Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
RFID-Based Car Parking System
Authors: Prof. Minal Barhate, Rudra N. Mondal, Monish R. Wadile, Aayush G. Mor, Sandesh Moralwar, Deepak N. More
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.56160
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
This research paper presents a comprehensive study on the design, implementation, and evaluation of an RFID-based car parking system. The proposed system aims to address the challenges associated with traditional car parking systems, such as inefficiency in parking space utilization, long waiting times, and manual ticketing processes. By leveraging Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology, the system offers improved accuracy, real-time monitoring, and enhanced security. The paper discusses the system architecture, key components, and algorithmic approaches used. Furthermore, a comparative analysis is conducted to evaluate the performance of the proposed system against traditional parking systems, highlighting its advantages in terms of efficiency, convenience, and customer satisfaction.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
In recent years, the rapid urbanization and the ever-increasing number of vehicles have posed significant challenges to parking management in urban areas. Conventional parking systems, relying on manual processes and outdated technologies, are unable to cope with the increasing demand and are plagued by several issues. Long wait times, confusion in finding available spaces, and security vulnerabilities are just a few of the challenges that persist in traditional parking systems.
To address these shortcomings, this research paper introduces an RFID-based car parking system that leverages advanced technology to revolutionize parking management. RFID technology, widely known for its ability to uniquely identify and track objects, offers a promising solution for optimizing parking operations. By integrating RFID tags and readers into the infrastructure, this system enables seamless monitoring, tracking, and management of vehicles within parking facilities.
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
- The paper introduces a new automatic parking system that tracks vehicles using RFID tags and includes a central server, entrance and exit RFID readers, and RFID tags on vehicles. The entrance reader scans the tag to open the gate and updates the server when a vehicle enters, while the exit reader does the same when the vehicle exits and closes the gate. This system offers efficiency, security, and convenience compared to traditional systems, using passive RFID tags operating at 13.56 MHz, and demonstrates high accuracy and potential for handling high traffic volumes in simulations. Overall, the system has the potential to revolutionize parking.
- The paper introduces a new RFID-based automatic parking system that utilizes RFID tags to track vehicle movement in parking lots. It includes a central server, RFID readers, and tags. The entrance reader scans the tag to open the gate and update the server when a vehicle enters, and the exit reader does the same when the vehicle exits and closes the gate. The system offers advantages in efficiency, security, and convenience, with simulation results showing its capability to handle high traffic volumes accurately. Overall, the system has the potential to revolutionize parking, providing a more efficient and secure experience for users.
- The paper introduces a Smart Parking System (SPS) that combines RFID and WSN technologies to track parking space occupancy in real-time and inform drivers about available spaces. The system is efficient and user-friendly, enabling drivers to easily find parking spots and make payments through a mobile app.The authors emphasize the potential of smart parking systems to improve urban transportation efficiency and encourage further research and development in this area.
- The paper proposes a novel RFID-based automatic parking system (APS) that utilizes RFID tags and a robotic arm for efficient and user-friendly parking. The APS offers advantages in speed and accuracy compared to traditional systems. Simulation and performance evaluations demonstrate its effectiveness in different traffic conditions and real-world scenarios. The authors envision RFID-based APSs as a revolutionary approach to parking and emphasize the need for further research and development in this field.
- The paper discusses an automatic car parking system using RFID technology. It employs RFID readers and tags, along with a central computer system, to automate the parking process. When a car enters or exits the parking lot, RFID readers scan the car's tag and update the system's database of available spaces. The system is designed to be efficient, user-friendly, and secure, with potential benefits including reduced traffic congestion, increased parking availability, improved safety, and enhanced convenience. While still in development, the system holds promise for revolutionizing parking practices.
- The paper "RFID Implemented Parking System" discusses the use of RFID technology to create a more efficient and secure parking system. RFID tags are used to identify vehicles as they enter and exit the parking lot, enabling access control and occupancy tracking. The system incorporates features like barriers and cameras for enhanced security. The paper highlights the system's design, implementation, and benefits, such as improved efficiency, enhanced security, and reduced costs. While still in development, the RFID implemented parking system holds the potential to transform parking lot management.
III. COMPONENTS
A. The MFRC-522 Sensor Module
The MFRC-522 sensor module is a well-known contactless RFID reader/writer that is widely utilised in access control, identification, and NFC applications. It runs at 13.56 MHz, according to the ISO/IEC 14443A standard, and accepts a variety of RFID card protocols. The module features an antenna as well as an integrated circuit for communication and control. It can be easily integrated by connecting it to microcontrollers such as Arduino.
D. Servo Motor
Servo motors are motors that are meant to control angular or rotational motion precisely. They consist of a DC motor, a gearbox, and a feedback system. By utilising closed-loop control systems with feedback devices such as potentiometers or encoders, they provide accurate positioning and control across a wide range of motion. This allows them to compare desired and actual positions in real time, allowing the motor to maintain the desired position. Servo motors offer great torque, variable speed control, and a small size. They are commonly employed in robotics, automation, and other applications that need precise and regulated motion.
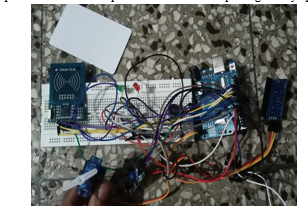
IV. METHODOLOGY
The methodology for implementing an RFID-based car parking system involves several steps and considerations. Here is a general outline of the methodology:
- Requirement Analysis: Thoroughly analyze the parking facility's requirements and goals to identify challenges and objectives that the RFID-based car parking system aims to address, including optimizing space utilization, improving efficiency, enhancing security, and providing a seamless user experience.
- System Design: Based on the requirements analysis, design the architecture and components of the RFID-based car parking system. Strategically place RFID readers in the parking facility, considering entry and exit points, parking spots, and critical areas. Establish a communication infrastructure for real-time data exchange between the readers, control system, and other components.
- RFID Reader Installation: Install RFID readers at designated locations in the parking facility, ensuring proper positioning for accurate tag reading. Configure readers to communicate with the centralized control system and establish communication protocols. Test the functionality and reliability of the RFID readers to ensure seamless tag reading and data transmission.
- Centralized Control System Development: Develop the software and hardware components of the centralized control system. This involves creating an administrator user interface for monitoring and managing the parking system, integrating a database to store tag information and parking data, and implementing algorithms for processing real-time data from RFID readers. Test the control system's functionality needed.
- Integration with Entry/Exit Equipment and Payment Systems: Integrate the RFID-based car parking system with entry and exit equipment, such as barriers or gates. Ensure that the RFID readers are seamlessly connected to the entry/exit equipment to automate access control based on tag information. Integrate the system with payment systems to enable automated and cashless transactions for parking fees. Test the integration to ensure proper functionality and synchronization between the RFID system, entry/exit equipment, and payment systems.

6. Testing and Evaluation: Conduct comprehensive testing of the RFID-based car parking system in real-world scenarios. Evaluate key performance indicators such as system responsiveness, accuracy in detecting parking occupancy, security measures, user satisfaction, and overall system performance.
7. Deployment and Training: Once the RFID-based car parking system is deemed effective and reliable, deploy it in the parking facility. Provide training to the parking facility staff and administrators on system operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting procedures.
8. Monitoring and Continuous Improvement: Monitor the RFID-based car parking system's performance continuously and gather feedback from users and administrators. Address any issues or concerns promptly and make continuous improvements to enhance the system's efficiency, security, and user experience. Stay updated with advancements in RFID technology.
By following this methodology, you can effectively implement an RFID-based car parking system that optimizes parking operations, enhances security, and provides a seamless experience for drivers and parking facility operators.
V. LIMITATIONS
While RFID-based car parking systems offer numerous benefits, they also have certain limitations that need to be considered. Here are some common limitations associated with RFID-based car parking systems:
- Tag Placement and Read Range: The accuracy and reliability of RFID-based car parking systems are contingent on appropriate tag placement and read range. Incorrect tag positioning on vehicles or limited read range in RFID readers may lead to inaccurate occupancy data and delays in entry/exit processes.
- Interference and Signal Limitations: RFID systems can be susceptible to interference from environmental factors, such as metal structures, electromagnetic fields, or other RFID readers operating in proximity. Proper system design and positioning of readers can help mitigate such interference issues.
- Scalability: Scaling up an RFID-based car parking system for larger facilities or higher vehicle traffic poses challenges.Managing and maintaining system performance and ensuring seamless data exchange become more complex. Therefore, consider system scalability in initial plannings.
- Privacy Concerns: RFID technology inherently involves the collection and storage of vehicle identification data. Privacy concerns may arise, as the system tracks and associates vehicles with their owners or drivers. To address these concerns, it is essential to implement appropriate data protection and privacy measures, such as encryption, access controls, and compliant data handling practices.
- Environmental Factors: RFID tags and readers can be susceptible to environmental factors such as extreme temperatures, moisture, dust, or physical damage. Proper protection and maintenance measures should be implemented to ensure reliable and durable operation in various environmental conditions.
VI. FUTURE SCOPE
A. Advanced Analytics and Data-driven Insights
RFID-based car parking systems provide abundant data on parking occupancy, traffic patterns, and user behavior. Utilizing advanced analytics techniques on this data can optimize parking space allocation, predict parking demand, manage traffic flow, and improve overall system efficiency, offering promising future possibilities.

Conclusion
1) In conclusion, RFID-based car parking systems offer efficient, secure management of parking spaces, benefiting drivers and facility operators through RFID tags, readers, centralized control, and integration with entry/exit equipment. 2) RFID tags and readers enable real-time vehicle identification and tracking in parking facilities. A centralized control system manages data, streamlines access control, and integrates with entry/exit equipment for cashless transactions. 3) RFID car parking systems offer advantages but face limitations like costs, read range, privacy, and scalability. Proper planning and implementation can overcome these issues. 4) In summary, RFID-based car parking systems revolutionize parking management, providing reliable, efficient solutions for urban mobility, with continued advancements in technology.
References
[1] Prabakaran, N., Baskaran, R., & Rajendran, M. (2016). RFID based automatic parking system. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering, 6(11), 1554-1559. [2] Soni, E. (2017). Design and development of RFID-based automated car parking system. International Journal of Innovative Technology and Research, 6(1), 1-10. [3] Mainetti, L., Palano, L., Patrono, L., Stefanizzi, M. L., &Vergallo, R. (2014). Integration of RFID and WSN technologies in a Smart Parking System. 2014 22nd International Conference on Software, Telecommunications and Computer Networks (SoftCOM). doi:10.1109/softcom.2014.7039099 [4] Salah B. Design, simulation, and performance-evaluation-based validation of a novel RFID-based automatic parking system. SIMULATION. 2020;96(5):487-497. doi:10.1177/0037549719890676 [5] Cho, D. H., Kim, Y. G., & Shin, J. W. (2019). RFID-based automatic car parking management system. 2019 IEEE 7th International Conference on Smart Energy Grid Engineering (SEGE), Oshawa, ON, Canada. DOI: 10.1109/SEGE.2019.884917 [6] More, V., Ravariya, K., Shah, S., &Solkar, A. (2017). Automatic Car Parking System using RFID. International Journal of Engineering Science and Innovative Technology (IJESIT) Volume, 4. [7] Li, C., & Zhu, Y. (2018). Design and implementation of RFID-based parking lot management system. 2018 2nd International Conference on Control, Automation and Robotics (ICCAR), Auckland, New Zealand. DOI: 10.1109/ICCAR.2018.8384671 [8] Yadav, S. (2014). RFID Implemented Parking System. International Journal of Information and Computation Technology, 4(4), 369-372.
Copyright
Copyright © 2023 Prof. Minal Barhate, Rudra N. Mondal, Monish R. Wadile, Aayush G. Mor, Sandesh Moralwar, Deepak N. More. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET56160
Publish Date : 2023-10-15
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

