Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Study on Impact of GST on Construction Sector and Real Estate Sector
Authors: Miss Neha R Chaudhari, Prof. Pranav K. Lende
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.54521
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
The Real Estate sector is a umbrella sector that caters to the need of housing and infrastructure within a nation. Five sub divisions - housing, hospitality, retail, infrastructure, and commercial - are significantly enhanced. As a standard practice throughout the nation, the Real Estate industry lacked professionalism, standardization and consumer protection. The introduction of the Real Estate Regulator Bill (RERA) that had been approved by the Indian Parliament in March 2016 (Differently categorized for various states) has assured a brand new era in the Indian Real Estate industry. The parliament of India has passed a bill that provides a much more transparent and reliable system within the construction industry, primarily concerned with the property market of selling and purchasing properties. The Real Estate Market underwent significant changes because of the implementation of the new Taxation system (GST - Goods and Service Tax). The Real Estate Market experienced a slowdown during its Initial Stages, causing Builders and Contractors to withdraw from the Business for a certain time to adjust to the new regulations and taxation system. The introduction of GST is among the significant changes in the indirect taxation system of India since its inception. Its main aim is to prevent duplication of taxes. The emphasis is on one country one tax. It also aims to expand the tax base. The real estate industry in India is projected to expand by 12 % annually till 2020. New acts and norms are also being implemented in the real estate sector to implement structural reforms. India is implementing affordable housing schemes to meet up with its goal of providing homes to all by 2022, with the government aiming to do so. The aim of this paper is to look at the effect of GST on real estate market in India. In addition, this particular paper aims at understanding the impact of earlier taxes and the impact of GST on Real Estate in the current situation.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Tax is a fiscal compensation or charge required on the taxpayer by the government of the country to that the taxpayer belongs, whether the taxpayer is an individual or maybe a company. It
is applied so as to raise funds for the government's social support. If the taxpayer fails to pay the tax as per the law of the country, they may be charged. India is a country that is democratic, republican, and communist. The Indian constitution is the country's most fundamental rule. The Income Tax Act, the GST, along with many other laws are either derived from or are subordinate to the Indian Constitution. India, the Central government and also the State governments in our country have been empowered to levy taxes. Local agencies such as the Municipality may impose minor penalties as an alternative. The Indian Constitution contains a clause that prohibits the collection of taxes by any person other than the legal authority. Therefore, every tax collected must always be collected by way of a law which has been passed by Parliament or State legislature. The Constitution contains three lists, or the Seventh Schedule contains 3 lists. The schedule grants both the State Government as well as the Central Government greater authority to raise and collect revenue on the various goods listed in the schedules.
A. Indirect Taxes
A government requires funds to function or govern A country. The money comes from many sources. The money is required for various purposes that aid in the administration or functioning of the national government. These tasks include health care, security & defense, and sometimes even law and order maintenance. Other activities also require this money. All the other sources are largely funded by taxation. Furthermore, all taxes paid by the population are used to develop and enhance the society where they live.
The main difference between direct taxes and indirect tax is the fact that direct taxes are paid entirely by a single individual. If we examine indirect taxes, we may conclude the expense is fairly shared between two individuals. Each of these taxes possesses distinct characteristics; therefore, they can be categorized as either progressing or regressive. Taxation can be seen as progress. When we take into consideration elements such as taxable income or taxes on purchases, sales, and sometimes even the production
Money is taken from the seller for this component. All of these collections are dealer oriented. These indirect taxes are the ones that are initially collected from customers. The collecting department receives the tax money from the dealers, who then return it to them. This shows to us that the sellers bear the entire burden of direct tax.
B. GST
It is a fee levied on the delivery of services and products. The tax is divided into several slabs of 0 %, 5 %, 12 %, 18 %, and 28 % tax. The collection of tax is managed.
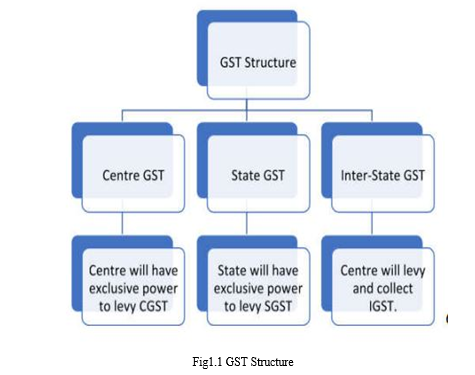
By the GST Council the GST aimed to bring together all indirect taxes. The Service and goods tax went through an online transformation of all procedures. The GST has replaced a number of other indirect taxes, including purchase tax, entertainment tax, sales tax, excise duty and a lot more. The three main components of GST are CGST, SGST, and IGST the introduction of The brand new tax, referred to as The "GST," on July 1, 2017 totally changed all sectors of Indian economy. The tax system of India has undergone a significant change due to this.
After its independence and modernized the indirect taxation system. The primary objective of the GST is to simplify the tax structure applicable to services delivery. The adjustments helped initially to alleviate a few of the short term adverse effects, but they were not without difficulty. The previous indirect tax structure faced the difficulties of duplicate and tax evasion and was freed from additional problems or obstacles, both complex and the perception of low income activities, such as increasing debt, decreasing prices, worldwide inflation, free movement of goods, and so on. The GST aims to help make the credits much more visible, thereby eliminating tax cascading. The objective is to ensure that firms operate as tax exempt entities. It aims to get rid of the tense tax system between the organization and also the national Government and stop tax fraud. The GST has widened the tax base for collecting indirect taxes and simplified the tax computation process. The use of GST directly or indirectly affects almost every sector of the economy.
The Indian real estate market is going through slower sales, higher prices as well as stagnant prices since the Great Recession of 2008-09 and demonetization activity. The industry is getting ready for the coming GST. Developers are taking all necessary safety and preparation measures while consumers wait for the right moment to sign the contract. In spite of the implementation of the GST a long time ago, we would like to explore how indirect property taxes impacted the pre-and post-GST governments.
C. Real Estate
Real estate isn't a profession as it's a small business. Real estate is a business despite the common misconception that it is a job. Science, however, requires demonstrable skill craftsmanship, or the capability to figure out how to be invaluable to other people, to help as much as you can from the work or individual who utilizes it and also the company is operated mostly for profit, with the income going to the proprietor of the company. Obtaining access to certain information is what expertise calls for. Real estate includes both undeveloped land as well as developed areas such as buildings, roads and energy infrastructure. Property rights grant title to property ownership, building and natural resources such as minerals, water, animals, flora, etc.
Estate Tax
Inheritance tax is also referred to as estate tax. If a person inherits an asset, it is imposed. In India, this tax is exempted.
D. Types of Real Estates
There are numerous kinds of Real estates, each one with a distinct objective and use.
The primary categories are: i. Land; ii.Residential; iii. Commercial as well as iv. Industrial
The following will provide an understanding of the way the industry operates and the major categories that each one belongs.
- Land: The land is the foundation of all genuine wealth. Uncultivated and uninhabited land is generally described as "land." Developers purchase land, combine it along with other buildings (called the Assemblies) and rebuild it to boost traffic and property values.
- Residence: Homes for one person, a family or a group of people are referred to as residential dwellings. This type of asset is the most familiar to most people because it's the most common type of asset. The compound also houses family homes, condos, flats, city homes or other lodging options.
- Commercials: The facilities and land which businesses employ to carry out their daily activities are known as commodities. Shopping malls, office towers, lone stores, hotels and parking lots are all examples of lodging.
- Industry: Industrial real estate consists of land and buildings frequently used by industrial companies for factories, machinery development, research and development, construction, transportation of goods and logistics.
E. Objectives of Study
- To investigate different indirect taxes on real property in both pre & post GST regimes.
- To comprehend the current modifications in GST in relation to real estate industry.
- In order to determine the effect of GST on different stakeholders on real estate industry.
- In order to research the Pros and Cons of GST on Real Estate.
II. LITERATURE SURVEY
Govinda Rao (2009) "Goods and Service Tax - Some progress towards clarity" the author in his article express his views on the 1st empowered committee report of state finance ministers on the implementation of Goods and Service tax in India. He explains the key features and drawbacks of the proposed GST. He claims that the proposed GST model should deal with the drawbacks of the VAT system. He talked about the difficulties associated with the implementation of GST in India.
Ehtisham Ahmed and Satya Poddar (2009) carried out a study titled "Goods and Service tax Reforms and Intergovernmental Consideration in India" and concluded that the implementation of GST will result in a straightforward and transparent Tax system that will enhance the productivity and output of the Indian economy. The rational design of GST is crucial for the advantages of GST.
Ehtisham Ahmed and SatyaPoddar (2009) carried out a study on Goods and service tax reforms and intergovernmental consideration in India and concluded that the implementation of GST will result in a transparent and implies tax system that will enhance the productivity and output of the Indian economy. The rational design of GST is crucial to the advantages of GST.
Dr. R. Vasanthagopal (2011). A study was conducted on GST in India: The indirect Taxation system has undergone a significant change and it was concluded that implementing a seamless GST System in India is a beneficial development of the Indian economy. Successful implementation of GST will result in its acceptance by over 130 nations in world along with a brand new ideal type of Indirect Tax System in Asia too.
Dr. R. Vasanthagopal (2011) studied "GST in India: A Big Leap in the Indirect Taxation System" and also realized that moving over to seamless GST from present complex indirect tax system in India is an optimistic step in booming Indian economy.
If GST is successful, it is going to be accepted by over 130 countries around the world and become a new preferred indirect tax system in Asia as well.
Dr. R. Vasanthagopal, (2011)"GST in India: The positive impacts are reliant on a rational and neutral design of the GST, according to "a Big Leap in the Indirect Taxation System." The technique of valuation for levying the tax must be balanced between the competing interests of different stakeholders and a political commitment to a fundamental tax reform through a constitutional amendment.
Nishitha Guptha (2014) in her study stated that implementation of GST in the Indian framework will lead to commercial benefits which were untouched by the VAT system and would essentially lead to economic development.
Panda and Ratel (2015) analyzed the impact of GST (Goods and Services Tax) on Indian Tax Scenario. The historic Indian taxation system as well as its tax structure are described in great detail by them. The authors of this paper discuss the background, silent features and the effect of GST in the current tax situation in India and the need for a change in tax structure from previous tenure.
Kumar, C. R. (2015) in his paper on. "GST in Indian Economy: It's Benefits and Impact" explore about basic concept of GST and it impact. GST benefit to business person as well as consumer inter of reduction of tax rate and compliance burden.
Dani, S. (2016) in his paper on, research paper on an impact of goods and service tax (GST) on Indian economy. Explain about GST concept in Indian economy. Paper limited to descriptive study. Data taken from published sources.
Kumar,V. (2016) in his paper on. "GST-A boon or a bane for India" explain about recommended GST model and its benefit. Study published prior to GST era which explore about concept of GST in Indian economy. Paper made analysis between pre GST model i.c. VAT and new GST model.
Dani S (2016) A Research Paper on an Impact of Goods and Service Tax (GST) on Indian E stated that GST would impact negatively on the real esstate market. It would add up to 8percentage to the cost of new homes and reduce demand by about 12 percentage
Poonam (2017) in her study cleared that in the system of indirect taxation GST plays a very important role. The cascading and double taxation effects can be reduced by combing central and state taxes. Consumer's tax burden will approximately reduce to 25% to 30% when GST is introduced and then after Indian manufactured products would become more and more inexpensive in the domestic and international markets. This type of taxation system would directly encourage economic growth. GST with its transparent features will prove easier to administer. With the above reviews we can assume that GST is a tax reform which will change the scenario of the country as a support for this review study.
III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Methodology
Research is a systematic and logical search for new and helpful information on a specific topic. A systematic approach to solving a problem is known as research methodology. It's a science that studies how research should be conducted. The ways in which researchers describe, explain and predict phenomena are referred to as research methodology.
B. Research Design
A good research design has characteristics viz. problem definition, time required for research project and estimate of expenses to be incurred the function of research design is to ensure that the required data are collected and they are collected accurately and economically. A research design is purely and simply the framework for a study that guide the collection and analysis data. In this project the two basic types of research design are used
C. Descriptive Research
The descriptive study generally concentrates on determining The frequency with which a thing happens or the way 2 variables interact. the apex of The research is The design. It calls for the development of more specific hypotheses and their testing through experiments. The technique of statically inference, This is the research concept of the study after which it comes to create the analysis program, which means that how to proceed prior to choosing the real interpretation and it's talked about below.
IV. RESULT AND DISSCUSSION
- To study the various indirect taxes on real estate in the pre and post GST regime
For the purpose of checking out the different old and also new informal taxes, the information collected in the GST compliance manuals in which the Goods and Service Tax (GST) is levied on the availability of services and goods.
The Indian Goods and Services tax Act is a broad - based, categorized Tax that is liable for all value additions. The following table shows the tax rates throughout the VAT regime and now under the GST regime, as per the set.
Table 4.1 To study the various indirect taxes on real estate in the pre and post GST regime
|
Nature of Duty |
Tax Rate(Percentage) |
Time of Payment of Tax |
|
VAT |
1.00--4.00 |
On Sale of Under Construction Properties |
|
Service Tax |
4.50 |
|
|
Registration Charges |
0.50- 1.00 |
|
|
Stamp Duty charges |
5.00- 7.00 |
Source: IJRE, March 2019
VAT, Registration Charges, Stamp Duty Charges vary from state to state. VAT was not applicable on completed or ready to sale properties. Under the erstwhile indirect tax regime, Cenvat Credit on inputs used for the construction of a building or a civil structure or any part thereof was restricted too
COMPARISON OF APPLICABLE TAXES BEFORE AND AFTER GST
The Goods and Services tax (GST) is an indirect Tax that is applicable across India and has replaced a number of cascading taxes imposed by the central and state governments. It had been incorporated as The Constitution (One Hundred and First Amendment) Act 2017.
Comparison of applicable taxes before and after GST
|
Construction Materials |
Previous Taxes |
Taxes under GST |
Impact |
|
Cement |
31% |
28% |
Cheaper |
|
TMT Bars |
18% |
18% |
Neutral |
|
Flyash Bricks |
5% |
12% |
Costlier |
|
Tiles |
26% |
28% |
Costlier |
|
Paint |
28% |
28% |
Neutral |
|
Sanitaryware |
28% |
28% |
Neutral |
|
Plywood |
28% |
28% |
Neutral |
|
Electrical Goods |
12% |
28% |
Costlier |
V. FUTURE-SCOPE
Some suggestions for enhancing the administrative framework for implementing the Goods and Services Tax Act in India::
- Standardization of procedures and systems.
- Tax relief in case of branch transfer
- Job works procedures are clearly defined
- There is a Uniform dispute settlement mechanism.
- Proper training for both taxpayers and taxen forcers.
- Re-organization of management apparatus for GST implementation..
Conclusion
Real estate sector plays a crucial role in Indian GDP due to numerous sectors. The GDP of India is contributed by this sector at a rate of almost 7.3 %. It also provides services to individuals, employment generation, professional service providers and also numerous other activities undertaken in these sectors. Special consideration was given under the new GST regime in terms of tax reduction and credit availability. GST has a positive effect on real estate as rate of tax has been reduced, which is beneficial for both home buyers and consumers. Single point taxation is now in place. Nevertheless, there are a number of points that must be addressed prior to consideration, such as the payment of tax under the reverse charge mechanism, where the tax credit is not available. Buyers will be required to pay a higher price than under a normal arrangement in this scenario. The GST has had a positive impact on real estate in general. The implementation of GST has inevitably resulted in an increase in the revenue generated by the sector, which is also the largest employment generator. The quality of work carried out by the contractors is improved as cash flow in a project has a fixed duration. A panel has been established by builders and other agencies involved in this industry to explore unexplored areas of working on the principles of construction management & risk management of projects that hold significant importance in the construction society. The cost impact of GST has been countered by an innovative approach to the different technological option to do the work.
References
[1] Adhana, D. K. (2015) Tax on goods and services (GST): Indian economy needs a panacea. The International Journal of Engineering and Management Research, 5 (4), 333 - 338. [2] Agogo Mawuli (2014) Presentation at the PNG Taxation Research and Review Symposium, PortMoresby, Holiday Inn, 29-30. \"Goods and Service Tax- An Appraisal\" [3] AgogoMawulli (2014) \"Goods and Service Tax - An assessment Paper presented at the PNG Taxation Research and Review Symposium\" Holiday inn port meoresby, Pg No.29-30, April2014 [4] Chakraborty, P., & Rao, P. K. (2010, Jan 2) In India: Goods and services tax: An evaluation of the base. the Economic and Political Weekly, 45 (1), pp. 49 -54 [5] Dr. R. Vasanthagopal (2011), \"GST in India: An overview.\" International Journal of Trade, Economics and Finance, No. 2, Vol.2, April2011 \"A Big Leap in the Indirect Taxation System\" [6] Dani, S. (2017). A Research Paper on the Effect of Goods and Service Tax (GST) on Indian Economy The Business and Economics Journal, pp. 1-2. [7] EhtishamAhamad and SatyaPoddar (2009), \"Goods and Service Tax Reforms and Intergovernmental Consideration in India,\" \"Asia Research Center,\" LSE-2009 8-Fabian and Erik Hoelzl (2015), Price, Perception and confirmation bias within the context of a VAT increase, Journal of Economic Psychology 32 (1) volume 2 Pg No. 131-- 141in20. [8] Garg, G.(2013). Indian Journal of Scientific Management and Research (IJSRM) 2 (2), 542-549. Basic concepts and characteristics of goods and services tax
Copyright
Copyright © 2023 Miss Neha R Chaudhari, Prof. Pranav K. Lende. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET54521
Publish Date : 2023-06-29
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

