Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Experimental Study of Plastic Bricks Made from Waste Plastics
Authors: Shraddha Suman Bhoia, Abhijit Mangaraj
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.62459
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
This study describes the use of municipal plastic waste (MPW) in the construction industry. Plastic is a non-biodegradable material that takes thousands of years to decompose and causes soil and water pollution. The amount of plastic waste in municipal solid waste (MSW) is increasing rapidly. Usage is estimated to double every decade. Plastic consumption is high and one of the largest plastic wastes is polyethylene (PE). The use of earth-derived clay materials has caused resource depletion and one of these efforts is the efficient use of plastic waste and laterite quarry waste, along with small amounts of asphalt, to meet the growing demand for traditional building materials, which are less absorbent than laterite bricks. The challenge is to develop alternative building materials, such as brick, that have little but sufficient strength. The use of MPW as a building material, especially in brick production, is one of the promising steps towards sustainable resource and waste management. Plastic waste can partially or completely replace one or more raw materials in brick production. Further research based on recent research and a better understanding of the use of waste plastics in bricks is needed to produce high-quality and durable bricks and to achieve an optimal balance in all aspects, especially in terms of cost and functionality.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Plastics are made up of synthetic organic polymers which are widely used in different applications ranging from water bottles, clothing, food packaging, medical supplies, electronic goods, construction materials, etc. In the last six decades, plastics became an indispensable and versatile product with a wide range of properties, chemical composition and applications. Although, plastic was initially assumed to be harmless and inert, however, many years of plastic disposal into the environment has led to diverse associated problems. Environmental pollution by plastic wastes is now recognized widely to be a major environmental burden, especially in the aquatic environment where there is prolong biophysical breakdown of plastics,detrimental negative effects on wildlife, and limited plastic removal options.
A. Present Scenario Of Waste Generation In India
Globally, plastic production was estimated to be 380 million tonnes in 2018. Since 1950 to 2018, plastics of about 6.3 billion tonnes have been produced worldwide, 9% and 12% of which have been recycled and incinerated, respectively. Plastics of about 5 million tonnes are yearly consumed in UK alone, with only about one-quarter recycled, and the rest landfilled. It has been suggested by researchers that by 2050, oceans might contain more plastics than fish in terms of weight. Yearly, approximately 500 billion plastic bags are used out of which an estimated 13 million tonnes ends up in the ocean, killing approximately 100,000 marine lives.
B. Objective
- To compare strength of plastic bricks with normal clay bricks.
- To vary the percentage of plastic in bricks to determine the strength performance.
- Cost comparison in between plastic bricks and normal clay bricks.
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
Alaa.A.Shakir, et.al (2013) – In the review of utilization of those waste, this paper reviewed recycling various waste material in bricks production. The effects of those wastes on the bricks properties as physical, mechanical properties will be reviewed and recommendations for future research as out comings of this review will be given. This reviewed approach on bricks making from waste is useful to provide potential and sustainable solution.
Maneeth P D, et.al, (2014) - In this paper, bricks of different mix proportions were prepared with varying plastic (PET, PP), laterite soil (passing 2.36mm IS Sieve) and bitumen content, and the bricks were tested for compressive strength and water absorption. This study showed that strength of these bricks was dependent on plastic percentage and minimum 60% of plastic by weight is required for plastic soil bricks by trial and error method. 70% of plastic by weight was considered as the optimum dosage of plastic in the view of workability criteria and 2% of bitumen was taken as optimum binder content which resulted in compressive strength of 8.16N/mm2 which is higher than laterite stone (3.18N/mm2 )and has less water absorption of 0.9536% than laterite stone.
Dinsh.S, et.al, (2016) -This paper is the attempt made to study regard the properties of the bricks and paver blocks which are manufactured using plastic wastes, river sand and some colouring agents like red oxide. Various mix proportion of plastic and river sand (1:2, 1:3, 1:4, 1:5, and 1:6) were made and tested for compressive strength using compressive testing machine and water absorption test. From this study it was concluded that plastic soil bricks possess more advantages like cost effective because the natural resources consumed for the manufacturing of these bricks and paver blocks are very much less when compared to conventional one.
Arvind Singhal, Dr. Om Prakash Netula(2018) - They used the mixture of plastic and stone dust in the molten form in the ratio of 3:7 in standard brick mould for which stone dust was sieved through 4.75 mm using sieve analysis and conducted test on water absorption to be found as 0%. Compressive strength of plastic sand bricks is 5.6 N/mm2 at the compressive load of 96 KN.
S S Chauhan, Bhusan Kumar(2019) - They mixed the river sand and the PET plastic (molten form) in the ratio of 1:2, 1:3, 1:4 for mould size of (230*100*75) mm for which they found maximum compressive strength on the ratio of 1:2 mixture for the same size of the bricks. The water absorption of these bricks was observed less than 5% that is less than conventional clay bricks i.e. 15-20%. However, they failed in maintaining fire resistance property of these bricks.
Aman Kumar, Mainak Biswas,(2020) - Plastic waste which is increasing day by day becomes eyesore and in turn pollutes the environment, especially in high mountain villages where no garbage collection system exists. A large amount of plastic is being brought into the tourist trekking regions are discarded or burned which leads to the contamination of environment and air.
III. COMPONENTS AND SPECIFICATION
A. Cement
Cement is made by heating limestone (calcium carbonate) with small quantities of other materials (such as clay). In this project Ordinary Portland cement of 53 grade conforming to IS456-2000 was used. Tests were carried out on various physical properties of cement and the results are shown in test data of materials. Cement will act as a binding material.
B. Sand
Natural river sand was used as a fine aggregate. The properties of sand were determined by conducting tests as per IS:2386(Part-1). The results are shown in test data of materials. The results obtained from sieve analysis are furnished. The results indicate that the sand conformsto zone 11 of IS:383-1970.

Properties of Sand
|
SLNO |
TESTS |
RESULTS |
|
1 |
Specific Gravity |
2.62 |
|
2 |
Bulk Density |
1690????????/????3 |
|
3 |
Fineness Modulus |
2.92 |
C. Water
Water used for mixing and curing of concrete shall be clean and free from oils, acids, alkalies, salts and organic materials or other substances they may be deleterious to concreteor steel. Portable water shall be used for mixing of concrete. Suspended solid matter in the water shall not exceed more than 200mg/l. The pH value of the water shall not be less than 6.
D. Waste Plastic
Plastics are commonly used substances which play an important role in almost every aspect of our lives. The wide spread generation of plastics waste needs proper end of-life management. The highest amount of plastics is found in container sand packaging’s (i.e. bottles, packaging, cups etc.), but they also are found in durables (e.g. tires, building materials, furniture, etc.) and disposable goods (e.g. medical devices). Diversity of plastics applications is related with their specific properties, low density, easy processing, good mechanical properties, good chemical resistance, excellent thermal and electrical insulating properties and low cost(in comparison toot her materials). Post-production and post-consumer plastics are utilized in a wide range of applications.

IV. METHODOLOGY
A. Process of Casting Plastic Sand Brick
- First, we need to collect the plastic waste and separate it from other wastes.
- Second, we should dry the plastic waste if it is wet and has a content of moisture.We have to use dry plastic waste.
- Then, we crush the plastic waste in small particles by crushing machine.
- Then, the small particles crush into fine size particles.
- The ratio of plastic and stone dust which we use is 3:7.
- The stone dust which we use in manufacturing of bricks / tiles sieved for a size less than 4.75mm using sieve analysis.
- Then, we heated the stone dust on a furnace (Bhatti).
- The fine particles of plastic waste also heated on a furnace (Bhatti) till it is in a liquid form.
- Then, we add the stone dust in to melt plastic.
- Then, we can mix it properly and make a mix.
- Then, we poured the mix into moulds.
- Then keep it the mould for dry and de mould it on next day.
- The weight of the brick is 2.5Kg
B. Fixing the Proportion of Sandand Plastic
For the fabrication of plastics and bricks, plastic and sand are mixed in different proportions and bricks containing different amount of plastic and sand are made. Plastic and rivers and are mixed in different ratios 1:2,1:3,1:4.
The reason behind taking different proportions of plastic and Sand is to find the optimum proportion which gives the desired results. The bricks made of these ratios will further be investigated for various desired properties.
C. Preparation of Brick Mould
The moulds use dare wooden mould sand are made in the carpentry shop. All the side sand surfaces of the mould should be even for the brick to have better surface finish. Both fixed and movable mould scan be used for the purpose. Wooden mould will be cost effective and serve the purpose whereas if better surface finish is needed then cast-iron moulds can be used. Mould size would be (190*90*75)mm Mould.
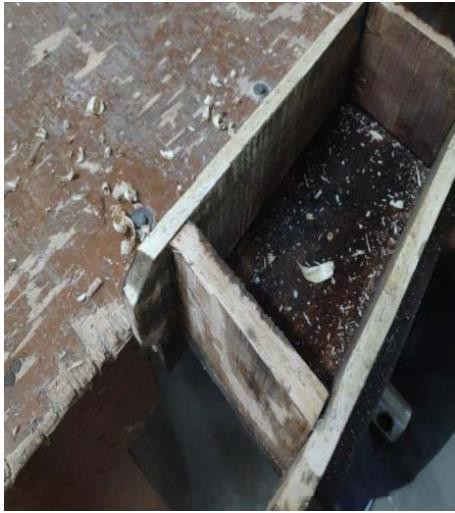

Fig: preparation in the carpentry shop
D. Collection of Material
The process is incredibly simple. Put the dustbin in the canteen for collection of waste bottles. Select the plastic bottles of cold drink sand water from canteens. Bring river sand for plastic brick.IS2386(Part-I) Them ore you collect hemore plastic you will divert from the land fill or clean up out of the environment.

E. Batching
Measurement of materials is known as batching. The waste bottles are rinsed with water and then dried after which the weights of bottles are measured. Sieving of sand is done by 600-micronsieve. And this sand will be used for making bricks. Various proportions of plastic bottles with sand is taken for bricks. The differentratios we use dare 1:2,1:3 and 1:4.Fig:The

Fig: weighing of sand (left) & Fig: Sand sieving process on the sand sieving machine on 600ugauge. Plastic (right) for the batching process
F. Mixd Design
In order to find the plastic soil bricks that they possess high compressive strength with various mix proportions are made and they are tested using compressive testing machine [CTM]. The mix proportions were in ratio of (1:3,1:4,and1:5). These are the ratio which represents the plastic, M-sand respectively.
Mix Design Calculations
1) Ratio(1:2)
Size of brick=19X9X9cm
=0.19X0.09X0.09m
Volume of brick =0.00153m3 Sum of proportion=1+2=3
Amount of plastic=(0.00153/2)x1=(5.1x10-4)x1390……(1390PET density)
Amount of plastic=0.7089kg of plastic. Amount of sand =0.00153x2
2
=(1.02x10-3)x1620….(1620 Sand density)
Amount of sand=1.65kg of sand.
2) Ratio(1:3)
Size of brick =19X9X9cm= 0.19X0.09X0.09m Volume of brick = 0.00153m3
Sum of proportion=1+3=4
Amount of plastic=0.00153x1
2
=(3.825x10-4)x1390…(1390PETdensity)
Amount of plastic=0.53kg of plastic.
Amount of sand=0.00153x3 = (1.14x10-3)x1620….(1620Sand density)
4
Amount of sand=1.85kg of sand
G. Burning
In this burning of plastic bottles is done. Plastic bottles are cut into pieces and then these pieces are put in drum for melting. In the first step stones, drum and fire wood are arranged. The stones hold the drum and the fire wood is ignited. Drum is heated to remove moisture from the drum.
The plastic is then put into the drum and allowed to melt.
H. Mixing
Pieces of plastic are added into drum for melting until the proportion required by us is achieved. River sand is used for addition in plastics and mixture. When the temperature of the melted plastic in the drum is around 180oC-200oC then the sand is added into the drum. The rivers and the melted plastic is stirred continuously so that both gets bonded perfectly. As the plastic pieces melt it start getting bonding with the sand particles and hence the mixture required for brick is created.
I. Moulding
In moulding process, the prepared mixture is then filled into wooden mould and then compressed by tamping rod. The pressure is applied by the tampering rod so as the mixture gets filled properly in the mould. Then it is left for cooling in air but before filling the mould apply oil on the walls of mould so that at last brick can be removed easily. The application of oil on the inner surfaces of the mould is must as after solidification the brick will not come out easily and to remove the mould some pressure must be applied that would wear the edges of the brick. So proper oiling is needed before filling the mixture in the mould. The brick then can be removed from mould after 24hours.
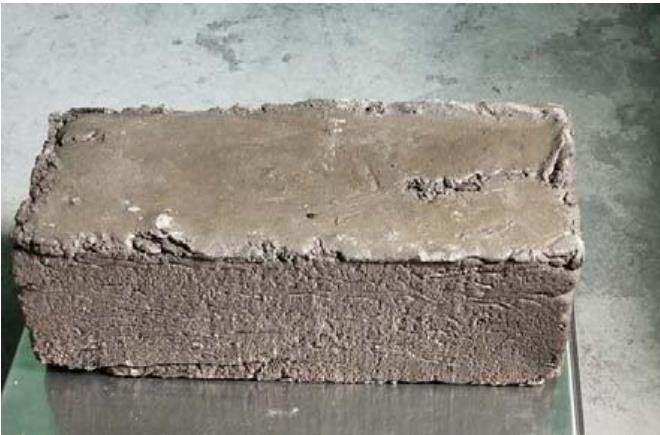

Fig: Plastic Sand Brick after removing it from the mould
V. RESULT
A. Tests On Bricks
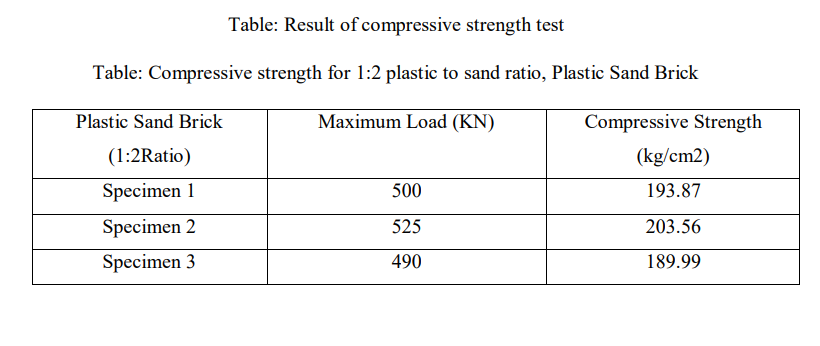
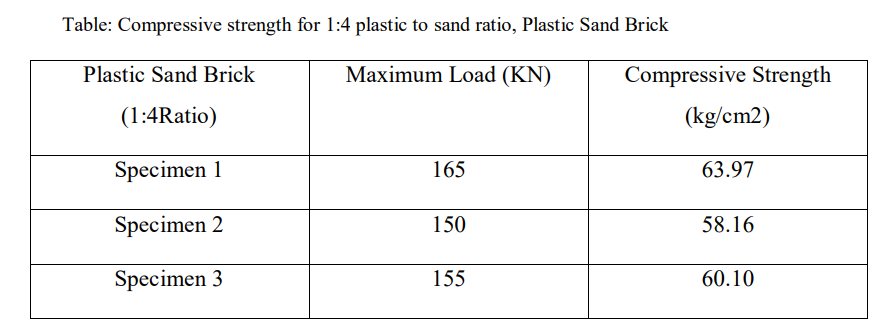
Compression Strength Test (bs 5628: part 1: 1992)
In this test, the cubical brick specimen is placed in the compression strength testing machine. After placing it we will apply the load on the brick without any shock. The load will be increased at a rate of 140kg/cm2 min continuously till the specimen’s resistance to increasing load breaks down and it cannot withstand any greater load further. Recording the maximum load applied to the brick specimen and the appearance and type of failure is also noted along with any unusual features.
COMPRESIVE STRENGTH= MAXIMUM LOAD APPLIED
SPECIMEN AREA
COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH = F/A
Where, F - Maximum load
A – Specimen Area (mm2)



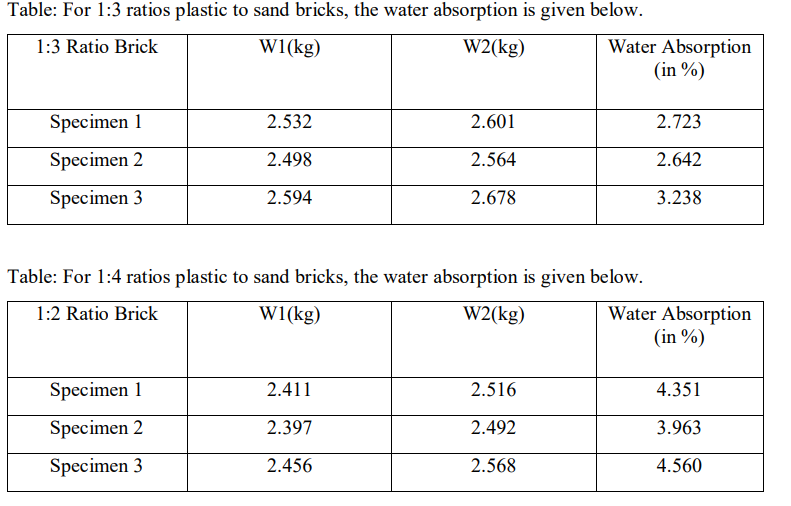
B. Water Absorption Test (IS 1077-1970)
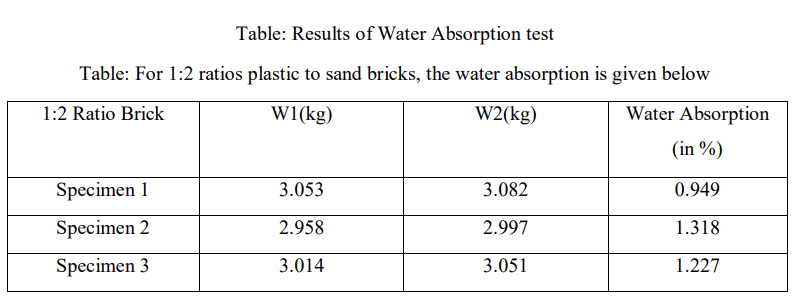
In this test at first the bricks are weighed in total dry conditions. Then they will be allowed to be dipped in fresh water for about 24 hours in a container. The bricks are taken out of the water after 24 hours and are wiped with a cloth. The wet brick is weighed using a weighing machine. For the calculation of water absorption, the difference between wet brick and dry brick is done. The difference is the amount of water absorbed by the brick. After that the percentage of water absorption is calculated using the data. Water absorption of bricks tells about the bonding of bricks with mortar. Although other factors such as grooves and design on bricks also improve the bonding. For sand bricks which have less water absorptivity leaner mortar layer is used for bonding bricks and mortar. Greater quality bricks absorb less amount of water. For a good quality brick, the water absorption should be less than 20% of its own weight.
Water absorption = {[Weight of wet brick–Weight of dry brick]/Weight of dry brick} *100
C. Efflorescence Test
The standard used for the test is ISS 1077-1970. It is done to detect the presence of alkalis in PET bricks which is harmful. The alkalis form a grey or white patch on the surface of the brick. A flat bottom container is used in which sufficient distilled water is poured. The depth of immersion is 25mm.The brick is immersed into the distilled water and left for 24 hours. The container is covered with a glass sheet to prevent excessive evaporation. After that the brick is removed from the container and left to dry for the same amount of time wherein the same amount of water must have evaporated from the open container without the brick or the sheet.
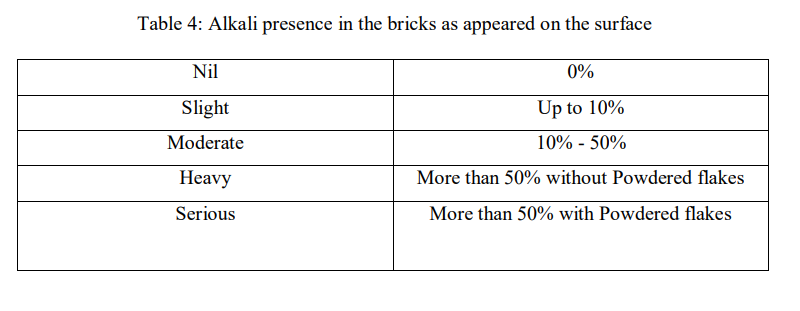
The efflorescence in the brick can be categorised into the above categories on the basis of area covered by salt/alkalis.
D. Fire Resistance Test
The standard used for the test is BIS 3809 1979. The plastic alone is readily susceptible if not flammable to elevated temperatures and in case of fire, the sand and plastic mixture may withstand temperatures that plastics alone usually cannot.
It has been observed that the structural integrity of the bricks holds very well up to 180oC. In this test we will first heat and maintain the brick at the standard testing temperature in the furnace and then we will do the compressive strength test to check whether the properties change or not.
Conclusion
The proposed project presented above intends to resolve in reducing the plastic waste disposal problem as it utilizes the waste even in its finest form and converts that useless material into a useful construction material. Extruder machine plays a prominent role in the conversion of waste plastic into its melted form. Also, extruder does not possess any threats to the environment and hence can be used without any restriction. It also helps in reducing the usage of natural resources which are utilized during the manufacturing of burnt bricks, also it reduces the pollution which is generated from kiln during brick manufacturing. The final end product can be used as brick, which is having a higher strength than conventional brick. Also, the water absorption capacity is higher in comparison to conventional brick with a lower weight. Its uses are not restricted as only brick; it can even be utilized as a building block by increasing the dimension of the mould. Also, it reduces the use of wire used for fencing. Floor tiles, sleepers, etc. can also be produced from it. This brick also turns out to be economical than conventional brick, by reducing the cost of incinerators for burning purpose and landfills.
References
[1] SSChauhan, BhusanKumar, PremShankarSingh, AbuzaidKhan, HrithikGoyal, ShivankGoyal, “Fabrication and testing of Plastic Sand Bricks” on ICCEMME 2019. [2] Rajarapu Bhushaiah, ShaikMohammad, D.SrinivasaRao, “An Overview of Study of Plastic Bricks Made From Waste Plastic” International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) (April2019) [3] V.Velumurugan, R.GokulRaj, A.Harinisree, “AnOverview of Rebuilding of Plastic Waste to Pavement Bricks” International Journal for Research in Applied science & Engineering and Technology (April2019) [4] ArvindSinghal, Dr.OmPrakashNetula, “Utilization of plastic waste in manufacturing of plastics and bricks” on 17th June 2018 at 3rd International conference on New Frontiers of Engineering, Science, Management and Humanities.ISBN:978-93-87433-29-8. [5] SitiNabilahAmir&NurZulaikhaYusof,“PlasticinBrickApplication”on4thSeptember2018byLUPINEPUBLISHERS.ISSN:2637-4668.DOI:10.32474/TCEIA.2018.03.000152. [6] AiswariaK, Khansa Abdulla, EB Akhil, Haritha LakshmiVG, Jerin Jimmy “Manufacturing and Experimental Investigation of Bricks with Plastic And M-Sand” International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology Vol.7, Issue6, June 2018 [7] RonakShah, Himanshu Garg, Parth Gandhi, Rashmi Patil, Anand Daftardar. “Study of plastic dust brick made from waste plastic.” on International journal of mechanical and production engineering. ISSN:2320-2092, volume-5, issue-10, OCT-2017. [8] A.S. Manjrekar, Ravi, D.Gulpatil, VivekP. Patil, RanjitS. Nikam, ChetaliM.Jeur(2017). \"Utilization of Plastic Waste in Foundry Sand Bricks\", International Journal for Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology(IJRASET). [9] Loukham GerionSingh, Pongsumbam BossSingh, Suresh Thokchom(2017).\"Manufacturing Bricks from Sand and Waste Plastics\",National Conference on Innovations in Science and Technology(NCIST-17).
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Shraddha Suman Bhoia, Abhijit Mangaraj. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET62459
Publish Date : 2024-05-21
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

