Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Studies on Properties of Sisal Fiber Reinforced Self Compacting Concrete
Authors: M. Aravinda Samy, Dr. V. Ramasamy, S. Selvakmar
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.56019
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
To evaluate the mechanical properties of self-compacting concrete (M30) with sisal fibers. Self-compacting concrete (SCC) mixes are produced by replacing the cement with Fly ash and with addition of sisal fiber of 0, 0.5%, 1% and 1.5% and length of fibers considered are 5mm, 10mm, and 20mm to the SCC concrete. Sulphonated naphthalene Formaldehyde condensates-based SP is used as water reducing agent. Compressive strength of SCC mix has to be determined at 7, 14 and 28 days. Flexural strength of SCC mix has to be determined at 14 and 28 days. Impact strength of SCC mix has to be determined at 28 days.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
The term fibre reinforced concrete (FRC) is defined as a concrete containing dispersed randomly oriented fibres. Inherently concrete is brittle under tensile loading and mechanical properties of concrete may be improved by randomly oriented short discrete fibres which prevent or control initiation and propagation of cracks. The discrete fibres, dispersed throughout the matrix improve the mechanical properties of concrete through stress redistribution. However, the use of fibres reduces the workability of the matrix.
On the other hand, use of self-compacting concrete (SCC) in the construction industry has grown significantly due to its technical advantages. SCC is a new type of concrete that can be cast into a framed work and fill it completely under its own weight without the need of any type of compaction or external vibration. SCC also has a great resistance to segregation and a high ability to flow around obstacles such as reinforcements or narrow sections.
By incorporating fibre in SCC, a homogeneous composite material namely fibre reinforced self-compacting concrete (FRSCC) is achieved. Due to the high flowable nature of SCC uniform dispersion of fibre takes place and a higher degree of stress redistribution is ensured.
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
Ahmed (2013), investigated Properties and microstructural characteristics of linen fiber reinforced self-compacting concrete in slender column. In this study the linen fibers used to reinforce SCC with 2kg/m3 and 4kg/m3 contents. Lime stone powder is used as a mineral admixture to increase the paste volume. High range water reducing admixture RHEOBUILD 1100 was used to obtain the required workability without increasing w/c ratio. Mansur and Aziz (1982) investigated A study of jute fibre reinforced cement composites: This study was centred at determining the tensile, flexural, compressive and impact strengths of the matrices and composites. Three different matrices corresponding to cement sand ratios of 1:0, 1:1 and 1:2 were employed. The major variables were the length and volume fraction of the fibres. Badrinath and Senthilvelan (2014), investigated Comparative Investigation on mechanical properties of banana and sisal reinforced polymer-based composites in this study sisal fiber and banana fibers have been used as the main reinforcing materials with epoxy resin as the matrix in order to increase the effectiveness of natural fibers. Jayaram et al (2014), investigated Experimental Investigation of Hybrid Fiber Reinforced Concrete In this study addition of two fibers (Sisal & glass) of different properties can improve the properties of fresh concrete. Nan su (2001), investigated A Simple Mix Design Method for Self-Compacting Concrete In this study a new mix design method for self-compacting concrete (SCC).
The number of aggregates, binders and mixing water, as well as type and dosage of superplasticizer (SP) to be used are the major factors influencing the properties of SCC. Slump flow, V-funnel, L-flow, U-box and compressive strength tests were carried out to examine the performance of SCC. The result indicate that the compressive strength of SCC decreased with increasing Packing Factor value. Elinwa, Ejeh and Mamuda (2007), investigated Assessing of the fresh concrete properties of self-compacting concrete containing sawdust ash:.
The aim of this study is to determine the self-compacting characteristics for concrete containing sawdust ash. Burcu Akcay, Mehmet Ali Tasdemir (2011), investigated Mechanical behaviour and fibre dispersion of hybrid steel fibre reinforced self-compacting concrete.In this study five different concrete mixes were prepared keeping the cement, silica fume, aggregate and water content the same and varying the amount of steel fibre. El-Dieb and Reda Taha (2001) investigated Flow characteristics and acceptance criteria of fibre reinforced self-compacting concrete This paper states that the flow characteristics of SCC can be affected by inclusion of fibres, but it is quite possible to achieved self-compacting properties while using fibre reinforcement. Khatib (2007), investigated Performance of self-compacting concrete containing fly ash. In this paper the author discussed the need for super plasticizer and role of fly ash in the matrix. In the present work selected properties of SCC containing FA at constant water binder ratio of 0.36 were investigated. The properties comprised workability, density, compressive strength, absorption, ultrasonic pulse velocity and drying shrinkage. According to this paper chemical admixtures are necessary to increase the workability and reduce segregation.
III. EXPERIMENTAL DETAILS
A. Cement
Grade 53 ordinary Portland cement (OPC) confirming to IS: 12269-1987 has been used. The physical properties of the cement such as consistency, initial and final setting time and specific gravity were tested in accordance with IS: 4031-1968 and given in Table 3.1.
Table 3.1. Physical Properties of Cement
|
Sl.no |
Property |
Value |
|
1 |
Standard consistency |
32% |
|
2 |
Initial setting time |
53min |
|
3 |
Final setting time |
283min |
|
4 |
Specific gravity |
3.15 |
B. Coarse Aggregate
The coarse aggregate used in the concrete mixtures was crushed stone of size 20mm and 12. 5mm.It has a specific gravity of 2.75 and was determined according to IS: 2380 (Part- 111) of 1963. The physical properties were also determined and given in Table 3.2.
Table 2.2. Physical Properties of Coarse Aggregates
|
Sl.No |
Property |
Value |
|
1 |
Specific gravity |
2.71 |
|
2 |
Fineness modulus |
8.07 |
|
3 |
Bulk density |
1320kg/m3 |
|
4 |
Water absorption |
1.5% |
C. Fine Aggregate
Natural sand was used as fine aggregate with a maximum size of 4.75mm. The specific gravity of the fine aggregate is 2.63 and was determined according to IS:2386(Part-111) of 1963. Sieve analysis was performed on the fine aggregate according to IS: 383-1970. The physical properties are given in Table 3.3.
Table 3.3. Physical Properties of Fine Aggregate
|
Sl.No |
Property |
Value |
|
1 |
Specific gravity |
2.63 |
|
2 |
Fineness modulus |
3.49 |
|
3 |
Bulk density |
1430 kg/m3 |
|
4 |
Water absorption |
1% |
D. Fly ash
Fly ash of class F type having a specific gravity of 2.01 has been used in the present study. The fly ash is obtained from Ennore, Chennai.
E. Sisal Fibres
The Sisal fibre used in this investigation is locally available in processed form. These fibres are cut into pieces manually to a length of 5mm, 10mm, 20mm respectively. The extent of fibre content that can be used in FRSCC can be fixed either on the basis of volume of concrete or by the weight of the cement. Among these two, most of the investigators have adopted the fibre content based on the volume of the concrete. Hence in this experimental investigation also volume of concrete is considered for determining the fibre content. The fibre content adopted for the study is 0.5%, 1%, 1.5% volume of cement and fibre lengths 5mm, 10mm, 20mm were considered.



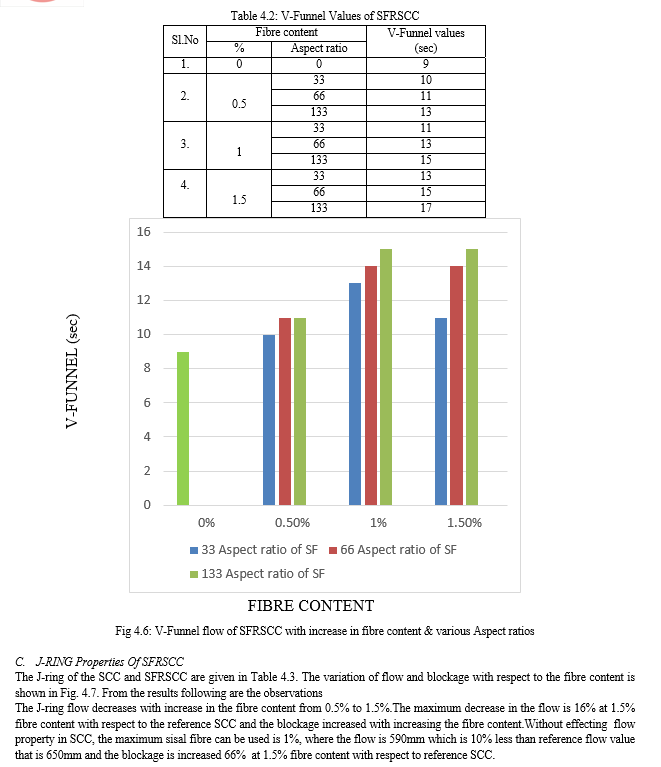
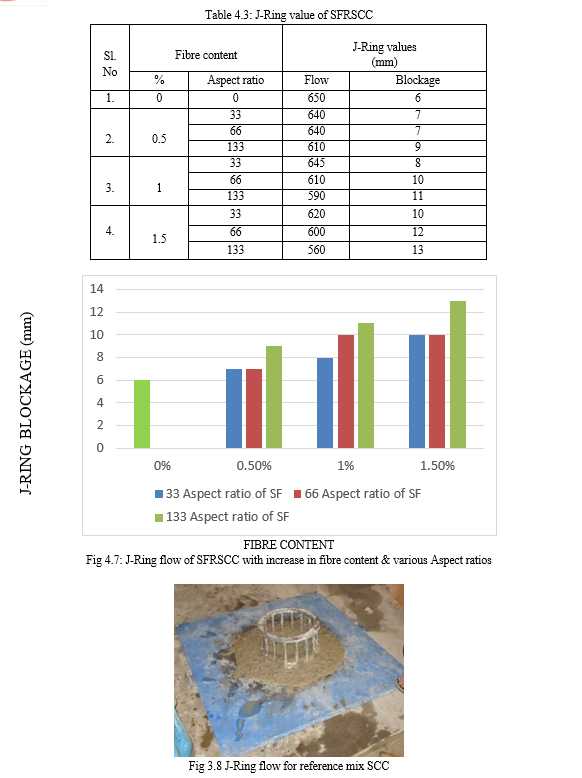

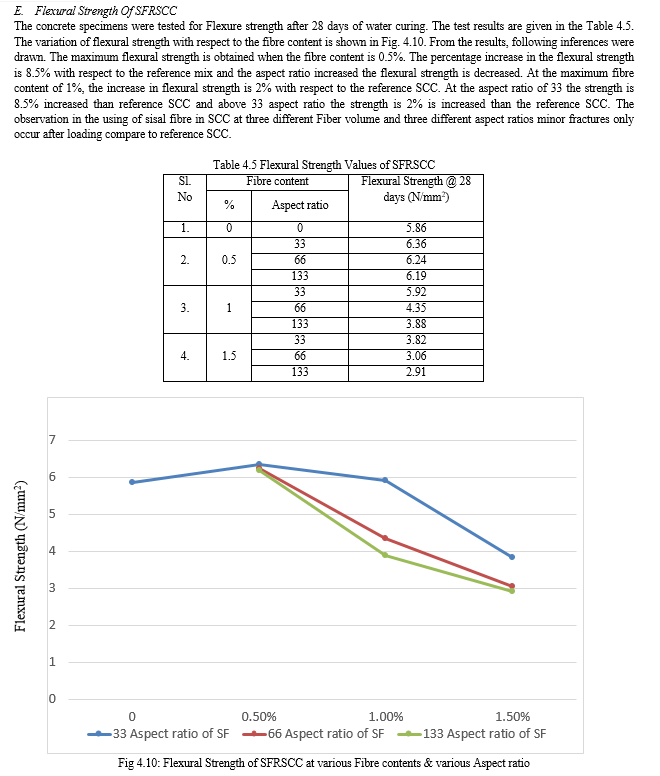

Conclusion
1) In the present investigation the maximum sisal fibre content can be used in SCC is 1%, where the slump flow is 17.24% less than the reference slump flow value. 2) At the sisal fibre content of 1.5%, the mix proportion of SCC for M30 grade of concrete has to be revised especially with respect to the finer portions of the mix, so that the mix will be consistent, without separation of sisal fibres from the cement matrix. 3) The maximum compressive strength of SFRSCC is at 0.5% fibre content and it is 10% higher than that of the compressive strength of reference mix of SCC. 4) Across the age of curing from 14 days to 28 days of the SFRSCC, there is no loss of strength. Instead, the compressive strength improved in the range of 4% to 10%. Hence the sisal fibre are durable in alkaline environment. 5) The maximum impact strength of SFRSCC is at the aspect ratio of 33 and at 0.5%, 1%, 1.5% fibre content and it is 93.5% higher than that of the impact strength of reference mix of SCC. 6) The maximum flexural strength of SFRSCC is at 0.5% fibre content and it is 8.53% higher than that of the flexural strength of reference mix of SCC. 7) Within the limit of study, where in without affecting the slump flow and strength of the composite, it is possible to use a maximum sisal fibre content of 1%.
References
[1] Ramakrishna, G and Sundararajan, T, Impact Strength Of a Few Natural Fibre Reinforced Cement Mortar Slabs, a Comparative Study Cement and Concrete Composites 27 (2005) 547- 553. [2] Ahmed A, Properties and mesostructural Characteristics of Linen Fiber Reinforced Self Compacting Concrete in Slender Column, Ain Shams Engineering Journal production and hosting by Elsevier (2013)4,155-161. [3] Nan su, Kung-Chung Hsu, His- Wen Chai, A Simple Mix Design Method for Self-Compacting Concrete, Cement and Concrete Research 31(2001)1799-1807. [4] Yan Li , Yiu-Wing Mai, Lin ye, Sisal fiber and its composites: a review of recent developments, Composites science and technology 60(2000)2037-2055. [5] Pajak, M Ponikiewski, T, Flexural behaviour of self-compacting concrete reinforced with different types of steel fibers, Construction and building materials 47(2013)397-408. [6] Majid Ali, Xiayang Li, Nawawi Chouw., Experimental investigation on bond strength between coconut fiber and concrete, Material and design 44 (2013) 596-605. [7] Badrinath, R and senthilvelan,T, Comparative Investigation on mechanical properties of Banana and Sisal Reinforced polymer based composites ,Material science 5 (2014) 2263-2272. [8] Tonoli,G.H.D, Savastano,H, Jhon,V.M, Dias,C.M.R, Lahr,F.A.R, Hybrid reinforcement of sisal and polypropylene fibers in cement-based composites,10.1061(ASCE)MT. 1943-5533.0000152. [9] Jayaram,R Sathanandham,T Gnanasundar, S Naveenprabhu,M, Experimental Investigation Of Hybrid Fiber Reinforced Concrete , International journal of innovative research & studies (2014), 699-707. [10] Muthupriya, Strength Study on Fiber Reinforced Self Compacting Concrete with Fly ash and GGBFFS, International Journal of Advanced Structures and Geotechnical Engineering (2014)2, 75-79. [11] European Federation of National Associations Representing for Concrete (EFNARC) guidelines for Self-compacting concrete. [12] Khatib,J.M (2007), Performance of self-compacting concrete containing fly ash. Construction and building materials. [13] Mansur, M.A and Aziz, M.A (1982), A study of jute fibre reinforced cement composites. The International Journal of Cement Composites and Lightweight Concrete. [14] Mustafa Sahmaran, I.Ozgur Yaman (2005), Hybrid fibre reinforced self-compacting concrete with a high volume coarse fly ash . Construction and building materials. [15] Valeria Vorinaldesi, GiacomoMoriconi (2011) Characterization of self-compacting concretes prepared with different fibres and mineral additions. Cement & Concrete Composites. [16] Okamura.H, Self-Compacting High-Performance Concrete, concr. Int. 19(7)50-54. [17] I.S: 2386(Part-3)-1997. Method of test for aggregates for concrete- Part-3: Specific gravity, density, Voids, absorption, and bulking. Bureau Of Indian Standards, New Delhi, India. [18] IS: 10262-2009 Guidelines for concrete mix proportioning, Bureau of Indian standards- New Delhi. [19] Beaudoin JJ.Handbook of Fiber- reinforced Concrete: Principles, properties, developments and applications. Building Materials Science Series.USA: Noveyes Publications; 1990; 330 pp. [20] Silva F.A, Nikhilesh Chawla, Toledo Filho, R.D Tensile Behaviour of High. [21] Vengadesh Marshall Raman, J & Ramasamy, V 2021, ‘Augmentation of dissimilar Technique for Enhancing the Concrete properties with Recycled Coarse Aggregate and Manufactured Sand’, Journal of Material Research and Technology, vol.14, pp.1180-1190. ISSN: 2238-7854, Impact Factor – 5.039.-Annexure I https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.06.094 (Elsevier) [22] Kandasamy S, Gowthaman M , Gowdhamramkarthik P, Vengadesh Marshall Raman J, Magenthiran B,2022, “Strength and durability performance of concrete cast using permeable formwork liner’, Journal of Building Pathology and Rehabilitation (2022) 7:89, https://doi.org/10.1007/s41024-022-00231-9 (Springer) [23] J.Vengadesh Marshall Raman, R. Aswini.\"Studies on Self Compacting Fuel Dispenser Hose Pipe Rubber in Concrete\", Volume 4, Issue XII, International Journal for Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology (IJRASET) Page No: , ISSN : 2321-9653,www.ijraset.com [24] J.Vengadesh Marshall Raman, M. Sriram .\"Experimental Investigation on Fully Replacement of Steel Slag as Course Aggregate in M30 Grade Concrete\", Volume 5, Issue II, International Journal for Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology (IJRASET) Page No: , ISSN : 2321-9653, www.ijraset.com [25] J. Vengadesh Marshall Raman, R. Senthil Raj.\"Mechanical Studies of Self Compacting Concrete Using Plastic Aggregate\", Volume 5, Issue II, International Journal for Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology (IJRASET) Page No: , ISSN : 2321-9653,www.ijraset.com [26] J. Vengadesh Marshall Raman, R. Kirubakaran.\"Experimental Investigation of Partial Replacement of Sand by Laterite Soil in Concrete\", Volume 5, Issue II, International Journal for Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology (IJRASET) Page No: , ISSN : 2321-9653, www.ijraset.com [27] J.Vengadesh Marshall Raman, M. Sriram.\"Study on Replacement Level of Concrete Waste as Fine Aggregate in Concrete\", Volume 5, Issue II, International Journal for Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology (IJRASET) Page No: , ISSN : 2321-9653,www.ijraset.com [28] J.Vengadesh Marshall Raman , K.Jaiganesan , \"Durability Study on Replacement Level of Concrete Waste as Fine Aggregate in Concrete\" Vol. 2 - Issue 2 ( January - February 2017), International Journal of Research in Engineering Technologys (IJRET) , ISSN: 2455- 1341 , www.ijretjournal.org [29] J.Vengadesh Marshall Raman , K.Jaiganesan , \"Non-Destructive Test and Durability Studies of Self Compacting Concrete Using Plastic Aggregate\" Vol. 2 - Issue 2 ( January - February 2017), International Journal of Research in Engineering Technologys (IJRET) , ISSN: 2455- 1341 , www.ijretjournal.org [30] J.Vengadesh Marshall Raman and K Ajeeth Kumar , “Studies on Partially Replacement of Municipal Solid Waste Ash as Cement in Concrete” Vol. 2, No. 2, April 2017, International Journal of civil engineering and construction structures (IJCECS), ISSN: 2455-7714, www.trpubonline.com [31] J Vengadesh Marshall Raman and R Kirubakaran,” Durability Properties on Fuel Dispenser Hose Pipe Rubber as a Coarse Aggregate in Self Compacting Concrete” Vol. 2, No. 2, April 2017 , International Journal of civil engineering and construction structures (IJCECS),ISSN:2455-7714, www.trpubonline.com [32] J Vengadesh Marshall Raman and S Kirubakaran, “ Study on Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregate by Crushed Waste Bottles in Concrete” Vol. 2, No. 2, April 2017, , International Journal of civil engineering and construction structures (IJCECS),ISSN 2455-7714, www.trpubonline.com [33] J.Vengadesh Marshall Raman, V.Murali Krishnan \"Partial Replacement of Cement with GGBS in Self Compacting Concrete for Sustainable Construction\", SSRG International Journal of Civil Engineering (SSRG-IJCE),V4(3),24-28March2017.ISSN:2348–8352. www.internationaljournalssrg.org/IJCE/index.html. Published by: Seventh Sense Research Group [34] J Vengadesh Marshall Raman and K Chellaperumal,” Study on Mechanical Properties of Glass Fiber Reinforced Concrete” Vol. 2, No. 2, April 2017, International Journal of civil engineering and construction structures (IJCECS),ISSN:2455-7714, www.trpubonline.com [35] J. Venkatesh Marshall Raman “Planning and Design of Seismic Resistant Structure using Base Isolation Technique” Vol. 6, Issue 02, 2018, IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development, ISSN (online): 2321-0613, www.ijsrd.com. [36] J.Vengadesh Marshall Raman and N.Vijay “Experimental Study On Glass Fiber Reinforced Concrete Using Metakaolin As Mineral Admixtures” Volume 10, Issue 5, May-2019 ,IJSER - International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, ISSN 2229-5518 , http://www.ijser.org [37] J.Vengadesh Marshall Raman and P.Soundarya “An Experimental Study On Rapid Hardening Cement Concrete Paver Blocks By Using Corundum As A Mineral Admixture” Volume 16, Issue 3 Ser. I (May. - June. 2019),IOSR- Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-ISSN: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, , PP 01-09 www.iosrjournals.org [38] J.Vengadesh Marshall Raman and P.Soundarya “Planning, Designing and Estimation of High Ceiling Residential Building(G+1)” Vol. 9,Issue 5 (Series -V) May 2019, pp 60-75 ,Journal of Engineering Research and Application w.ijera.com ISSN : 2248-9622 Vol. 9,Issue 5 (Series -V) May 2019, pp 60-75 [39] J.Vengadesh Marshall Raman, V.Gnanadevi and V.Anitha “Experimental Investigation on Quarry Dust and Recycled Aggregates in Concrete”, International Journal of Civil Engineering and Applications. ISSN 2249-426X Volume 9, Number 1 (2019), pp. 1-9 © Research India Publications http:// www.ripublication.com [40] J.Vengadesh Marshall Raman, R.Rajesh and P.Sabari Velswaran “Study on Strength of High Performance Concrete by Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregate by Copper Slag” International Journal of Applied Engineering Research ISSN 0973-4562 Volume 14, Number 11 (2019) pp. 2795-2798 © Research India Publications. http://www.ripublication.com [41] J. Vengadesh Marshall Raman “Sustainable Technological Solutions For Faster And Cost Effective Construction Of Mass Housing (A Case Study Of Rapid - Monolithic - Disaster Proof Technology) “Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (JCIET) Volume 06, Issue 01, January - December 2019, pp. 01-16. [42] Vengadesh Marshall Raman, J & Ramasamy, V 2020, ‘various treatment techniques involved to enhance the recycled the recycled coarse aggregate in concrete: A review’, Material Today Proceedings, vol.45, no.7, pp.6356-6363, ISSN: 2214-7853, Impact Factor -1.46. (Elsevier) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.10.935
Copyright
Copyright © 2023 M. Aravinda Samy, Dr. V. Ramasamy, S. Selvakmar. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET56019
Publish Date : 2023-10-05
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

