Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Summarization and Translation Using NLP
Authors: Chiranjeevi Joshi, Balaji K, Sai Saketh B, Abhishek R, Dr. C N Shariff
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.61391
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Text summarization and translation are two critical tasks in natural language processing with significant applications in various domains such as news aggregation, document summarization, machine translation, and information retrieval. In recent years, there has been remarkable progress in the development of techniques and models for both tasks, leveraging advancements in deep learning and neural network architectures. This paper presents a comprehensive review and comparative analysis of state-of-the-art methods in text summarization and translation. First, we provide an overview of the different approaches to text summarization, including extractive, abstractive, and hybrid methods, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses. We discuss various evaluation metrics and datasets commonly used for benchmarking summarization systems, shedding light on the challenges and opportunities in this field. Next, we delve into the realm of machine translation, exploring the evolution from statistical machine translation to neural machine translation and beyond. We examine the architecture of neural machine translation models, including sequence-to-sequence models with attention mechanisms and transformer-based architectures, which have shown remarkable performance improvements over traditional methods. Furthermore, we conduct a comparative analysis of text summarization and translation techniques, identifying commonalities and differences in their approaches, architectures, and evaluation methodologies. We discuss transfer learning techniques and pre-trained language models, such as BERT and GPT, and their adaptation to both tasks, elucidating their impact on performance and efficiency. Finally, we present insights into future directions and emerging trends in text summarization and translation research, including the integration of multimodal information, hidden markup model, and the application of deep generative models for text generation tasks. We conclude by emphasizing the importance of continued research and collaboration in advancing these fundamental tasks in natural language processing.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
In today's interconnected world, the deluge of textual information available across various languages poses both a challenge and an opportunity. Text summarization and translation have emerged as indispensable tools in handling this wealth of linguistic data efficiently and effectively. text summarization is the process of condensing a large body of text into a concise and coherent summary, capturing the essential information while discarding redundant details. This task is particularly useful in scenarios where time and attention are limited, such as news articles, research papers, and legal documents. By automatically extracting key points, text summarization enables users to grasp the main ideas of a document swiftly, facilitating quicker decision-making and information digestion.
Translation, on the other hand, bridges linguistic divides by rendering text from one language into another while preserving its meaning and intent. In a globalized world where communication knows no boundaries, translation serves as a vital conduit for sharing knowledge, facilitating commerce, and fostering cultural exchange. From literature and business contracts to user manuals and social media posts, the need for accurate and efficient translation spans across diverse domains and industries.
Both text summarization and translation have witnessed significant advancements in recent years, owing largely to the advent of natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning techniques. From rule-based approaches to more sophisticated neural network models, the evolution of these technologies has unlocked new possibilities for automating and enhancing these tasks. As a result, businesses, researchers, and individuals alike can leverage these capabilities to streamline workflows, access information across languages, and break down language barriers in unprecedented ways.
In this era of information overload and linguistic diversity, the synergy between text summarization and translation holds immense promise. By distilling vast amounts of textual data into manageable summaries and facilitating seamless communication across languages, these technologies empower individuals and organizations to navigate the complexities of our interconnected world with greater ease and efficiency.
II. LITERATURE SURVEY
- In paper [1], The process of transfiguring a large documental information into a clear and concise form. In this article, They present a detailed comparative study of various extractive methods for automatic text summarization on Hindi and English text datasets of news articles. We consider 13 different summarization techniques, namely, TextRank, LexRank, Luhn, LSA, Edmundson, Chunk Rank, TGraph, UniRank, NN-ED, NN-SE, FE-SE, Summa RuNNer, and MMR-SE, and we evaluate their performance using various performance metrics, such as precision, recall, F1, cohesion, non-redundancy, readability, and significance. A thorough analysis is done in eight different parts that exhibits the strengths and limitations of these methods, effect of performance over the summary length, impact of language of a document, and other factors as well. A standard summary evaluation tool (ROUGE) and extensive programmatic evaluation using Python 3.5 in Anaconda environment are used to evaluate their outcome.
- In paper [2] This paper provides applicability of the Real Coded Genetic Algorithm to the Natural Language Processing Task, i.e., Text Summarization. The purpose of text summarization is to reduce an extensive document into a concise format such that the essence of the content is retained. By doing so, users can utilize the summarized document for vivid applications such as Question Answering, Machine Translation, Fake News Detection, and Named Entity Recognition to name a selected few.
- In paper [3], With the widespread use of Machine Trans-lation(MT) techniques, attempt to minimize communication gap among people from di-verse linguistic backgrounds. We have par-tic pated in Workshop on Asian Translation 2019 (WAT2019) multi-modal translation task. There are three types of submission track namely, multi-modal translation, Hindi-only image captioning and text-only translation for English to Hindi translation. The main challenge is to provide a precise MT output. The multi-modal concept incorporates textual and visual features in the translation task. In this work, multi-modal translation track re-lies on pre-trained convolutional neural net-works (CNN) with Visual Geometry Group having 19 layered (VGG19) to extract image features and attention-based Neural Machine Translation (NMT) system for translation. The merge-model of recurrent neural network(RNN) and CNN is used for the Hindi-only image captioning. The text-only translation track is based on the transformer model of them system. The official results evaluated atWAT2019 translation task, which shows that our multi-modal NMT system achieved Bilingual Evaluation Understudy (BLEU) score20.37, Rank-based Intuitive Bilingual Eval-auction Score (RIBES) 0.642838, Adequacy-Fluency Metrics (AMFM) score 0.668260 for challenge test data and BLEU score 40.55,RIBES 0.760080, AMFM score 0.770860 for evaluation test data in English to Hindi multi-modal translation respectively.
- In paper [4], Today with the advent of the Internet huge volume of text in the form of news articles, editorials, blogs etc. are available for access to the users. Summarization of these contents becomes an essential requirement to enable faster and efficient search of such documents. Manual text summarization consumes a plenty of time, effort, and money, and it's even impractical when there's a lot of text. Since the 1950s, researchers are working to develop various ATS techniques. There are three types of ATS approaches: extractive summarization, abstractive summarization and hybrid. The extractive method picks out the most important sentences from the input documents and combined them to produce the summary. The abstractive method translates the input documents into
- In paper [5], Automatic Text Summarization (ATS) methods have been proposed for resource-rich languages, such as English, Chinese. However, resource-limited languages like Hindi realized very little attention from researchers. The lack of resources still makes the ATS task for the Hindi language a challenging and open problem. Capturing semantic features and hidden relationships among the text units are the two main characteristics of an informative summary. In the current work, we propose an ATS model based on the document vector method to explore the semantic relations existing in the document. Moreover, we suggest two algorithms: sentence ranking and summary generation based on three main characteristics including, redundancy, diversity, and compression rate to create a clear and coherent summary. The proposed model is language independent with some language-specific preprocessing. Further, we evaluate our model on two different language datasets as literary novels in Hindi and DUC 2007 news articles in English. We apply the ROUGE metric to measure the performance of the generated summaries. Besides, we also compare the proposed model against four baseline methods: TextRank, Lexrank, Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA), and Mudasir et al. models. The overall macro-Average F-Score (18.5% for Hindi, 26% for English) for very short length summaries of sizes 5% and 15% compression rates produced by our model is higher than the baseline approaches. In case of very lengthy summaries of size 50% compression rate, our model has the highest MacroAverage values, 18% for the Hindi novels and 25% for the English news articles against all the comparison methods. From the result analysis, we perceive that the proposed model beats all the baselines from the experimental outcomes and leads to diverse, least-redundant, semantic-rich, and compressed text summary generation.
- In paper [6], In the era of digital world, online information is growing exponentially. It leads to emergence of inconvenient searching of relevant information in relevant time. In this regard, automatic text summarizer proves to be a good tool. It helps in creating a brief and meaningful form of the given text using natural language tool kit so that users can access the information in quick manner. Today, a lot of summarization tools are available for rich resource languages such as English. But, it seems difficult to summarize the text for Indian languages (low resource languages) due to limited availability of NLP tools and techniques for Indian languages. In this paper, we present a survey on existing text summarization methods and NLP tools for Indian languages. We also discuss about the issues associated with the Indian languages that are the bottlenecks for summarizing Indian language text.
III. METHODOLOGY
A. Block Diagram
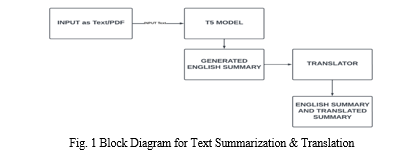
- Input Text Preprocessing: This process involves methods for data cleaning, such as removing unnecessary characters, special symbols, white spaces, and formatting. The goal is to prepare the input text for further processing.
- Tokenization: After preprocessing, the input text is tokenized into smaller units, such as words, sub-words, or characters. This step is performed using a pre-trained tokenizer, which converts the input text into a format suitable for input to the model.
- Model Inference: In this step, the tokenized input text is fed into a pre-trained T5 model for conditional generation. The T5 model, based on a transformer architecture, generates text based on the provided input and a task-specific prefix. It processes the input tokens, attends to relevant information, and generates a summary sequence using learned parameters and attention mechanisms.
- Post-processing: Once the model generates a summary sequence, it is decoded from token IDs back into human-readable text. Post-processing involves removing special tokens like padding tokens and end-of-sentence tokens. Additionally, the summary is refined to ensure coherence, readability, and grammatical correctness.
- Output: The final output of the algorithm is the summarized text in English. Users have the option to translate the summary into different languages for better comprehension and understanding. tokenize sentences into words or sub words using language-specific tokenization tools or libraries.
IV. RESULTS


Conclusion
In conclusion, text summarization in Hindi or Telugu languages presents a promising avenue for natural language processing research and application. The challenges involved in summarizing text in languages other than English are multifaceted, encompassing linguistic diversity, morphological variations, and the availability of quality language resources. However, the development of effective and accurate summarization models for Hindi or Telugu languages is of paramount importance for enhancing global information access and communication. As researchers continue to innovate and adapt existing techniques to suit the specific needs of various languages, the potential for improved cross-linguistic understanding and knowledge dissemination remains substantial. While challenges persist, the progress made in the field of Hindi or Telugu text summarization offers hope for more inclusive and accessible information dissemination in a multilingual world.
References
[1] Verma, Pradeepika, Sukomal Pal, and Hari Om. \"A comparative analysis on Hindi and English extractive text summarization.\" ACM Transactions on Asian and Low-Resource Language Information Processing (TALLIP) 18, no. 3 (2019): 1-39. [2] Jain, Arti, Anuja Arora, Jorge Morato, Divakar Yadav, and Kumar Vimal Kumar. \"Automatic text summarization for Hindi using real coded genetic algorithm.\" Applied Sciences 12, no. 13 (2022): 6584. [3] Rani, Ruby, and D. K. Lobiyal. \"Document vector embedding based extractive text summarization system for Hindi and English text.\" Applied Intelligence (2022): 1-20. [4] Laskar, Sahinur Rahman, Rohit Pratap Singh, Partha Pakray, and Sivaji Bandyopadhyay. \"English to Hindi multi-modal neural machine translation and Hindi image captioning.\" In Proceedings of the 6th Workshop on Asian Translation, pp. 62-67. 2019. [5] Rawat, Sunita, Kavita Kalambe, Sagarika Jaywant, Lakshita Werulkar, Mukul Barbate, and Tarrun Jaiswal. \"English to Hindi Cross-Lingual Text Summarizer using TextRank Algorithm.\" International Journal of Next-Generation Computing 14, no. 1 (2023). [6] Verma, Pradeepika, and Anshul Verma. \"Accountability of NLP tools in text summarization for Indian languages.\" Journal of scientific research 64, no. 1 (2020): 258-263.
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Chiranjeevi Joshi, Balaji K, Sai Saketh B, Abhishek R, Dr. C N Shariff. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET61391
Publish Date : 2024-04-30
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

