Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Rising Threat of AI-Driven Cybersecurity Attacks: Implications for National Security
Authors: Swathi Priya Karthikeyan
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.64042
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
This article examines the growing threat of AI-driven cybersecurity attacks and their implications for national security. It explores three critical case studies: the SolarWinds hack, which demonstrated AI-enhanced data exfiltration; DeepLocker, an AI-powered malware concept showcasing precision targeting capabilities; and AI-enhanced disinformation campaigns. These examples illustrate how artificial intelligence is weaponized in cyberspace, presenting unprecedented challenges to national security. The article analyzes the key features, potential impacts, and lessons learned from each case, highlighting the urgent need for adaptive defense strategies, international cooperation, and ethical AI development practices to safeguard national interests in the digital age.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
In recent years, the rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized various sectors, including cybersecurity. Integrating AI into cybersecurity practices has led to significant improvements in threat detection, incident response, and overall network protection [1]. However, this progress has also paved the way for sophisticated cyber threats that pose significant risks to national security. As AI technologies become more accessible and powerful, malicious actors increasingly leverage these tools to enhance their attack capabilities, evade detection, and maximize the impact of their operations [2].
The intersection of AI and cybersecurity presents a double-edged sword. While AI-powered defensive measures can bolster an organization's security posture, the same technologies in the hands of adversaries can lead to unprecedented challenges. This dynamic has given rise to an AI-driven arms race in the cyber domain, where the stakes for national security have never been higher [3].
This article examines three critical case studies highlighting the potential dangers of AI-driven cybersecurity attacks and their implications for national interests. By analyzing real-world incidents and proof-of-concept demonstrations, we can gain valuable insights into the evolving threat landscape and develop strategies to mitigate these emerging risks.
The case studies we will explore include:
- The SolarWinds hack demonstrated the use of AI in data exfiltration and analysis.
- DeepLocker is an AI-powered malware concept that showcases the potential for highly targeted attacks.
- AI-enhanced disinformation campaigns that threaten to undermine social cohesion and democratic processes.
These examples illustrate how AI is weaponized in cyberspace and discuss the urgent need for adaptive defense strategies, international cooperation, and ethical AI development practices to safeguard national interests in the digital age.
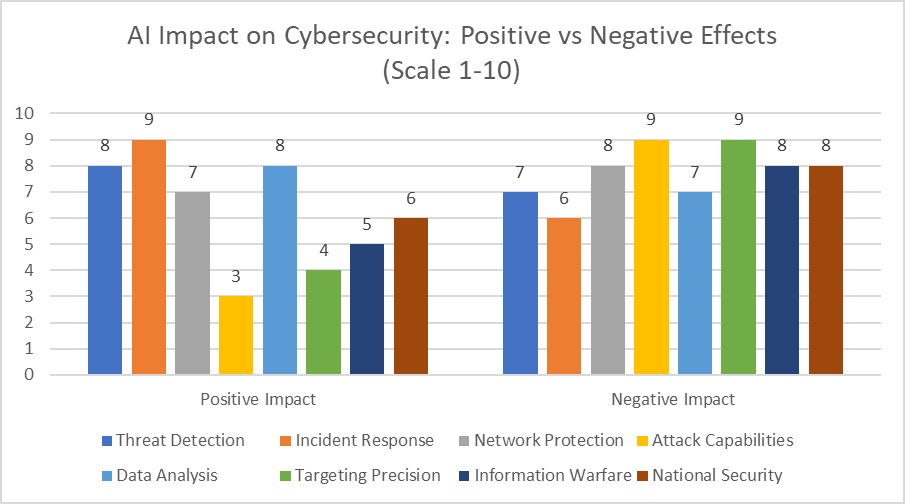
Fig. 1: Quantifying the Dual-Edged Nature of AI in Cybersecurity: A Comparative Analysis [1-3]
II. THE SOLARWINDS HACK: AI-ENHANCED DATA EXFILTRATION
The SolarWinds hack, uncovered in December 2020, represents a watershed moment in cybersecurity history. It exposed the vulnerabilities of even the most secure networks and the sophisticated capabilities of state-sponsored threat actors. This breach, attributed to the Russian foreign intelligence service (SVR), infiltrated the software supply chain of SolarWinds, a prominent IT management software provider, affecting an estimated 18,000 organizations worldwide, including multiple U.S. government agencies [4]. While the initial intrusion leveraged traditional cyber-espionage techniques, such as the insertion of malicious code into SolarWinds' Orion platform updates, the post-exploitation phase demonstrated a level of sophistication indicative of AI-enhanced operations. Cybersecurity experts believe the attackers employed advanced machine learning algorithms to sift through the vast troves of exfiltrated data, efficiently identifying high-value targets and sensitive information within the compromised networks [5].
The AI-driven approach allowed the threat actors to:
- Analyze network traffic patterns to evade detection
- Prioritize data exfiltration based on perceived intelligence value
- Identify potential lateral movement opportunities within victim networks
- Adapt malware behavior to mimic legitimate system processes
A. Key Impacts
- Critical sectors affected: The breach penetrated deep into the U.S. government and private sector, compromising agencies such as the Department of Energy, National Nuclear Security Administration, and Treasury Department. Major telecommunications companies and cybersecurity firms were also impacted, raising concerns about the integrity of national communication infrastructure [4].
- Compromised sensitive government operations: The attackers accessed email communications within the Department of Justice and other federal agencies, potentially exposing classified information and ongoing operations. The full extent of the breach remains unknown, with investigations ongoing more than a year after the initial discovery [6].
- Exposed vulnerabilities in software supply chains: The SolarWinds hack highlighted the critical weaknesses in software supply chain security, demonstrating how a single compromised vendor can lead to widespread infiltration across numerous organizations and sectors.
B. Lessons Learned
- Implement AI-driven threat detection systems: The incident underscored the need for advanced, AI-powered security solutions capable of detecting subtle anomalies and potential indicators of compromise that may evade traditional signature-based detection methods. Machine learning algorithms can analyze patterns in network traffic, user behavior, and system logs to identify potential threats in real-time [5].
- Strengthen software supply chain security: Organizations must implement rigorous security measures throughout the software development lifecycle, including regular code audits, integrity checks, and secure update mechanisms, to prevent supply chain attacks. This includes adopting practices such as Software Bills of Materials (SBOMs) and implementing zero-trust architectures [6].
- Enhance cross-sector collaboration for collective defense: The SolarWinds hack demonstrated the interconnectedness of public and private sector cybersecurity. Improved information sharing, joint threat intelligence analysis, and coordinated incident response strategies are crucial for building a more resilient national cybersecurity posture. Initiatives like the Cyber Threat Alliance and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)'s Joint Cyber Defense Collaborative are steps in the right direction [4].
The SolarWinds hack serves as a stark reminder of the evolving threat landscape and AI's potential to amplify cyber adversaries' capabilities. As nations and organizations grapple with the implications of this breach, it is clear that a paradigm shift in cybersecurity strategies is necessary to defend against future AI-enhanced attacks.
|
Category |
Element |
Description |
|
AI-driven Techniques |
Network Traffic Analysis |
Evade detection |
|
Data Prioritization |
Identify high-value targets |
|
|
Lateral Movement |
Find opportunities within networks |
|
|
Malware Adaptation |
Mimic legitimate processes |
|
|
Affected Sectors |
Government |
Dept. of Energy, National Nuclear Security Administration, Treasury Dept. |
|
Private |
Telecommunications companies, Cybersecurity firms |
|
|
Key Impacts |
Critical Infrastructure |
Compromised national communication infrastructure |
|
Sensitive Information |
Exposed classified information and ongoing operations |
|
|
Supply Chain Vulnerability |
Demonstrated widespread infiltration risk |
|
|
Lessons Learned |
AI-driven Detection |
Implement advanced threat detection systems |
|
Supply Chain Security |
Strengthen software development lifecycle security |
|
|
Cross-sector Collaboration |
Enhance information sharing and joint response strategies |
Table 1: Impact and Lessons from the SolarWinds Hack [3-6]
III. DEEPLOCKER: AI-POWERED PRECISION TARGETING
In 2018, researchers at IBM Security unveiled DeepLocker, a groundbreaking proof-of-concept malware that demonstrated the potential for highly targeted and evasive cyber attacks powered by artificial intelligence. This revolutionary concept represented a significant leap forward in malware sophistication, showcasing how AI could be leveraged to create cyber weapons with unprecedented precision and stealth capabilities [7]. DeepLocker utilizes advanced AI techniques, including deep neural networks and computer vision algorithms, to remain dormant until it positively identifies its specific target. This identification can be based on various factors, such as facial recognition, voice recognition, geolocation, or even specific behaviors of the target system. Once the target is confirmed, DeepLocker "unlocks" its malicious payload, executing the attack with surgical precision.
A. Key Features
- Precise targeting: DeepLocker can be programmed to activate only when it encounters a specific individual, device, or environment, significantly reducing the risk of detection during propagation.
- AI-driven stealth and evasion: The malware leverages machine learning algorithms to adapt its behavior, making it extremely difficult for traditional antivirus and endpoint detection systems to identify it as malicious.
- Polymorphic capabilities: DeepLocker can dynamically alter its code and appearance, further enhancing its ability to evade detection and analysis.
- Multi-modal targeting criteria: The malware can use a combination of visual, audio, and behavioral data to ensure it only activates on the intended target, minimizing collateral damage and improving operational security for the attacker.
B. Potential Impacts
- Targeting of critical national infrastructure: DeepLocker-like malware could be used to infiltrate and remain dormant within critical systems, such as power grids, water treatment facilities, or transportation networks, activating only when specific conditions are met to cause maximum disruption [8].
- Precision attacks on government officials or military systems: This technology could enable highly targeted attacks against specific individuals or systems, potentially compromising sensitive information or disrupting critical operations without alerting broader security measures.
- Enhanced capabilities for espionage and sabotage: The ability to precisely target specific individuals or systems while remaining undetected makes DeepLocker-like malware an ideal tool for long-term espionage operations or carefully timed sabotage attempts.
- Psychological warfare: The mere existence of such precisely targeted malware could create a climate of fear and mistrust, potentially influencing decision-making processes at the highest levels of government and industry.
C. Lessons Learned
- Invest in AI-powered defensive measures: To counter AI-driven threats like DeepLocker, organizations and governments must invest in equally sophisticated AI-powered security solutions capable of detecting subtle anomalies and predicting potential attack vectors. This includes the development of advanced anomaly detection systems and predictive threat intelligence platforms [9].
- Promote responsible AI development practices: The cybersecurity community must work together to establish ethical guidelines and best practices for AI development in security applications, ensuring that defensive capabilities keep pace with offensive innovations. This involves creating frameworks for the responsible disclosure of AI vulnerabilities and promoting transparency in AI-driven security research.
- Develop comprehensive national cybersecurity strategies incorporating AI: Nations must adapt their cybersecurity strategies to account for the potential of AI-powered threats, including funding research into defensive AI technologies and establishing regulatory frameworks to govern the development and use of AI in cybersecurity contexts. This may involve creating specialized task forces dedicated to AI-driven cyber threats and fostering collaboration between academia, industry, and government agencies.
- Enhance international cooperation: Given the global nature of cyber threats, increased collaboration between nations is crucial for sharing threat intelligence, coordinating responses to AI-powered attacks, and establishing norms for the responsible use of AI in cyberspace. This could include the creation of international working groups focused on AI and cybersecurity and the development of shared protocols for responding to AI-driven cyber incidents.
The emergence of DeepLocker serves as a stark warning of AI's potential to revolutionize cyber warfare. As this technology continues to evolve, it is imperative that defensive capabilities and strategic planning keep pace to ensure the security of critical systems and national interests in the face of these emerging threats.
|
Category |
Element |
Description |
|
Key Features |
Precise targeting |
Activates only for specific targets |
|
AI-driven stealth |
Adapts behavior to evade detection |
|
|
Polymorphic capabilities |
Dynamically alters code and appearance |
|
|
Multi-modal targeting |
Uses visual, audio, and behavioral data |
|
|
Potential Impacts |
Critical infrastructure |
Targets power grids, water facilities, transportation |
|
Government/military attacks |
Precision attacks on officials and systems |
|
|
Espionage and sabotage |
Long-term undetected operations |
|
|
Psychological warfare |
Creates climate of fear and mistrust |
|
|
Lessons Learned |
AI-powered defenses |
Invest in advanced anomaly detection |
|
Responsible AI development |
Establish ethical guidelines and practices |
|
|
National cybersecurity strategies |
Incorporate AI in defensive planning |
|
|
International cooperation |
Share threat intelligence and coordinate responses |
Table 2: Characteristics and Implications of DeepLocker AI Malware [7-9]
IV. AI-ENHANCED DISINFORMATION CAMPAIGNS
The proliferation of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies has significantly escalated the sophistication and scale of disinformation campaigns. These AI-enhanced operations aim to influence public opinion, destabilize governments, and manipulate social discourse by spreading false or misleading information across digital platforms [10].
A. AI Involvement
- Generation of convincing fake news and deepfakes: Advanced natural language processing (NLP) models, such as GPT-3 and its successors, can generate highly convincing articles, social media posts, and even video scripts that mimic legitimate news sources. This capability, combined with deepfake technology that can create realistic audio and video content, enables the production of false narratives that are increasingly difficult to distinguish from genuine information [11].
- Creation and management of automated social media bots: AI algorithms power sophisticated bot networks capable of mimicking human behavior on social media platforms. These bots can engage in conversations, share content, and even build seemingly authentic online personas. The scale and complexity of these networks make them challenging to detect and neutralize.
- Amplification of false narratives at scale: Machine learning algorithms analyze user engagement data to optimize the spread of disinformation. By identifying receptive audiences and tailoring content to specific demographics, AI systems can significantly enhance the reach and impact of false narratives. This targeted approach exploits cognitive biases and echo chamber effects, reinforcing beliefs and polarizing communities [12].
B. Impacts on National Security
- Undermining public trust in institutions: AI-driven disinformation campaigns can erode confidence in government agencies, democratic processes, and traditional media outlets. This erosion of trust can lead to social instability and make it more difficult for authorities to effectively communicate during crises.
- Influencing election outcomes: Targeted disinformation campaigns can sway voter opinions, suppress turnout, or amplify divisive issues. The precision and scale afforded by AI technologies make these efforts particularly potent, potentially altering the course of democratic elections and undermining the legitimacy of elected officials.
- Exacerbating social divisions: AI-powered algorithms can identify and exploit existing social fault lines, amplifying controversial topics and promoting extremist viewpoints. This targeted polarization can lead to increased social tension, political gridlock, and in extreme cases, civil unrest.
C. Lessons Learned
- Develop AI tools for information verification: Invest in advanced AI systems capable of detecting and flagging potential disinformation. These tools should leverage natural language processing, image analysis, and network behavior detection to identify suspicious content and its sources. Collaboration between tech companies, academia, and government agencies is crucial for developing robust, adaptable verification systems [10].
- Educate the public on identifying disinformation: Implement comprehensive digital literacy programs in schools and public institutions to equip citizens with the skills needed to critically evaluate online information. These programs should cover topics such as source verification, understanding algorithmic bias, and recognizing emotional manipulation tactics commonly used in disinformation campaigns [11].
- Implement regulations to hold platforms accountable: Develop and enforce regulatory frameworks that require social media platforms and content distributors to implement robust content moderation systems, increase transparency in algorithmic content recommendation, and cooperate with law enforcement in cases of coordinated disinformation campaigns. These regulations should balance the need for free speech with the imperative to protect democratic institutions and public safety [12].
D. Additional Strategies
- Foster international cooperation: Establish multilateral agreements and task forces to combat cross-border disinformation campaigns. Share best practices, threat intelligence, and technological solutions among allied nations to create a united front against state-sponsored and non-state actor disinformation operations.
- Promote responsible AI development: Encourage the development of ethical AI guidelines and standards within the tech industry. This includes implementing safeguards against the misuse of language models and other AI technologies that could be exploited for disinformation.
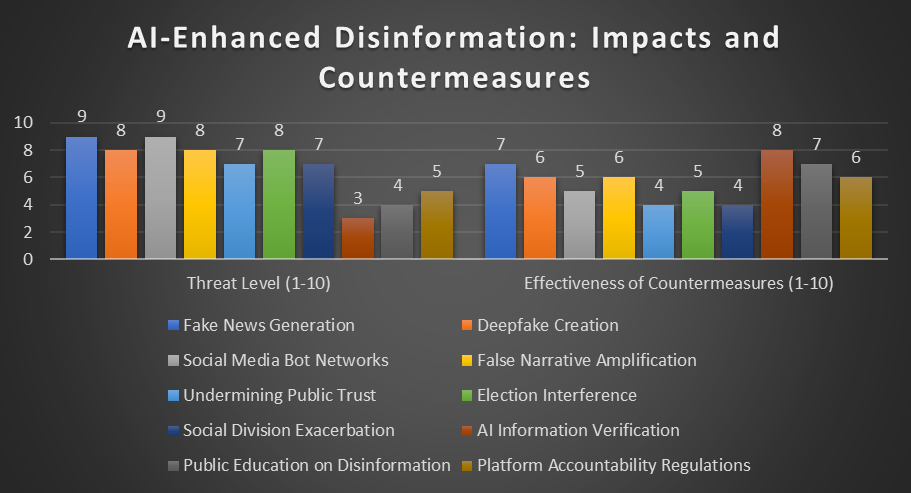
Fig. 2: Quantifying the Threat and Response to AI-Driven Disinformation [10-12]
By implementing these strategies and continuously adapting to evolving threats, nations can better protect their information ecosystems and maintain the integrity of their democratic processes in the face of AI-enhanced disinformation campaigns.
Conclusion
The rise of AI-driven cyber threats represents a paradigm shift in the national security. As demonstrated by the SolarWinds hack, DeepLocker concept, and AI-enhanced disinformation campaigns, artificial intelligence has the potential to amplify the capabilities of cyber adversaries significantly. To counter these evolving threats, nations and organizations must invest in AI-powered defensive measures, strengthen software supply chain security, enhance cross-sector collaboration, and develop comprehensive cybersecurity strategies incorporating AI. Furthermore, promoting responsible AI development, fostering international cooperation, and educating the public on digital literacy are crucial steps in building resilience against AI-enhanced cyber attacks. As the AI arms race in cyberspace continues to escalate, it is imperative that defensive capabilities and strategic planning keep pace to ensure the security of critical systems and preserve the integrity of democratic processes in the face of these emerging challenges.
References
[1] S. M. Albladi and G. R. S. Weir, \"Artificial Intelligence and Cybersecurity: A Systematic Mapping Study,\" IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 59090-59109, 2021. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9395542 [2] M. Brundage et al., \"The Malicious Use of Artificial Intelligence: Forecasting, Prevention, and Mitigation,\" arXiv:1802.07228 [cs.AI], Feb. 2018. https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.07228 [3] R. Sommer and V. Paxson, \"Outside the Closed World: On Using Machine Learning for Network Intrusion Detection,\" in 2010 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, Oakland, CA, 2010, pp. 305-316. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5504793 [4] B. Jaikaran, \"The SolarWinds Orion Supply Chain Compromise: Cyber and Critical Infrastructure Security Considerations,\" Congressional Research Service, Jan. 2021. https://sgp.fas.org/crs/homesec/IN11559.pdf [5] S. Morgan, \"AI In Cybersecurity Market Size To Reach $46.3 Billion By 2027,\" Cybercrime Magazine, Nov. 2021. https://cybersecurityventures.com/ai-in-cybersecurity-market-size-to-reach-46-3-billion-by-2027/ [6] U.S. Government Accountability Office, \"SolarWinds Cyberattack Demands Significant Federal and Private-Sector Response,\" Apr. 2022. https://www.gao.gov/products/gao-22-104746 [7] M. Osborne, \"DeepLocker: When malware turns artificial intelligence,\" IBM Security Intelligence, Aug. 2018. https://securityintelligence.com/deeplocker-when-malware-turns-artificial-intelligence/ [8] N. Kshetri and J. Voas, \"Thoughts on General Purpose AI,\" in Computer, vol. 53, no. 11, pp. 20-24, Nov. 2020. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9247563 [9] S. Shen et al., \"A Deep Learning Perspective on the Origin of Adversarial Examples,\" in 2021 IEEE International Conference on Cyber Security and Resilience (CSR), Rhodes, Greece, 2021, pp. 243-248. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9527945 [10] S. Shahsavari et al., \"Conspiracy in the time of corona: automatic detection of emerging COVID-19 conspiracy theories in social media and the news,\" Journal of Computational Social Science, vol. 3, pp. 279-317, 2020. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42001-020-00086-5 [11] R. K. Kaliyar, A. Goswami, and P. Narang, \"DeepFakE: improving fake news detection using tensor decomposition-based deep neural network,\" The Journal of Supercomputing, vol. 77, pp. 1015-1037, 2021. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11227-020-03294-y [12] K. Shu et al., \"Disinformation, Misinformation, and Fake News in Social Media: Emerging Research Challenges and Opportunities,\" in IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 65379-65393, 2020. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9042252
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Swathi Priya Karthikeyan. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET64042
Publish Date : 2024-08-22
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

