Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs) and Application Security
Authors: Samikya Reddy Balguri
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.64230
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
This article explores the critical component in safeguarding personal information in the digital age. This comprehensive exploration delves into the definition, scope, and key characteristics of PETs, examining their crucial role in modern data protection. The article discusses fundamental PET categories, including data encryption and anonymization/pseudonymization techniques, and their implementation in application security. It highlights the importance of Privacy Impact Assessments, Privacy by Design principles, and strong access controls in effectively integrating PETs into security strategies. By addressing the challenges of balancing data utility with privacy protection, PETs offer organizations a pathway to compliance with stringent data protection regulations while building trust with users and gaining a competitive edge in an increasingly privacy-conscious market.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
In an era dominated by digital interactions and data-driven decision-making, the protection of personal information has become a paramount concern for individuals, organizations, and governments alike. The rapid advancement of technology, while bringing unprecedented convenience and efficiency, has also ushered in an age of increased vulnerability to data breaches, unauthorized access, and privacy infringements. In 2023 alone, the average cost of a data breach reached a staggering $4.45 million,
marking a 15% increase over three years [1]. This alarming trend underscores the critical need for robust security measures that go beyond traditional approaches.
Enter Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs), a suite of innovative tools and techniques designed to safeguard personal information and ensure data privacy throughout the entire data lifecycle.
PETs have emerged as a crucial component of modern application security, offering a proactive approach to privacy protection that complements and enhances existing security frameworks. These technologies aim to minimize the collection and exposure of sensitive data while maintaining the utility and functionality of applications and services.
The significance of PETs in today's digital ecosystem cannot be overstated. As regulatory landscapes evolve with the introduction of stringent data protection laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, organizations are under increasing pressure to implement effective privacy measures. PETs provide a technological response to these legal requirements, enabling companies to demonstrate compliance and build trust with their users [2].
Moreover, the adoption of PETs extends beyond mere regulatory compliance. In an age where data is often referred to as the "new oil," the ability to process and analyze information while preserving individual privacy has become a competitive advantage. Companies that successfully implement PETs can unlock the value of their data assets while mitigating the risks associated with data breaches and privacy violations. This dual benefit of PETs – enhancing privacy while enabling data utility – positions them as a cornerstone of modern data governance strategies.
As we delve deeper into the world of Privacy-Enhancing Technologies, this article will explore the various types of PETs, their applications in real-world scenarios, and their integration into the broader framework of application security. From advanced encryption techniques to innovative data anonymization methods, we will examine how these technologies work in concert to create a robust privacy infrastructure. By understanding the principles and practices of PETs, developers, security professionals, and business leaders can make informed decisions about implementing these technologies to protect their users' privacy and maintain the integrity of their digital ecosystems.
The journey towards a more privacy-centric digital world is complex and ongoing. As threats evolve and new challenges emerge, so too must our approaches to privacy and security. Privacy-Enhancing Technologies represent a significant step forward in this journey, offering powerful tools to safeguard personal information in an increasingly interconnected world. Through a comprehensive exploration of PETs, this article aims to equip readers with the knowledge and insights necessary to navigate the intricate landscape of data privacy and application security in the modern era.
II. UNDERSTANDING PRIVACY-ENHANCING TECHNOLOGIES (PETS)
In an era where data breaches and privacy concerns are increasingly prevalent, Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs) have emerged as a critical component in safeguarding personal information. PETs encompass a diverse range of tools and techniques designed to protect individual privacy throughout the entire data lifecycle, from collection and storage to processing and sharing [3].
Definition and Scope
Privacy-Enhancing Technologies can be defined as a set of coherent computer technologies that protect privacy by eliminating or minimizing personal data without losing the functionality of the information system [3]. These technologies go beyond traditional security measures by specifically addressing the privacy aspects of data handling and processing.
The scope of PETs is broad and continually expanding, covering various aspects of data protection:
- Data Minimization: PETs include technologies that reduce the amount of personal data collected or processed. This adheres to the principle that organizations should only collect and retain the minimum amount of personal data necessary for their purposes.
- Data Anonymization and Pseudonymization: These techniques remove or modify identifying information within datasets, making it difficult or impossible to link data back to specific individuals.
- Encryption: Advanced encryption methods secure data both at rest and in transit, ensuring that even if data is intercepted or accessed, it remains unreadable without the proper decryption keys.
- Access Control: Sophisticated systems manage and restrict access to sensitive information, ensuring that only authorized individuals can view or manipulate personal data.
- Transparency Tools: These technologies provide individuals with visibility into how their data is being used, collected, and shared, empowering users with greater control over their personal information.
III. KEY CHARACTERISTICS OF PETS
Privacy-Enhancing Technologies are characterized by several key features:
- Proactive Rather than Reactive: PETs aim to prevent privacy issues before they occur, rather than offering remedies for violations after the fact.
- Default Privacy Protection: Many PETs are designed to offer maximum privacy protection automatically, without requiring user intervention.
- Privacy Embedded into Design: Privacy is an integral part of the system, not an add-on feature.
- Full Functionality: PETs aim to deliver robust privacy protection without compromising system functionality.
- End-to-End Security: These technologies protect the entire lifecycle of the data involved.
- Visibility and Transparency: PETs often include features that make data practices more transparent to users.
- Respect for User Privacy: The overarching goal of PETs is to keep the interests of the individual uppermost by offering strong privacy defaults, appropriate notice, and user-friendly options [4].
- The Role of PETs in Modern Data Protection
As data becomes increasingly central to business operations and decision-making, the role of PETs in modern data protection cannot be overstated. These technologies offer several crucial benefits:
- Regulatory Compliance: PETs help organizations meet the requirements of data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States.
- Trust Building: By implementing robust privacy protections, organizations can build trust with their users and customers, differentiating themselves in an increasingly privacy-conscious market.
- Data Utility vs. Privacy Balance: PETs enable organizations to derive value from data while minimizing privacy risks, striking a balance between data utility and privacy protection.
- Risk Mitigation: By minimizing the collection and exposure of personal data, PETs significantly reduce the risk and potential impact of data breaches.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, so too do Privacy-Enhancing Technologies. From advanced encryption methods to innovative anonymization techniques, PETs are constantly adapting to address new privacy challenges and threats. As such, they represent a critical area of focus for organizations seeking to protect user privacy and maintain trust in an increasingly data-driven world.
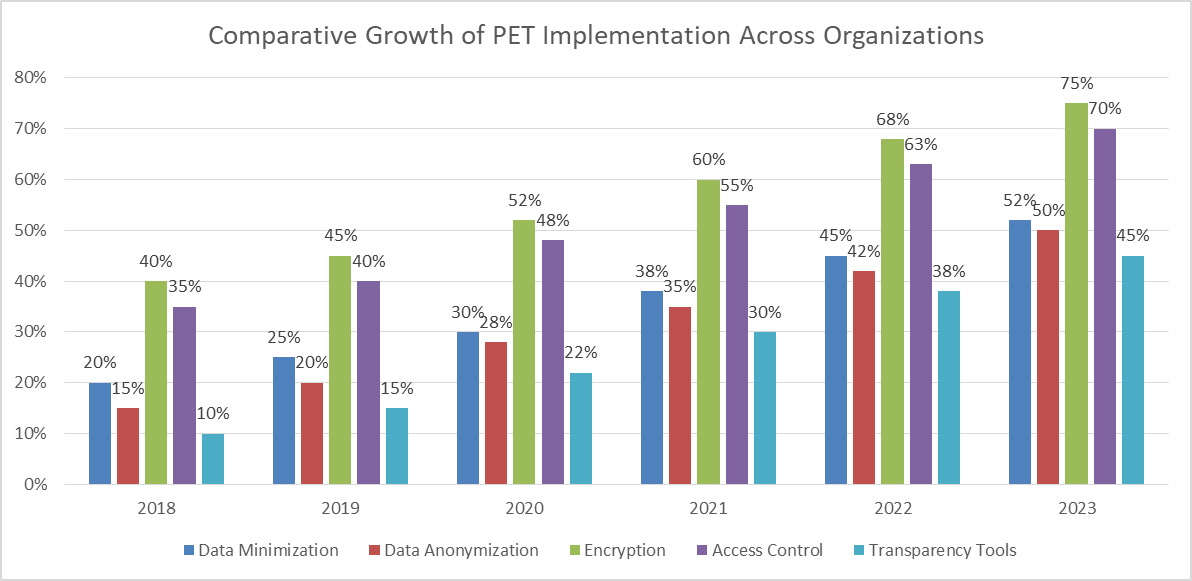 Fig. 1: Trends in Adoption of Privacy in percentage-Enhancing Technologies (2018-2023) [1, 2]
Fig. 1: Trends in Adoption of Privacy in percentage-Enhancing Technologies (2018-2023) [1, 2]
IV. KEY PRIVACY-ENHANCING TECHNOLOGIES
Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs) encompass a wide range of tools and techniques designed to protect personal information throughout the data lifecycle. As data breaches and privacy concerns continue to rise, the importance of PETs in safeguarding sensitive information has become paramount. This article focuses on two fundamental categories of PETs: Data Encryption and Data Anonymization/Pseudonymization.
A. Data Encryption
Data encryption is widely recognized as one of the most effective ways to secure sensitive data. It involves encoding information to make it unreadable without the proper decryption key. The strength of modern encryption algorithms makes it extremely difficult for unauthorized parties to access the protected data, even if they manage to obtain the encrypted files [5].
B. Encryption at Rest
Encryption at rest protects data stored on disk from unauthorized access. This is crucial for safeguarding data in case of physical theft of devices or unauthorized access to storage systems. Key methods include:
- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES): AES is a symmetric encryption algorithm widely used for securing sensitive files and databases. It offers different key lengths (128, 192, and 256 bits) for varying levels of security. AES-256, with its 256-bit key length, is considered highly secure and is used by governments and financial institutions worldwide.
- File-level Encryption: This method involves encrypting individual files or folders to protect specific data assets. It allows for granular control over which data is encrypted, enabling organizations to prioritize their most sensitive information. File-level encryption is particularly useful in collaborative environments where different users may need access to different files.
- Full Disk Encryption (FDE): FDE encrypts entire storage devices to safeguard all data on a system. This method provides comprehensive protection against physical theft of devices. When implemented correctly, FDE ensures that even if a device is lost or stolen, the data remains inaccessible without the proper authentication.
C. Encryption in Transit
Encryption in transit secures data as it travels across networks, preventing interception and eavesdropping. This is essential for protecting data during transmission over potentially insecure networks like the internet. Common protocols include:
- Transport Layer Security (TLS): TLS is a cryptographic protocol that provides end-to-end security for data sent between applications over the Internet. It's the successor to SSL and is widely used to secure web browsing, email, instant messaging, and voice over IP (VoIP). TLS uses a combination of symmetric and asymmetric encryption to ensure both the confidentiality and integrity of data in transit.
- HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure): HTTPS is an extension of HTTP that uses TLS to encrypt all communication between a client and a server. It's essential for securing online transactions and protecting user privacy on the web. HTTPS not only encrypts the data exchanged but also authenticates the website, protecting against man-in-the-middle attacks.
V. DATA ANONYMIZATION AND PSEUDONYMIZATION
Data anonymization and pseudonymization techniques aim to protect individual privacy by altering or removing identifying information from datasets. These methods are crucial for maintaining data utility while adhering to privacy regulations, allowing organizations to analyze and share data with reduced risk of exposing individual identities [6].
A. Anonymization
Anonymization involves transforming data in such a way that individuals cannot be identified directly or indirectly. This is particularly important for research and analytics where individual identities are not necessary. Common techniques include:
- Generalization: This method involves replacing specific values with broader categories. For example, replacing exact age with age ranges (e.g., 20-30, 31-40) or replacing specific job titles with more general job categories. Generalization helps to obscure individual identities while still preserving the overall statistical properties of the dataset.
- Suppression: This technique involves removing certain attributes or records entirely from the dataset. It's often used for highly sensitive or uniquely identifying information. While suppression can be effective at protecting privacy, it needs to be balanced against the need to maintain data utility.
- k-anonymity: This is a model of privacy that ensures that each record is indistinguishable from at least k-1 other records for certain identifying attributes. For instance, in a 3-anonymous dataset, each record would be identical to at least two other records when considering the specified attributes. K-anonymity provides a quantifiable measure of anonymity, allowing organizations to balance privacy protection with data utility.
B. Pseudonymization
Pseudonymization replaces identifying fields within a dataset with pseudonyms or tokens, making it difficult to identify individuals without additional information. This technique helps maintain data utility while enhancing privacy. Methods include:
- Tokenization: This involves replacing sensitive data with non-sensitive placeholder tokens. The original data is stored securely elsewhere, with the tokens acting as references. Tokenization is particularly useful in financial systems for protecting credit card numbers, allowing organizations to process transactions without exposing the actual card details.
- Data Masking: This method obscures original data with modified content of a similar type. For example, replacing real names with fictional names, or scrambling digits in a number while preserving its format. Data masking allows organizations to use realistic-looking data for testing and development without risking exposure of real personal information.
These Privacy-Enhancing Technologies form the foundation of many data protection strategies. When implemented correctly, they can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information, while still allowing organizations to derive value from their data assets. As privacy regulations become more stringent and cyber threats more sophisticated, the adoption and advancement. PETs will continue to play a crucial role in safeguarding personal information in the digital age.
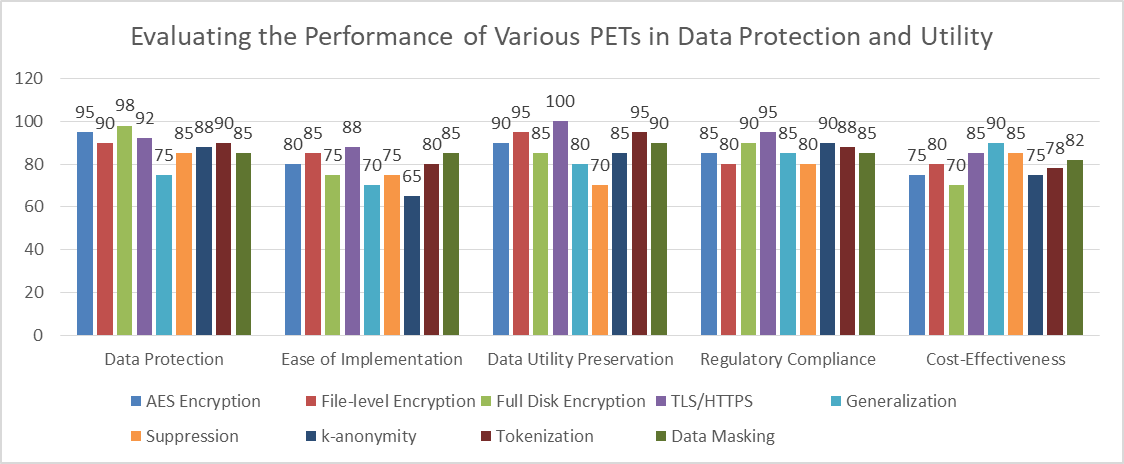
Fig. 2: Trends in Adoption of Privacy in percentage-Enhancing Technologies (2018-2023) [5, 6]
VI. IMPLEMENTING PETS IN APPLICATION SECURITY
In an era where data breaches and privacy violations are increasingly common, integrating Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs) into application security has become paramount. PETs not only protect user data but also help organizations maintain compliance with stringent privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. This article explores best practices for effectively implementing PETs in application security.
VII. CONDUCT PRIVACY IMPACT ASSESSMENTS (PIAS)
Privacy Impact Assessments are crucial tools for identifying and mitigating privacy risks associated with data processing activities. Regular PIAs help organizations proactively address potential privacy issues throughout the application lifecycle [7].
Key steps in conducting a PIA include:
- Identify Personal Data: Thoroughly catalog all personal data collected and processed by the application. This includes direct identifiers (e.g., names, email addresses) and indirect identifiers that could be used to single out individuals.
- Assess Necessity and Proportionality: Evaluate whether the data processing is necessary for the intended purpose and proportionate to the benefits. This aligns with the data minimization principle of many privacy regulations.
- Evaluate Risks: Conduct a comprehensive analysis of potential risks to individuals' rights and freedoms. This might include risks of data breaches, unauthorized access, or misuse of personal data.
- Determine Mitigation Measures: Based on the identified risks, develop and implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to address these risks. This might include implementing specific PETs, enhancing access controls, or modifying data processing practices.
- Document and Review: Maintain detailed documentation of the PIA process and findings. Regularly review and update the PIA as the application evolves or new risks emerge.
VIII. ADOPT A PRIVACY BY DESIGN APPROACH
Development lifecycle, organizations can ensure that privacy is an integral part of the system, not an afterthought [4].
|
Practice |
Type |
Importance (1-10) |
Implementation Complexity (1-10) |
Privacy Protection Impact (1-10) |
|
Identify Personal Data |
PIA |
9 |
7 |
8 |
|
Assess Necessity and Proportionality |
PIA |
8 |
8 |
9 |
|
Evaluate Risks |
PIA |
10 |
9 |
9 |
|
Determine Mitigation Measures |
PIA |
9 |
8 |
10 |
|
Document and Review |
PIA |
7 |
6 |
7 |
|
Proactive not Reactive |
PbD |
8 |
7 |
9 |
|
Privacy as the Default |
PbD |
9 |
8 |
10 |
|
Privacy Embedded into Design |
PbD |
10 |
9 |
10 |
|
Full Functionality |
PbD |
8 |
9 |
8 |
|
End-to-End Security |
PbD |
9 |
9 |
9 |
|
Visibility and Transparency |
PbD |
8 |
7 |
8 |
|
Respect for User Privacy |
PbD |
10 |
8 |
9 |
Table. 1: Evaluating the Effectiveness of PIA and PbD Practices in Enhancing Application Security [7, 4]
Key principles of Privacy by Design include:
- Proactive not Reactive; Preventative not Remedial: Anticipate and prevent privacy-invasive events before they occur. This involves thorough planning and risk assessment during the design phase.
- Privacy as the Default Setting: Ensure that personal data is automatically protected in any given IT system or business practice. No action should be required on the part of the individual to protect their privacy.
- Privacy Embedded into Design: Privacy should be an integral component of the system's core functionality. It should not be treated as an add-on feature.
- Full Functionality – Positive-Sum, not Zero-Sum: Demonstrate that it is possible to have both privacy and security, not one at the expense of the other. This often involves creative solutions that satisfy multiple, sometimes competing, objectives.
- End-to-End Security – Full Lifecycle Protection: Ensure strong security measures are in place throughout the entire lifecycle of the data involved. This includes secure data collection, storage, use, and timely destruction at the end of the process.
- Visibility and Transparency: Keep the business practices and technologies involved open and visible to users and providers alike. This builds trust and enables verification of stated promises and objectives.
- Respect for User Privacy: Above all, keep the interests of the individual uppermost. Offer strong privacy defaults, appropriate notice, and user-friendly options.
|
Principle |
Importance (1-10) |
Implementation Difficulty (1-10) |
Impact on User Trust (1-10) |
|
Proactive not Reactive |
9 |
8 |
8 |
|
Privacy as the Default Setting |
10 |
7 |
9 |
|
Privacy Embedded into Design |
9 |
9 |
8 |
|
Full Functionality |
8 |
9 |
7 |
|
End-to-End Security |
10 |
9 |
9 |
|
Visibility and Transparency |
8 |
7 |
10 |
|
Respect for User Privacy |
10 |
8 |
10 |
Table. 2: Comparative Analysis of Privacy by Design Principles in PET Implementation [4]
A. Implement Strong Access Controls
Robust access control mechanisms are essential for limiting data exposure and reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Key strategies include:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA for all user accounts, especially those with elevated privileges. This adds an extra layer of security beyond just passwords.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Design and enforce a least-privilege access model where users are only given access to the data and functions necessary for their role. Regularly review and update these access rights as roles change.
- User Activity Monitoring: Implement systems to monitor and log user activities, especially those involving sensitive data. This can help detect unusual patterns that might indicate a security breach.
- Regular Access Reviews: Conduct periodic reviews of user access rights to ensure they remain appropriate and necessary.
B. Regularly Update and Patch Systems
Keeping all software components up-to-date is crucial for addressing known vulnerabilities. This includes:
- Robust Patch Management: Establish a comprehensive process for identifying, testing, and applying patches across all systems and applications.
- Vulnerability Assessments: Conduct regular scans and assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities in your systems.
- Automated Updates: Where possible, implement automated update mechanisms to ensure timely application of security patches.
- Software Inventory: Maintain a detailed inventory of all software components and their versions. This helps in tracking which systems need updates and identifying potential vulnerabilities.
C. Provide User Controls
Empowering users with control over their data not only builds trust but is also a requirement of many privacy regulations. Consider implementing:
- Granular Privacy Settings: Provide clear, easy-to-understand privacy settings that allow users to control how their data is collected, used, and shared.
- Data Access and Portability: Offer tools for users to access, download, or delete their personal data. This aligns with the "right to access" and "right to be forgotten" principles in regulations like GDPR.
- Consent Management: Implement robust consent mechanisms that allow users to give or withdraw consent for specific data processing activities.
- Transparency Reports: Provide clear, accessible information about how user data is used, protected, and shared with third parties.
D. Conduct Regular Security Audits
Regular security assessments are crucial for identifying and addressing potential privacy vulnerabilities. This should be an ongoing process that includes:
- Internal and External Audits: Conduct both internal security reviews and engage external auditors for an unbiased assessment.
- Comprehensive Testing: Use a combination of automated tools and manual testing to thoroughly evaluate your systems' security.
- Prompt Remediation: Address identified vulnerabilities promptly, prioritizing based on risk and potential impact.
- Documentation and Tracking: Maintain detailed records of all identified issues, remediation efforts, and ongoing monitoring.
E. Train Development Teams
Creating a culture of privacy within the organization is crucial for effective PET implementation. Comprehensive training should cover:
- Privacy Fundamentals: Ensure all team members understand basic privacy concepts, relevant laws, and regulations.
- PET Implementation: Provide hands-on training on specific Privacy-Enhancing Technologies and how to integrate them into application development.
- Secure Coding Practices: Train developers in secure coding techniques and best practices for preventing common vulnerabilities.
- Ethical Considerations: Discuss the ethical implications of privacy in technology and the responsibility developers have in protecting user data.
- Ongoing Education: Provide regular updates and refresher courses to keep the team informed about evolving threats and new privacy-enhancing technologies.
By following these best practices, organizations can effectively integrate Privacy-Enhancing Technologies into their application security strategies. This not only protects user privacy but also helps maintain compliance with regulations, build user trust, and differentiate the organization in an increasingly privacy-conscious market.
Conclusion
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs) stand at the forefront of protecting personal information and maintaining data privacy. By implementing PETs such as robust encryption, data anonymization, and pseudonymization techniques, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information. The integration of PETs into application security strategies not only aids in regulatory compliance but also fosters trust with users and provides a competitive advantage. As privacy regulations become more stringent and cyber threats more sophisticated, the adoption and advancement of PETs will play an increasingly crucial role in shaping the future of data protection. It is imperative for developers, security professionals, and business leaders to stay informed about emerging PETs and to cultivate a culture of privacy within their organizations, ensuring that privacy remains a fundamental right in our increasingly interconnected digital world.
References
[1] IBM Security, \"Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023,\" IBM, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.ibm.com/reports/data-breach. [Accessed: 04-Sep-2024]. [2] G. Danezis, J. Domingo-Ferrer, M. Hansen, J.-H. Hoepman, D. Le Métayer, R. Tirtea, and S. Schiffner, \"Privacy and Data Protection by Design - from policy to engineering,\" European Union Agency for Network and Information Security (ENISA), Dec. 2014. [Online]. Available: https://www.enisa.europa.eu/publications/privacy-and-data-protection-by-design. [Accessed: 04-Sep-2024]. [3] G. Danezis and S. Gürses, \"A critical review of 10 years of Privacy Technology,\" Proceedings of Surveillance Cultures: A Global Surveillance Society?, 2010. [Online]. Available: https://homes.esat.kuleuven.be/~sguerses/papers/DanezisGuersesSurveillancePets2010.pdf [4] A. Cavoukian, \"Privacy by Design: The 7 Foundational Principles,\" Information and Privacy Commissioner of Ontario, 2011. [Online]. Available: https://privacy.ucsc.edu/resources/privacy-by-design---foundational-principles.pdf [5] M. Bellare, A. Desai, E. Jokipii, and P. Rogaway, \"A concrete security treatment of symmetric encryption,\" in Proceedings 38th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, 1997, pp. 394-403. [Online]. Available: https://doi.org/10.1109/SFCS.1997.646128 [6] L. Sweeney, \"k-anonymity: A model for protecting privacy,\" International Journal of Uncertainty, Fuzziness and Knowledge-Based Systems, vol. 10, no. 05, pp. 557-570, 2002. [Online]. Available: https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218488502001648 [7] D. Wright, \"The state of the art in privacy impact assessment,\" Computer Law & Security Review, vol. 28, no. 1, pp. 54-61, 2012. [Online]. Available: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clsr.2011.11.007
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Samikya Reddy Balguri. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET64230
Publish Date : 2024-09-13
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

