Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Review Paper on Techniques of 2D to 3D Image Reconstruction
Authors: Himanshu Tanwar, Gaurav Kumar
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.55996
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
The review paper emphasize on reducing technologies for 2D and 3D imaging, as well as model conversion. Although the popularity of 3D hardware is growing rapidly in the present era, 3D content is still dominated by its 2D counterpart. There are two main categories of image processing now available in the market, namely analogue and digital image processing. To produce hard copies such as scanned pictures and printouts, with images being the most common output, the analogue IP technique is used. On the other hand, Digital IP is used to manipulate digital images using computers, the outputs are often information related to images, mainly being data on features, edging characteristics, or masks. Image processing techniques, including Machine Learning and Deep Learning, can get more powerful.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
The difficulty of reconstructing 3D representation of face from 2D photographs is a key topic in graphics of computer ,with applications such as image processing, a 2D image consists only two dimensions: height and breadth; it lacks depth in face identification and animation. As on loss of data during projection of camera and the requirement of sufficient prior knowledge of 3D shapes, this challenge is extremely difficult. In it.
Therefore, a 2D image can be expressed as function in a plane i.e. f(x, y) , where x and y are coordinates of plane at that point. Intensity or gray level of image at any point in the plain is defined as amplitude of function, f at that couple of coordinates (x, y). Any image is kept in the category of digital when all the pairs of (x, y) are finite and discrete. On the other hand the one that incorporates depth information in addition to height and width. 3D is currently available on TVs, Blu-Ray players, gaming products, smart mobile phones and many other things is known as 3D image. These 3D media create a sense of immersion or a more lifelike viewing experience for the audience.As 3D texture available, on the other hand, does not keep up with its production. To make 3D shape like material, so there are two important methods. The first methodcaptures by cameras is to capture the content directly with several cameras, while the second method is to convert 2D conventional footage to 3D. The former method produces the best results, but it is difficult and expensive to apply since it requires specialized equipment and a powerful production system.
3D imaging is otherwise called as stereoscopy. With the use of binocular vision, this approach is widely applied to create or enhance a 2D image by increasing the appearance of depth. The issue of estimating depth from a single 2D picture, which is the first stage in 2D to 3D translation, may be expressed in a variety of ways, such as a shape from shading problem[].
This issue, however, is highly under-controlled; brilliant depth estimates can only be discovered under exceptional circumstances. Given details about lighting, surface resource, and projection of camera, this algorithm is computer insight algorithm, that results in 3D form from shade variations in 2D pictures. These strategies take advantage of the information provided by extrinsic factors such as shade. Other techniques, such as Blanz and Vetter's 3D Morphable Model [] (3DMM), express a linear combination of the sample faces. Due to its simplicity, 3DMM is a common parametric face model that has served as the foundation for more complex face reconstruction approaches. Mostly methods need multiple images for reconstruction which is time consuming and computationally expensive.
So some effective methods are used by researchers.
II. APPLICATIONS
Image processing to create models and images is one of the most rapidly evolving technologies, and it's evolved tremendously over time. It is now employed by a wide range of enterprises and organisations for a wide range of applications. It can be said that now 3D image reconstruction can be used in each and every field. Entertainment is one of applications of image processing. People enjoy 3D movies more than 2D. Today there are many games based on 3D visualisation. Robotics and reverse engineering has also been benefited by image processing.
Augmented reality has a great future scope and it can be made better by using 3D images and animation. It is used in medical field to increase the quality and quantity of information and makes the content easier to understand. To increase the quality of 3D picture reconstruction, several comparisons of different methodologies have been conducted.
3d image reconstruction has numerous applications in various domains. Some of them are discussed below:
- Image Processing: The foundation, inclination, and canopy type of an effort to consolidate a building footprint.
- Multimedia: Determining structure altitudes and functioning together to improve footprint detection.
- Video Technology: A 3D model reformation of a planar-faced intricate manifold item is constructed from a 2D linear drawing.
- Pattern Analysis and Machine Learning
a. A mesh evolution framework based on a new self-intersection removal technique called TransforMesh.
b. A novel object-based rendering and 3D reconstruction programme is constructed by combining the linear and non-linear morphable neutral face models in an optimization framework. c.) A unique methodology and multiple kinect capturing system for the construction of accurate, realistic.
c. In order to generate the shape and handle patches necessary for a 3D global object, shading information is used in more generic scenarios.
5. Computer Graphics: For a scene captured under several unknown illuminations, MVS and photometric stereo are integrated to build watertight 3D reconstructions.
III. LITERATURE REVIEW
John D. Bustard and Mark S. Nixon, 2010, [1] believed in the paper that the human ear can be used to recognize them. This is because it varies crucially between person to person. In a detection algorithm, accuracy and robustness had been improved by using ears in addition with face recognition, especially for non-frontal viewpoints. Face Recognition Grand Challenge dataset was utilised. The model is resistant to occlusion as well as noise. It was achieved by marking areas of the mesh as invalid. The fitting process was not aided by these invalid regions. The labelling is done automatically by a classifier that has been trained. The labelling is done automatically with the help of a classifier that was trained on 30 humanly labelled photographs. To classify the surface, a collection of labelled feature points were used to align and distort the model. The range scan was then approximated by computing the mesh surface points that were closest to the range scan pixels.
The results suggest that the proposed methodology extracts a decent performance linked with an individual's identity. It also displays that the used training samples are approximately attaining model convergence within the registration process' error margins.
Luo Jiang, Bailin Deng, Juyong Zhang, Ligang Liu[8]: used the example-based algorithm to acquire an approximation of the targeted 3d model of face. The prosess started when the input image was attached with example-based parametric face model. Faceware House and the Basel Force Model were used to create the guideline model. Two datasets was used in the paper. Those dataset consisted of 3D face images that had larger diversity in facial expression and recognition respectively. A network model was created, that clearly reflects the target face's largely contour.
- After that, they apply smooth deformation to the coarse face model to capture medium facial characteristics.
- Finally, a height face surface is prosuced depending on the shade variance of the input image, the lighting parameter and the augmented face model.
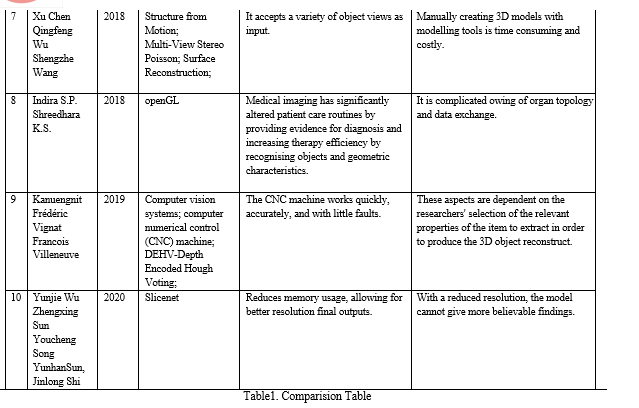
Yunjie Wu,Zhengxing Sun, YouchengSong,YunhanSun,JinlongSh[], introduce an unique network that successively outputs 2D slices for 3D reconstruction using shared-weight 2D deconvolution. Also a sliceaware attention mechanism was build. It allows a 3D model to bring out all important and relevant information for each and every slice. Finally, the utility of the technique using both synthetic and real data was demonstrated.
Yunjie Wu, Zhengxing Sun, YouchengSong,Yunhan Sun, Jinlong Shi[],introduce the latest 2D-to-3D picture conversion technique that is improved and technically much more efficient. It was discovered by K stereopairs or image + depth pairs whose photometric data is approximately equivalent to that of a 2D interrogation, so that it could be translated from a library of 3D photographs.
Following that, the k matched depth fields are blended, and its depth is aligned with the query of 2D image. XiaoMei Bai and Yang Kuan[] used 3D modeling as the starting point, foundation, and core of virtual reality. In addition to the built-in geometric models, 3DS MAX provides a variety of model creation schemes.
By default, 3DS MAX models loaded into Unity 3d have a ratio of 0.01:1. It also includes texture map generation, map baking and other features, and can also generate automatic animations, animations and more in virtual reality. File format generated (FBX, 3DS, OBJ in Unity can be read in 3D) and scale factor in Unity 3D.
Meng Yang, Zhen Wang, Shilong Xiao[], The article investigates collision detection and artificial intelligence technology in three-dimensional game technologies, designs three-dimensional game systems, and proposes a collision detection algorithm based on segment detection based on extensive research on various collision detection algorithms. The experiment reveals that the revised collision detection algorithm can successfully decrease system calculation amount and promote operational speed, with calculation amount reduced by 11.85 percent and game operational speed increased by 5.33 percent. The paper proposes a technique for ranking different searched path and brush up the 765 A * algorithm to address most of the shortcomings of high storage capacity, heavy computation each node, and lengthy search time. When the game map is not very complicated, the enhanced method may accomplish optimum path search. According to the testing results, the enhanced. A * path search algorithm may reduce number of visitors traffic by 34.76 percent for inner storage while increasing game rendering frequency by 2.56 percent.

Conclusion
The recent conversion methodology used in reconstruction of 2D pictures and animations to 3D were discussed in this literature study. Many approaches, such as Shape from Shading, Coarse to Find Method, Slicenet, Robust Registration Algorithm, and 3D Morphage model, can be used to convert (3DMM). There is an increasing need for 3D content, and these solutions can help bridge the difference among both i.e. 2D and 3D image. Even though the discussed strategies produce positive outputs, there is still scope of development.Every discussed algorithm has its own advantages and disadvantages. Since the methods discussed in the paper are computer vision algorithms, accomplishment of future hardware to minimize the design metrics for practical implementation and optimization can be researched. Hence, it is concluded that slicenet is the best algorithm that can be used for transformation 2d images to 3d, because it had less limitation as compare to other methods.
References
[1] Chen, X., Wu, Q., & Wang, S. (2018, August). Research on 3D reconstruction based on multiple views. In 2018 13th International Conference on Computer Science & Education (ICCSE) (pp. 1-5). IEEE. [2] Patoommakesorn, K., Vignat, F., & Villeneuve, F. (2019, April). The 3D Edge Reconstruction from 2D Image by Using Correlation Based Algorithm. In 2019 IEEE 6th International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Applications (ICIEA) (pp. 372-376). IEEE. [3] Yun, J., Lee, J., Han, D., Ju, J., & Kim, J. (2017, February). Cost-efficient 3D face reconstruction from a single 2D image. In 2017 19th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT) (pp. 629632). IEEE. [4] Afzal, H. R., Luo, S., & Afzal, M. K. (2018, March). Reconstruction of 3D facial image using a single 2D image. In 2018 International Conference on Computing, Mathematics and Engineering Technologies (iCoMET) (pp. 1-5). IEEE. [5] Bustard, J. D., & Nixon, M. S. (2010, June). 3D morphable model construction for robust ear and face recognition. In 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 2582-2589). IEEE. [6] Wu, T., Zhou, F., & Liao, Q. (2017, September). Real-time 3D face reconstruction from one single image by displacement mapping. In 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP) (pp. 2204-2208). IEEE. [7] Li, B., Zhao, Y., & Wang, X. (2020, June). A 2D face image texture synthesis and 3D model reconstruction based on the Unity platform. In 2020 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Applications (ICAICA) (pp. 870-873). IEEE. [8] Assuja, M. A., & Suwardi, I. S. (2015, May). 3D coordinate extraction from single 2D indoor image. In 2015 International Seminar on Intelligent Technology and Its Applications (ISITIA) (pp. 233-238). IEEE. [9] Wu, Y., Sun, Z., Song, Y., Sun, Y., & Shi, J. (2020, May). Slicenet: Slice-wise 3D shapes reconstruction from single image. In ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (pp. 1833-1837). IEEE. [10] Indira, S. P., & Shreedhara, K. S. (2018, December). 3D Image Reconstruction Using Polygonal Based 2D Cross Sections. In 2018 3rd International Conference on Computational Systems and Information Technology for Sustainable Solutions (CSITSS) (pp. 317-323). IEEE. [11] Yang, M., Wang, Z., & Xiao, S. (2010, July). Research on of 3D game design and development technology. In 2010 3rd International Conference on Computer Science and Information Technology (Vol. 9, pp. 762-765). IEEE. [12] Kuang, Y., & Bai, X. (2018, August). The research of virtual reality scene modeling based on unity 3D. In 2018 13th International Conference on Computer Science & Education (ICCSE) (pp. 1-3). IEEE.
Copyright
Copyright © 2023 Himanshu Tanwar, Gaurav Kumar. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET55996
Publish Date : 2023-10-03
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

