Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Text, Image and Audio Steganography
Authors: Ms. T N Aruna , L R Nandika , C I Sneha, Timothy Jerald Xavier, Treesa Mary George
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.51091
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Steganography refers to the concealment of confidential data within a common medium, like a text, image, or audio file, without altering its original appearance, to evade detection. This method is used for several purposes, including protecting data privacy, preventing unauthorized access to data, and ensuring safe information transmission over insecure networks. While steganography can be used for legitimate purposes such as by military, law enforcement, and journalism, it can also be employed for malicious activities like cybercrime and terrorism. The least significant bit (LSB) of each letter in text & audio and the LSB of each pixel in images are altered in steganography to make the alterations invisible. Advanced steganography algorithms like Masking & Filtering and Encrypt & Scatter have improved security against steganalysis assaults while producing higher-quality stego images. The method’s capability for concealing text with an unlimited hidden text size in text, audio, and images will be employed in the outcome.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Steganos a Greek word, which means covered or concealed, and graphy which means writing or drawing, are the roots of the word "steganography". The art of steganography involves hiding the presence of information within seemingly innocent carriers. Steganography, in its broadest meaning, refers to the process of concealing messages within images. More specifically, the purpose of steganography is to conceal communications among other, unimportant messages in such a way that no adversary can even tell that a second secret message is present.
Today, steganography is widely used in digital communication to ensure the security and privacy of sensitive information. The main advantage of steganography is that it allows messages to be hidden in plain sight, without arousing suspicion. Steganography techniques involve modifying the least significant bits of the pixels in an image or the samples in an audio file.
These modifications are usually imperceptible to the human eye or ear and do not significantly alter the overall quality of the medium.
The hidden message can only be retrieved by someone who knows where to look and how to extract it. Steganography is often used in combination with cryptography to provide an additional layer of security. Cryptography involves scrambling the message using mathematical algorithms so that it can only be read by someone who has the correct key. Steganography, on the other hand, ensures that even if the message is intercepted, it cannot be detected without prior knowledge of its existence. This combination of techniques makes it extremely difficult for an attacker to intercept and decipher the message, even if they have access to the medium in which it is hidden
II. METHODOLOGY
A. Text Steganography
Text steganography involves the concealment of confidential messages within the plain text, without the awareness of unintended recipients. In order to produce readable texts, it is essential to do things like changing the format of the preexisting text, altering the words within a text, creating random character sequences, or using a context-free grammar. Various methods include the following to conceal the data in the text:
- Format-Based Method: Format-based text steganography is a technique of concealing secret information by altering the format or structure of a document while keeping the visible text unchanged. This method is often used to hide information within documents like Microsoft Word files or HTML pages. In this approach, the document's formatting, such as font size, color, or spacing, is manipulated to create a hidden message without altering the visible content of the document. The hidden message is embedded within the document's structure in a way that is not noticeable to the human eye but can be extracted by the intended recipient using appropriate steganography tools. The primary objective of format-based text steganography is to ensure that confidential information is transmitted without arousing suspicion from unauthorized users.
- Random and Statistical Generation: Random and Statistical Generation is a type of text steganography that involves using random and statistical methods to embed hidden information within a text document. This technique typically involves the replacement of certain characters or words with other characters or words that are chosen using random or statistical algorithms. The method utilizes the statistical properties of the text, such as the frequency of occurrence of certain characters or words, to ensure that the embedded message is hidden in plain sight and is not easily detectable by unauthorized users. The randomness of the chosen characters or words also ensures that the hidden message is not easily decipherable without the appropriate decoding algorithm. The primary goal of Random and Statistical Generation text steganography is to ensure the confidentiality of the hidden message while keeping the original text document's readability and appearance intact.
- Linguistic Method: The linguistic Method is a type of text steganography that involves hiding secret information within the text by using linguistic techniques. This method usually employs natural language processing techniques to hide the message in the structure of the text, such as word order, sentence structure, and grammar. For example, the technique may involve using homophones (words that sound the same but have different meanings) or synonyms (words with similar meanings) to convey hidden information. The method may also use punctuation, capitalization, or other formatting techniques to hide the message. The primary objective of the Linguistic Method is to ensure that the hidden message is not easily detectable by unauthorized users, while still maintaining the text's natural flow and readability. The method is often used in applications where the detection of a hidden message by an attacker could have severe consequences, such as in military or intelligence communications.
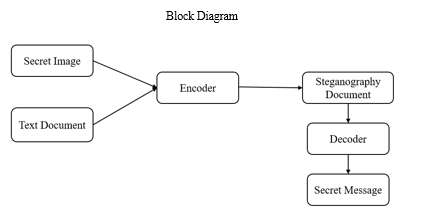
B. Audio Steganography
Audio steganography is the practice of hiding secret information within audio files in a way that is imperceptible to human ears. This technique involves modifying the audio signal in such a way that the hidden message is embedded within the audio file without affecting its perceptual quality. Audio steganography can be implemented using various methods, such as modifying the least significant bits (LSBs) of the audio samples, altering the amplitude or phase of specific audio segments, or using spread spectrum techniques to distribute the hidden message across multiple audio samples. The primary goal of audio steganography is to ensure that the hidden message remains confidential and secure while being transmitted across public channels. Audio steganography is used in various applications, including audio watermarking for copyright protection, audio surveillance for law enforcement, and secure communication for military and intelligence purposes.
- LSB Coding: LSB (Least Significant Bit) coding is a popular technique used in audio steganography for hiding secret messages within digital audio files. The LSBs of the audio samples are modified by replacing them with the bits of the hidden message. Since the LSBs of the audio samples contribute the least to the perceptual quality of the audio signal, modifying them is unlikely to cause noticeable distortion to the human ear. The modification process is performed by comparing the binary representation of the audio sample's LSB with the corresponding bit of the hidden message. If they are different, the LSB is replaced with the hidden message bit, and if they are the same, the LSB remains unchanged. This process is repeated for all the audio samples in the file until the entire message is embedded. The primary objective of LSB coding in audio steganography is to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of the hidden message while keeping the perceptual quality of the audio file intact. LSB coding is a widely used technique in digital watermarking, copyright protection, and secure communication applications.
- Parity Coding: Parity coding is a technique used in audio steganography to hide secret messages within digital audio files by modifying the parity of audio samples. In this method, the parity bit (the least significant bit in the audio sample) is modified to represent the message bit. If the message bit is a 1, the parity bit is flipped; if the message bit is 0, the parity bit remains unchanged. The parity coding technique ensures that the modified audio samples still have the same statistical distribution as the original audio samples. The technique is designed to prevent detection by statistical analysis techniques that might be used to detect LSB coding. The primary goal of parity coding in audio steganography is to ensure that the hidden message is not easily detectable by unauthorized users while keeping the perceptual quality of the audio file intact. Parity coding is used in various applications, including digital watermarking and secure communication, where attackers must protect the message from detection.
- Phase Coding: Phase coding is a technique used in audio steganography to hide secret information within digital audio files by modifying the phase of the audio signal. This technique involves the manipulation of the phase of the audio samples in such a way that the hidden message is encoded within the changes. The phase is modified in a way that the changes are not audible to human ears and are imperceptible to the listener. Phase coding is based on the principle that small changes in the phase of an audio signal can be used to convey information, while not affecting the amplitude or frequency of the signal, and thus not affecting its perceptual quality. The phase coding technique involves dividing the audio signal into small segments and modifying the phase of each segment based on the message to be encoded. The modification process is performed by adding or subtracting a small amount of phase from each segment, depending on the message bit. The changes are usually very small and imperceptible, but when the modified signal is decoded, the original message can be recovered. The primary objective of phase coding in audio steganography is to ensure that the hidden message is not easily detectable by unauthorized users while keeping the perceptual quality of the audio file intact. Phase coding is used in various applications, including digital watermarking, copyright protection, and secure communication.
C. Image Steganography
Image steganography is a technique of hiding secret information or data within an image. The aim of image steganography is to conceal the existence of the secret message within the image, making it undetectable by unauthorized viewers. The process involves selecting an image as a cover object and embedding a message within it by modifying the pixels in a specific way. The modifications made to the image are usually very subtle and do not visibly affect the image's appearance. The hidden message can be extracted using a decoding algorithm or software, which is designed to recover the original message from the modified image. Image steganography has various applications, including information security, digital watermarking, and copyright protection. However, it can also be used maliciously, making it crucial to be aware of its existence and possible uses.
- LSB Encoding: LSB encoding is a popular technique in image steganography that involves hiding information within the pixels of an image without altering its visual appearance significantly. The method works by replacing the least significant bits of selected pixels in an image with the bits of the message to be hidden. Since the least significant bits have the least impact on the pixel's value, the alteration usually goes unnoticed by the human eye. The hidden message can be retrieved by identifying the pixels used for encoding and extracting the least significant bits to reconstruct the original message. Although LSB encoding is a simple and widely used technique, it can be detected by advanced image processing algorithms. Hence, it's often used in combination with other advanced techniques to enhance the security and robustness of the steganographic method.
- Encrypt and Scatter: Encrypt and Scatter is a technique used in image steganography to enhance the security of hidden messages in images. The process involves first encrypting the message using a cryptographic algorithm to make it secure and unreadable to unauthorized viewers. Next, the encrypted message is split into smaller segments, and each segment is embedded into different locations within the image. The locations for embedding the message are chosen based on a predetermined strategy, such as a pseudo-random sequence, to make the message more challenging to detect and extract. This technique can provide a higher level of security since an attacker would need to know the exact embedding locations and the encryption key to extract the message, making it a more challenging task. However, the increased security comes at the cost of increased complexity, which can make the process of encoding and decoding more time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Masking and Filtering: Masking and filtering are techniques used in image steganography to embed and extract hidden messages in images. Masking is the process of creating a cover image with a specific pattern or texture that makes it difficult to distinguish between the original and the modified pixels. This process involves overlaying the message on the cover image in a way that minimizes the distortion of the cover image. Filtering, on the other hand, involves applying specific image processing algorithms to the image to enhance or reduce specific frequencies or patterns.
The filtering process is used to create a mask that will be applied to the message before embedding it in the cover image. The aim of these techniques is to make the embedded message undetectable by the human eye and difficult to detect by image processing algorithms. The hidden message can be extracted by reversing the process and applying the appropriate filters or masks to the image. These techniques are useful for ensuring message security in scenarios where the cover image cannot be modified, such as when the image is already distributed or publicly available.
 ???????
???????
Conclusion
In conclusion, text, image, and audio steganography are powerful techniques that can be used to hide sensitive information from prying eyes. These techniques are widely used in different fields such as national security, digital forensics, and digital rights management. Text steganography is relatively simple, but it is also easily detectable. Image steganography is more complex and offers better security, but it also requires more resources to implement. Audio steganography, on the other hand, is even more secure than image steganography but is also more complex and resource-intensive. Therefore, the choice of which technique to use will depend on the level of security required, the resources available, and the specific needs of the user.
References
[1] Samruddhi Deshmukh, Mitalee Manware, Radhika Chhablani, Shweta Meshram (A Review Paper on Text steganography - July 2022 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science) [2] Muhammad Adnan Aslam, Muhammad Rashid, Farooque Azam, Muhammad Abbas, Yawar Rasheed, Saud S. Alotaibi, Muhammad Waseem Anwar (Image Steganography using Least Significant Bit (LSB) - A Systematic Literature Review - January 2022 2nd International Conference on Computing and Information Technology) [3] Amitava Podder, Piyal Roy, Smaranika Roy (Steganography Techniques - An Overview - November 2022 International Journal of Scientific Research in Computer Science Engineering and Information Technology) [4] Vivek Sharma S, Monika Raj, Swathi S (A Survey of Text Steganography Methods - May 2021 International Journal of Scientific Research in Science and Technology) [5] Rini Indrayani (Modified LSB on Audio Steganography using WAV Format - January 2021 3rd International Conference on Information and Communications Technology) [6] R Shanthakumari, E M Roopa Devi, R Rajadevi, B Bharaneeshwar (Information Hiding in Audio Steganography using LSB Matching Revisited - May 2021 Journal of Physics Conference Series) [7] Nandhini Subramanian, Omar Elharrouss, Somaya Al-Maadeed, Ahmed Bouridane (Image Steganography: A Review of the Recent Advances - January 2021 IEEE) [8] Pranati Rakshit, Sreeparna Ganguly, Souvik Pal, Ayman A. Aly, Dac-Nhuong Le (Securing Technique Using Pattern-Based LSB AudioSteganography and Intensity-Based Visual Cryptography - November 2020 Computers, Materials and Continua 67(1):1207-1224) [9] Olawale Timothy Adeboje, Arome Junior Gabriel, Adebayo Olusola Adetunmbi (Development of an Audio Steganography System Using Discrete Cosine Transform and Spread Spectrum Techniques - September 2020 International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications) [10] Sonali K. Powar, H.T. Dinde, Radhika.M. Patil (A Study and Literature Review on Various Image Steganography Techniques - August 2020 International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology)
Copyright
Copyright © 2023 Ms. T N Aruna , L R Nandika , C I Sneha, Timothy Jerald Xavier, Treesa Mary George. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET51091
Publish Date : 2023-04-26
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

