Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- References
- Copyright
Urban Heat Island Mitigation Through Blue, Green & Grey Infrastructure - A Case Study of BMC-Bhubaneswar
Authors: Tapas Kumar Parida, Santosh Kumar, Supriya Priyadarshini Prusty
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2024.62688
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
The rapid development in urban areas, especially in the central business district can result a number of consequences related to urban heat island (UHI), as it increases both the surface albedo and anthropogenic heat which led to rise the temperature in the certain areas. This research aims to investigate existing actions and determine possible strategies for mitigating UHI, a case study of Bhubaneswar, Odisha. Qualitative method using field survey analysis was used, as well as document review and stakeholder interview to recommend strategies of Blue, Green & Grey space utilization for mitigating the UHI effect. The Bhubaneswar city development document is being used as document review. The results of this research can be used as a baseline study for more understanding and addressing the UHI effects in Bhubaneswar and other cities. The result shows that despite lack of understanding to the concept of UHI, Bhubaneswar Municipality Corporation has been implemented several strategies for mitigating UHI effects, such as increasing provision of Blue & Green space, reducing electricity consumption and replacing asphalt with cool pavement. Comprehensive approaches to the participation of stakeholders are needed to invent and implement the Strategies, in addition to growing greater plans and applications for mitigating the UHI effects.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Rapid increase of populace and ensuing urbanization is gaining momentum in which city regions are evolved in widespread share in India main to adjustments in current landscape, buildings, roads, and different helping infrastructure. Such a change replaces open land, vegetation and waterbodies in the form of permeable surfaces with concrete surfaces which are impermeable and dry in nature which leads to the formation of Urban Heat Islands (UHI) whereby urban regions experience warmer temperatures than their adjacent rural surroundings. Such heat Island effect increases social, physical & economical discomfort in urban areas along with other negative impacts.
A. Aim of the Study
To investigates the potential of Blue, Green & Grey spaces as a strategic intervention for mitigating urban heat, with a specific focus on the case study of Bhubaneswar, the capital city of Odisha, India.
B. Objectives
- To study the existing scenario of urban heat island effect on Bhubaneswar and over-view the causes
- To assess the impact of urban heat island effect in Bhubaneswar.
- To analyse the role of Blue/Green/Grey Spaces in mitigating the urban heat.
- To evaluate the existing policies and initiatives for supporting Blue, Green & Grey infrastructures in Bhubaneswar.
C. Need of the Study
- Reduced heat-related health risks for urban residents.
- Enhanced outdoor and indoor thermal comfort.
- Sustainable development.
- Lower energy demand for cooling in urban areas.
D. Expected Outcomes
- Reduce urban heat island effect.
- Policies to enhance public health, comfort and productivity of citizens.
- Lower energy consumption.
- Sustainable Development.
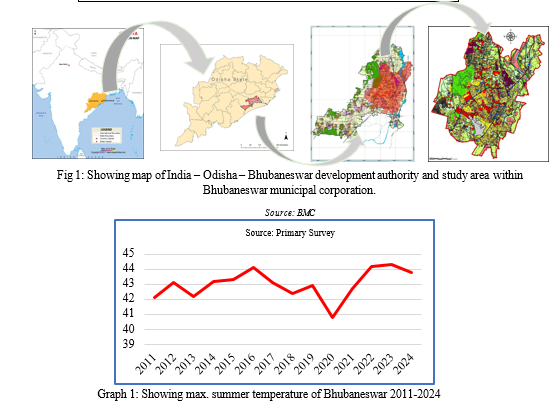
E. Study Area
City Profile - Bhubaneswar city is the largest city and capital of Odisha and located on the east coast of the Indian peninsula. Bhubaneswar is categorised as Tier-2 city. An rising records technology (IT) and training hub, Bhubaneswar is one of the country's fastest-growing cities (Fig. 1). The weather in Bhubaneswar is tropical savanna. Monthly average temperatures range from 22 0C to 32 °C, with an annual mean of 27.4 0C. The low 30 °C summers (March to June) are heat and muggy; at some stage in dry periods, most temperatures regularly surpass 40 °C in May and June (TABLE 1)
TABLE 1 - Study AREA PROFILE
|
Study Area |
146.4 Sq. Km. |
|
No. of wards |
67 |
|
Total population |
8,40,834 (Census 2011) |
|
Population density |
6228 /sqkm |
|
Climate |
Tropical climate |
|
Avg. Annual Maximum Temp. |
32 °C |
|
Avg. Annual Minimum Temp. |
27 °C |
|
Avg. Annual rainfall |
1505mm |
|
Avg. Annual Humidity |
70% |
|
Source: BMC Bhubaneswar |
|
F. Site Justification
- For the previous 3 decades, the state of Odisha and in particular, Bhubaneswar town has been experiencing unprecedented Contrasting excessive climate conditions; from warmth waves to cyclones; from droughts to floods. The city recorded 44.1OC in April, 2016, maximum recorded in closing three decades, with the best recorded in 1985 at 45OC. The wide variety of Heat wave and intense warmness wave days have multiplied over decades, recording nearly 25 days in 2014, 19 days in 2015 and 10 days in 2024 (IMD).
- Main reason to take BMC area as study area is, if we observe the avg. summer temperature of Bhubaneswar from 2011-2024{(Graph- 1). The avg. temperature increasing year to year. Considering the extreme variation in temperature for next couple of years it is going to be a big issue in near future.
G. What is Urban Heat Island (UHI)?
Urban Heat Island refers to the phenomenon where urban areas experience higher temperature compared to their surrounding rural or peri urban areas due to human activities and built environment.

H. Factors Causing Urban Heat Island in Urban Area.
- Reduced Natural Landscapes in Urban Areas - Trees, vegetation, and water our bodies generally tend to cool the air with the aid of using presenting shade, transpiring water from plant leaves, and evaporating surface water, respectively. Hard, dry surfaces in city areas which incorporates roofs, sidewalks, roads, buildings, and parking lots offer much less shade and moisture than green landscapes and consequently make contributions to high temperatures. (Fig.3)
- Urban Material Properties - Conventional human-made substances utilized in city environments which include pavements or roofing have a tendency to mirror less solar radiation, and soak up and emit extra radiation in comparison to trees, vegetation, and different herbal surfaces. Often, heat islands construct for the duration of the day and grow to be extra said after sundown because of the gradual release of heat from city materials. (Fig.4)
- Urban Geometry - The dimensions and spacing of buildings within an urban area affect wind flow and concrete materials’ capacity to absorb and release solar energy. In closely advanced areas, surfaces and structures obstructed with the aid of using neighbouring buildings turn out to be massive thermal loads that cannot release heat readily. Cities with many slim streets and tall homes end up city canyons, that may block natural wind flow that might carry cooling effects. (Fig.5)
- Anthropogenic Heat Generated from Human Activities - Vehicles, air-conditioning units, buildings, and industrial facilities all emit heat into the urban environment. These sources of human-generated or anthropogenic waste, heat can make contributions to UHI effects. (Fig.6)
- Weather and Geography - Calm and clean climate situations bring about extra extreme heat islands by maximizing the quantity of solar radiation accomplishing city surfaces and minimizing the quantity of temperature that may be carried away. Conversely, sturdy winds and cloud cowl suppress heat island formation. Geographic functions also can affect the warmth island effect. For example, close by mountains can block wind from accomplishing a city, or create wind styles that by pass through a city.

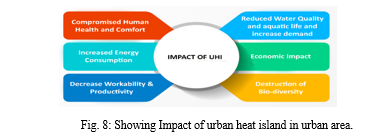
I. Impact of Urban Heat Island in Urban Area
- Compromised Human Health and Comfort - Urban heat islands contribute to higher daytime temperatures, reduced nighttime cooling, and higher air-pollution levels. These, in turn, make a contribution to heat-associated deaths and ailments such as discomfort, breathing difficulties, heat cramps, exhaustion, and non-deadly heat stroke. Urban heat islands can also exacerbate the impact of naturally occurring heat waves, which are periods of abnormally hot, and humid, weather. Sensitive populations like older adult, children, low-income category, casual outdoor labour and people in poor health are particularly at risk during these events.
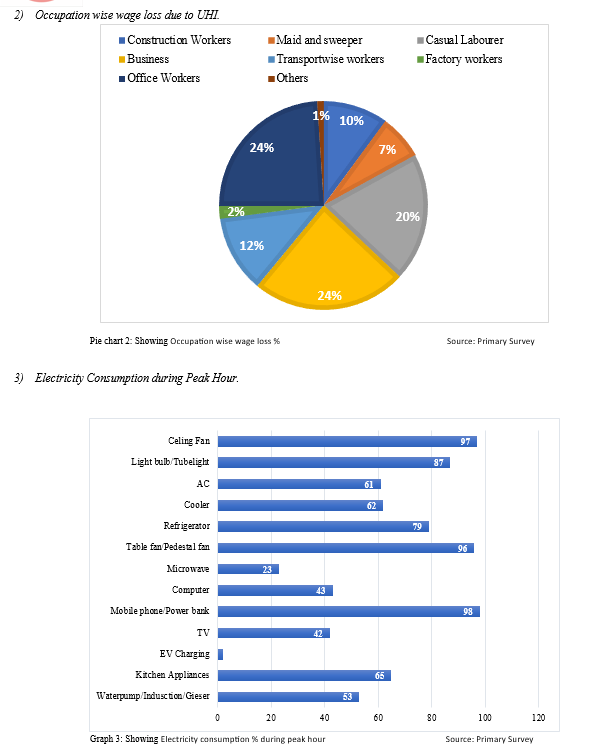
- Increased Energy Consumption - Heat islands increase both overall electricity demand, as well as peak energy demand. Peak demand generally occurs on heat summer season weekday afternoons, while places of work and homes are running air-conditioning systems, lights, and appliances. During excessive heat events, which can be exacerbated through heat islands, the multiplied call for air condition can overload systems and require a mechanism to institute controlled, rolling brownouts or blackouts to keep away from energy outages.
- Decrease Workability & Productivity - The new International Labour Organization (ILO) report, (Working on a warmer planet: The impact of heat stress on labour productivity and decent work), attracts on climate, physiological and employment facts and offers estimates of the contemporary and projected productiveness losses at national, nearby and global level. According to the report an increase in heat stress resulting from Urban heat island (UHI) is projected to result in international productiveness losses equal to eighty million full-time jobs withinside the 12 months 2030. xcess heat at some point is an occupational fitness risk; it restricts workers’ bodily features and capabilities, work potential and thus, productivity. In severe instances it is able to result in heatstroke, which may be fatal. The sector expected to be worst affected, globally, is agriculture 60% and construction 19% of global working hours lost due to heat stress by the year 2030. Other sectors especially at risk are environmental goods and services, refuse collection, emergency, repair work, transport, tourism, sports and some forms of industrial works.
- Reduced Water Quality and aquatic life and increase demand - Rising temperatures in cities can also harm water quality. Impermeable surfaces that reach throughout cities, including roads and rooftops, absorbs heat. When it rains, water that collects on those surfaces heats up because it drains into sewers. This hotter water then flows into natural water bodies, disturbing the natural ecosystems. Minor temperature changes because of UHIs should have devastating effects on aquatic life. It can boost up the boom and replica of bacteria, algae, and different species, which in flip may want to show annoying or maybe deadly to fish and different aquatic life. Unbalanced eco-system can purpose unfavorable consequences to water quality. As city heat islands end up extra intense, human beings ought to use extra water from the place to cool themselves, water their plants, and offer supplemental watering to pets and different dwelling creatures withinside the environment. Often, urban areas get their potable water from sources nearby. Overuse of water from nearby sources put stress on the water supplies and can lead to massive water shortages. This makes it difficult to maintain a good quality of life, and can stress on ground water and water sources farther and farther from the urban area as the reach for water widens.
- Economic impact - To manage issues like increase energy consumption, human health risks of urban citizen, water and air quality degradation, biodiversity conservation and decrease productivity there is an extra burden on urban economy.
- Impact on Bio-diversity - Naturally, rising urban temperatures will cause increased levels of discomfort and premature deaths to citizens, however it's going to additionally take its toll at the animal populations inside towns too. Some animal populations are much more likely to conflict to discover food, water, and refuge in warmer cities. Or there’s the alternative aspect of the coin, in which a few animal species can also additionally discover towns extra attractive than the desert wherein they belong, and become city pests that convey disorder and emerge as a nuisance. Due to warmer temperatures in city areas, the UHI will increase the colonization of species that like heat temperatures, along with lizards and geckos. Insects along with ants are greater ample right here than in rural areas.
II. METHODOLOGY
To accomplish the study two types of techniques have been used.
A. Remote Sensing Data & Field Survey
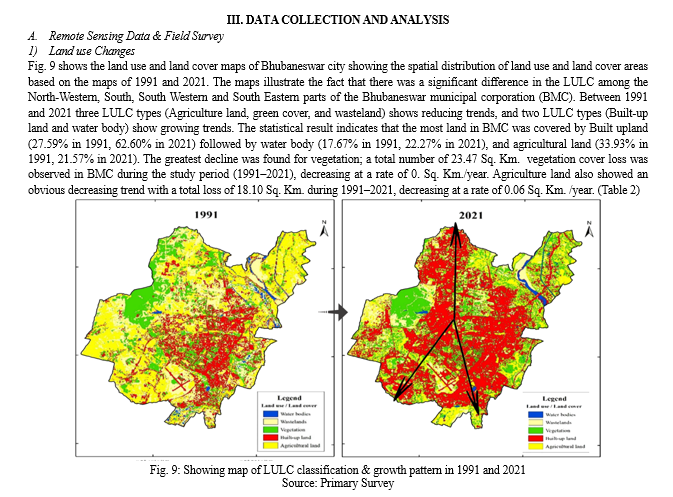
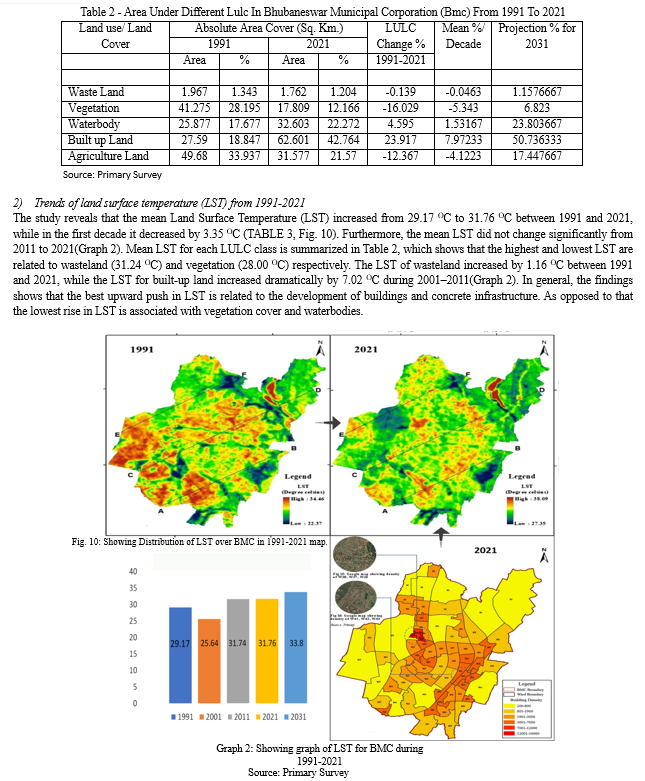
To know the temperature difference in last four decades and to know the major area affected due to increase in built-up area and decrease in waterbodies/vegetation which causing Land Surface Temperature (LST). With the assist of USGS data built-up transformation map and Land Surface Temperature (LST) map were organized for the year 1991 and 2021. To know the current max temperature field survey conducted through the help of IR Thermometer and hygrometer.
B. Primary Survey
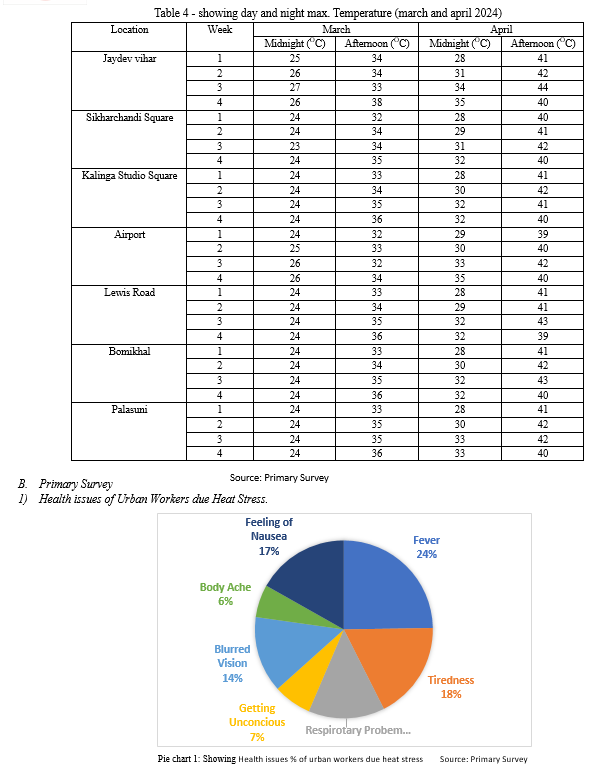
- To know, how the city population suffers because of growth of temperature and to examine how their social, academic and expert lifestyles impede because of heat stress. A useful random sampling achieved in Bhubaneswar to get records on how underprivileged city employees deal with heat stress.
- Since the people in those places are impoverished, the pattern became decided on from as a substitute busy and underdeveloped marketplace region of the cities, along with the ones close to to educate stations, bus stops, etc.
- By choosing 10 people from some low- and mid-income categories, the pattern became randomly selected. The survey was carried out in higher temperature.
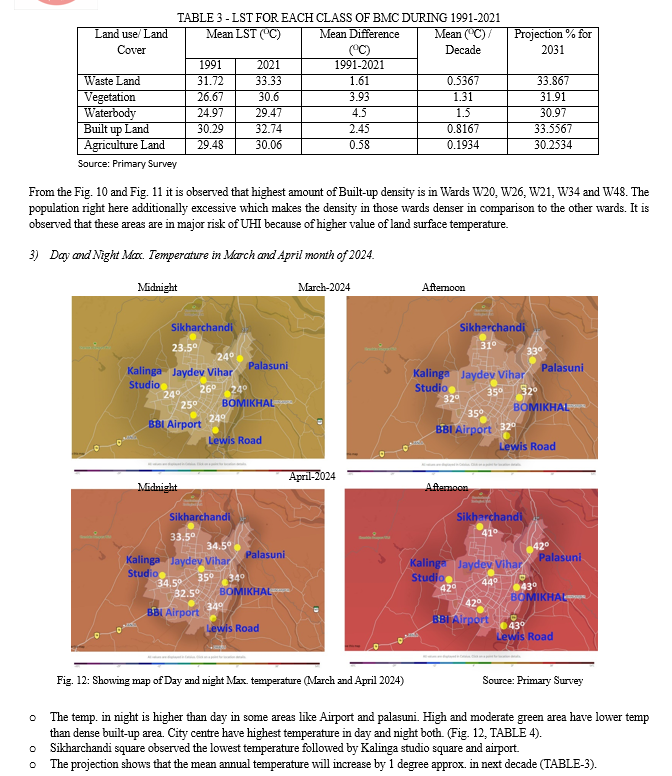
IV. RESULTS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
A. Results
- As per Bhubaneswar Land use scenario and Temperature analysis we come to the conclusion that Central and south western Zone of the city is more vulnerable. Northern part of the city has more vegetation and eastern and south eastern zone have more waterbodies. Again, as per wind flow of Bhubaneswar city the wind flows from south west direction in summer which brings hot air and dust particles into the city. So major Heat mitigation policy and strategy required in this zone.
- The main causes of temperature cause in study area are less vegetation and waterbodies, use of impervious and low albedo material.
- Most of the roads are made up of black coloured asphalt which have low albedo value and high emissivity. Most of the roads are not having shading and exposed to direct sunlight.
- Ward no 20, 26, 21, 34 and 48 having major built up density. Apartments forming city canyon in those region and Huts on this region are having tin roof which absorbs greater heat. Thus these areas having higher LST than other wards.
- Heat strain lessen the worktime of people, it additionally hampers the education of students and the social existence of senior citizen.
- Reduced productivity, Wage loss, Health issues, Education disturbance of children and Discomfort for senior citizens are major issues arising due to UHI.
B. Recommendations
- Mitigation Strategies
- Through Green Space - Creating green cover and vegetation, installation of green roofs, vertical garden or green walls will reduce city temperature through shading and evapotranspiration.
- Through Blue Space – By creating new waterbodies, linking creeks, canals and drains, rainwater harvesting, providing fountains in high density area and rejuvenate existing waterbodies, temperature can be reduced through evaporation of moister to the atmosphere.
- Through Grey Space – By using high albedo, Impervious and high reflective material like glazed window, cool roofing, impervious pavements, green facades and traditional material for urban built up which will absorb less heat and reflect more to the atmosphere back. Use of vertical and roof top solar panels will also create shading.
- Social Behaviour - Urban planning can encourage more sustainable and adaptive lifestyles, such as using public transportation, cycling, walking, and sharing spaces and resources. Urban planning can also promote social cohesion, participation, and awareness, by creating inclusive, accessible, and diverse public spaces and facilities.
2. Policy Interventions
- As city have very few areas to propose vegetation. Area out of BMC boundary and in BDPA boundary there are many Westland and agriculture land are remained unused. Govt. should make guidelines for Private owner having land in these areas which are unused for plantation until they started using it.
- BMC must ensure that People are following ODA bylaws guidelines for min, green area, min. setback, Solar water heating and cooling system in high rise building, F.A.R. Violation, Street and pedestrian encroachment.
- Development authority should do plantation in peri urban areas, special towards south west direction as most solar radiation and hot wind comes from this direction.
- Promote more high raised buildings towards south west direction for shading to the city.
- Bylaws should ensure that plotting schemes are in such a way that building will construct in future with a chess board pattern so that wind flow into the city can be evenly distribute.
- BMC should Construct new waterbodies and rejuvenate the older waterbodies. Rainwater harvesting practice should be done in south west direction as this area have very few waterbodies.
- Information should be provided to the citizens about various heat mitigation techniques like green roofing and use of high albedo materials in pre summer season.
- Govt. must ensure regarding on site cooling and rehydration facility of construction worker by publish advisory for builders and contractors. Shading facility should be provide to these labors.
- Rest rooms with toilets should be constructed during extreme heat wave to stay peoples for some hour.
References
[1] https://www.epa.gov/heatislands/heat-island-compendium [1] [2] https://wgbis.ces.iisc.ac.in/energy/paper/Bangalore_heatisland/results.htm [2] [3] https://www.researchgate.net/publication/288094520_Remote_sensing_of_land_cover\'s_effect_on_surface_temperatures_A_case_study_of_the_urban_heat_island_in_Bangalore_India [3] [4] https://www.preventionweb.net/news/increase-climate-change-related-heat-stress-predicted-bring-productivity-loss-equivalent-80 [4] [5] https://doi.org/10.3390/earth2030038 [5] [6] https://www.mdpi.com/2073-445X/12/2/308 [6] [7] https://www.researchgate.net/publication/356220632_Spatio-temporal_pattern_of_land_use_and_land_cover_and_its_effects_on_land_surface_temperature_using_remote_sensing_and_GIS_techniques_a_case_study_of_Bhubaneswar_city_Eastern_India_1991-2021 [7] [8] Sari, D.P. A Review of How Building Mitigates the Urban Heat Island in Indonesia and Tropical Cities. Earth 2021, 2, 653–666. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth2030038 [8] [9] Distribution of green spaces across socio-economic groups: a study of Bhubaneswar, India https://doi.org/10.3846/jau.2023.17026 [9] [10] Addressing the Urban Heat Islands Effect: A Cross-Country Assessment of the Role of Green Infrastructure. Sustainability 2021, https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/13/2/753 [10] [11] https://www.tudelft.nl/citg/over-faculteit/afdelingen/watermanagement/studeren/msc-onderzoek-waterhuishouding/completed-msc-theses-water-resources/mitigation-of-the-urban-heat-island-effect-by-using-water-and-vegetation [11]
Copyright
Copyright © 2024 Tapas Kumar Parida, Santosh Kumar, Supriya Priyadarshini Prusty. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET62688
Publish Date : 2024-05-25
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online