Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Trends of Investment Banking and Growth Potential in India till 2030
Authors: Mr. Vivek Gupta , Jaivardhan Haritwal , Bhimarth Jain , Hemanth Kumar , Kyraa Pires , Nawaz Parvez
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.59469
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
This research delves into the intricate world of investment banking, offering insights into its multifaceted nature as both a cornerstone of financial systems and a dynamic career path. It emphasises the importance of traditional qualifications while also underscoring the significance of passion and relevant skills in navigating this field. Furthermore, it highlights the accessibility of the industry to individuals from diverse academic and professional backgrounds, emphasising that success in investment banking is not limited to those with strictly financial pedigrees. Additionally, the study examines the pivotal role of investment banking amidst the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic. It illustrates how investment banks have served as critical agents of stability, channeling capital to support struggling sectors and driving innovation in response to rapidly changing market dynamics. This portrayal underscores the resilience and adaptability of investment banking, showcasing its capacity to thrive in times of uncertainty and emerge as a catalyst for economic recovery and growth. In essence, this abstract presents investment banking as a dynamic and essential component of the global financial landscape, blending tradition with innovation to navigate evolving markets and contribute to long-term economic sustainability.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
The realm of investment banking encompasses a range of specialized financial activities, including facilitating fundraising initiatives for businesses and offering tailored financial advisory services. It's important to distinguish investment banking from traditional banking, as it operates as a distinct subset within the broader financial sector, catering primarily to corporate clients and institutional investors rather than the general public. Viewed both as a conceptual framework and a career trajectory, investment banking demands a cadre of highly skilled professionals with deep expertise in financial instruments, market dynamics, and strategic advisory. While a background in finance has traditionally been a prerequisite for entry into the field, contemporary trends highlight the growing significance of passion and proficiency over formal academic credentials. The industry's evolution has shifted the focus from conventional qualifications to a holistic assessment of an individual's commitment and aptitude for the profession.
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic posed unprecedented challenges to the global economy, triggering widespread disruptions across various sectors. However, amidst the turmoil, the investment banking sector emerged as a resilient force, demonstrating remarkable adaptability in the face of adversity. Recognising the enduring nature of the pandemic, the industry has embraced a proactive approach, leveraging liquidity injections and strategic investments to stimulate market activity and drive economic recovery. Despite the initial setbacks experienced during the pandemic, characterised by plummeting equity prices and heightened market volatility, the investment banking landscape has witnessed a gradual resurgence. This resurgence is attributed to a resurgence in investor confidence, fueled by increased market liquidity and a growing appetite for strategic investments. Consequently, investment banking has played a pivotal role in facilitating the revitalization of industries and fostering the emergence of new market segments, such as the cosmetic industry, which demonstrated resilience amid economic downturns.
Investment banking has served as the lifeblood of the economy during the pandemic, channeling vital resources and mitigating the impact of economic disruptions. Its ability to navigate turbulent market conditions underscores its indispensable role in driving economic resilience and fostering sustainable growth across diverse industries.
A. Emerging Trends in Investment Banking in India: Projections until 2030
- Technological Advancements and Automation: The landscape of investment banking in India is poised to witness a significant influx of technology and automation, with developments such as algorithmic trading, AI-driven analytics, blockchain transactions, and the emergence of robo-advisors for wealth management. These advancements aim to streamline operations, drive cost efficiencies, and enhance overall operational effectiveness.
- Digital Transformation: A profound digital transformation is underway within the Indian investment banking sector, aimed at enhancing both customer experiences and operational efficiencies. Online platforms for trading, investment research, and client communication are expected to become increasingly sophisticated and user-friendly, reflecting a broader shift towards digital-first strategies.
- Emphasis on Sustainable Finance and ESG Investing: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations are gaining momentum globally, and India's investment banking landscape is not exempt. There is a growing recognition of the importance of sustainable finance and ESG-aligned investment strategies, driven by regulatory mandates and evolving investor preferences. Investment banks are expected to play a pivotal role in facilitating such investments and fostering sustainable economic growth.
- Rise of Fintech Collaborations: Collaboration between traditional investment banks and fintech startups is anticipated to become more prevalent in the Indian market. This trend is driven by a mutual desire to leverage innovative solutions for customer engagement, risk management, and market analysis. Such partnerships have the potential to unlock new opportunities and drive operational efficiencies for both parties involved.
- Shift in Client Demographics: The traditional client base of investment banks is likely to undergo a transformation, with a growing emphasis on catering to the needs of retail investors, particularly tech-savvy millennials. While institutional clients will continue to remain significant, investment banks are expected to adapt their offerings to meet the evolving preferences of a diverse clientele, thereby ensuring long-term sustainability and relevance in the market.
In the years ahead, several key areas are expected to contribute to progress, including:
a. Economic Expansion: The nation's youthful and expanding populace, coupled with a sizable consumer base and a rising middle class, are poised to propel economic growth forward. Furthermore, initiatives targeting reforms in taxation, business facilitation, and infrastructure enhancement hold the potential to foster heightened GDP growth rates.
b. Digital Transformation and Technological Advancements: The proliferation of e-commerce platforms, advancements in financial technology (FinTech), artificial intelligence (AI), and telecommunications infrastructure is anticipated to enhance productivity, streamline operations, and foster innovation across various industries.
c. Development in Manufacturing and Infrastructure: Government-led endeavors such as the "Make in India" campaign seek to bolster the manufacturing sector and infrastructural growth. Augmented investments in manufacturing, construction, and logistics industries could significantly contribute to economic expansion and employment generation.
d. Growth in the Services Industry: India's robust services sector, encompassing information technology (IT) and business process outsourcing (BPO), has historically served as a cornerstone of economic growth. Continued expansion is anticipated, driven by global outsourcing trends, technological breakthroughs, and the availability of skilled manpower.
e. Emphasis on Renewable Energy and Sustainable Practices: A steadfast commitment to renewable energy, including solar and wind power, holds the promise of substantial strides in sustainable development. By addressing environmental concerns and creating avenues for investment and innovation, this focus area presents opportunities for economic growth and job creation.
B. The Projected Path Of Investment Banking In India Until 2030 Encompasses Several Key Elements
- Economic Growth: The investment banking sector in India is poised for significant expansion driven by the nation's overall economic growth. Demographic shifts, rising discretionary incomes, and an expanding middle class are anticipated to fuel heightened demand for investment banking services.
- Integration of Financial Technology (Fintech): The adoption of financial technology (fintech) is set to revolutionize the investment banking arena. The emergence of more efficient and accessible platforms for trading, asset management, and other financial services is expected to transform traditional banking practices.
- International Investment: India's deeper integration into the global economy could lead to increased international investments, mergers, and acquisitions. Investment banks will play a pivotal role in facilitating these transactions, providing expertise on regulatory matters and ensuring compliance with global standards.
- Infrastructure Investments: India's ambitious plans for infrastructure development are likely to attract substantial investment. This presents opportunities for investment banks to raise capital for large-scale projects in sectors such as transportation, energy, and urban development.
- Expansion of Financial Markets: The Indian financial markets, encompassing both equity and debt markets, are poised for expansion. This growth is expected to create new avenues for investment banking activities such as underwriting, initial public offerings (IPOs), and bond issuances.
Here are some potential variations:
a. Data-Driven Insights: Investment banks may increasingly rely on advanced data analytics to derive actionable insights. The capacity to analyze extensive datasets in real-time could bolster risk evaluation, portfolio management, and investment strategies.
b. International Transactions: Cross-border mergers, acquisitions, and investments could undergo streamlining owing to technological advancements and regulatory alignment. Investment banks would need to navigate intricate international regulations and provide expertise in global transactions.
c. Tailored Services: With advancements in artificial intelligence and customer data analysis, investment banks might offer highly personalized services to their clients. Customized investment strategies, products, and advisory services could be crafted based on individual financial objectives and risk profiles.
d. Regulatory Dynamics: Regulatory frameworks are poised to undergo significant transformations by 2030, impacting the operational landscape of investment banks. Stringent regulations pertaining to financial stability, consumer safeguarding, and data confidentiality could reshape the modus operandi of investment banks and their risk management practices.
e. Remote Work and Global Collaboration: The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of remote work and virtual collaboration tools. By 2030, investment banks could embrace more flexible work arrangements, leveraging technology for seamless cross-border collaboration.
II. AIMS AND OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
To analyze the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic UPON investment banking sector and its subsequent adaptation and growth.
A. Objectives
- Explore the traditional understanding of investment banking as a concept and career path.
- Examine the changing nature of qualifications for entering the investment banking field.
- Analyze the specific challenges faced by investment banking during the COVID-19 pandemic, including:
- Falling share prices
- Market volatility
- Client hesitancy
- Dynamic financial regulations
- Evaluate the strategies adopted by the investment banking sector to adapt to the pandemic, including:
- Embracing the "new normal"
- Facilitating capital flow into struggling industries
- Capitalizing on new market opportunities
- Highlight the role of investment banking in:
- Stabilizing the economy during the pandemic
- Supporting the emergence of new industries
- Draw conclusions about the resilience and adaptability of the investment banking sector in the face of unforeseen circumstances.
III. EXPLORING OBJECTIVES IN INVESTMENT BANKING
Investment banks play a pivotal role in the financial landscape, serving as intermediaries between corporations, governments, and financial markets. Their primary mission involves capital raising, assisting companies in securing funds for growth and operations. This intricate process entails expertly managing the issuance of stocks and bonds in the primary market, meticulously structuring offerings, setting prices, and identifying suitable investors. Investment banks assume the risk by underwriting these securities, facilitating quick and efficient access to capital. Moreover, they provide invaluable guidance in mergers and acquisitions (M&A), offering advice, valuation, and transaction negotiation services. Their advisory roles extend to various financial and strategic matters, such as restructuring and risk management.
The multifaceted research objectives of investment banking are pivotal to its functioning in the global financial landscape. At its core, investment banking aims to provide actionable insights and information to facilitate informed financial decisions for both clients and the broader market. Investment banks conduct extensive research spanning diverse sectors, industries, and financial instruments, with the overarching goal of delivering value to their clients. This research encompasses comprehensive analyses of companies, evaluating their financial health, growth prospects, and competitive positioning. It delves deep into market dynamics, identifying trends, opportunities, and potential risks that could impact investment strategies. Investment bankers also scrutinize macroeconomic factors, regulatory changes, and geopolitical developments, recognizing their potential influence on financial markets and investment decisions. Furthermore, investment banks produce research reports that offer investors and clients valuable insights into market conditions, investment strategies, and asset allocation. These reports serve as critical tools for decision-making, guiding stakeholders in optimizing their portfolios and capitalizing on emerging opportunities. In essence, the research objectives of investment banking are intertwined with its commitment to providing expert advice, fostering transparency, and empowering clients and investors with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the financial world effectively.
Additionally, investment banks engage in various financial services beyond research, including managing investment portfolios, private equity investments, initial public offerings (IPOs), debt financing, and securities services such as custody, clearing, and settlement. They cater to high-net-worth individuals in wealth management, offering personalized investment strategies, financial planning, and asset allocation to help clients grow and protect their wealth. Investment banking encompasses a broad spectrum of functions and objectives that are vital to the functioning of modern economies. These institutions drive economic growth, facilitate transactions, and provide essential financial services to clients worldwide.
IV. POTENTIAL OF INDIAN INVESTMENT BANKING
As we delve into the realm of investment banking and its future, it’s imperative to explore its scope in India. The banking landscape is on the brink of significant transformations, driven by evolving customer expectations, emerging technologies, and innovative business models. To navigate this shifting terrain effectively, banks must proactively formulate strategies to adapt to the future of banking. An analysis of the current scenario reveals promising prospects for investment banking in India. However, success in this domain hinges on stringent adherence to rules and regulations.
A. Ensuring the Stability of Banks
Preserving the stability of banks, particularly industry giants, is paramount to prevent future repercussions. The President and CEO of the Federal Reserve Bank of America have emphasized the importance of preventing any banks from becoming “too big to fail.” In the context of India’s current economic conditions, several banks wield significant magnitude, and their potential failure could precipitate severe economic turmoil.
B. Mitigating Bankruptcy Risks
There’s a growing consensus within the global economy regarding the need for enhanced scrutiny of banks. Governments worldwide are actively exploring various schemes and initiatives to mitigate the risk of bank failures and bankruptcy.
C. Legislative Reforms for Bank Strengthening
The enactment of the Financial Regulation Depositors Insurance Bill stands as a noteworthy example of comprehensive legislative reform aimed at fortifying banks and shielding them from potential harm amidst impending economic downturns.
D. Debates and Advocacies
While some advocate for the introduction and enhancement of diverse mechanisms for bank development and fortification, others advocate for the complete elimination of investment banks from the economy. Their rationale is rooted in the belief that such banks primarily serve the interests of a select few, rather than benefiting society as a whole.
E. Navigating Uncertainties in Banking
Banking is inherently unpredictable, yet with the right foresight, one can anticipate future developments and manage actions accordingly. From the analysis of investment banking, it’s evident that the sector possesses resilience and the ability to stabilize itself in times of hardship, demonstrating its endurance over time.
V. REVIEW OF LITERATURE
A. The Future Landscape of Investment Banking
The future of investment banking appears uncertain amidst recent stock market fluctuations, ongoing pandemics, and emerging outbreaks. However, it's anticipated that competition from other industries and the process of digitization won't pose significant threats. Despite recent challenges, the investment banking sector has shown resilience and is expected to continue performing well in the foreseeable future.
B. Predictions and Emerging Trends
Several predictions and emerging trends are expected to shape the future of the investment banking sector:
- Seamless Capital Flow
- Emergence of Unstressed Liquidity
- Advancements in Technologies
- Evolving Consumer Expectations
- Changes in Business Models
- Potential for Higher Returns (subject to changes in business models)
Despite recent fluctuations, the market has been functioning normally, even amidst significant currency fluctuations. Higher customer returns are projected in the near future, although modifications in business models are likely.
C. Market Growth Projections
According to the "Investment Banking Global Market Report 2022" by ResearchAndMarkets.com, the global investment banking market is expected to grow significantly, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.9% from 2021 to 2022. By 2026, the market is forecasted to reach $231.12 billion, reflecting a CAGR of 10.4%.
D. Focus on Mergers and Acquisitions
Investment banking is increasingly focusing on mergers and acquisitions to broaden its product offerings and expand market share. Large investment banks are acquiring boutique firms specializing in various industries such as technology, healthcare, finance, media, and entertainment. The presence of numerous niche-focused small firms presents significant opportunities for larger investment banking firms, driving a surge in merger and acquisition activity within the industry.
E. Technological Advancements Shaping the Future
Advancing technology and evolving market dynamics are expected to shape the future of investment banking in several ways:
- Digitization: Investment banking is increasingly embracing digital platforms and tools to streamline processes, enhance efficiency, and improve client experiences.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology has the potential to transform investment banking through enhanced security, transparency, and decentralization of transactions and asset transfers.
- AI & Automation: Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation are revolutionizing various aspects of investment banking, enabling data-driven decision-making and streamlining processes such as risk assessment and compliance.
- Cybersecurity: With the growing risk of cyber threats, investment banks are prioritizing robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive client data and ensure the integrity of financial transactions.
- ESG Investing: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors are becoming increasingly important in investment decision-making, with investment banks incorporating ESG principles into their analysis and offering ESG-focused investment products and services.
Ultimately, the future of investment banking is expected to be shaped by technological advancements, evolving market dynamics, and a growing focus on sustainability and ethical practices. As the industry continues to adapt to these changes, investment banks are poised to deliver enhanced services and drive sustainable growth in the global economy.
VI. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Investment Banking in a Changing Landscape- RECENT TRENDS
Turning to recent trends in investment banking, several key developments have shaped the industry landscape:
- Technology Integration: Investment banks have increasingly adopted technology, including artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, to enhance their operations. These technologies are used for data analysis, risk assessment, and the development of advanced trading strategies. The technological integration of investment banking is a dynamic process aimed at enhancing various aspects of the financial industry. This integration involves the automation of critical functions like trade execution and compliance checks, reducing manual intervention and speeding up transactions. Advanced data analytics and machine learning are harnessed to analyse vast volumes of financial data, enabling trend identification and informed investment decisions. Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology offer secure and transparent transaction capabilities, potentially streamlining settlement processes. Mobile apps empower clients with real-time access to their accounts and investments, while robust cybersecurity measures protect sensitive financial data. AI-driven chatbots provide client assistance, and cloud computing enables scalable and remote-access infrastructure. Investment banks also utilise quantitative models, high-frequency trading algorithms, and fintech collaborations to stay competitive in this technology-driven landscape. Ultimately, this ongoing integration serves to adapt to market changes, reduce risks, and provide improved services to clients, shaping the future of investment banking.
- Sustainable Finance: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations have gained prominence in investment banking. Banks are offering ESG-focused financial products and services, reflecting a growing interest in socially responsible investing. Sustainable financing in investment banking encompasses a multifaceted approach to aligning financial activities with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations. Investment banks play a pivotal role in facilitating sustainable finance by issuing green bonds dedicated to eco-friendly projects, integrating ESG factors into investment decisions, and promoting impact investing that seeks positive societal and environmental outcomes. They offer advisory services to help clients adopt sustainable practices, conduct due diligence to assess sustainability risks and opportunities, and assist in ESG reporting to enhance transparency. Investment banks also create and manage sustainable investment funds, enabling investors to allocate capital in line with ESG principles. They stay abreast of evolving ESG regulations, promote socially responsible investing strategies, provide ESG research and analysis, and support companies in their journey toward ethical and sustainable finance. This comprehensive approach reflects the growing importance of responsible and value-driven investing in today's financial landscape
- Digital Banking: Investment banks are exploring digital banking services and partnering with fintech firms to expand their reach and provide clients with more accessible and efficient financial services. Digital banking has revolutionised the landscape of investment banking in profound ways, fundamentally altering how financial institutions operate and serve their clients. Firstly, it has streamlined traditional processes through automation, reducing operational costs and enhancing efficiency. Investment banks now use digital platforms for trading, asset management, and risk assessment, allowing for quicker and more data-driven decision-making. Furthermore, digital banking has democratized investment opportunities by providing retail investors access to complex financial products and research tools previously reserved for institutional clients. This has broadened the customer base and increased competition within the industry. Cybersecurity and data privacy have become paramount concerns, necessitating significant investments in safeguarding sensitive financial information. Additionally, the rise of fintech startups and partnerships between traditional banks and tech companies has spurred innovation in areas such as robot advisory services and blockchain-based settlement systems, further shaping the future of investment banking. In summary, digital banking has not only modernized operational aspects but also reshaped the competitive landscape and the way individuals engage with investment opportunities.
- Regulatory Changes: The industry continues to grapple with evolving regulatory frameworks aimed at increasing transparency and reducing systemic risk. Regulatory changes affect various aspects of investment banking, from risk management to reporting requireents. Regulatory changes in the field of investment banking have evolved significantly in recent years, reshaping the industry's landscape. Following the global financial crisis of 2008, governments and regulatory bodies worldwide implemented a series of reforms aimed at enhancing transparency, stability, and investor protection. These changes included the Dodd-Frank Act in the United States, which imposed stricter regulations on banks, enhanced risk management practices, and established the Volcker Rule to limit proprietary trading. Additionally, the Basel III framework was introduced to strengthen capital requirements and liquidity standards for banks globally. MiFID II in Europe aimed to increase transparency and investor protection through regulations on trading and reporting. Moreover, the SEC's Regulation Best Interest set higher standards for broker-dealers in the U.S., requiring them to act in the best interest of clients. These measures collectively aimed to reduce systemic risk, improve market integrity, and protect investors in the complex world of investment banking. The regulatory landscape continues to evolve, with ongoing discussions about digital asset regulations, sustainable finance, and the impact of technology on trading and compliance. As a result, investment banks must remain agile and adaptive to navigate this ever-changing regulatory environment.
- Remote Work: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote work practices in investment banking. Firms are reevaluating their office space needs and embracing flexible work arrangements. Remote work in the field of investment banking has witnessed significant growth and transformation in recent years, offering several advantages to both professionals and institutions. Firstly, it enables greater flexibility, allowing investment bankers to work from diverse geographical locations, which can be particularly appealing for those seeking work-life balance or relocating. Additionally, cost savings are notable, as firms can reduce expenditures on office space and related infrastructure. The talent pool expands as remote work breaks down geographical barriers, facilitating access to a broader range of skilled professionals. Collaboration tools and advanced technology have enhanced communication and data security, supporting the seamless execution of complex financial transactions. Despite these benefits, remote work also presents challenges, including the potential for reduced team cohesion and the need for robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive financial data. Nevertheless, investment banking's shift towards remote work appears to be a long-lasting trend, shaping the industry's future in fundamental ways.
VII. GROWTH POTENTIAL OF INVESTMENT BANKING IN INDIA
In India, the investment banking sector has experienced significant expansion, driven by robust economic growth, increased foreign investments, and a favourable regulatory framework.
It has emerged as a central hub for financial institutions, multinational corporations, and domestic companies seeking expertise in capital markets. Investment banking in India has experienced remarkable growth and is poised for continued expansion, presenting abundant opportunities in the financial sector. This growth can be attributed to several key factors that have shaped the landscape of investment banking in the country.
India's robust economic development has played a pivotal role in driving the growth of investment banking. The nation's burgeoning middle class, increasing disposable income, and thriving entrepreneurship have created a fertile ground for investment opportunities. This economic dynamism has led to a surge in demand for financial services, particularly capital raising, mergers and acquisitions, and advisory services, all of which are core functions of investment banks.
India has witnessed a significant influx of foreign investments, both in terms of foreign direct investment (FDI) and foreign portfolio investment (FPI). This has not only injected capital into the country but has also increased the complexity of financial transactions, thereby necessitating the expertise of investment banks in navigating the intricacies of cross-border deals and compliance with regulatory requirements. The regulatory environment in India has become more conducive to investment banking activities. Regulatory reforms and policies aimed at enhancing transparency and ease of doing business have created a favourable climate for financial institutions. The introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST), insolvency and bankruptcy code, and other structural reforms has streamlined business processes and bolstered investor confidence. Further more , India's position as an emerging market with a young demographic dividend presents unique growth prospects. Investment banks are well-positioned to capitalise on the country's demographic trends by providing innovative financial products and services tailored to the needs of a young and aspirational population.
In the realm of technology, India has become a global hub for information technology and digital innovation. Investment banks are increasingly leveraging technological advancements such as artificial intelligence, data analytics, and blockchain to enhance their operations, risk management, and customer engagement. The integration of technology not only improves efficiency but also opens new avenues for fintech collaborations and digital banking services, expanding the scope of investment banking in the digital age. Moreover, the government's focus on infrastructure development, renewable energy, and sustainable finance aligns with global trends towards responsible investing. Investment banks are well-positioned to facilitate investments in these sectors, fostering sustainability and economic growth.
Investment banking in India stands at a pivotal juncture, driven by economic growth, foreign investments, regulatory reforms, demographic advantages, technological innovation, and a focus on sustainable finance. The industry is poised to play an increasingly vital role in shaping the financial landscape of the nation and offers a multitude of growth opportunities for professionals and institutions looking to participate in India's thriving financial ecosystem.
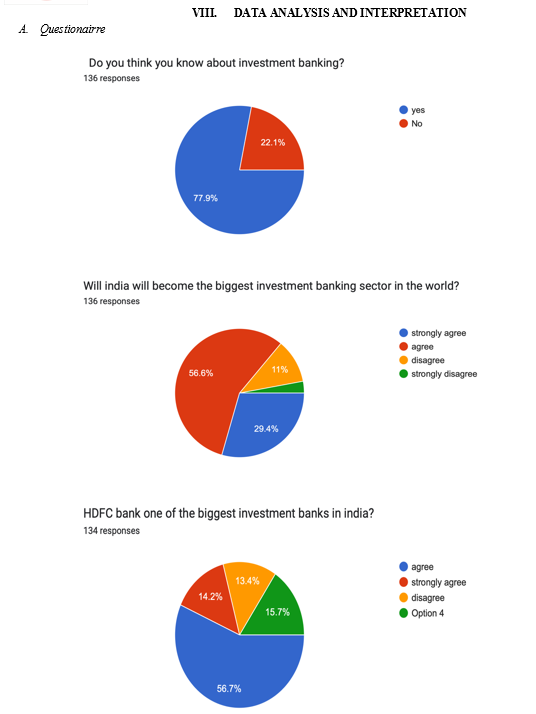
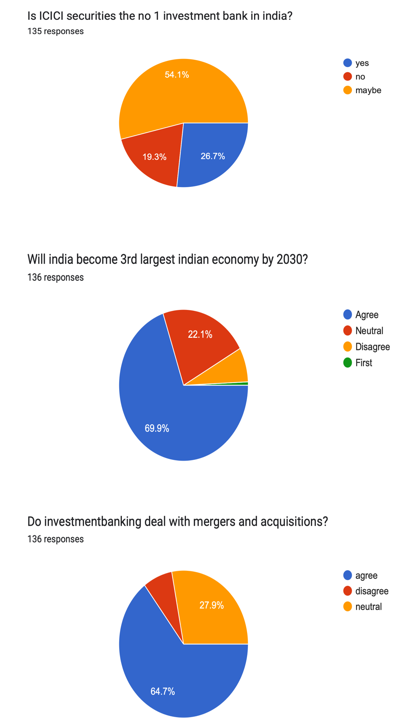

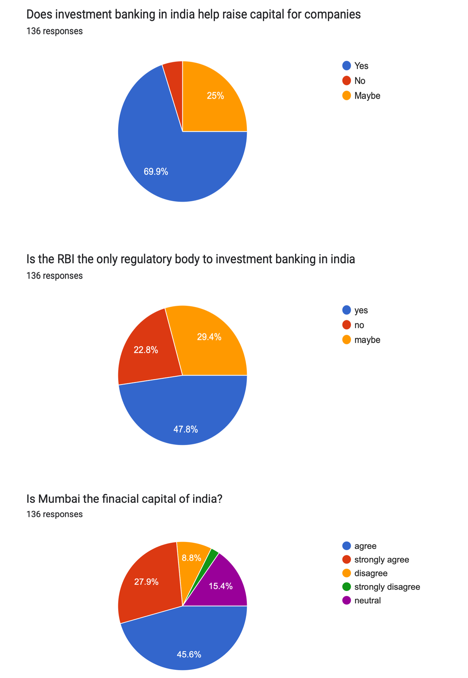
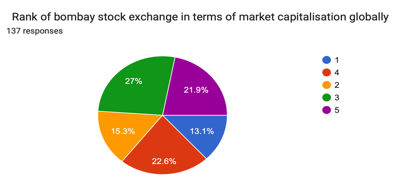
IX. FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
A. Findings
- Investment Banking Demonstrates Adaptability: While traditionally rigid in its qualifications, the industry shows an openness to individuals with passion and relevant skills, even from non-financial backgrounds, suggesting a more inclusive approach.
- The Pandemic's impact on Investment Banking is Multifaceted: The COVID-19 pandemic presented unique challenges like falling share prices, market volatility, and client hesitancy, impacting the industry significantly.
- Investment Banking Emerges as a Resilient Force: Despite facing challenges, the investment banking sector displayed remarkable resilience, adapting to the pandemic and emerging as a catalyst for growth.
- Investment Banking Plays a Crucial Role in Economic Stabilization: During the pandemic, investment banking activities helped stabilize the economy by facilitating the movement of funds into struggling sectors, enabling their survival and fostering the rise of new industries.
B. Discussion
- Evolving Skillsets for Investment Banking Careers: The emphasis on passion and relevant skills, alongside traditional qualifications, opens doors for a wider range of candidates, potentially enriching the industry with diverse perspectives.
- Learning from the Pandemic's Impact: Analyzing the challenges faced during the pandemic can help investment banking institutions develop robust contingency plans to navigate future crises more effectively.
- Investment Banking's role in Future Economic Landscapes: The paper can explore how investment banking can leverage its adaptability and resilience to contribute to future economic growth, considering factors like technological advancements and evolving market dynamics.
- Ethical Considerations in Investment Banking: Briefly discuss the importance of ethical practices in investment banking, especially during times of economic turmoil, to ensure sustainable growth and minimize negative societal impacts.
VII. LIMITATIONS AND FUTURE SCOPE `
A. Limitations
- Vulnerability to Economic Downturns: The paper acknowledges the vulnerability of investment banking to economic downturns, as evidenced by the challenges faced during the COVID-19 pandemic. This highlights the need for the industry to develop robust risk management strategies and maintain a diversified portfolio to weather future economic storms.
- Ethical Concerns: The paper could acknowledge potential ethical concerns surrounding certain investment banking practices, such as short-term profit prioritization over long-term sustainability and potential conflicts of interest. Addressing these concerns can help build trust and enhance the industry's reputation.
- Limited Accessibility: While the paper notes the shift towards valuing relevant skills over specific degrees, investment banking might still be perceived as a career path accessible only to individuals from specific educational and socioeconomic backgrounds. Exploring solutions to improve accessibility and inclusivity within the industry would be beneficial.
B. Future Scope
- Integration of Technology: The paper emphasizes the importance of embracing technology. Further exploration of how emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and big data can be leveraged to streamline processes, enhance risk management, and unlock new opportunities within the investment banking landscape could be valuable.
- Focus on Sustainable and Impact Investing: The growing interest in environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors presents an opportunity for investment banking to play a significant role in promoting sustainable and impact-driven investments. Exploring this growing trend and its implications for the future of the industry would be relevant.
- Evolving Regulatory Landscape: The paper could acknowledge the ever-evolving regulatory landscape within the financial sector. Exploring how investment banks can adapt to comply with new regulations while maintaining their competitiveness would be insightful.
Conclusion
A. Conclusions 1) Investment Banking Demonstrates Remarkable Adaptability: The paper highlights the industry\'s ability to not only survive but also thrive amidst the unprecedented challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic. This adaptability demonstrates the sector\'s resilience and its potential to navigate future crises. 2) Shifting Priorities in Qualifications for Investment Banking Careers: The paper emphasizes the growing importance of passion and relevant skills over traditional academic qualifications for entering the investment banking field. This shift offers opportunities for individuals from diverse backgrounds to pursue careers in this sector. 3) Investment Banking plays a Crucial role in Economic Stability: The analysis underscores the critical role investment banking played in mitigating the economic damage caused by the pandemic. By facilitating the flow of funds into struggling sectors and enabling the emergence of new industries, investment banking acted as a vital engine of growth during a time of crisis. B. Recommendations 1) Investing in Continuous Learning and Skill Development: Given the increasing emphasis on skills over traditional qualifications, individuals interested in pursuing a career in investment banking are recommended to invest in continuous learning and the development of relevant skills, such as financial modeling, valuation, and data analysis. 2) Building Industry Networks and Fostering Collaboration: Building strong networks within the investment banking industry can provide valuable insights and opportunities. Fostering collaboration between diverse individuals with complementary skill sets can also be beneficial for driving innovation and navigating complex market environments. 3) Embracing Technological Advancements: The paper encourages investment banks to embrace technological advancements, such as artificial intelligence and big data analytics, to enhance their efficiency, decision-making capabilities, and risk management strategies.
References
[1] Smith Jr, C. W. (1986). Investment banking and the capital acquisition process. Journal of financial economics, 15(1-2), 3-29. [2] Davis, S., McMann, P. J., & Schmitt, T. P. (2003). Investment Banking. Addressing the Management Issues, New York [3] Liaw, K. T. (2011). The business of investment banking: A comprehensive overview. [4] Fohlin, C. (2014). A brief history of investment banking from medieval times to the present. In The Oxford Handbook of Banking and Financial History. [5] Kapoor, G. P. (2004). Commercial Banking. APH Publishing. [6] Saluja, M. S., & Wadhe, T. (2015). Impact of e-banking on profitability of commercial banks in India. International Journal in Management and Social Science, 3(2), 478-483. [7] Malik, S. (2014). Technological innovations in Indian banking sector: changed face of banking. International Journal, 2(6), 45. [8] Singh, B. J., & Rajender, K. (2023). A MEDIATING ROLE OF CUSTOMER ENGAGEMENT, EXPERIENCE IN BANKING INNOVATIONS AND CUSTOMER SATISFACTION. Journal of Research Administration, 5(2), 11838-11838. [9] Unnithan, C., & Swatman, P. (2001). eBanking adaptation and dot. com viability: A comparison of Australian and Indian experiences in the banking sector. [10] Prokopenko, O. V., Biloshkurska, N. V., Biloshkurskyi, M. V., & Omelyanenko, V. A. (2019). The role of banks in national innovation system: general strategical analytics. Financial and credit activity problems of theory and practice, 3(30), 26-35. [11] Desai, R. GLOBAL INNOVATION STRATEGIES FOR PROGRESSION OF INDIAN BANKS. DR. DY PATIL B-SCHOOL, PUNE, INDIA, 735. [12] Innis, H. A. (1942). The newspaper in economic development. The Journal of Economic History, 2(S1), 1-33. [13] O\'Connell, B. (2002). CNBC creating wealth: an investor\'s guide to decoding the market. John Wiley & Sons. [14] Wuyts, S., & Dutta, S. (2014). Benefiting from alliance portfolio diversity: The role of past internal knowledge creation strategy. Journal of Management, 40(6), 1653-1674.
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Mr. Vivek Gupta , Jaivardhan Haritwal , Bhimarth Jain , Hemanth Kumar , Kyraa Pires , Nawaz Parvez. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET59469
Publish Date : 2024-03-27
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

