Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Corporate Social Responsibility
Authors: Arun Kumar S, Chaitra , Fiza , Shreya
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.58024
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is recognized as a strategic and long-term investment that brings about various economic advantages for companies. Consistent implementation of CSR not only enhances consumer preference for products but also attracts interest from potential investors, making CSR an innovative and continuous marketing tool that significantly contributes to a company\'s success. This paper explores the impact of Corporate Social Responsibility Disclosure (CSRD) and Leverage on Firm Value, with Profitability acting as the moderating variable. Analytical tools such as Moderated Regression Analysis (MRA) and Multiple Linear Regression are employed in this study, utilizing a dataset covering 68 firm-years of information from listed companies in Indonesia, including CSR reports from 2012 to 2015.The findings reveal that leverage has a substantial influence on firm value, whereas CSRD alone does not exhibit a significant effect on firm value. Additionally, the profitability variable is identified as an effective moderator, strengthening the correlation between corporate social responsibilities and firm value, as well as reinforcing the relationship between leverage and firm value. These results have critical implications for practitioners, especially in shaping CSR disclosure strategies to effectively address firm value considerations.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a voluntary business strategy where companies willingly take responsibility for their impact on stakeholders, the environment, and society. Beyond legal obligations, CSR aims to positively contribute to the company's well-being, stakeholders, and the broader community. Companies adopting CSR hold themselves accountable to internal values, making it a cornerstone for their initiatives. Large corporations, recognizing the importance of societal contribution, often embrace CSR as a deliberate strategy, setting ethical benchmarks for the industry. This concept is gaining popularity, with businesses considering financial, social, and environmental consequences. According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO, 2022), CSR involves achieving a balance between economic, environmental, and social aspects, known as the "Triple-Bottom-Line-Approach," addressing shareholder and stakeholder expectations. CSR is a voluntary cooperation to enhance community well-being, recognized by the World Bank Group (2004) for its positive contribution to societal goals. It involves managing costs and benefits for internal and external stakeholders, including employees, shareholders, investors, customers, suppliers, civil society, and community groups. The European Commission (2006) underscores government's crucial role in CSR, even though it remains voluntary, emphasizing collaboration between developed and developing countries, as highlighted by the COVID-19 pandemic. This passage discusses the strategic aspect of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and the growing interest in its implementation by organizations. CSR is seen as an opportunity for companies, driven by top management's vision and values, aiming to differentiate themselves strategically. The focus is on extrinsic CSR practices, emphasizing the organization's desire for returns from benefiting direct and indirect stakeholders. Despite CSR being in the academic and industrial spotlight since the 1950s, its implementation has not received adequate attention until recent years. Scholars are increasingly exploring how CSR is implemented, leading to the emergence of a budding field of research.
The text identifies the lack of comprehensive reviews on CSR implementation, prompting the need for a multi-level and multi-dimensional perspective. It proposes an integrative framework for CSR implementation, defining it as a process that includes raising awareness, embedding values, internal and external communication, and progress evaluation. The study aims to fill the knowledge gap in CSR implementation literature and contribute to future research prospects. The review is guided by the growing dedication of organizations to CSR, their interest in strategic CSR, and the acknowledgment among scholars of the importance of understanding how CSR strategies are implemented.
II. LITERATURE SURVEY
some experts believed that a company's only responsibility is making profits, as long as it follows the rules. However, others, like Bowen, argued that businesses should also consider societal goals and values.
Definitions of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) vary, but it generally involves businesses voluntarily contributing to social and environmental well-being. The triple bottom line idea, focusing on People-Planet-Profit, gained popularity, emphasizing the importance of economic, social, and environmental aspects. Despite this, turning these theories into practical guidance for businesses remains a challenge. We need a comprehensive theory that considers economic, political, social, and ethical factors for a balanced business and society relationship. [1].
The conventional gauge of corporate success revolves around generating profits for shareholders, often overlooking the broader impact on stakeholders. Early attempts to address social issues within corporations introduced the Corporate Social Response matrix by Preston in 1977, evaluating corporate actions through stages of awareness, analysis, planning, and response. Donna Wood further developed the Corporate Social Performance (CSP) concept, creating a framework that scrutinizes social responsibility across business processes, policies, programs, and outcomes. The aim of CSP is to enhance corporate behaviour for the betterment of society. Porter and Kramer delved into the connection between CSR and a company's competitive advantage, presenting the idea of "shared value," where both companies and society derive mutual benefits. This includes advantages such as an improved reputation and business opportunities resulting from CSR activities. Laszlo and Zhexembayeva argued that companies fostering stakeholder value can secure a competitive edge through "embedded sustainability," integrating environmental and social values into the core of business operations. Rather than treating CSR as an isolated activity, companies should seamlessly incorporate sustainability into their overall business strategies. [2].
For the past three decades, corporate executives have grappled with the question of a firm's responsibility to society. Initially, the focus was on providing maximum financial returns to shareholders, but this perspective shifted as societal expectations broadened. The establishment of governmental bodies in the early 1970s, Environmental Protection Agency and the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission emphasized the acknowledgment of the environment, employees, and consumers as valid stakeholders. underscored the recognition of the environment, employees, and consumers as legitimate stakeholders. Corporate leaders now face the challenge of balancing commitments to shareholders with obligations to a widening array of stakeholders who possess legal and ethical rights. [3].
The research sample comprises 935 companies, with 422 being members of the UNGC and 513 non-members. Additionally, the sample is diversified based on decisions about non-financial reporting. Among the companies, 50% used independent assurance for non-financial information. Excluding entities from countries where assurance is mandatory, 46% of 729 companies used external assurance. The companies vary in experience, with the majority having a medium level of experience in preparing non-financial reports and seeking independent assurance. This diversity in the research sample allows for a comprehensive exploration of voluntary corporate social responsibility reporting and assurance practices. [4].
The article discusses the role of CSR fund companies in the contemporary business landscape where corporate social responsibility (CSR) is a crucial aspect of a company's strategy. CSR fund companies act as intermediaries, managing and distributing funds for CSR initiatives, facilitating alignment with corporate goals, and handling administrative tasks associated with charitable donations. Working with CSR fund companies offers advantages such as expertise in identifying impactful projects, streamlining philanthropic efforts, and enhancing transparency and accountability. These organizations contribute significantly to creating a sustainable future by channelling resources towards environmental and social causes. CSR fund companies are expected to play an increasingly vital role as the importance of CSR grows, with closer collaborations between businesses and these entities to address complex societal challenges.
CSR fund companies serve as intermediaries, managing and distributing funds for corporate social responsibility initiatives. They aid businesses in aligning philanthropic goals with corporate strategy, offering expertise in identifying impactful projects and handling administrative tasks. Partnering with CSR fund companies provides advantages such as streamlined philanthropic efforts, expertise in project selection, and enhanced transparency. These organizations contribute significantly to environmental sustainability, addressing issues like climate change through support for renewable energy and conservation projects. In addition, CSR fund companies play a pivotal role in tackling social challenges like education, healthcare, poverty alleviation, and gender equality. As CSR gains importance, these companies are expected to evolve, forming closer collaborations with businesses and leveraging technology for efficient management. The future sees CSR fund companies playing a crucial role in helping businesses navigate complex societal challenges and shaping a better future through impactful philanthropy. [5].
III. BENEFITS OF CSR
CSR initiatives are strategically crafted to create positive effects on the world, encompassing direct benefits for society, the environment, and the local community in which a business operates.
While the external advantages are apparent, companies participating in CSR initiatives also enjoy internal benefits. One significant internal advantage is the improvement of employee satisfaction. When employees are aware of their company's active involvement in promoting meaningful causes, it nurtures a sense of pride and purpose, contributing to a more engaged and motivated workforce. This, in turn, positively influences overall employee satisfaction levels.Further more, the implementation of CSR initiatives can lead to stronger staff retention. Employees are more likely to remain loyal to a company that aligns with their values and demonstrates a commitment to social and environmental responsibility. The perception that their employer actively contributes to the betterment of society fosters loyalty among employees, reducing turnover rates and cultivating a stable and dedicated workforce.Externally, the positive impact of CSR initiatives extends to the broader community. In today's consumer landscape, there is an increasing awareness of the ethical and social practices of the companies consumers choose to support. Businesses actively involved in CSR activities are more likely to attract socially conscious consumers. Members of society may prefer to engage with companies that exhibit a commitment to making a positive difference, thereby extending the influence of CSR beyond the immediate community and into the marketplace.
IV. PROPOSED WORK
CSR involves a method where stockholders contribute funds for specific societal needs. These funds are allocated to areas like women's empowerment, education, NGO support, road infrastructure, and transportation. An organization plays a crucial role in overseeing and maintaining these CSR activities. They act as a central hub for funding, ensuring that the allocated funds reach the intended beneficiaries.
To streamline the process, individuals and entities interested in CSR activities can provide details to this overseeing organization, identifying themselves as contributors. This transparency helps in accountability and ensures that the funds are used efficiently. organization often take charge of NGOs and implementing CSR initiatives, addressing specific issues and working towards the betterment of society. As a result, individuals who benefit from CSR activities are identified, creating a positive impact on their lives and addressing various societal challenges.
V. METHODOLOGY
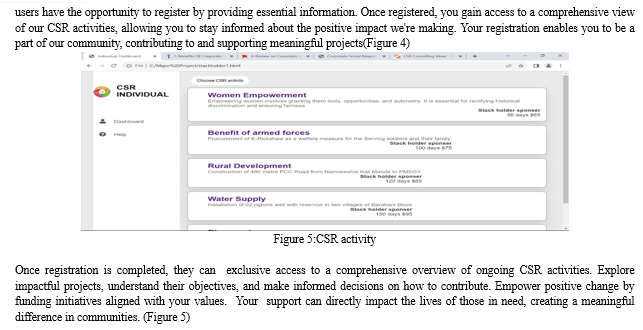
CSR activity app: This app contains meaningful change begins! On home page use to Discover ongoing initiatives dedicated to helping those in need. Whether you're an individual, organization, or stakeholder, you can join hands with us to make a difference. Explore the ongoing CSR activities, learn about impactful projects, and consider joining as a stakeholder, organization, or individual contributor. By this we can create positive change and uplift communities. Join hands with us as we embark on a mission to create a positive impact and improve the world.

Conclusion
In conclusion, Corporate Social Responsibility is a voluntary business strategy aimed at positively contributing to stakeholders, the environment, and society. Organizations adopting CSR go beyond legal obligations to align their activities with internal values, making it a cornerstone for their initiatives. The strategic importance of CSR is evident, with large corporations embracing it as a deliberate strategy to set ethical benchmarks for the industry. The literature survey highlights the evolving nature of CSR, emphasizing the need for a comprehensive theory that considers economic, political, social, and ethical factors. Scholars recognize the importance of understanding how CSR strategies are implemented, leading to the proposal of an integrative framework for CSR implementation. The benefits of CSR extend beyond external impacts, encompassing internal advantages such as enhanced employee satisfaction and stronger staff retention. External benefits include positive contributions to the broader community and increased appeal to socially conscious consumers. The proposed work introduces a CSR activity app, providing a user-friendly platform for stakeholders, organizations, and individuals to engage in meaningful change. The methodology outlines the registration process, exploration of ongoing CSR activities, and the opportunity for contributors to fund initiatives aligned with their values. In essence, CSR remains a dynamic and evolving concept, integral to businesses seeking to make a positive impact on society. The integration of technology, such as the CSR activity app, further facilitates engagement, transparency, and collaboration, positioning CSR as a powerful tool for societal betterment. As businesses and stakeholders continue to embrace CSR, its role in shaping a more sustainable and socially responsible future becomes increasingly significant patients will experience a heightened level of engagement and personalized care. In essence, the proposed medical healthcare application emerges as a valuable tool that not only simplifies the information-sharing process but also empowers both healthcare providers and patients alike. The envisioned benefits include improved efficiency, enhanced accessibility to health data, and a streamlined healthcare experience that ultimately contributes to the broader welfare of society
References
[1] Hortensia Gorski,Mircea fuci Research on CSR in the development region centre in Romania,2021 [2] Julian D .Riano and Natalia on CSR,2020 [3] Archie B.Carroll The pyramid of CSR: towards the moral management of organization stakeholders,2022 [4] Kjartan Sigurdsson pawel zieniuk voluntary CSR reporting and assurance practices among UNG compact member companies,2020 [5] The importance of CSR fund companies in corporate philanthropy,2023 [6] Jason Fernando\'s corporate social responsibility is explained with example,2023 [7] Lars Isaksson ; Timothy Kiessling CSR and engineering management and performance implications,2021 [8] Roman RM, Hayibor S, Agle Revitalizing the Depiction of the Interplay Between Social and Financial Performance: A Critical Review Business & Society,2021 [9] Simpson WG, Kohers T. Exploring the Nexus Between Corporate Social and Financial Performance: Insights from the Banking Sector Journal: Journal of Business Ethics,2002 [10] Hall, J., Environmental supply chain dynamics. Journal of Cleaner production,2000
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Arun Kumar S, Chaitra , Fiza , Shreya . This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET58024
Publish Date : 2024-01-13
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

