Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
The Evolution of Generative AI: Implications for the Media and Film Industry
Authors: Ketan Totlani
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.56140
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
This research paper scrutinizes and explores the substantial impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Generative AI on the media and film industry. It delves into the continuously evolving applications of AI algorithms and advanced models, emphasizing their profound implications for content creation, production workflows, and distribution strategies. The paper offers comprehensive insights into the operational mechanics of key AI models, underscoring their direct relevance within the domain of media and film. This inquiry provides a timeless and academic perspective on the transformative influence of AI and Generative AI in these industries, facilitating a deeper understanding of their applications and implications.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
The confluence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) with the realms of media and film represents a pivotal and revolutionary moment in the application of advanced technology. This research seeks to shed light on the profound and far-reaching influence of AI, with a specific focus on Generative AI, as it undergoes a transformative evolution. In an epoch defined by the breakneck pace of technological and interdisciplinary advancements, AI emerges as an indispensable and transformative force, fundamentally reshaping the creative and problem-solving capacities within the spheres of media and filmmaking.
This exploration constitutes a comprehensive examination of the underpinnings of AI, encompassing its foundational principles, intricate algorithms and the burgeoning landscape of Generative AI. It dives into notable models and their practical applications, illustrating how Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and similar AI models are becoming instrumental tools in augmenting human creativity. Within this context, the research not only highlights AI's technological innovations but also underscores its real-world applications.
Beyond the realm of technological advancement, this inquiry probes into the ethical dimensions accompanying AI's rise with a particular focus on bias mitigation, while also exploring the evolving symbiosis between AI-facilitated efficiency and human ingenuity, highlighting instances where AI amplifies creative processes. By emphasizing transformative possibilities and practical use cases, this study illuminates AI's potential within the media and film industry, recognizing challenges while primarily showcasing its profound impact on creativity, content generation, and problem-solving in these domains.
II. UNDERSTANDING GENERATIVE AI AND THE LANDSCAPE OF AI
A. Definition and Types of Generative AI
Generative AI, or Generative Artificial Intelligence, refers to a subset of artificial intelligence focused on the development of algorithms and models capable of autonomously producing content that closely imitates human-created data. These models can generate various types of content, including text, images, music, and more. Notable examples of Generative AI types include text generation using models like GPT-3 [1], image synthesis with models like DALL-E [2], and music composition through systems like MuseNet [3].
B. Historical Perspective of Generative AI
The historical development of Generative AI traces its roots to early explorations in artificial intelligence and machine learning. Early attempts involved rule-based systems and symbolic AI, but significant progress was achieved with the advent of deep learning and neural networks.
The field has evolved from basic rule-based approaches to sophisticated neural architectures capable of generating complex and creative content [4].
C. Core Concepts and Techniques
Understanding Generative AI necessitates familiarity with fundamental concepts and techniques:
- Probability Distributions: Generative AI models employ probability distributions to capture and replicate the statistical patterns found in human-generated data. This enables the generation of content that appears coherent and realistic.
- Latent Spaces: Latent spaces are abstract, lower-dimensional representations where Generative AI models learn to manipulate data. These spaces allow for the exploration of content diversity and creative generation by altering specific latent variables.
- Neural Architectures: Generative AI heavily relies on neural network architectures. Variants such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs), recurrent neural networks (RNNs), and transformer models like GPT-3 form the backbone of many Generative AI systems [5].
Overview of Prominent Generative AI Platforms (e.g., Midjourney, Runway, WonderDynamics)
Prominent Generative AI platforms play a pivotal role in democratizing AI-powered creativity:
a. Midjourney: Midjourney is renowned for its innovative AI-powered creative tools, facilitating the generation of art and animations. This platform empowers artists and creators with AI-assisted tools for visual content generation [6].
b. Runway: Runway offers a creative toolkit that integrates a wide array of Generative AI models and tools. Artists, filmmakers, and designers leverage Runway's accessible interface for experimenting with text, images, and video generation [7].
c. WonderDynamics: WonderDynamics specializes in AI-driven video production and animation. It streamlines video creation by automating tasks such as generating animations, captions, and visual effects [8].
These platforms exemplify the accessibility and versatility of Generative AI, enabling a broader community of creators to harness AI's creative potential in media and film.
III. GENERATIVE AI MODELS AND ALGORITHMS
Generative AI has witnessed substantial growth through the development of various models and algorithms that enable the creation of diverse content. In this section, we probe into three pivotal categories of Generative AI models and their implications for the media and film industry.
A. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
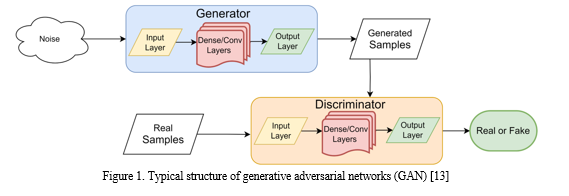
- Architecture and Functioning: GANs, introduced by Goodfellow et al. [9], consist of two neural networks, a generator, and a discriminator, engaged in a game. The generator generates data, and the discriminator evaluates its authenticity. These networks are trained adversarially, with the generator aiming to produce content indistinguishable from real data, while the discriminator seeks to improve its discrimination capabilities.
- Applications in Media: GANs have found extensive applications in the media and film industry. They are used for upscaling and enhancing images and videos, generating realistic CGI and visual effects, and even creating deepfake videos [10]. In film production, GANs assist in scene generation and background replacement, reducing the need for physical sets.
B. Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)
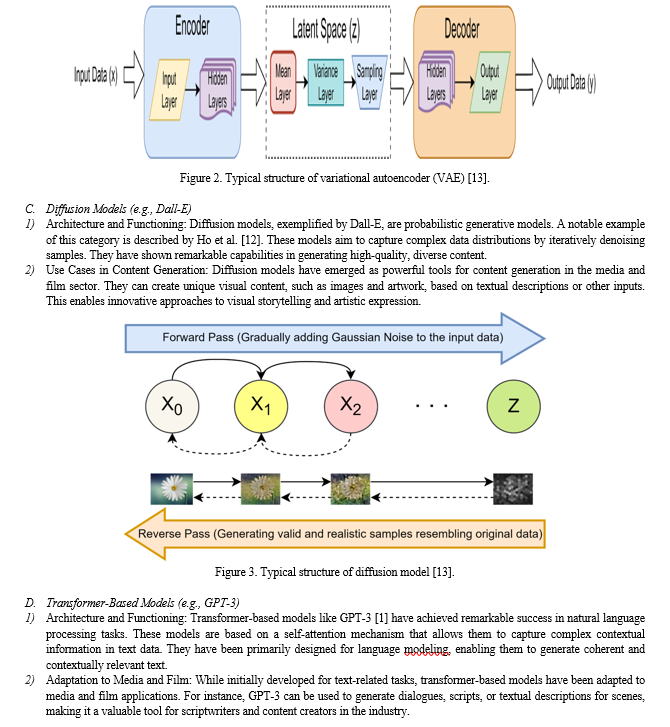
- Architecture and Functioning: VAEs, introduced by Kingma and Welling [11], are generative models that aim to learn the underlying structure of data in a probabilistic manner. They consist of an encoder network that maps data into a latent space and a decoder network that reconstructs data from the latent representations. VAEs are trained to minimize the reconstruction loss and ensure that data can be generated from a continuous and structured latent space.
- Use Cases in Content Generation: VAEs are valuable for content generation tasks in the media and film industry. They can be employed for generating new scenes or frames in animations, creating novel characters or objects, and even assisting in the generation of diverse and engaging scripts.

IV. APPLICATIONS OF GENERATIVE AI IN THE MEDIA AND FILM INDUSTRY
Generative AI has ushered in a new era of possibilities within the media and film industry. It empowers creators and professionals across various domains, offering innovative solutions that enhance both the creative process and audience engagement.
A. Content Generation and Enhancement
Generative AI is a game-changer in content creation, capable of generating vast quantities of diverse content. For instance, it can produce:
- Creative Artwork Generation: AI models like DALL-E are proficient in creating images from textual descriptions, expanding the horizons of concept art, storyboarding, and visual aesthetics [14].
- Music and Soundscapes: AI-generated music through models like Jukebox and WaveNet adds a unforeseen dimension to film scoring and sound effects [15].
B. Visual Effects and CGI
The realm of visual effects (VFX) and computer-generated imagery (CGI) has greatly benefited from Generative AI:
- Photorealistic Visuals: AI-driven tools, such as GANs have made it possible to create highly realistic 3D elements [8], from creatures and characters to entire environments, greatly enhancing the visual aspects of films [16].
- Animation Assistance: Generative AI can simplify the animation process by generating intermediate frames, reducing manual labour traditionally required in animation [17].
C. Scriptwriting and Story Generation
Generative AI assists in the creative process of scriptwriting and storytelling:
- Idea Generation Process: AI models like GPT-3, can generate story ideas, character backgrounds, and plot twists, providing inspiration to screenwriters [18].
- Dialogue Writing: AI can help in crafting dialogues that align with the tone and style of a screenplay, speeding up the scriptwriting process significantly [19].
D. Personalized Content Recommendations
Generative AI contributes to enhancing user experiences by offering personalized content recommendations:
- Content Customization: Algorithms driven by AI analyse user preferences, viewing history, and behaviour to suggest films and series suited to individual tastes, enhancing user engagement on streaming platforms [20].
- Dynamic Trailers: AI can generate personalized movie trailers by highlighting scenes and elements that correlate with a specific viewer's preferences.
E. Post-production and Editing
AI plays a pivotal role in the post-production phase:
- Editing Assistance: Generative AI streamlines editing processes by automating tasks like colour correction, visual effects integration, element addition and detail enhancement. [21].
- Voice Dubbing and Localization: AI-driven tools enable rapid subtitling, dubbing, and accessibility features like audio descriptions, making content accessible to global audiences [22].
In summary, Generative AI presents a broad spectrum of applications in the media and film industry, transforming content creation, enhancing visual effects, simplifying scriptwriting, personalizing recommendations, and streamlining post-production processes. These innovations offer creators and professionals new tools to augment their creativity and engage audiences more effectively.
a. Exploring the Implications and Addressing Challenges
Generative AI, with its capacity to create and enhance content autonomously, presents profound implications and challenges for the media and film industry. This section examines the potential impacts and ways to address associated challenges.
- Fostering Creativity and Artistic Expression
Generative AI intermingles and fosters new forms of creative collaboration by allowing artists and AI systems to co-create. It enables artists to explore uncharted territories and styles they might not have ventured into independently. AI tools, such as DALL-E and DeepDream, amplify artistic capabilities by providing fresh perspectives and aiding in ideation. However, this augmentation sparks a discussion on the impact of AI on traditional artistic processes, questioning how human creativity is affected by collaboration with machines [14].
- Enhancing Efficiency and Cost Savings
Generative AI streamlines content creation workflows by automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks. It accelerates the content generation process, potentially reducing production time and costs. This efficiency implies potential economic benefits for the industry. However, it necessitates a careful analysis of the trade-offs between automation and human labor. While automation may save costs, a balance must be struck to ensure that human creativity and ingenuity remain central [23].
- Navigating Ethical Considerations and Biases
The integration of Generative AI into the creative process raises ethical concerns. Addressing ethical considerations involves ensuring that AI-generated content does not infringe upon copyrights or mislead consumers into thinking it's human-made. Additionally, there is a need to identify and mitigate biases present in the training data, which can perpetuate stereotypes and inequalities in the generated content [24].
Responsible AI usage in media and film requires the development and adherence to guidelines that uphold ethical standards.
- Confronting Challenges and Acknowledging Limitations
Generative AI, while promising, faces technical limitations. Current AI models may struggle with producing truly human-level creativity and understanding context deeply. Acknowledging these limitations is crucial to set realistic expectations and guide further advancements.
The evolving nature of AI challenges in the media and film industry calls for continuous research and innovation to overcome hurdles and enhance the capabilities of Generative AI [25].
b. Envisioning the Future of Generative AI in the Media and Film Industry
As generative AI continues to evolve, it promises to reshape the landscape of the media and film industry in profound ways. This section delves into the potential future scenarios that Generative AI might bring to the industry, touching upon emerging trends, potential disruptions, and the prospects of AI-generated films and content.
Emerging Trends in Generative AI
- Evolving Generative AI Architectures and Algorithms: Generative AI is not stagnant; it continues to evolve. Future developments may include more advanced architectures and algorithms that push the boundaries of content generation [26]. These innovations could result in even more realistic, diverse, and context-aware media production.
- Advances in Multimodal AI for Richer Content Generation: The integration of multimodal AI, combining text, images, and audio, is poised to enable richer and more immersive content generation. This could revolutionize storytelling by allowing AI models to generate multimedia narratives seamlessly [27].
- Real-Time Collaboration Between Creators and AI Models: Real-time collaboration between human creators and AI models is an emerging trend [26]. Filmmakers, writers, and artists might work alongside AI systems during the creative process, generating content iteratively, and dynamically, potentially leading to entirely new storytelling formats.
- Potential Disruptions in the Media and Film Industry
- Shifting Business Models and Revenue Streams: Generative AI could disrupt traditional business models in the industry. AI-generated content might challenge the established norms of production, distribution, and monetization [28]. New models may emerge, including AI-driven content marketplaces.
- Changing Roles and Skill Requirements for Industry Professionals: The roles and skillsets required in the industry may undergo significant transformations. Professionals may need to adapt to working alongside AI collaborators and managing AI-driven workflows [29]. Traditional job descriptions might evolve to incorporate AI expertise.
- Impacts on Distribution, Marketing, and Audience Engagement: Generative AI's ability to personalize content and predict audience preferences could revolutionize distribution and marketing strategies [30]. Targeted content recommendations and dynamic marketing campaigns may become the norm, enhancing audience engagement.
c. Prospects for AI-Generated Films and Content
- The Emergence of AI as a Creative Collaborator: AI's role is likely to shift from a mere tool to a creative collaborator. It could inspire filmmakers and artists by offering novel ideas, suggesting creative directions, and helping to overcome creative blocks [18].
- Exploring AI's Role in Revitalizing Classic Content and Genres: Generative AI might breathe new life into classic content and underexplored genres. It could reimagine and recreate classics with modern twists, potentially introducing younger audiences to timeless stories.
- Navigating Copyright, Ownership, and Creative Attribution Issues: The industry will grapple with copyright and ownership concerns related to AI-generated content. Clear guidelines and legal frameworks will be essential for determining creative attribution and ownership [32].
- The Potential for AI-Generated Content to Cater to Niche Audiences: AI's capacity for content personalization could enable the creation of niche content that caters to underserved audiences. This could lead to a diversification of content and audience segments [33].
In conclusion, the future of Generative AI in the media and film industry holds great promise, but it also raises complex challenges. Industry professionals, policymakers, and creators must proactively engage with these possibilities and dilemmas to harness the full potential of AI while preserving the industry's creative and ethical foundations.
Conclusion
The rapid and relentless evolution of Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands as a monumental force, poised to reshape the expansive landscape of the media and film industry. Throughout this paper, we have embarked on a comprehensive expedition, dissecting the far-reaching implications, multifaceted applications, and future prospects that Generative AI opens up within these domains. Generative AI, driven by models like GPT-3, DALL-E, and advanced algorithms such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), has ushered in a new era of creativity and efficiency. It is like a crucible which mixes everything and enables new content generation and enhancement, facilitates visual effects and CGI, streamlines scriptwriting and story generation, offers personalized content recommendations, and enhances post-production processes. These applications empower creators and industry professionals, expanding the horizons of what is possible in media and film. However, embracing Generative AI also requires addressing critical challenges. The collaborative relationship between AI and human creators necessitates thoughtful consideration of its impact on traditional artistic processes. While AI enhances efficiency and offers potential cost savings, an equilibrium must be struck to preserve the essential role of human ingenuity and technological prowess. Ethical considerations, including copyright, ownership, and biases, must be addressed to ensure responsible AI usage. Looking ahead, the future of Generative AI in the media and film industry is packed with promise and potential disruptions. Emerging trends point to the evolution of AI architectures and algorithms, the integration of multimodal AI, and real-time collaboration between creators and AI models. These trends are poised to revolutionize content generation and storytelling. Generative AI has the potential to disrupt existing business models and redefine the roles and skill requirements of industry professionals. It may transform distribution, marketing, and audience engagement strategies, offering personalized and dynamic content experiences. Moreover, Generative AI could lead to AI-generated films and content, with AI serving as a creative collaborator and revitalizing classic content and genres. Navigating copyright, ownership, and creative attribution issues will be essential to ensure a fair and ethical landscape. In summation, Generative AI stands as a indominable force in the realm of media and film, augmenting human creativity and efficiency. It offers new horizons for content creation and storytelling. However, realizing its full potential requires proactive engagement with challenges and a commitment to ethical, responsible, and creative AI usage. The future of Generative AI in media and film holds the promise of innovative, diverse, and engaging content while preserving the essence of human creativity in these industries.
References
[1] Brown, T. B., et al. (2020). Language Models are Few-Shot Learners. arXiv:2005.14165. [2] Esser, P., et al. (2021). Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention. arXiv:2110.11533. [3] OpenAI. (2019). MuseNet: A deep generative model for music composition. Retrieved from https://openai.com/research/musenet. [4] LeCun, Y., et al. (2015). Deep learning. Nature, 521(7553), 436-444. [5] Vaswani, A., et al. (2017). Attention Is All You Need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 30. [6] Midjourney. (n.d.). About Midjourney. Retrieved from https://midjourney.com/about. [7] Runway. (n.d.). About Runway. Retrieved from https://runwayml.com/about. [8] WonderDynamics. (n.d.). About Us. Retrieved from https://www.wonderdynamics.com/about-us. [9] Goodfellow, I. J., et al. (2014). Generative Adversarial Nets. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 27. [10] Abdal, R., et al. (2019). Image2StyleGAN: How to Embed Images Into the StyleGAN Latent Space? arXiv:1904.03189. [11] Kingma, D. P., & Welling, M. (2013). Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes. arXiv:1312.6114. [12] Ho, J., et al. (2020). Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models. arXiv:2006.11239. [13] Bandi, A., Adapa, P. V. S. R., & Kuchi, Y. E. V. P. K. (2023). The Power of Generative AI: A Review of Requirements, Models, Input–Output Formats, Evaluation Metrics, and Challenges. Future Internet, 15(8), 260. [14] Lyu, Y., Wang, X., Lin, R., & Wu, J. (2022). \"Communication in Human–AI Co-Creation: Perceptual Analysis of Paintings Generated by Text-to-Image System.\" Applied Sciences, 12(22), 11312. [15] Dhariwal, P., et al. (2020). Jukebox: A Generative Model for Music. arXiv:2005.00341. [16] Li, C., Zhang, C., Waghwase, A., Lee, L.-H., Rameau, F., Yang, Y., Bae, S.-H., & Hong, C. S. (2023). \"Generative AI meets 3D: A Survey on Text-to-3D in AIGC Era.\" arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.06131 [cs.CV]. [17] Ranzato, M., Szlam, A., Bruna, J., Mathieu, M., Collobert, R., & Chopra, S. (2016). \"Video (language) modeling: a baseline for generative models of natural videos.\" arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6604. [18] Antony, V. N., & Huang, C.-M. (2023). \"ID.8: Co-Creating Visual Stories with Generative AI.\" arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.14228. [19] Coenen, A., Davis, L., Ippolito, D., Reif, E., & Yuan, A. (2021). \"Wordcraft: a Human-AI Collaborative Editor for Story Writing.\" arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.07430. [20] Wang, W., Lin, X., Feng, F., He, X., & Chua, T.-S. (2023). \"Generative Recommendation: Towards Next-generation Recommender Paradigm.\" arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.03516. [21] Xu, Y., AlBahar, B., & Huang, J.-B. (2022). \"Temporally Consistent Semantic Video Editing.\" arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.10590. [22] Lin, K., Li, L., Lin, C.-C., Ahmed, F., Gan, Z., Liu, Z., Lu, Y., & Wang, L. (2022). \"SwinBERT: End-to-End Transformers with Sparse Attention for Video Captioning.\" Proceedings of Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2022. [23] Briggs, K., & Kodnani, (2023). \"The Potentially Large Effects of Artificial Intelligence on Economic Growth.\" Goldman Sachs Economics Research. [24] Crawford, K., & Calo, R. (2016). There is a blind spot in AI research. Nature, 538(7625), 311-313. [25] Hassabis, D., Kumaran, D., Summerfield, C., & Botvinick, M. (2017). Neuroscience-inspired artificial intelligence. Neuron, 95(2), 245-258. [26] Epstein, Z., et al. (2023). Art and the science of generative AI: A deeper dive. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.04141. [27] Sun, Q., Yu, Q., Cui, Y., Zhang, F., Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Gao, H., Liu, J., Huang, T., & Wang, X. (2023). \"Generative Pretraining in Multimodality.\" arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.05222 [cs.CV]. [28] Kanbach, D.K., Heiduk, L., Blueher, G. et al. The GenAI is out of the bottle: generative artificial intelligence from a business model innovation perspective. Rev Manag Sci (2023). [29] Noy, S., & Zhang, W. (2023). \"Experimental Evidence on the Productivity Effects of Generative Artificial Intelligence.\" Retreived from SSRN. [30] Yang, X., Li, H., Ni, L., & Li, T. (2021). \"Application of Artificial Intelligence in Precision Marketing.\" Journal of Organizational and End User Computing (JOEUC), 33(4). [31] Gallego, A. J., & Llinás, P. (2018). A generative model for exploring audio-visual correspondences in a video dataset. Neural Networks, 108, 147-157. [32] Zhong, H., Chang, J., Yang, Z., Wu, T., Arachchige, P. C. M., Pathmabandu, C., & Xue, M. (2023). \"Copyright Protection and Accountability of Generative AI: Attack, Watermarking, and Attribution.\" arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.09272. [33] Cao, Y., Li, S., Liu, Y., Yan, Z., Dai, Y., Yu, P. S., & Sun, L. (2023). \"A Comprehensive Survey of AI-Generated Content (AIGC): A History of Generative AI from GAN to ChatGPT.\" arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.04226.
Copyright
Copyright © 2023 Ketan Totlani. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET56140
Publish Date : 2023-10-13
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

