Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
A Study on The Social Media Influence on Financial Decisions
Authors: Smrithi S, Dr. Selvi S
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.60160
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
This research explores how social media influences investment decisions among Generation X, millennials, and Generation Z, known for their heavy use of digital technology. Using quantitative methods and surveys, the study examines individuals from different age groups on social media platforms. Results show a significant link between social media engagement and investment choices across all generations. Investment firms are urged to use social media for marketing and communication to reach a wider audience. The study emphasizes the need for financial literacy across generations in an era where social media plays a crucial role in financial decision-making. It advocates for tailored strategies to engage each demographic while promoting universal financial literacy.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
In today's digital era, social media profoundly shapes how we communicate, share information, and manage finances. This study aims to explore its impact on money decisions across generations, acknowledging diverse experiences and social media habits. Generational differences influence financial perspectives; older generations prioritize stability, while younger ones lean towards digital tools and instant gratification. Social media provides a wealth of financial resources, yet also poses risks like misinformation and impulsive spending. Understanding how each generation interacts with financial content on social media is crucial for empowering informed decision-making. Platforms like YouTube and Instagram serve as valuable hubs for financial education, but also propagate scams and targeted advertising. Financial institutions can enhance customer engagement by tailoring their approaches to generational preferences. By unraveling the complexities of social media's influence on finances, this research aims to equip individuals with the knowledge to navigate digital spaces responsibly. Collaboration and education are key to harnessing social media's potential while mitigating its risks, promoting financial empowerment across all age groups.
II. SCOPE OF STUDY
A. Objective
The main objective of this study is to investigate the potential distinctions in financial decision-making among individuals belonging to Generation X. Millennials and Generation Z, particularly when influenced by social media. By concentrating on these two specific generations, the research aims to uncover any unique patterns or trends in their financial behaviors resulting from their engagement with social media platforms.
B. Demographic Focus
The study centers on individuals within the age range of 12 to 55, covering both Generation X, typically born between 1965 and 1980, Millennials born between 1981 and 2000, and Generation Z, born between the mid-2000 and early 2012. By including respondents from both generations, the research aims to capture a comprehensive understanding of how social media impacts financial decision-making across different age groups.
C. Geographical Focus
Participants selected for the study predominantly reside in Bangalore, India. Focusing on a specific geographical location allows for a localized perspective on the influence of social media on financial decisions within a particular cultural and socioeconomic context. Understanding how individuals in Bangalore, a metropolitan city known for its vibrant tech culture, engage with social media in the context of financial decision-making can provide valuable insights.
D. Research Methods
The research adopts a quantitative research approach, utilizing structured questionnaires as the primary method of data collection. Quantitative methods allow for the systematic gathering of numerical data, enabling researchers to analyze and quantify the extent of social media influence on financial decisions among respondents. The structured nature of the questionnaires ensures consistency and comparability in responses, facilitating rigorous analysis.
E. Source of Data Collection
Primary data was collected through Convenience Sampling, a method that selects participants based on their accessibility and willingness to participate. This sampling technique ensures a diverse representation of individuals from different age groups within Generation X, Millennials, and Generation Z. By gathering data from a varied sample, the research aims to enhance the reliability and generalizability of its findings, allowing for broader insights into the influence of social media on financial decision-making.
F. Type of Research
The research adopts a quantitative approach, emphasizing numerical analysis to uncover patterns and relationships, therefore it is Descriptive Research
G. Significance of the Study
This study holds significance in its potential to offer insights into the evolving landscape of financial decision-making behaviors influenced by social media in the digital age. By understanding how individuals from different generations engage with social media platforms to make financial decisions, the research aims to contribute to our understanding of consumer behavior in an increasingly interconnected and technology-driven world. These insights can have implications for various stakeholders, including marketers, policymakers, and financial institutions, in adapting their strategies to meet the evolving needs and preferences of consumers influenced by social media.
III. REVIEW OF LITERATURE
The widespread use of social media and its increasing importance in sharing information means we need to understand how it affects the decisions people make about money, especially when it comes to investing. This review looks at what other studies have found to see how social media influences the decisions people from different generations make about investing. We'll talk about the main ideas and what other researchers have discovered.
- Lusardi, A., & Mitchell, O. S. (2011): This research is seminal in understanding how different generations approach financial decisions. By examining factors such as financial literacy, risk aversion, and retirement planning, they provide valuable insights into the financial behaviors and attitudes of Generation X and Generation Z. Their work underscores the importance of education and life experiences in shaping individuals' financial decision-making processes across various age groups.
- Dholakia, U. M., Bagozzi, R. P., & Pearo, L. K. (2004): The study explores the influence of social media on consumer behavior, including financial decision-making. By analyzing how social media platforms shape consumer attitudes, intentions, and behaviors, they highlight the significant impact of digital channels on individuals' financial choices. Their research underscores the need for understanding and leveraging social media dynamics in financial marketing strategies.
- Hampton, K. N., & Sessions, L. F. (2019): They delve into the intricacies of social media usage across different generations. By examining the preferences, motivations, and behaviors of users on various platforms, they uncover generational differences in online engagement. Their findings provide valuable insights for businesses and marketers aiming to effectively target and engage diverse age groups through social media channels.
- De Vries, L., Gensler, S., & Leeflang, P. S. H. (2012): This research focuses on the effectiveness of social media marketing strategies, including their impact on financial decision-making. Through empirical analysis and theoretical frameworks, they identify key factors influencing consumer behavior on social media platforms. Their findings contribute to a deeper understanding of how companies can leverage digital channels to influence financial outcomes and drive consumer engagement.
- Fernandes, D., Lynch Jr, J. G., & Netemeyer, R. G. (2014): Their research examines the role of financial education interventions in enhancing financial literacy and decision-making skills. By assessing the effectiveness of educational programs across different demographic groups, they highlight the importance of promoting financial literacy from an early age. Their research underscores the potential for educational initiatives to empower individuals to make informed financial choices and achieve long-term financial well-being.
- Raghavan, V., & Jun, M. (2017): Their study addresses ethical considerations surrounding social media marketing practices, particularly in the context of financial decision-making. Through ethical frameworks and regulatory analysis, they highlight the potential risks and challenges associated with digital marketing tactics. Their research underscores the importance of transparency, consumer protection, and responsible marketing practices in mitigating potential harms and ensuring fair treatment of consumers.
- Zhang, Y., & Benyoucef, M. (2016): They discuss future trends and implications of social media influence on financial decision-making. By forecasting emerging issues and potential research directions, they provide valuable insights for scholars, practitioners, and policymakers. Their work highlights the need for ongoing monitoring and adaptation to the evolving landscape of social media and consumer behavior, emphasizing the importance of informed decision-making and proactive intervention strategies.
- Chaitanya, & Nordin (2021) conducted research on information dissemination and decision-making biases in social media platforms, particularly regarding financial matters. They highlighted the potential biases inherent in the information circulated on these platforms, emphasizing users' struggle in discerning credible sources amidst a vast array of content. Cognitive biases, such as overconfidence, were identified as prevalent challenges, urging users to exercise critical evaluation when consuming financial information online.
- Lusardi & Mitchell (2007); Grable & Joo (2001); Pew Research Center (2023) explore generational differences in financial attitudes and behaviors, as well as variations in social media usage patterns across different age cohorts. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for tailoring financial education initiatives and investment strategies to effectively engage each demographic.
- Fang & Huang (2020); US Federal Trade Commission (2023) discuss the dual nature of social media as a source of financial information, delineating the risks of misinformation and fraudulent activities alongside the benefits of knowledge dissemination and community support. Despite potential hazards, users also have access to valuable learning opportunities and peer networks for sharing experiences and insights.
- Jumpstart Coalition (2023); European Commission (2023); Securities and Exchange Commission (2023) outline strategies for responsible investment decisions encompassing financial education programs, regulatory frameworks, and ethical standards for financial institutions. These strategies aim to empower individuals with the knowledge and tools necessary to make informed investment decisions while safeguarding against exploitation and misconduct.
- Barber & Odean (2008) investigate the intricate relationship between social media usage patterns and financial behavior, uncovering how the constant influx of information and interactions on these platforms can shape individuals' perceptions and decisions regarding investments. Notably, studies have observed tendencies toward overconfidence among users, potentially influencing their investment strategies.
- Christodoulou et al. (2017) highlight social media platforms as conduits for the dissemination of financial knowledge, facilitating access to diverse resources such as news articles, expert opinions, and personal anecdotes. Through social networks, individuals can enhance their financial literacy and understanding of investment concepts by engaging with a myriad of content tailored to their interests and needs.
- Baker & Wurgler (2007) discuss the significant impact of social influence on individuals' investment decisions, with social media platforms amplifying this effect by providing platforms for observing and emulating others' behaviors. Peers, influencers, and celebrities alike can influence investment choices, underscoring the importance of understanding and navigating social dynamics in financial decision-making.
- Bollen et al. (2011) delve into sentiment analysis techniques, enabling researchers to extract valuable insights from social media data, offering glimpses into public sentiment towards specific stocks or market sectors. Despite its benefits, social media's pervasive influence on financial decision-making also poses significant risks and challenges, including the prevalence of misinformation and fake news.
- Singh and Mishra (2019); Gupta and Mohan (2018) explore social media's role in disseminating financial information and shaping public awareness of investment opportunities in the Indian context. Regulatory bodies like the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) play a pivotal role in addressing regulatory challenges and safeguarding consumer interests in the realm of social media-driven financial activities.
IV. RESEARCH OBJECTIVES
A. To understand the generational differences in using Social Media platforms for seeking Investment Decisions.
B. To analyze the influence of demographic profile on the Investment Decisions.
C. To understand the Social Media influence on Investment Decisions.
D. To assess the Risks and Benefits associated with using Social Media for making Investment Decisions.
E. To offer Findings and Recommendations found in the result,
V. RESEARCH METHODS
Title: A Study on the "Social Media Influence on Financial Decisions" of Gen X, Millennials and Gen Z
The title encapsulates the main focus of the research, which is to explore how social media impacts individuals' financial decisions.
A. Objective
- To understand the generational differences in using Social Media platforms for seeking Investment Decisions.
- To analyze the influence of demographic profile on the Investment Decisions.
- To understand the Social Media influence on Investment Decisions.
- To assess the Risks and Benefits associated with using Social Media for making Investment Decisions.
- To offer Findings and Recommendations found in the result,
VI. RESEARCH DESIGN
- Type of Research: The research adopts a quantitative approach, emphasizing numerical analysis to uncover patterns and relationships, therefore it is Descriptive Research.
- Type of Sampling: A convenience random sampling technique is employed, allowing for flexibility in participant selection while ensuring a random representation.
- Type of survey/Data Collection Method: Data is collected through a structured questionnaire with 14 Questions, carefully designed to get information on participants' social media habits and financial behaviors.
- Type of Data: The questionnaire collects primary data directly from participants of the study.
A. Tools or Techniques Used for Analysis
To conduct analysis both Descriptive Statistics and Influential Statistics are used.
Descriptive Statistics- Representation of the data was drawn using Tables and Graphs.
Influential Statistics- The Chi-Square Test was conducted to know the relationship between the two variables of the study.
B. Software Used
SPSS Statistics software is used for data analysis, providing comprehensive tools for statistical analysis and interpretation.
C. Sample Size
There are around 55 responses consisting of Individuals of the age group between 12- 55 who are spread across different occupations such as Full-time and Part-time employees, Self-employed, Students, and Retired individuals.
D. Significance
Understanding the relationship between social media usage and financial decisions has significant implications across various sectors. The findings of the research can inform individuals, financial institutions, policymakers, and marketers, guiding decision-making processes and strategies about social media and finance.
VII. HYPOTHESIS TESTING AND METHODS
- Hypothesis 1
Null Hypothesis (Ho1): There is no significant relationship between the age and Hours spent on Social media.
Alternative Hypothesis (H11): There is a significant relationship between the age and Hours spent on Social media.
2. Hypothesis 2
Null Hypothesis (Ho2): There is no significant relationship between the age group and Individual Influence on Social media.
Alternative Hypothesis (H12): There is a significant relationship between the age group and Individual Influence on Social media.
3. Hypothesis 3
Null Hypothesis (Ho3): There is no significant relationship between the Highest Level of Education and Individual Trust on Social Media
Alternative Hypothesis (H13): There is a significant relationship between the Highest Level of Education and Individual Trust on Social Media
A. Statistical Tool Used
The CHI-SQUARE TEST is a statistical tool we're using to examine whether social media has an impact on how people make decisions about their money. In this study, we're trying to understand if there's a connection between how much someone uses social media and the choices they make regarding their finances.
By using the Chi-square test, we're looking to see if there's a significant relationship between how active people are on social media and the different ways they handle their money. Essentially, we're trying to find out if there's evidence that social media use affects financial decision-making.
VIII. DATA COLLECTION AND INTERPRETATION
S. Hypothesis between Age and Hours spent on Social Media
Hypothesis Testing:
Null Hypothesis (Ho): There is no significant relationship between the age and Hours spent on Social media.
Alternative Hypothesis (H1): There is a significant relationship between the age and Hours spent on Social media.
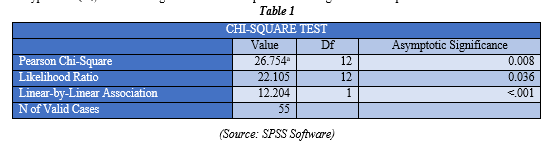
(Source: SPSS Software)
Level of Significance-95%
If,
P Value < 0.05 Reject Ho
P Value > 0.05 Reject H1
P Value = 0.008
Interpretation
Since P Value 0.008<0.05, H0 is Rejected
Therefore, there is a significant relation between the age and Hours spent on Social Media
Inference
The chi-square test results reveal a statistically significant relationship between age and hours spent on social media, as indicated by a p-value of 0.008, which falls above the conventional threshold of 0.05. Consequently, the alternative hypothesis, which posits an association between these variables, is rejected. While the direction of this relationship is explicitly elucidated by the test, the findings underscore the importance of age as a determinant factor in individuals' social media usage patterns. This insight holds practical implications for understanding and targeting specific age demographics in digital engagement strategies, marketing initiatives, and interventions aimed at promoting responsible social media usage.
B. Hypothesis between Age group and Individual Influence on Social media
Hypothesis Testing
Null Hypothesis (Ho): There is no significant relationship between the age group and Individual Influence on Social media.
Alternative Hypothesis (H1): There is a significant relationship between the age group and Individual Influence on Social media.
Table 2
|
|
Value |
df |
Asymptotic Significance |
|
Pearson Chi-Square |
12.806a |
16 |
0.687 |
|
Likelihood Ratio |
13.193 |
16 |
0.659 |
|
Linear-by-Linear Association |
1.244 |
1 |
0.265 |
|
N of Valid Cases |
55 |
|
|
(Source: SPSS Software)
Level of Significance-95%
If,
P Value < 0.05 Reject Ho
P Value > 0.05 Reject H1
P Value = 0.687
Interpretation
Since P Value 0.687>0.05, H1 is Rejected.
Therefore, there is no significant relationship between the age group and Individual Influence on Social media.
Inference
The interpretation of the chi-square test results indicates that there is no significant relationship between age group and individual influence on social media. With a p-value of 0.687, which is greater than the conventional threshold of 0.05, we fail to reject the null hypothesis (H0), which suggests that there is no association between these variables.
This finding suggests that individuals' perceptions of influence on social media are not significantly influenced by their age group. In other words, regardless of age, respondents' views on the influence of individuals on social media remain consistent. This implies that factors other than age may play a more significant role in shaping perceptions of influence on social media platforms.
C. Hypothesis between the highest level of Education of respondents and Trust in Social Media Information
Null Hypothesis (Ho): There is no significant relationship between the Highest Level of Education and Individual Trust on Social Media
Alternative Hypothesis (H1): There is a significant relationship between the Highest Level of Education and Individual Trust on Social Media
Table 3
|
|
Value |
df |
Asymptotic Significance |
|
Pearson Chi-Square |
15.623a |
15 |
0.408 |
|
Likelihood Ratio |
16.91 |
15 |
0.324 |
|
Linear-by-Linear Association |
0.553 |
1 |
0.457 |
|
N of Valid Cases |
55 |
|
|
(Source: SPSS Software)(Souce: SPSS Software)
Level of Significance-95%
If,
P Value < 0.05 Reject Ho
P Value > 0.05 Reject H1
P Value = 0.408
Interpretation
Since P Value 0.408>0.05, H1 is Rejected.
Therefore, there is no significant relationship between the Highest Level of Education and Individual Trust on Social Media
Inference
The interpretation of the chi-square test results indicates that there is no significant relationship between the highest level of education and individual trust in social media information. With a p-value of 0.408, which is greater than the conventional threshold of 0.05, we fail to reject the null hypothesis (H0), suggesting that there is no association between these variables.
This finding suggests that an individual's level of trust in social media information is not significantly influenced by their highest level of education. In other words, regardless of educational attainment, respondents' trust in social media information remains consistent. This implies that factors other than education level may play a more significant role in shaping trust in social media information.
Therefore, in this study, the highest level of education alone may not be a reliable predictor of individuals' trust in social media information.
IX. RESEARCH FINDINGS AND OUTCOMES
A. Hypothesis 1
Age and Social Media Usage:
- Research shows that age does not affect how much time individuals spend on social media platforms.
- Older and younger people have same patterns of social media usage.
- While the study didn't specify the exact ways in which age influences social media habits, it highlights the significance of age demographics in digital engagement strategies.
- This suggests that businesses and organizations should consider targeting specific age groups with tailored social media content and campaigns.
- Understanding age-related differences in social media usage can help in promoting responsible social media usage among different age demographics.
B. Hypothesis 2
Age and Perception of Influence on Social Media:
- Despite age differences in social media usage, age does not significantly impact individuals' perception of influence on social media.
- Regardless of age, people tend to have consistent views on the influence of individuals on social media platforms.
- This implies that factors other than age play a more significant role in shaping perceptions of influence on social media.
- Factors such as trust in social media, past experiences with influencers, and general attitudes towards online content may be more influential in determining perceptions of influence on social media platforms.
C. Hypothesis 3
Education Level and Trust in Social Media Information:
- There is no significant relationship between individuals' level of education and their trust in social media information.
- Having a higher level of education does not necessarily lead to greater trust in social media content.
- Other factors such as media literacy, critical thinking skills, and experiences with misinformation may have a stronger influence on trust in social media information.
- This highlights the need for considering a broader range of factors beyond education level when studying trust in social media information.
- Future research should explore the interplay between various factors to better understand the dynamics of trust in social media content.
Conclusion
In conclusion, our research has provided valuable insights into the complex world of social media usage and trust in digital information. This research discovered that age plays a significant role in shaping how individuals interact with social media platforms. Older and younger demographics exhibit distinct patterns of engagement, suggesting that age influences the way people use social media. This underscores the importance of tailoring digital marketing strategies and content to specific age groups to effectively reach and engage with target audiences. While age impacts social media usage behaviors, our findings revealed that it does not significantly influence individuals\' perceptions of influence on social media platforms. Regardless of age, people tend to hold consistent views on the impact of individuals and influencers in the online space. This suggests that factors beyond age, such as personal beliefs, values, and past experiences, may have a more profound influence on individuals\' perceptions of influence on social media. The study found no substantial relationship between education level and trust in social media information. Contrary to expectations, higher levels of education did not necessarily translate to greater trust in digital content. Instead, factors such as media literacy, critical thinking skills, and prior experiences with misinformation emerged as key determinants of trust in online information. The research highlights the multifaceted nature of social media usage and trust in digital content. It emphasizes the need for comprehensive approaches that consider various individual differences and experiences when addressing challenges related to social media engagement and trust in online information. By understanding these complexities, we can develop more effective strategies to promote responsible social media usage and foster trust in digital platforms.
References
[1] Gupta, A., Garg, P., & Jain, N. (2020). Impact of social media on investment decisions: A study of Indian investors. Journal of Social and Economic Development, 22(1), 67-83. [2] Jha, P. K., & Sinha, R. K. (2019). Role of social media in financial decision making: A study of Indian youth. Global Journal of Management and Business Research: C Finance, 19(1), 35-42 [3] Mohanty, B. K., & Mohanty, M. (2018). Influence of social media on investment decisions: A study of Indian stock market investors. International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews, 5(4), 846-857. [4] Pooja, A., & Roy, P. K. (2019). Impact of social media on investment decision of Indian investors: A study of stock exchange investors in India. International Journal of Management, IT and Engineering, 9(2), 158-169. [5] Sharma, S. K., & Chauhan, A. (2020). Impact of social media on investment decisions: A study of Indian investors. International Journal of Finance and Managerial Accounting, 5(2), 23-34. [6] Singh, A., & Verma, S. K. (2017). Influence of social media on investment decisions of Indian investors: An empirical study. The Indian Journal of Commerce, 70(4), 21-32. [7] Soman, S., & Tiwari, R. (2021). Influence of social media on investment decision making in the Indian stock market. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering, 9(2), 4885-4891. [8] Yadav, S., & Rani, R. (2020). Impact of social media on investment decision making: A study of Indian investors. Indian Journal of Management Science, 10(1), 1-12. GLOSSARY [1] Social Media: Online platforms and websites that enable users to create and share content or participate in social networking, often including platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn, and TikTok. [2] Financial Decisions: Choices made by individuals or entities regarding their finances, including budgeting, saving, investing, borrowing, and spending. [3] Influence: The capacity or power of social media to affect or shape individuals\' attitudes, behaviors, and decisions related to financial matters. [4] Engagement: The level of interaction, participation, or activity exhibited by individuals on social media platforms, including actions such as liking, sharing, commenting, and posting content. [5] Behavioral Finance: An area of study that combines principles from psychology and economics to understand how psychological factors influence financial decision-making, including the role of social media in shaping financial behaviors. [6] Budgetary Decisions: Choices are made regarding the allocation of financial resources to various categories such as expenses, savings, investments, and discretionary spending. [7] Investment Decisions: Choices are made regarding the allocation of financial resources into assets or securities with the expectation of generating returns or profits over time. [8] Purchasing Decisions: Choices made regarding the acquisition of goods or services in exchange for money or other forms of payment. [9] Savings Decisions: Choices made regarding the allocation of income or financial resources towards saving or investing for future goals, emergencies, or retirement.
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Smrithi S, Dr. Selvi S . This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET60160
Publish Date : 2024-04-11
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

