Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Network Topologies in Optical Systems
Authors: Muhammad Arif Bin Jalil
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.64345
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Topology is the process of arranging objects in a certain connection, order, or configuration. Network topology, then, is the process of configuring or joining various devices inside a network. Network topologies are the various ways that devices can be connected to one another. Based on how devices are connected to one another and how data moves between them, these network topologies are categorized into several groups. System architecture uses a variety of topologies, including star, ring, hybrid, mesh, tree, and bus, in different sectors. This study has examined the advantages and disadvantages of several topologies based on connections and data flow. In this study, the significance of network topology will be discussed.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Setting up links and nodes, among other network components, is known as networking topology. It can be seen as a geometric depiction of the connections and communication across several systems[1]. There are several reasons why the network architecture is important. It is crucial for any network's operation and effectiveness above all. In order to ensure optimal network health, choosing the right network topology for an organization's operating model can improve performance, make problem discovery and resolution easier, and encourage more cautious resource distribution throughout the network[2]. A software-generated network topology diagram is widely used to display and modify a network architecture and configuration. The main advantage of employing these diagrams is their ability to give users visual representations of both physical and logical layouts, which helps them during troubleshooting by helping them comprehend how the links between devices function[3].Reducing operational and maintenance expenses can be achieved by increasing data energy and efficiency through an efficient and well-managed topology. The configuration of a network can determine how successfully it connects, performs, and is safeguarded against outages. To guarantee that any network is dependable and efficient, efficient network administration and monitoring necessitate a thorough understanding of both the logical and physical topology[4]. There are several types of topologies that are employed to arrange systems. The main advantage of employing these diagrams is their ability to give users visual representations of both physical and logical layouts, which helps them during troubleshooting by helping them comprehend how the links between devices function[3].Reducing operational and maintenance expenses can be achieved by increasing data energy and efficiency through an efficient and well-managed topology. The configuration of a network can determine how successfully it connects, performs, and is safeguarded against outages. To guarantee that any network is dependable and efficient, efficient network administration and monitoring necessitate a thorough understanding of both the logical and physical topology[4]. There are several types of topologies that are employed to arrange systems.
II. THE IMPORTANCE OF NETWORK TOPOLOGY
The performance of a network is largely dependent on its configuration, or topology. The arrangement of a network, including the logical or physical description of how nodes and links are connected to one another, is known as network topology.A network can be configured in a variety of ways, each with their own advantages and disadvantages with some applications better suited to a certain situation than others. When it comes to selecting a network topology, administrators have a number of options to consider. These include the goals, budget, and size and scope of the firm. Effective network topology management involves a number of responsibilities, such as visual mapping, configuration management, and overall performance monitoring. The key is to understand your objectives and requirements to create and manage the network topology in the right way for industries and business.Following an in-depth network topology definition, this article will look at the main types of network topologies, their benefits and drawbacks, and considerations for determining which one is best to be used. The physical or logical arrangement of different nodes, devices, and connections inside your network with respect to one another is known as network topology. Consider the topology of your network as the city's road map. There are numerous methods to set up and manage a city, such as ensuring that avenues and boulevards allow traffic to flow between the areas of the city that receive the greatest volume of traffic. Similarly, there are numerous methods to set up a network.
Each has benefits and drawbacks, and different setups can offer you a higher level of security and connectivity based on your company's needs. Network topology can be approached in two ways: logically and physically. As the name implies, physical network topology describes the actual wires, cables, and other physical links and interconnections that exist between nodes and the network. A bit more strategic and abstract, logical network topology refers to the conceptual knowledge of how and why the network is set up the way it is and how data flows across it. [5]
The cables, wires, and other physical connections that connect different nodes are the subject of physical topology. It entails positioning devices, installing code, and configuring different network elements, like links and nodes. It is more easily defined as the physical arrangement of the network's cables, workstations, and nodes[6]. The arrangement of a network's different components is referred to as its physical topology. It shows how the connections and hardware that make up a network are actually configured. Minor factors like device kind and data flow are disregarded in favour of the network's primary priorities. The configuration of the network's nodes and network cables will vary depending on how easy it is to construct and set up. Logical topology reflects the configuration and communication of devices. Physical topology and node configurations have no bearing on data transmission via it.It is focused on the smallest details of the network, like the kind and quality of switches and routers, which affect the rate and speed at which data packets are transmitted. The logical topology of the network ensures optimal and controllable flow control. Either a linear pattern called a logical bus or a circular logical ring can represent the data flow.
The network's architecture is crucial for a number of reasons. Most importantly, it is crucial to the operation of the network. In addition to improving performance, selecting the appropriate topology for one company's operational model helps facilitate the efficient allocation of resources throughout the network to maintain optimal network health and facilitate the identification and troubleshooting of errors. Reducing operating and maintenance expenses can be achieved by increasing energy and data efficiency through a well-managed and optimised network architecture. To maintain the effectiveness and health of your network, effective management and monitoring require a solid understanding of the logical and physical topology of a network.
III. TYPES OF NETWORK TOPOLOGY
A. Bus Topology
Every system and device in a network with a bus architecture is connected to a single wire. It transfers data in a single direction from one end to the other. The shared channel has line terminators at both ends. Sending a message to the network is a prerequisite for each node that wishes to send a signal through it. Any reachable station in the network will get the message, regardless of the intended recipient. This does not have any bi-directional features. It is a multipoint connection with a non-robust topology since the topology collapses if the backbone is hacked[7]. It is also known as backbone topology and line topology. The direction of data travel on the cable is constant. If multiple hosts try to send data at the same time, things could go wrong. As a result, it either assigns one host to be the bus master or uses CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collision Avoidance) technology to resolve the issue. This type of networking is basic in that the malfunction of one device does not affect the operation of the others. However, in the event that the shared communication channel malfunctions, all other devices will cease to operate. It is widely used in well-established networks, such as 802.4 and 802.3 (Ethernet) networks[8]. The bus topology displayed in Figure 2 demonstrates how devices can be networked to one another and how data is transferred between ends.
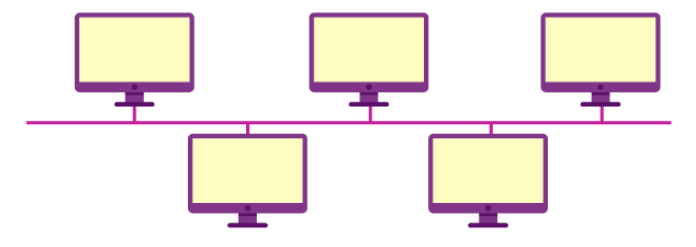
Figure 1: Bus Topology [12]
B. Ring Topology
Each host computer in this kind of design is linked to precisely two other hosts, creating a circular network topology. If a host wants to talk to or send a message to another host that is not right next to it, the data is routed through all of the intermediary hosts. The message is sent to the system after it by the one that gets it from the one before it[9]. It may only take the administrator to connect one additional wire to add a host to the current configuration. Its connected endpoints are the sole thing that sets it apart from bus topology. In this instance, too, data flow is unidirectional and takes place in an endless cycle. In contrast, dual ring topology is a bidirectional topology that may be accomplished by giving every network node two connections. Since the two ends are connected, there isn't a termination point. It is traversed by data in a clockwise manner. Since data in a ring topology with 90 nodes must pass through 89 nodes before reaching the 90th node, a significant number of repeaters are needed when a ring topology with many nodes is used[10]. As a result, the network uses repeaters to guard against data loss. Figure 3 illustrates the looping data flow and the Ring topology configuration of the devices.
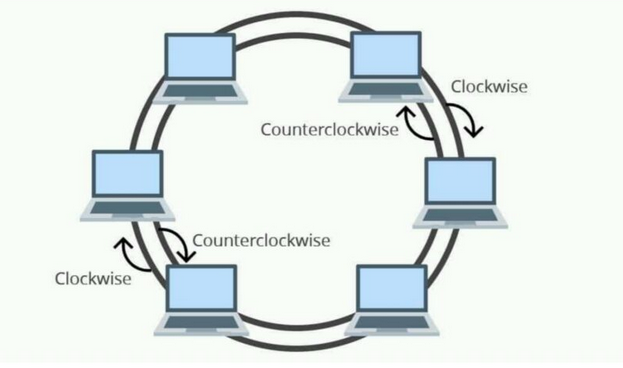
Figure 2 : Double Ring Topology [13]
C. Star Topology
It is the topology that is most frequently used. Each system in this configuration is connected to a different hub by a wire.This hub acts as the centre node and is connected to the other nodes. This hub could be passive that is, not intelligent, like broadcasting devices or intelligent that is, active hubs. Repeaters are found in operational hubs. The main computer is referred to as a server, and the devices connected to it as clients. The devices are connected by coaxial cable or RJ-45 connectors[11]. In a physical star design, hubs or switches are typically employed as connecting elements. In this case, there is not a direct device connection; instead, all systems must speak with the hub first. To reach its destination, information transferred from each network node must pass through the main system, which acts as a repeater and guards against data loss. The data flow and Star topology of connected devices are depicted in Figure 4.
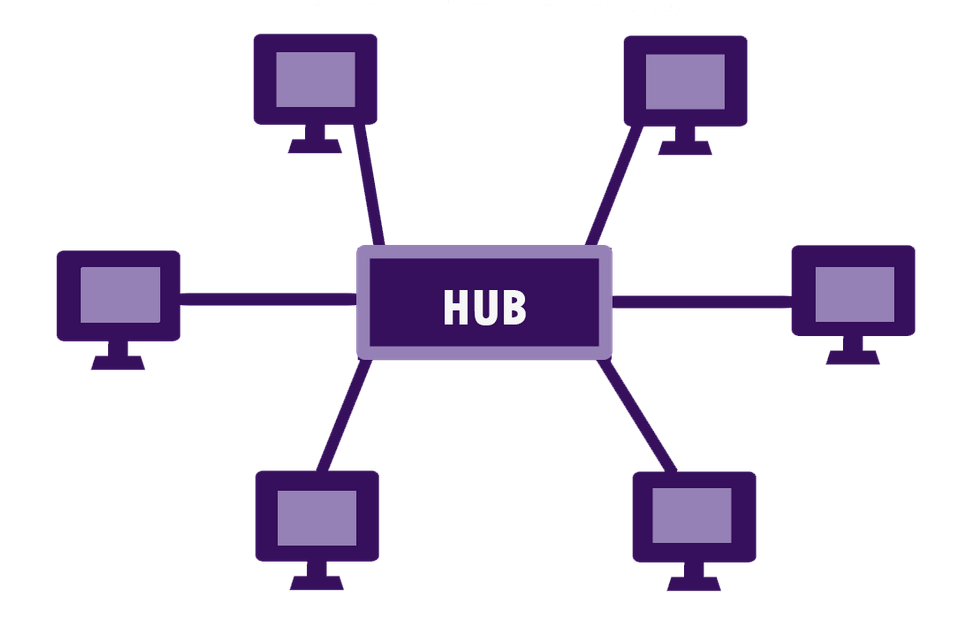
Figure 3: Star Topology [13]
D. Mesh Topology
This is establishing connections between a host and multiple other systems. Any two systems can establish point-to-point connections with one another. There could be a number of gadgets out there, just a few of which are point-to-point connected. There are two types of mesh networks: complete mesh and partial mesh. Mesh topologies that are partially interconnected have fewer nodes with only two or three connections, but fully linked mesh topologies, as seen in Figure 4, have all connected nodes.
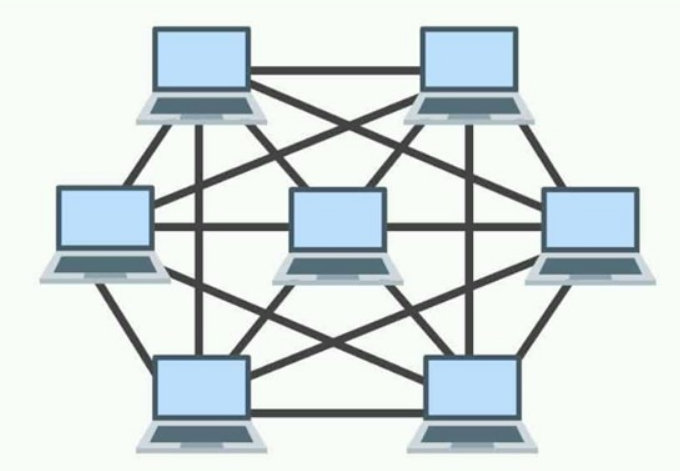
Figure 4: Mesh Topology [17]
E. Tree Topology
The network is divided into numerous tiers and layers using this design. A network is made up of three types of network devices, most of which are found in LANs. Systems are connected at the lowest layer, known as the access layer. The distribution layer is the layer that sits between the top and bottom layers. The uppermost layer, sometimes referred to as the core layer, houses the network's central nervous system. A point-to-point link connects all of the adjacent hosts. Topology faces a problem if the root node fails since it impacts the entire network, much like a bus does. It is not, however, the only point of failure. The network is divided into areas that cannot be accessed in the event of a link failure, with each link acting as a single point of failure.
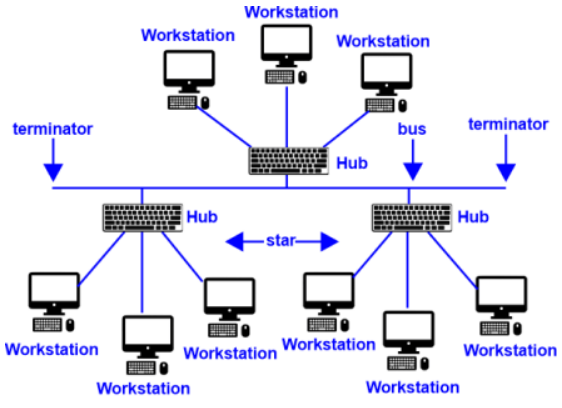
Figure 5 : Tree Topology [16]
F. Hybrid Topology
It can be explained as a synthesis of several topologies. These are often used in big, international companies with distinct organisational structures for every department. They greatly increase the network system's flexibility. Numerous topologies can be chosen and implemented according on the needs and requirements of the user.
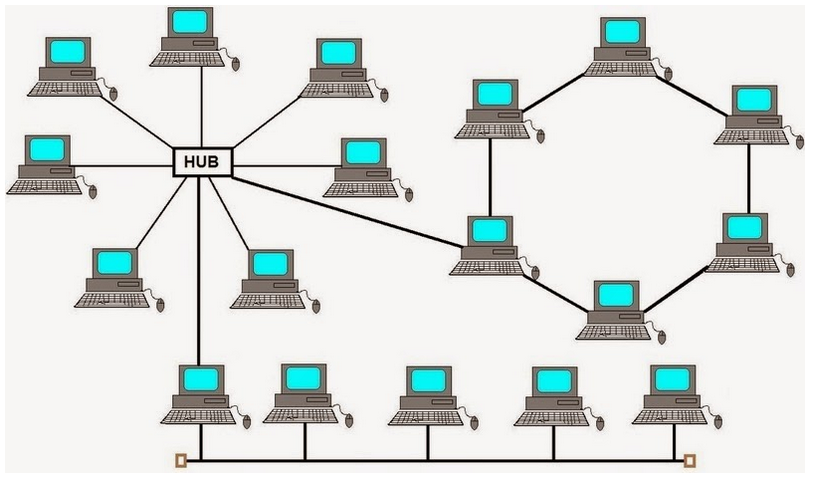
Figure 6 : Hybrid network Topology [15]
G. Wireless Topology.
According to the description, data is transmitted by non-guided medium, such as air, in a wireless topology. In essence, it sent data into space.Wireless topologies can be configured in a cellular, mesh, or star configuration. The wireless architecture in the star configuration is known as Basic Service Set (BSS). In this configuration, a base station called an access point (AP) or wireless access point (WAP) connects wireless devices to the wired LAN.
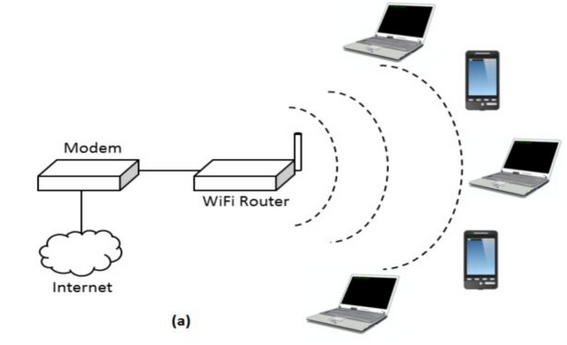
Figure: Wireless Topology [13]
Conclusion
One large and important topic of computer science and engineering is network topology.Students must grasp a number of concepts covered in the course, including networking, data structures, database administration, and algorithm analysis.It is imperative that you prepare for these courses in order to pass technical examinations, interviews, and competitive exams.These subjects cover the rules, ideas, and algorithms that provide the basis for developing various software programs.Networking is one subject that fits under this category. It includes terms related to networks, topologies (like star, bus, mesh, tree, and ring topologies), various kinds of computer networks, and protocols (like TCP and HTTP) that guarantee safe and efficient data transfer.
References
[1] E. Ozkan-Canbolat and A. Beraha, “Configuration and innovation related network topology,” J. Innov. Knowl., 2016, doi:10.1016/j.jik.2016.01.013. [2] E. Ozkan-Canbolat and A. Beraha, “A configurational approach to network topology design for product innovation,” J. Bus. Res., 2016,doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.04.115. [3] D. L. Harrington et al., “Network topology and functional connectivity disturbances precede the onset of Huntington’s disease,” Brain,2015, doi: 10.1093/brain/awv145. [4] G. Engels et al., “Clinical pain and functional network topology in Parkinson’s disease: a resting-state fMRI study,” J. Neural Transm.,2018, doi: 10.1007/s00702-018-1916-y. [5] https://www.dnsstuff.com/what-is-network-topology [6] X. Diego, L. Marcon, P. Müller, and J. Sharpe, “Key Features of Turing Systems are Determined Purely by Network Topology,” Phys.Rev. X, 2018, doi: 10.1103/PhysRevX.8.021071. [7] E. Heasley, N. Clifford, and J. Millington, “I ntegrating network topology metrics into studies of catchment-level effects on habitatdiversity,” Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss., 2018, doi: 10.5194/hess-2018-89. [8] V. Deshpande, H. Badis, and L. George, “BTCmap: Mapping bitcoin peer-to-peer network topology,” in 2018 IFIP/IEEE InternationalConference on Performance Evaluation and Modeling in Wired and Wireless Networks, PEMWN 2018, 2018, doi:10.23919/PEMWN.2018.8548904. [9] B. Bangerter, S. Talwar, R. Arefi, and K. Stewart, “Networks and devices for the 5G era,” IEEE Commun. Mag., 2014, doi:10.1109/MCOM.2014.6736748. [10] G. Rosell-Tarragó, E. Cozzo, and A. Díaz-Guilera, “A complex network framework to model cognition: Unveiling correlation structuresfrom connectivity,” Complexity, 2018, doi: 10.1155/2018/1918753. [11] L. M. Wierenga et al., “A multisample study of longitudinal changes in brain network architecture in 4–13-year-old children,” Hum.Brain Mapp., 2018, doi: 10.1002/hbm.23833 [12] https://byjus.com/gate/bus-topology-notes/ [13] https://www.itrelease.com/2019/06/what-is-star-topology-with-example/ [14] https://www.alamy.com/tree-network-topology-vector-black-linear-flat-style-icon-image270766404.html [15] https://lmntechnohub.blogspot.com/2015/01/hybrid-topology.html [16] https://www.javatpoint.com/tree-topology-advantages-and-disadvantages [17] https://www.edrawsoft.com/article/mesh-topology.html
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Muhammad Arif Bin Jalil. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET64345
Publish Date : 2024-09-25
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

