Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
A Study on the Role of MGNREGA in Fostering Economic Development via Welfare Initiatives, Employment Opportunities, and Asset Formation in Rural Bangalore
Authors: Ms. Suman Mishra, Dr. Selvi S
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.61957
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Over the years, the evolution of the Indian economy has witnessed substantial transformation and enhancement. The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) has emerged as a pivotal component in fostering the development of rural India, primarily through its dual impact of employment generation and asset formation. This research paper employs trend analysis to investigate the pivotal role of the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) in driving economic development in rural areas of Bangalore. MGNREGA, a flagship welfare initiative, is examined through its multifaceted impact on welfare enhancement, employment generation, and asset accumulation. The study delves into the effectiveness of MGNREGA in improving the socio-economic well-being of rural communities by providing critical welfare benefits, facilitating employment opportunities, and promoting asset formation. The findings of this study provide valuable insights into the nuanced relationship between MGNREGA initiatives and economic development outcomes in rural Bangalore. By uncovering significant trends and patterns, the research offers actionable recommendations for policymakers, practitioners, and stakeholders to optimize MGNREGA\'s impact on fostering inclusive and sustainable economic growth in rural areas.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) stands as a landmark social welfare program in India, aiming to address rural poverty and unemployment by guaranteeing 100 days of wage employment to every household in rural areas. Since its inception in 2005, MGNREGA has emerged as one of the largest and most ambitious social protection schemes globally, with the overarching goal of fostering economic development, enhancing welfare initiatives, and promoting asset formation among rural communities. Within the dynamic and diverse landscape of India, the implementation and impact of MGNREGA vary significantly across regions, necessitating localized studies to understand its effectiveness and challenges comprehensively. The Indian Economy development has been significantly changed and improved through the years. The scheme of MGNREGA has been an important part of the development of rural India through its employment generation and asset creation. Nazeer, (2015) in the paper “MGNREGA is it inclusive?” conducted a study through Focused Group Discussions and Key Informant Interviews conducted at a village of Tumkur District, Karnataka, and Madanapalle Village of Annamayya District, Andhra Pradesh. The study reveals that the scheme has been vital through poverty eradication and rural development. The study also discloses that the scheme has a scope of inclusive development of the social groups, minorities, and the backward classes. The case study of Rajappa from a village of Tumkur District, Karnataka reflects the challenges faced due to socio-economic factors and limited infrastructure. MGNREGA provided him with financial empowerment and improved his economic conditions. The case of Kempamma, a 37-year-old woman from the Dalit community in Madanapalli village, Andhra Pradesh, underscores the significance of MGNREGA in rural development, providing vital livelihood opportunities for the rural poor. Sarkar Prattoy, Kumar Jagdish, and Supriya, (2011) in their study conducted in the Burdwan district of West Bengal examined the socio-economic impact of MGNREGA on the rural poor comprised of small farmers and agricultural laborers. The study was conducted by taking a random sample of 102 beneficiary and non-beneficiary households and results showed that significant changes have been taken in the socio-economic variables for the households which are beneficiaries of the scheme as compared to the non-beneficiaries.
Bhargava, (2013) conducted a micro-level examination in the Ajmer district of Rajasthan. Both primary and secondary data are collected using interview schedules from implementing agencies and websites. Sample size selection employs a stratified random sampling technique. The study period spans from 2011-12 to 2012-13. Pooled regression analysis is employed to evaluate asset creation through employment (man-days, woman-days) and its impact on the economic progress of the sampled unit. Findings indicate that asset creation has occurred in select permissible works, with a notable dominance of women's involvement. This phenomenon has led to an enhanced status and decision-making role for women within families. Moreover, there has been an observed increase in children's enrollment in schools during the study period. A key insight from this study suggests that for optimal fund utilization and economic progress at the district level through asset creation, the permissible works undertaken should align with the specific geographical, economic, and social requirements of the area.
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
Dr. Suman Pamecha, Indu Sharma, (2015) MGNREGA is an ambitious program primarily aimed at the improvement of security of a household’s livelihood in rural India. In the study, the researcher attempts to analyze the socio-economic impact of the MGNREGA scheme on the livelihood of the households and the beneficiaries of the Dungarpur district. The study reveals the income and expenditure patterns of the beneficiaries in the district.
Ajay Kumar Singh, Niti Survey, and Sameer Lama, (2012) in the research paper entitled MGNREGA: A Critical Assessment of Issues and Challenges, analyze the performance of the scheme in fifteen selected states of India based on the proportion of the population that has been the beneficiaries under the scheme. The major issue and challenge faced by the beneficiaries at the ground level is found to be corruption.
Dr. G. Xavier, and G. Mari, (2014) in the paper titled Impact of MGNREGA On Women Empowerment with Special Reference to Kalakkanmoi Panchayat in Sivaganga District, Tamil Nadu aim to assess the influence of MGNREGA on the socio-economic empowerment of women in Kalakkanmoi panchayat, Sivaganga district, Tamil Nadu. Additionally, it examines the various risks women face during their participation in MGNREGA activities. The findings indicate that MGNREGA leads to an increase in household income and expenditure compared to the period before its implementation. Moreover, the scheme significantly enhances the social and economic decision-making power of women in traditionally male-dominated rural areas, thereby improving their overall standard of living, particularly among vulnerable populations. However, the study also identifies challenges such as poor worksite facilities, harsh climatic conditions, and reduced leisure time, which impose significant hardships on women during their engagement in MGNREGA activities.
Grace Carswell, (2014) in the study conducted in Tamil Nadu, a state often cited for the success of MGNREGA implementation, delves into the demographics of program participants and examines how success is perceived and articulated across various social and bureaucratic strata. Regarding the outcomes of MGNREGA, the study concludes that the scheme primarily benefits the poorest households, with a notable positive impact on Dalits and women, serving as both a safety net and a poverty alleviation tool. However, beyond these immediate benefits, MGNREGA has also engendered significant transformative effects for rural laborers. These include elevating rural wage levels, bolstering the bargaining power of low-caste workers in the labor market, and reducing their reliance on high-caste employers. These outcomes not only carry substantial weight but also hold transformative potential by reshaping rural production relations and contributing to the empowerment of marginalized rural laborers. Nonetheless, when it comes to creating lasting assets and fostering grassroots democracy, the scheme's outcomes are less promising.
Das, (2016) in the study aims to evaluate the impact and effectiveness of the MGNREGA Act in the Barpeta district of Assam for the financial year 2013-14. The study encompasses 2014-15 and the findings are based on the MIS reports on MGNREGA. The Act includes provisions that allow marginalized groups such as Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and others to develop their private lands, thereby enhancing the inclusivity of MGNREGA. Infrastructure development in villages is crucial for both rural and urban area development. However, there is a need for government amendments to MGNREGA to provide more regular employment opportunities for unskilled manual laborers. The recommendation is to expand the current program further into rural areas through meticulous planning, adequate supervision, effective implementation, and enhanced monitoring. This approach aims to yield substantial benefits for the country, including tackling unemployment, reducing migration, and alleviating poverty.
Bhargava, (2013) in the paper entitled An Empirical Study of Assets Creation through Employment Generation by MGNREGA in Rajasthan attempted to assess the creation of assets through employment generation facilitated by MGNREGA and its contribution to economic progress. MGNREGA has stood as one of the most significant employment programs in India for over a decade.
Basharat Bashir Bhat, (2015) conducted a descriptive study utilizing both primary and secondary data collected from Shanoo village in Kupwara district, Jammu and Kashmir. Out of 223 registered MGNREGA participants (comprising 217 males and 6 females, with 11 registrations deleted for various reasons), 50 respondents were purposively selected, representing 23.5% of total registrants. Structured interview schedules and observation techniques were employed to gather responses, incorporating a scaling technique to gauge opinions on MGNREGA's functions, benefits, and development. Findings indicate that the majority (84%) of respondents are male, with 44% having secondary education. Most live in kachha houses (74%) within joint family setups (62%), lacking proper sanitation and drinking water facilities. Despite challenges, 76% believe their economic condition has improved somewhat under MGNREGA, with 72% perceiving it as beneficial for rural communities, offering equitable work and wages. Additionally, 64% feel it elevates their living standards and 56% attest to its social benefits, including increased respect within families and communities. Moreover, 66% perceive economic benefits from the Act, with 58% recognizing its role in poverty eradication and 68% acknowledging its employment generation function for rural poor.
III. RESEARCH DESIGN
A. Statement of Problem
The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) emphasizes promoting economic development through social initiatives, job opportunities, and wealth creation in rural Bangalore. Despite the implementation of MGNREGA aimed at combating rural poverty and unemployment, there is still a need for a thorough assessment of its effectiveness and impact on economic development in certain areas such as rural Bangalore.
B. Purpose of Study
This study aims to address the gaps in understanding by examining how MGNREGA initiatives contribute to economic growth, welfare improvement, and wealth accumulation in rural communities in the Bangalore region. Key issues include the extent of MGNREGA's impact on poverty alleviation, the quality and sustainability of jobs created, the effectiveness of welfare programs, and the overall impact on rural livelihoods and wealth creation. By examining these dimensions, the study seeks to provide insights into optimizing the implementation of MGNREGA for sustainable economic development in rural Bangalore.
C. Objectives of the Study
- To understand the contribution of MGNREGA to the economic development through convergence
- To analyze the trend of employment generated to the beneficiaries of the scheme of Bangalore Rural
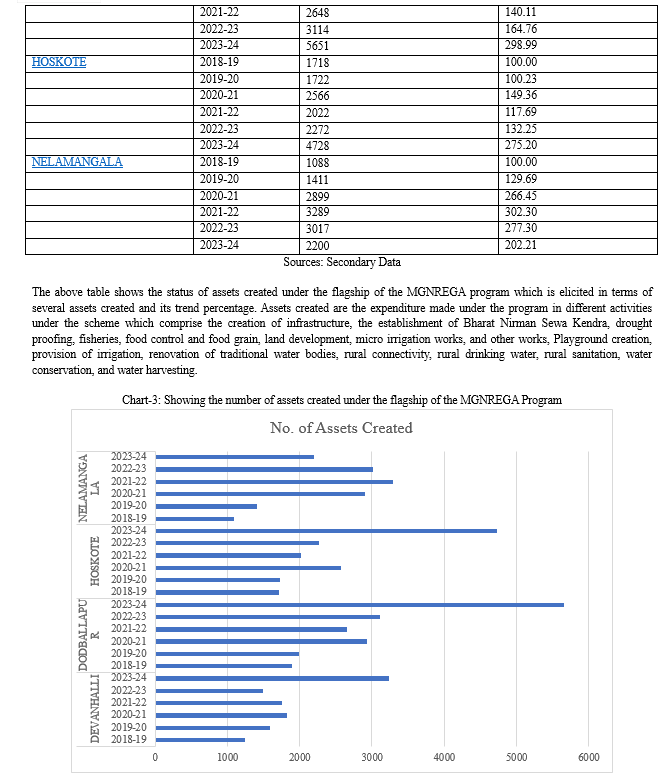
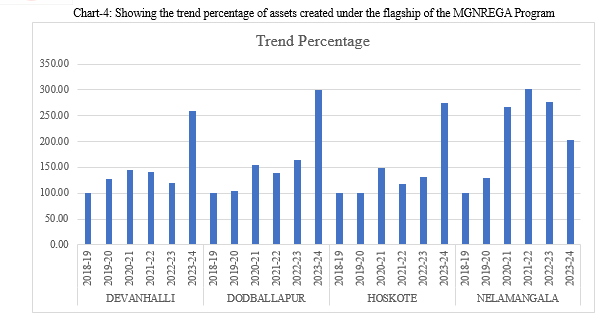
- To assess the status of assets created under the flagship of the MGNREGA program
D. Data Collection
The data for the study is taken from the secondary data from MIS reports of MGNREGA available on the official MIS website of the MGNREGA scheme. The study period spans from 2018-19 to 2022-23 (5 years).
E. Limitations of Study
- The study is based on the secondary data collected from the information available in the MIS reports of the MGNREGA scheme
- The study is limited to Bangalore and rural areas and covers only 5 years
- The study's findings may be influenced by external factors such as government policies, economic conditions, and socio-cultural dynamics
IV. RESULTS & DISCUSSIONS
A. Objective: To understand the contribution of MGNREGA to the economic development through convergence
Akhilesh Kumar Sharma, Atul Sarma, Charanjit Kaur & Deeksha Tayal, (2017) in a study conducted to evaluate the macroeconomic impacts of MGNREGA on the economic development of India through analyzing the GDP and household incomes, found that there has been a significant positive impact on the country’s GDP through the flagship program of MGNREGA.
The convergence of the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) with other schemes and programs is essential for maximizing its impact and ensuring efficient resource utilization. Here are some instances of how MGNREGA aligns with various initiatives:
- Rural Housing Schemes: MGNREGA collaborates with initiatives like the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) to generate employment through rural housing construction, effectively addressing housing needs while providing job opportunities.
- Water and Sanitation Programs: MGNREGA integrates with water and sanitation schemes such as the Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) to build sanitation facilities in rural areas, promoting hygiene practices and offering employment opportunities.
- Natural Resource Management: MGNREGA converges with programs like the Integrated Watershed Management Program (IWMP) and the National Rural Livelihoods Mission (NRLM) to implement activities like watershed development and afforestation, fostering sustainable resource management and livelihood enhancement.
- Livelihood Promotion: MGNREGA aligns with livelihood promotion initiatives like the Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDU-GKY) and the National Rural Livelihoods Mission (NRLM) by providing skill development training and employment opportunities, thereby boosting rural livelihoods and entrepreneurship.
- Agricultural Initiatives: MGNREGA collaborates with agricultural programs such as the National Agriculture Market (eNAM) and the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) to support agricultural development through activities like land development and irrigation works, enhancing productivity and water management.
- Infrastructure Development: MGNREGA aligns with infrastructure development schemes like the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) and the Rural Connectivity Scheme (RCS) to improve rural connectivity, leading to better access to essential services and markets.
- Social Security Schemes: MGNREGA converges with social security initiatives like the National Social Assistance Program (NSAP) to provide employment and social protection to vulnerable groups, thereby addressing rural poverty and promoting social inclusion.
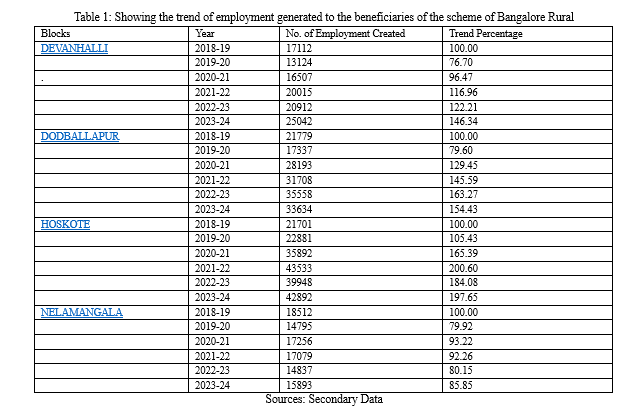
B. 2nd Objective: To analyse the trend of employment generated to the beneficiaries of the scheme of Bangalore Rural
A tool of trend percentage has been used to analyze the trend of employment generated to the beneficiaries of the scheme of Bangalore rural comprising of Devanahalli, Dodballapur, Hoskote, and Nelamangala blocks.

V. SUGGESTIONS
- Enhanced Monitoring and Evaluation Mechanisms: Implementing robust monitoring and evaluation systems to track the effectiveness and efficiency of MGNREGA initiatives in rural Bangalore. This would enable timely identification of gaps and opportunities for improvement.
- Capacity Building Initiatives: Investing in capacity-building programs for rural communities to enhance their participation and engagement in MGNREGA activities. This could include training programs on skill development, financial literacy, and entrepreneurship.
- Strengthening Convergence with Other Schemes: Further integrating MGNREGA with complementary schemes and programs aimed at rural development, such as agricultural initiatives, infrastructure projects, and social welfare programs. This convergence approach would maximize the synergistic benefits and optimize resource utilization.
- Promotion of Asset-Creating Activities: Encouraging the prioritization of asset-creating activities under MGNREGA, such as water conservation, afforestation, and infrastructure development. These initiatives not only generate employment but also contribute to long-term sustainable development and resilience.
- Community Participation and Empowerment: Facilitating greater involvement of local communities, particularly marginalized groups and women, in the planning, implementation, and monitoring of MGNREGA projects. Empowering communities to take ownership of their development initiatives fosters inclusivity and sustainability.
Conclusion
The study underscores the significant role of the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) in fostering economic development in rural Bangalore through welfare initiatives, employment opportunities, and asset formation. Trend analysis has provided valuable insights into the evolving dynamics of MGNREGA implementation and its impact on the socio-economic landscape of rural communities. The findings suggest that while MGNREGA has made substantial contributions to poverty alleviation, income enhancement, and asset creation in rural Bangalore, there remain areas for improvement. Strengthening monitoring mechanisms, enhancing community participation, and promoting convergence with other development schemes emerge as critical strategies to optimize the effectiveness of MGNREGA interventions. Moving forward, concerted efforts from policymakers, government agencies, civil society organizations, and local communities are essential to harness the full potential of MGNREGA in driving inclusive and sustainable economic development in rural Bangalore. By addressing the identified challenges and implementing the suggested recommendations, MGNREGA can continue to catalyze transformative change, empowering rural communities and fostering resilience in the face of socio-economic challenges.
References
[1] Ajay Kumar Singh, Niti Survey and Sameer Lama. (2012). MGNREGA: A Critical Assessment of Issues and Challenges. The Indian Journal of Commerce, 151-164. [2] Akhilesh Kumar Sharma, Atul Sarma, Charanjit Kaur & Deeksha Tayal. (2017). Macro-Economic Impact of MGNREGA in India: An Analysis in CGE Modeling Framework. SSRN - Elsevier. [3] Basharat Bashir Bhat, D. P. (2015). MGNREGA: A New Hope to Reduce Rural Poverty. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INNOVATIVE RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT, 347-351. [4] Bhargava, D. R. (2013). An Empirical Study of Assets Creation through Employment Generation by MGNREGA in Rajasthan . Journal of Economics and Sustainable Development, 117-126. [5] Das, M. D. (2016). Role of MGNREGA in Rural Employment: A Study of Barpeta District of Assam, India. International Journal of Humanities & Social Science Studies, A Peer-Reviewed Bi-monthly Bi-lingual Research Journal , 241-248. [6] Dr. G. XAVIER, G. MARI. (2014). IMPACT OF MGNREGA ON WOMEN EMPOWERMENT WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO KALAKKANMOI PANCHAYAT IN SIVGANGAI DISTRICT, TAMIL NADU. SSRG International Journal of Economics and Management Studies. [7] Dr. Suman Pamecha, Indu Sharma. (2015). Socio-Economic Impact of Mgnrega - A Study Undertaken among Beneficiaries of 20 Villages of Dungarpur District of Rajasthan. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications. [8] Grace Carswell, G. D. (2014). MGNREGA in Tamil Nadu: A Story of Success and Transformation? Journal of Agrarian Change. [9] Nazeer, U. (2015). MGNREGA for inclusive development in India: an analysis. Spanish Journal of Rural Development. [10] Sarkar Prattoy, Kumar Jagdish, Supriya. (2011). Impact of MGNREGA on Reducing Rural Poverty and Improving Socio-Economic Status of Rural Poor: A Study in Burdwan District of West Bengal. Agricultural Economics Research Review, 437-448. BIBLIOGRAPHY [1] https://nreganarep.nic.in/netnrega/MISreport4.aspx [2] https://nrega.nic.in/MGNREGA_new/Nrega_home.aspx [3] https://www.indiabudget.gov.in/economicsurvey/ [4] https://nregastrep.nic.in/netnrega/loginframegp.aspx?salogin=Y&state_code=15 [5] https://nregastrep.nic.in/netnrega/homestciti.aspx?state_code=15&state_name=KARNATAKA&lflag=eng MGNREGA Sameeksha: An Anthology of Research Studies on the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005, Ministry of Rural Development Government of India The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Ms. Suman Mishra, Dr. Selvi S. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET61957
Publish Date : 2024-05-11
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

