Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Navigating the Ethical Maze: Moral Dilemmas in the Age of AI
Authors: Ketan Totlani
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.56138
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
This research paper explores the ethical implications of artificial intelligence (AI) in various fields and domains. It delves into the potential benefits and risks of AI, focusing on its impact on employment, bias induced by AI systems, concerns over data privacy, and other factors affecting humanity. The paper emphasizes the importance of robust and dynamic AI regulation to mitigate the risks of AI. Additionally, it highlights the limited ability of governments and institutions worldwide to keep up with the rapid evolution of AI in the industry. The paper also provides recommended strategies and approaches grounded in philosophy to avoid negative implications.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become an integral part of society, raising important ethical considerations. As AI advances, it is crucial to understand and address the associated ethical implications. This introduction highlights the multifaceted ethical issues surrounding AI and emphasises the need for robust regulation and philosophical approaches with focus on those which go beyond high-level statements of principles. AI represents a watershed moment in human history as it will revolutionise industries and enhance decision-making processes, but it also poses risks. One concern is the impact of AI on employment, with apprehension about job displacement and its socio-economic consequences. This paper analyses the ethical dimensions of AI-driven employment changes and proposes strategies to address these concerns. Bias induced by AI systems is another major ethical concern. Machine learning algorithms trained on vast amounts of data can perpetuate societal biases. This bias can manifest in various domains, such as hiring processes and criminal justice systems. The paper examines the ethical implications of biased AI systems and also explores methods for ensuring accountability and fairness in AI development and deployment.Data privacy is of utmost importance in AI. AI systems rely heavily on personal data, raising concerns about privacy infringement and misuse. The paper delves into the ethical considerations surrounding data privacy in the context of AI and proposes measures to protect individuals' privacy rights. The rapid evolution of AI poses challenges for governments and institutions worldwide. Keeping up with advancements and understanding ethical implications requires proactive and adaptive regulation. The paper highlights the limitations of current regulatory frameworks and proposes strategies for developing robust and dynamic AI regulation.
In conclusion, this research paper sheds light on the ethical implications of AI. By examining the impact on employment, addressing bias, discussing data privacy concerns, and exploring the need for robust regulation, it provides highly in-depth insights and recommendations to navigate ethical challenges. It is imperative to develop, deploy, and regulate AI in a manner that upholds ethical principles and safeguards humanity's well-being. If proper checks and balances are not kept for artificial intelligence it might turn out to be a Frankenstein for the civilisation. The civilisation today stands on the road not taken it may turn out to be a boon or it may become the biggest bane not only for science but for mankind too.
II. JOB DISPLACEMENT AND ECONOMIC IMPACT
The extract from "The Future of Work in the Age of AI: Displacement or Risk-Shifting?" offers a compelling exploration of how AI technologies disrupt and reshape the landscape of employment, with a focus on the shifting of risks from employers to workers. This shift in risk allocation is extremely relevant in the context of AI-driven workplace dynamics (Moradi & Levy, 2018).
- Destabilizing Workers' Livelihoods: The mentioned practices, such as just-in-time scheduling and unpredictable work hours, indicate the destabilizing and unsettling effects of AI-driven scheduling systems on workers' lives. These practices destabilize workers' livelihoods by interfering with their non-work activities, like education, childcare, or second jobs. The consequences of such interference extend beyond financial stress, as they can lead to intergenerational cognitive dissonance and other harms, creating a ripple effect of social and economic challenges. It's notable that these effects disproportionately affect women and workers of colour, who are more likely to occupy service positions.
- Defining Compensable Work: The advancement of AI technologies provides firms with greater visibility and control over workers' activities, enabling them to narrowly define what constitutes compensable work. This aspect aligns with the Fair Labour Standards Act (FLSA), which mandates compensation for activities integral and indispensable to job tasks (Moradi & Levy, 2018). However, AI can potentially further restrict the definition of compensable work. For example, gig economy workers like Uber drivers are paid only for the time they are actively transporting passengers, excluding time spent waiting for ride requests or maintaining their vehicles. This approach, driven by AI algorithms, shifts the burden of unpaid tasks, such as vehicle maintenance and downtime, onto the worker despite these activities being essential for the job.
- Granular Measurement and Compensation Schemes: AI's granular measurement capabilities allow firms to recalibrate compensation schemes in favour of the organization. For instance, Amazon shifted its payment model for authors to a per-page-read basis, transferring the risk of reader disengagement from the company to the author. Analogously, music-streaming platforms like Spotify pay artists based on the number of track streams, which may incentivize homogeneity in production of music. This massive shift in compensation models focuses how AI-driven systems count specific tasks pertaining to profitability while disregarding others, potentially increasing the proportion of uncompensated work. This phenomenon is particularly evident in the gig economy, where tasks like vehicle cleaning or maintaining a high customer rating often go unpaid.
- Detecting and Predicting Loss and Fraud: AI is also utilized to redistribute the risk of deliberate damage or loss from employees acting against a firm's interests. This includes employee theft, embezzlement, or whistleblowing. Predictive AI systems aim to anticipate potential harm before it occurs, leading to implications for workers. Predictive accuracy and risk aversion can result in some workers being deemed "risky" and unhireable. Additionally, the use of predictive systems relies on data, often self-reported and shared among employers, potentially risky and inflected with biases that can disproportionately affect disadvantaged workers (Moradi & Levy, 2018).
- Incentivizing and Evaluating Productivity: AI-driven systems are deployed to measure, assess, and incentivize workers' performance. While productivity incentivization can be beneficial in certain contexts, it can also lead to invasive monitoring, erode trust, and impose significant physical and mental health burdens on workers. AI-enabled tracking, as seen in Amazon warehouses and ride-sharing platforms, has raised concerns about worker well-being and dignity.
III. ACCOUNTABILITY AND TRANSPARENCY
Accountability in Algorithmic Decision Making by Nicholas Diakopoulos is a seminal work that addresses the critical issues relating to accountability pertaining to the context of algorithmic decision-making systems which affects the biases of AI systems directly . Diakopoulos underscores the significance of transparency and accountability in the deployment of AI and algorithms, particularly in applications that impact individuals and society at large (Diakopoulos, 2016).
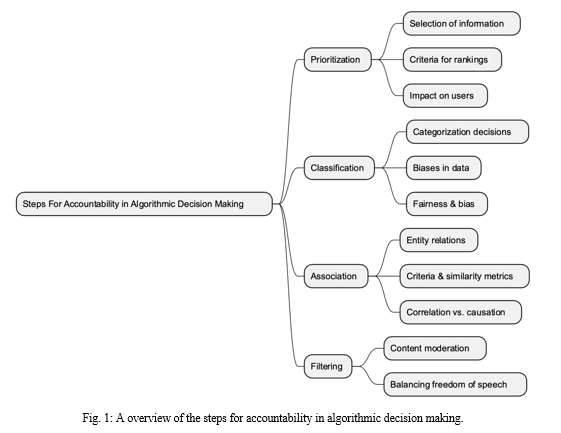
Nicholas Diakopoulos argues that accountability and algorithmic decision making mechanisms are essential to ensure that algorithmic systems are transparent, fair, and ethically sound. In his work, he highlights the following key points:
- Prioritization: Prioritization is the process of selecting and highlighting certain information while downplaying or excluding other information. Algorithms excel at prioritizing content, which can have far-reaching consequences. For example, search engines prioritize search results based on various factors, influencing what information users access. Designers must consider the criteria used in these rankings and their potential impact on individuals and entities.
- Classification: Classification decisions involve categorizing entities into specific classes based on key characteristics. These decisions can drive downstream actions and have implications for fairness and bias. The quality of training data is crucial, as biases present in the data can result in biased classifications. Designers must also consider the accuracy of classifications and the potential consequences of false positives and false negatives.
- Association: Association decisions create relationships between entities, and the semantics of these relationships can carry significant meaning. Algorithms, such as collaborative filtering, use associations to make recommendations. However, the criteria and similarity metrics used in associations can impact accuracy and interpretation. Distinguishing between correlative and causal associations is crucial to avoid misinterpretation.
- Filtering: Filtering decisions involve including or excluding information based on rules or criteria. These decisions are common in social media platforms, where content moderation and filtering are necessary to maintain a positive user experience. Striking the right balance between moderation and censorship is challenging, especially in cultures valuing freedom of speech.
The ethical implications of algorithmic decision-making are profound. As AI algorithms play an increasingly significant role in our society, it's crucial that they adhere to ethical principles.
These principles emphasize acting in the public interest, avoiding harm, being fair, and respecting privacy. Designers and developers must constantly consider the consequences of their algorithms, including the potential for discrimination, censorship, and other ethical issues (Diakopoulos, 2016).
IV. DATA PRIVACY AND BIAS
In the ever-evolving landscape of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), the growing dependence on big data has ushered in transformative advancements. Dilmaghani et al. (2019) conducted a comprehensive study illuminating this convergence, acknowledging its potential while highlighting significant challenges, notably those pertaining to data privacy and security. Their work encompasses an examination of risks within AI/ML workflows, introducing an adversarial model for threat assessment and presenting defensive strategies. Furthermore, it delves into the pivotal role of Standards Developing Organizations (SDOs), exemplified by ISO/IEC JTC 1, in shaping standards and guidelines that fortify data privacy and augment AI system security. This section critically reflects on this intricate interplay among AI, big data, and pressing privacy and security concerns, drawing inspiration from the seminal contributions of Dilmaghani et al. (2019) to align research endeavours with evolving standards.
A. Data Privacy Concerns in AI
- Data Breach: The rapid growth of AI systems, fueled by big data, raises concerns about the security of sensitive information. Any vulnerability in these systems can result in data breaches, with potentially disastrous consequences for privacy and security (Dilmaghani et al., 2019). These breaches can occur at various phases of AI, including data training, model development, and real-time inference.
- Biased Data: Bias in AI systems can have serious ethical implications, as it can lead to discrimination in decisions related to credit approvals, hiring, and the criminal justice system. Such bias often arises from biased training data and poses a significant challenge to ensuring fairness and privacy in AI applications.
- Data Poisoning: Data poisoning attacks involve adversaries injecting malicious data into training datasets, compromising the integrity and trustworthiness of AI models. These attacks can result in AI systems making incorrect predictions or classifications, potentially violating privacy (Dilmaghani et al., 2019).
- Model Extraction: Attackers may attempt to extract the trained AI model itself, which can lead to the disclosure of sensitive information or proprietary algorithms, violating both confidentiality and intellectual property rights.
- Evasion Attacks: Adversarial samples, which are carefully crafted input data, can manipulate AI systems into making incorrect decisions or misclassifying information (Dilmaghani et al., 2019). These evasion attacks can undermine the integrity and reliability of AI systems, posing privacy risks.
B. Solutions and Countermeasures
- Anonymization and De-identification: Privacy-preserving techniques, such as data anonymization and de-identification, can help protect sensitive information in AI training datasets (Dilmaghani et al., 2019).
- Privacy-Enhancing Techniques (PETs): Privacy-enhancing technologies like federated learning and secure multi-party computation enable collaborative AI without exposing raw data, enhancing privacy protection (Dilmaghani et al., 2019).

3. Bias Mitigation: Fairness-aware machine learning algorithms aim to reduce and mitigate biases in training data and model predictions, addressing privacy concerns associated with biased AI systems (Dilmaghani et al., 2019).
4. Data Poisoning Detection: Techniques such as anomaly detection can identify and remove poisoned data within training datasets, bolstering model integrity and privacy.
5. Model Robustness: Adversarial training techniques improve model robustness against evasion attacks, ensuring correct classifications and protecting privacy (Dilmaghani et al., 2019).
6. Access Control and Auditing: Implementing strict access controls and robust auditing mechanisms can limit unauthorized access to data and monitor AI model behavior to prevent data breaches.
7. Standards and Guidelines: Collaboration with Standards Developing Organizations (SDOs), such as ISO/IEC JTC 1, can lead to the development of industry standards and guidelines for data privacy and security in AI, ensuring consistency and trustworthiness in AI system development (Dilmaghani et al., 2019).
These solutions and countermeasures are essential for addressing the various data privacy concerns in AI systems. They aim to strike a balance between the benefits of AI and the protection of individual privacy rights, contributing to the responsible development and deployment of AI technologies.
V. AI REGULATION
A. Challenges and Considerations in AI Regulation
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) technology has brought to the fore a plethora of challenges for governments and regulatory bodies worldwide (Jobin, Ienca, & Vayena, 2019). The ongoing discourse surrounding AI regulation expands through ethical, legal, and practical dimensions, owing to the transformative and disruptive potential of AI systems. This potential extends beyond conventional technology regulation, necessitating a nuanced approach that reconciles various aspects of AI deployment.
AI technology possesses unique characteristics that warrant careful consideration in regulatory frameworks. Unlike traditional software, AI systems exhibit adaptive learning capabilities, which introduce unpredictability in their behavior. This adaptability can lead to unintended consequences, even when algorithms are correctly implemented. For instance, machine learning algorithms may exhibit biased behavior due to insufficient or biased training data, raising concerns about fairness and discrimination (Jobin, Ienca, & Vayena, 2019).
The challenge further compounds due to the opacity of certain AI systems, often referred to as "black boxes." This opacity hampers explainability and accountability, making it difficult to trace the causes of erroneous behavior. Consequently, there is a growing consensus on the need for regulations to address these issues, ensuring that AI systems are designed, deployed, and operated responsibly (Jobin, Ienca, & Vayena, 2019).
B. Proposed Regulatory Approach
To navigate these challenges, the passage proposes an approach to AI regulation that is both pragmatic and responsive to the evolving nature of technology (Ellul et al., 2021). It posits several key principles:
- Sector-Specific Regulation: Rather than imposing blanket regulation on all AI technologies, the approach advocates for sector-specific regulation. This targeted approach tailors regulation to the risks and requirements associated with specific sectors or activities. For instance, critical systems or sectors involving sensitive data may necessitate stricter regulation, while other applications might benefit from a lighter touch.
- Voluntary Assurance: Acknowledging the need to balance regulation with innovation, the framework allows for voluntary AI technology assurances. Developers and operators can seek certification voluntarily, signalling their commitment to ethical and responsible AI practices. This voluntary aspect encourages innovation while incentivizing responsible behaviour.
- Human-Centric Design: The regulatory framework emphasizes a human-centric approach to AI development. It underscores the importance of AI systems supporting and assisting humans rather than overriding their decisions. Furthermore, AI systems should operate equitably, ensuring that they do not discriminate against specific segments of society.
- Monitoring and Auditing: To uphold ethical and legal standards, the framework incorporates mechanisms for continuous monitoring and auditing of AI systems. This includes independent code reviews, data logging, and assessments conducted by accredited auditors. These measures help ensure ongoing compliance with established guidelines and standards.
- Alignment with International Standards: While international standards for AI are still emerging, the framework anticipates alignment with these standards once they mature. Harmonizing national guidelines with international best practices can facilitate global cooperation and consistency in AI regulation.
In summary, the proposed regulatory approach seeks to strike a balance between the imperative to regulate AI for ethical and legal reasons and the necessity of fostering innovation. By advocating for sector-specific regulation, voluntary assurances, and robust monitoring, the framework aims to guide the responsible development and deployment of AI technology in a rapidly evolving landscape (Ellul et al., 2021).
Conclusion
The ethical implications of artificial intelligence (AI) are not merely theoretical concerns; they are tangible and pressing issues that have profound implications for individuals, society, and the future of technology. This research paper serves as a comprehensive guide to navigating these complexities. It underscores the imperative to approach AI with a commitment to ethical principles, fairness, transparency, and accountability. To harness the immense potential of AI while safeguarding humanity\'s well-being, it is paramount that the recommendations presented here are embraced and implemented by all stakeholders. The ethical journey in the age of AI has just begun, and it is our collective responsibility to shape it into a force for good. This paper, by delving into AI\'s impact on employment, algorithmic bias, data privacy concerns, and regulatory challenges, highlights the tangible and urgent nature of these ethical concerns, urging responsible AI development and deployment that aligns with societal values and expectations.
References
[1] Jobin, A., & Ienca, M. (2019). The global landscape of AI ethics guidelines. Nature Machine Intelligence, 1(9), 389-399. doi: 10.1038/s42256-019-0088-2 Source: Nature Machine Intelligence [2] Dilmaghani, S., Brust, M. R., Danoy, G., Cassagnes, N., Pecero, J., & Bouvry, P. (2019). Privacy and Security of Big Data in AI Systems: A Research and Standards Perspective. Retrieved from IEEE Xplore. Source: IEEE Xplore [3] Diakopoulos, N. (2016). Accountability in Algorithmic Decision Making. Retrieved from ACM Digital Library. doi: 10.1145/2844110 Source: ACM Digital Library [4] Moradi, M., & Levy, K. N. (2018). The Future of Work in the Age of AI: Displacement or Risk-Shifting?. Retrieved from SSRN. Source: SSRN [5] Ellul, J., Pace, G., McCarthy, S., Sammut, T., Brockdorff, J., & Scerri, M. (2021). Regulating Artificial Intelligence: A Technology Regulator’s Perspective. Retrieved from ACM Digital Library. doi: 10.1145/3462757.3466093 Source: ACM Digital Library
Copyright
Copyright © 2023 Ketan Totlani. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET56138
Publish Date : 2023-10-13
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

