Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Virtual Interview Simulator: Leveraging AIML and Vision Technology
Authors: Sridevi R, Nithyabharathi S
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2025.66680
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
The AI-powered mock interview system offers realistic practice through virtual interactions, using ML to analyze responses and provide personalized feedback on content and delivery models evaluate verbal responses for coherence, relevance, and sentiment using Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques. These NLP algorithms are essential for understanding and interpreting the context and emotional tone of candidates\' answers, thereby providing a nuanced assessment of their communication skills. The system uses image processing techniques to analyze non- verbal cues. MediaPipe, a versatile tool for detecting and identifying facial key points, enables precise identification of facial expressions and movements. Techniques like face detection, landmark detection, and emotion classification are applied to interpret these non-verbal signals, offering insights into the candidate\'s emotional state and engagement level. The system\'s architecture also includes components for voice capture and analysis. Voice analysis examines tone, pitch, and speech speed to understand the clarity and emotional undertones of the responses. This multi-modal approach, which combines verbal, vocal, and visual data, ensures a comprehensive evaluation of the candidate\'s performance. Integrating advanced tech, the system effectively simulates and assesses interviews.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
The AI-driven mock interview system simulates realistic interviews, adapting questions based on user profiles. Machine learning analyzes responses, offering instant feedback on content and communication style. Image processing evaluates non-verbal cues like facial expressions, providing a comprehensive review. This interactive platform helps candidates improve their interview skills effectively. The study of this is carried out by some of the researchers has mirrored that AI analyzes interviewee emotions and behaviors through multimodal techniques for enhanced interview evaluation (Jadhav, Aaditya, et al. "AI Based Multimodal Emotion and Behavior Analysis of Interviewee." (2023)), The study explores how AI is developed and used for hiring, blending machine and expert insights (Van den Broek, Elmira, Anastasia Sergeeva, and Marleen Huysman. "When the Machine Meets the Expert: An Ethnography of Developing AI for Hiring." MIS quarterly 45.3 (2021)), AI system streamlines hiring with NLP, sentiment analysis, and recommendations. (Silva, G. L. L., et al. "An Automated System for Employee Recruitment Management." 2022 4th International Conference on Advancements in Computing (ICAC). IEEE, 2022), AI system evaluates candidate responses with NLP, sentiment analysis, and machine learning (Latha, Ch Sri, et al. "Automated Interview Evaluation." E3S Web of Conferences. Vol. 430. EDP Sciences, 2023), Automated technical interviews using multi-level chatbot and intelligent techniques for efficiency (Rathnayake, Devin I., et al. "Next Generation Technical Interview Process Automation with Multi-level Interactive Chatbot Based on Intelligent Techniques." World Conference on Information Systems for Business Management. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2023). This technology automates interview evaluation, enhancing assessment accuracy and efficiency (Harsh, G. Sri, et al. "Automated Interview Evaluation System Using RoBERTa Technology." 2024 1st International Conference on Cognitive, Green and Ubiquitous Computing (IC-CGU). IEEE, 2024).
II. PROBLEM STATEMENT
Job seekers often lack effective preparation tools for interviews, leading to poor performance and missed opportunities. Traditional mock interviews don't provide detailed, personalized feedback. To address this, we propose a mock interview system using AI, ML, and image processing. This system analyzes verbal and non-verbal cues, including facial expressions and speech patterns, to offer comprehensive feedback. By providing detailed insights into a candidate's performance, the system helps users improve their communication skills and confidence, enhancing their readiness for real job interviews.
The availability and caliber of mock interviews can place restrictions on interview preparation [6]. Conventional tech- niques mostly rely on human assessors, whose subjective comments might differ greatly in depth and consistency. A larger audience may not be able to attend these seminars since they are sometimes costly and time-consuming. Further- more, conventional interview preparation emphasizes verbal replies above non-verbal cues, which are just as important in projecting sincerity, professionalism, and confidence. It is unusual for non-verbal signs like body language, gestures, and facial expressions to be thoroughly examined, which makes it challenging for applicants to comprehend how these aspects affect their performance. The issue is made worse by the fact that typical mock interviews don’t provide real-time feedback. Frequently, candidates get generic recommendations instead of detailed, practical advice catered to their particular advan- tages and disadvantages. As a result, progress may be slower and interview preparation may be less successful. A more advanced, data-driven, and user-friendly interview preparation tool is required [7].
III. LITERATURE REVIEW
The literature study looks at a variety of interview prepa- ration strategies, including conventional approaches, devel- opments in AI-powered simulations, and the use of image processing to decipher nonverbal cues. The development of preparation techniques is highlighted in this section, with particular attention on how technology improves interview candidates’ evaluation and feedback procedures.
IV. PROPOSED SYSTEM
The proposed system leverages AI, ML, and image processing to provide an enhanced mock interview experience. This system offers an immersive environment where AI simulates diverse interview scenarios. ML algorithms analyze responses in real-time, delivering personalized feedback on content, communication skills, and confidence. Image processing technology interprets facial expressions and body language, offering insights into non-verbal communication. This comprehensive approach ensures detailed, data-driven feedback tailored to the individual, helping users identify strengths and areas for improvement. By integrating these advanced technologies, the system aims to significantly improve interview preparation and performance.
V. SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
Artificial Intelligence, machine learning, and image process- ing technologies are all seamlessly integrated into the Vir- tual Interview Simulator’s system architecture [19]. Together, these tools examine both spoken and nonverbal signs during interviews to provide consumers with thorough feedback. AI-driven question creation, real-time answer Together, these tools examine both spoken and nonverbal signs during interviews to provide consumers with thorough feedback. AI-driven question creation, real-time answer analysis, and image processing for body language and facial expression interpretation are just a few of the components that make up the system.
VI. WORKING
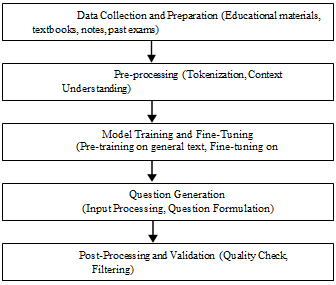
Fig 6.1: Working of Gemini in question generation
Integration of Gemini for Question Generation in a Mock Test System
- Data Collection and Preparation: To utilize Gemini effectively, begin by gathering a broad range of educational materials, such as textbooks, lecture notes, and past exam papers. This data must be cleaned to remove irrelevant content, correct errors, and standardize formats, ensuring high-quality input for the model.
- Pre-processing: Text tokenization involves breaking down text into smaller, manageable units called tokens, which the model processes.
- Model Training and Fine-Tuning: Gemini is pre-trained on extensive general text data to learn language patterns and nuances. It is then fine-tuned on domain-specific educational content, adjusting the model to generate questions tailored to educational contexts and learning objectives.
- Question Generation: The model processes specific sections of the educational content provided as input. It formulates questions that align with the learning goals and difficulty levels of the material, ensuring that they are suitable for educational purposes.
- Post-Processing and Validation: Generated questions undergo a quality check to verify their accuracy, relevance, and clarity. Any questions that are inappropriate or poorly formulated are filtered out to ensure that only high-quality questions are included in the mock test system.
B. Flow of MediaPipe in Analyzing Human Responses
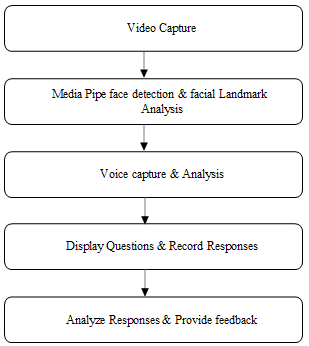
Fig 6.2: Working of MediaPipe
- Video Capture: The process begins with recording a video of the user, capturing facial expressions, movements, and overall demeanour. The quality of this video is critical, as clear visuals are necessary for accurate subsequent analysis. This initial step provides the foundation for examining non-verbal cues that reveal the user’s emotional state and engagement levels.
- MediaPipe Face Detection & Facial Landmark Analysis: Once the video is recorded, MediaPipe is employed for face detection and analysis. It Identifies human emotions. This detailed mapping of facial landmarks helps interpret expressions and movements, providing insights into emotions like happiness or frustration. Understanding these expressions is crucial for analyzing the user’s emotional responses.
- Voice Capture & Analysis: In parallel with video recording, the system captures the user’s voice, analyzing vocal characteristics such as tone, pitch, and pace. These attributes help in understanding the emotional context and clarity of the spoken responses. For instance, a shaky voice may indicate nervousness, whereas a steady tone suggests confidence. Analyzing these vocal traits provides additional context to the user’s emotional state and communication effectiveness.
- Display Questions & Record Responses: The system presents a series of questions to the user, recording both visual and audio responses. This step ensures that all interactions are captured comprehensively, with questions structured to elicit relevant and detailed answers. The recorded responses include both the verbal content and associated non-verbal cues, offering a complete view of the user’s reactions.
- Analyse Responses & Provide Feedback: The recorded data undergoes thorough analysis, evaluating both verbal and non- verbal aspects. The system assesses the clarity and emotional tone of spoken responses, along with facial expressions and gestures. This integrated analysis provides detailed feedback, useful for improving communication skills, conducting psychological assessments, or refining interactions with AI systems. Combining visual and auditory data ensures a nuanced understanding of the user’s responses.
Conclusion
The development and implementation of a mock interview system utilizing AI, ML, and image processing represent a significant advancement in the field of training and assessment. This innovative system offers a comprehensive solution for enhancing interview preparedness through detailed analysis of both verbal and non-verbal cues. By integrating AI and ML models, the system can accurately analyse facial expressions, tone of voice, and speech content, providing users with nuanced feedback that is critical for improving their communication skills. The use of image processing algorithms enables precise facial landmark detection, further enhancing the quality of feedback related to body language and facial expressions. Such a platform serves as an invaluable tool for job seekers, students,and professionals aiming to refine their interview skills in a simulated yet realistic environment. It allows for repeated practice, instant feedback, and targeted improvements, which are essential for building confidence and competence in real- world interview scenarios. Moreover, this technology-driven approach ensures scalability and consistency in the assessment process, making it accessible to a broader audience. The detailed analysis and personalized feedback provided by the system can significantly reduce the anxiety associated with interviews, leading to better performance outcomes.
References
[1] Harsh, G. Sri, et al. \"Automated Interview Evaluation System Using RoBERTa Technology.\" 2024 1st International Conference on Cognitive, Green and Ubiquitous Computing (IC-CGU). IEEE, 2024. [2] Rathnayake, Devin I., et al. \"Next Generation Technical Interview Process Automation with Multi-level Interactive Chatbot Based on Intelligent Techniques.\" World Conference on Information Systems for Business Management. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2023. [3] Latha, Ch Sri, et al. \"Automated Interview Evaluation.\" E3S Web of Conferences. Vol. 430. EDP Sciences, 2023. [4] Silva, G. L. L., et al. \"An Automated System for Employee Recruitment Management.\" 2022 4th International Conference on Advancements in Computing (ICAC). IEEE, 2022. [5] Van den Broek, Elmira, Anastasia Sergeeva, and Marleen Huysman. \"When the Machine Meets the Expert: An Ethnography of Developing AI for Hiring.\" MIS quarterly 45.3 (2021). [6] Jadhav, Aaditya, et al. \"AI Based Multimodal Emotion and Behavior Analysis of Interviewee.\" (2023) [7] Li, Jinze. ”Big Data-driven Decision Support: Enhancing Information Integration and User Experience with Mobile Integrated Technology.” Journal of Information Systems Engineering and Management, vol. 9, no. 2, 2024: 24148. [8] Dzardanova, Elena, et al. ”Exploring the impact of non-verbal cues on user experience in immersive virtual reality.” Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds, vol. 35, no. 1, 2024: e2224. [9] Costa, Pedro, and Helena Rodrigues. ”The ever-changing business of e-commerce-net benefits while designing a new platform for small companies.” Review of Managerial Science, vol. 18, no. 9, 2024: 2507 2545. [10] Tissen, Denis, et al. ”Spearhead Data-Driven Model-Based Systems Engineering: Interview Study on Definition, Preconditions, Challenges, Potentials, and Use Cases.” DS 130: Proceedings of NordDesign 2024, Reykjavik, Iceland, 12th-14th August 2024, 2024: 539-54 [11] Kushwaha, Abhiram. ”AI and Non-Verbal Communication: Enhancing Understanding of Emotional Cues for Hearing Impairment Children.” In *Transforming Learning: The Power of Educational* (2024): 13. [12] B´elanger, Jean, Philippe Venne, and Jean-Nicolas Paquin. ”The what, where and why of real-time simulation.” *Planet Rt* 1.1 (2010): 25-29 [13] Yeates, Peter, et al. ”Seeing the same thing differently: mechanisms that contribute to assessor differences in directly-observed performance assessments.” *Advances in Health Sciences Education* 18 (2013): 325 341. [14] Calvo, Rafael A., and Sidney D’Mello. ”Affect detection: An interdis ciplinary review of models, methods, and their applications.” *IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing* 1.1 (2010): 18-37. [15] Swider, Brian W., Ryan D. Zimmerman, and Murray R. Bar rick. ”Searching for the right fit: Development of applicant person organization fit perceptions during the recruitment process.” *Journal of Applied Psychology* 100.3 (2015): 880. [16] Namratha, M., et al. ”InterviewPal-Elevating Interview Automation with Deep Learning and Natural Language Processing Perspectives.” In *2024 International Conference on Emerging Technologies in Computer Science for Interdisciplinary Applications (ICETCS)*. IEEE, 2024. [17] Walker, Marilyn A., et al. ”Generation and evaluation of user tailored responses in multimodal dialogue.” *Cognitive Science* 28.5 (2004): 811-840.
Copyright
Copyright © 2025 Sridevi R, Nithyabharathi S. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET66680
Publish Date : 2025-01-25
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

