54 |
Highly Competent |
|
Overall |
3.59 |
Highly Competent |
It can be manifested from the table that the overall mean of the level of instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers as assessed by the respondents in terms of research is 3.59 verbally interpreted as “Highly Competent”. It may mean that the master teachers foster critical thinking and analytical skills through research and expanding their knowledge and understanding of a chose field outside of the classroom that can be helpful in improving the performance of the learners. It implies that master teachers demonstrated an understanding of research that could support students’ performance.
The findings is in parallel with the result of Buelo (2019) said that master teachers have average skills in searching, using and evaluating information including their awareness on the various sources of information and where to obtain them. They have fair skills in designing experimental study as well as selecting and developing research instruments, choosing appropriate statistical tools, and preparing manuscript for publication. They strongly value training in educational research but moderately apply research findings to real life context. They have high regards relative to the value of doing research to become better educator. Time, efforts and resources in learning about research findings were essential elements to create positive attitudes towards research. A research capability training program is hereby proposed as the output of the study. The program consists of various levels from lectures, hands-on workshop, and writing research articles for colloquium and for possible publication.
Table 3 presents the level of instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers as assessed by the respondents in terms of coaching and mentoring.
Table 3
Level of Instructional Leadership Skills and Competencies of Master Teachers as Assessed by the Respondents in Terms of Coaching and Mentoring
|
Supervising and Evaluating Teachers’ Performance |
Mean |
Verbal Interpretation |
|
3.56 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.59 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.75 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.62 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.53 |
Highly Competent |
|
Overall |
3.61 |
Highly Competent |
It can be depicted from the table that the overall mean of the level of instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers as assessed by the respondents in terms of coaching and mentoring is 3.61 verbally interpreted as “Highly Implemented”. It may mean that the master teachers guide teachers in the improvement of teaching skills and recognize and reinforce teaching excellence. This implies that master teachers are great instructional leaders because they provide assistance to teachers to improve the teaching learning process.
This goes with the findings of Marey (2020) said that differentiated supervision in which teacher evaluation is embedded can represent an effective instructional leadership tool. This suggested, integrated model encompasses professional growth, collegial development groups, peer coaching, self-directed professional development, mentoring, and portfolios. Such a model, if integrated correctly, will address all current problems arising from separating supervision and teacher evaluation and uphold a tradeoff between educators’ autonomy and accountability.
Table 4 presents the level of instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers as assessed by the respondents in terms of observation and supervision.
Table 4
Level of Instructional Leadership Skills and Competencies of Master Teachers as Assessed by the Respondents in Terms of Observation and Supervision
|
Observation and Supervision |
Mean |
Verbal Interpretation |
|
3.66 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.57 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.65 |
Highly Competent |
|
3.52 |
Highly Competent |
|
Overall |
3.63 |
Highly Competent |
It can be depicted from the table that the overall mean of the level of instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers as assessed by the respondents in terms of observation and supervision is 3.63 verbally interpreted as “Highly Implemented”. It may mean that the master teachers demonstrate all the time their responsibility in giving technical supervision and assistance to teachers that could improve supervisory practice and performance of teachers.
This goes with the findings of Barrogo (2020) showed those eight out of the ten statements regarding the standardized classroom observation tool yielded an overall response of “strongly agree”. The study concluded that a standardized classroom observation tool serves as a guide for the teachers to assess their performance and plan for their improvement, thus, enhancement of teachers’ preparation and competency. With the foregoing results, the researcher provided pertinent recommendations for professional and organizational development.
IV. EXTENT OF PROFESSIONAL GROWTH OF TEACHERS
Table 5 presents the extent of professional growth of teachers as assessed by the respondents.
Table 5
Extent of Professional Growth of Teachers
|
Professional Growth of Teachers |
Mean |
Verbal Interpretation |
|
3.76 |
To a Very Extent |
|
3.67 |
To a Very Extent |
|
3.55 |
To a Very Extent |
|
3.68 |
To a Very Extent |
|
3.82 |
To a Very Extent |
|
Overall |
3.70 |
To a Very Extent |
The table reveals that the extent of professional growth of teachers as assessed by the respondents has an overall mean of 3.70 interpreted as “To a Very Extent”. It may mean that teacher’s gain knowledge and new information on teaching techniques and methodologies that they could apply it in the teaching arena. It implies that teachers have access to and are participating in a variety of learning opportunities that addresses their needs and preferences.
The findings are consonant to the study of Badri (2016) provided some insights into the variations of those perceptions relative to other independent variables such as teachers’ age and gender, and type of schools. With regard to the perceived need for professional development activities, the most significant variation is observed with regard to public or private schools. With regard to the impact of those activities, male teachers almost consistently assign higher perceived impact scores than female teachers. Public schools also assign higher perceived impact scores for all activities that they participated in. However, female teachers assign significantly higher perceived barrier scores to five of the seven listed barriers to participating in professional development activities. The research has implications for professional development providers to ensure the effectiveness of professional development opportunities for educators
V. SIGNIFICANT RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE LEVEL OF INSTRUCTIONAL LEADERSHIP SKILLS AND COMPETENCIES OF MASTER TEACHERS AND THE EXTENT OF PROFESSIONAL GROWTH OF TEACHERS
Table 6 exhibits the significant relationship between the level of instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers and the extent of professional growth of teachers.
Table 6
Significant Relationship Between the Level of Instructional Leadership Skills and Competencies of Master Teachers and the Extent of Professional Growth of Teachers
|
Professional Growth of Teachers |
Level of Instructional Leadership Skills and Competencies of Master Teachers |
Pearson-r |
Sig. |
Decision |
Verbal Interpretation |
|
Extent of Professional Growth of Teachers |
Instruction |
-0.352 |
0.036 |
Reject Ho |
Significant |
|
Research |
-.351 |
.039 |
Reject Ho |
Significant |
|
|
Coaching and Mentoring |
-.367 |
.030 |
Reject Ho |
Significant |
|
|
Observation and Supervision |
-0.393 |
0.023 |
Reject Ho |
Significant |
It is reflected from the table that there is a significant relationship between the level of instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers with respect to instruction, research, coaching and mentoring, and observation and supervision, and the extent of professional growth of teachers, since the computed p-value is less than 0.05 thus the null hypothesis is rejected. The findings show that the instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers with respect to instruction, research, coaching and mentoring, and observation and supervision are significantly correlated with the professional growth of teachers.
It implies that master teachers demonstrated all the instructional leadership skills and competencies that could contribute to the professional growth and performance of teachers.
According to Parlar (2017) that the school principals performed the instructional leadership behaviors of determining and sharing the objectives of the school at the highest level. Among the organizational health dimensions of the schools, initiating structure was perceived at the highest level, while resource support and academic emphasis were perceived at lower levels compared to other dimensions. In the study, positive and significant correlations were found between the sub-dimensions of instructional leadership behaviors and those of organizational health of schools.
The sub-dimensions of instructional leadership together explained 49% of the variance in organizational health. On the other hand, only determining and sharing the objectives of the school and forming a regular instructional-learning environment and positive school climate among the instructional leadership behaviors were positive and significant predictors of organizational health of schools.
VI. DISCUSSION
Following are the summary of findings obtained through the conduct of this study including the conclusions and recommendations formulated by the research.
A. Summary of Findings
- Level of Instructional Leadership Skills and Competencies of Master Teachers as Assessed by the Respondents in terms of Instruction, Research, Coaching and Mentoring, and Observation and Supervision: In general, the master teachers are highly competent as regard to instructional skills and competencies in terms of instruction, research, coaching and mentoring, and observation and supervision.
- Extent of Professional Growth of Teachers: In general, the teachers had a great extent on their professional growth in gaining new knowledge and information as regard to teaching techniques and methodologies that they could apply it in the teaching arena.
- Significant Relationship Between the Level of Instructional Leadership Skills and Competencies of Master Teachers and the Extent of Professional Growth of Teachers: There is a significant relationship between the level of instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers with respect to instruction, research, coaching and mentoring, and observation and supervision, and the extent of professional growth of teachers, since the computed p-value is less than 0.05 thus the null hypothesis is rejected. The findings show that the instructional leadership skills and competencies of master teachers with respect to instruction, research, coaching and mentoring, and observation and supervision are significantly correlated with the professional growth of teachers.
B. Conclusions
The following conclusions were formulated based on the findings presented:
- The instructional skills and competencies of master teachers are highly competent in terms of instruction, research, coaching and mentoring, and observation and supervision.
- Teachers have a great extent on their professional growth in accessing to and are participating in a variety of learning opportunities that addresses their needs and preferences.
- Master teacher’s instructional skills and competencies in terms of instruction, research, coaching and mentoring, and observation and supervision were significantly related to the professional growth of teachers.
C. Recommendations
Based on the findings and conclusions, the following recommendations are hereby suggested:
- Master teachers should demonstrate knowledge and understanding of current and future trends in supervision.
- Teachers should attend various seminars and trainings that could help them in teaching diverse learners in this time of pandemic.
- Master Teacher should develop, implement, monitor, and evaluate an instructional supervisory plan.
- A similar study may be conducted to validate the results of the study using other samples, variables, and in other contexts.
VII. PROPOSED POLICY ENHANCEMENT ON PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT AND INSTRUCTIONAL LEADERSHIP COMPETENCIES OF MASTER TEACHERS AND TEACHERS
The following are the recommended actions for policy enhancement to support the professional development and instructional leadership of master teachers and teachers.
- Adopt standards for professional development and instructional competencies to guide the design, evaluation, and funding of professional learning provided to educators. These standards might reflect the features of effective professional learning outlined in this report as well as standards for implementation.
- Evaluate and redesign the use of time and school schedules to increase opportunities for professional learning and collaboration, including participation in professional learning communities, peer coaching and observations across classrooms, and collaborative planning.
- Regularly conduct needs assessments using data from staff surveys to identify areas of professional learning most needed and desired by educators. Data from these sources can help ensure that professional learning is not disconnected from practice and supports the areas of knowledge and skills educators want to develop.
- Identify and develop expert teachers as mentors and coaches to support learning in their area(s) of expertise for other educators.
- Integrate professional learning into the Education For All (EFA) school improvement initiatives, such as efforts to implement new learning standards, use student data to inform instruction, improve student literacy, increase student access to advanced coursework, and create a positive and inclusive learning environment.
- Provide technology-facilitated opportunities for professional learning and coaching, using funding available under EFA goals to address the needs of rural communities and provide opportunities for collaboration of different schools.
- Provide flexible funding and continuing education units for learning opportunities that include sustained engagement in collaboration, mentoring, and coaching, as well as institutes, workshops, and seminars.
The appropriate, necessary, well-designed, and implemented policy on professional development and instructional leadership competencies of master teacher and teachers should be considered an essential component of a comprehensive system of teaching and learning that supports students to develop the knowledge, skills, and competencies they need to thrive in the 21st century. To ensure a coherent system that supports teachers across the entire professional continuum, professional learning should link to their experiences in preparation and induction, as well as to teaching standards and evaluation. It should also bridge to leadership opportunities to ensure a comprehensive system focused on the growth and development of teachers.
References
[1] Badri, M. (2016). Perception of teachers’ professional development needs, impacts, and barriers: The Abu dhabi case. Sage Journals. [2] Barrogo, S.D. (2020). Teachers’ perception of standardized classroom observation tool. International Journal of Academic Pedagogical Research, 4(7): 33-37. [3] Bueno, D.C. (2019). Research skills and attitudes of master teachers in a division towards capability training. Philippine International Conference on Economics, Education, Humanities & Social Sciences. [4] Bukoye, R.O. (2018). Utilization of instruction materials as tools for effective academic performance of students: Implications for counseling. Innovative and Creative Education and Teaching International Conference [5] Marey, R. (2020). Re-conceptualizing teacher evaluation and supervision in the light of educational reforms in Egypt. Social Sciences & Humanities Open, 2(1). [6] Parlar, H. (2017). Examining the relationship between instructional leadership and organizational health. Journal of Education and Training Studies, 5(4).
Copyright
Copyright © 2022 Dr. John Marco F. Quisquino. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET47974
Publish Date : 2022-12-08
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

